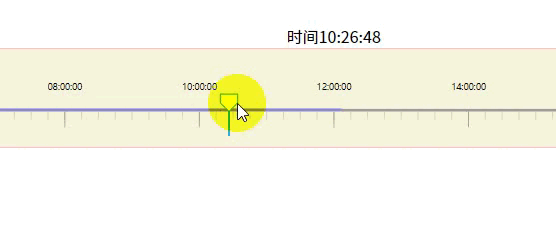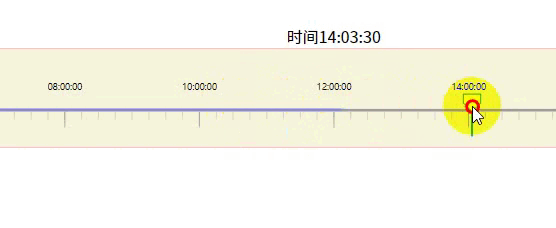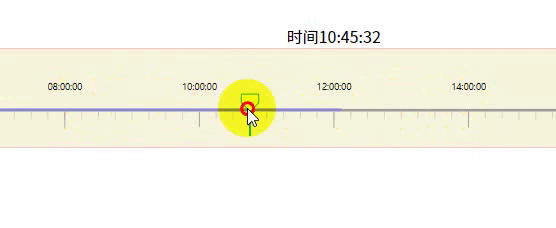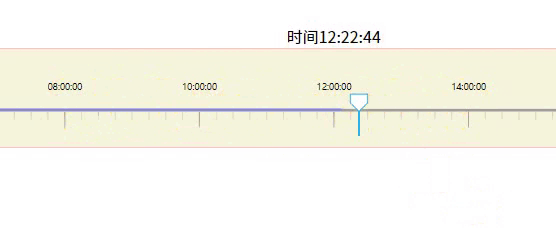

效果如上面所示
1.安装D3.js
官网传送带:Getting started | D3 by Observable
2.创建所需数据
这里需要1天的时间数据,用for循环模拟了一下
for (let index = 0; index <= 24; index++) {
this.list.push({
time: `2023-12-26 ${index.toString().padStart(2, '0')}:00:00`
});
}
3. 创建一个dom容器
<div ref="rulerRef" :class="$style.ruler"></div>
const height = 100;
const margin = { top: 10, right: 30, left: 30, bottom: 30 };
const svg = d3.create('svg').attr('viewBox', [0, 0, this.width, height]).attr('font-size', 16);
this.$refs.rulerRef.appendChild(svg.node());4.初始化刻度
4-1.用2个x轴重叠模拟刻度
const scale = d3
.scaleTime()
.domain(d3.extent(this.list, d => new Date(d.time)))
.range([margin.left, this.width - margin.left]);
const xAxis = d3
.axisBottom(scale)
.ticks(d3.timeHour.every(2))
.tickSize(20)
.tickSizeOuter(0)
.tickFormat((d, i) => {
return i == 12 ? '23:59:59' : d3.timeFormat('%H:%M:%S')(d);
})
.tickPadding(-50);
const axis = d3
.axisBottom(scale)
.ticks(80)
.tickSize(10)
.tickFormat(() => null);
svg
.append('g')
.attr('class', 'lines')
.attr('transform', `translate(0,${height - margin.bottom})`)
.call(axis)
.select('.domain')
.remove();
svg
.append('g')
.attr('class', 'base')
.attr('transform', `translate(0,${height - margin.bottom})`)
.call(xAxis)
.selectAll('path')
.style('stroke', '#a19d9d')
.style('stroke-width', 3);
// 更改线段颜色
svg.selectAll('.base line').style('stroke', '#999');
svg.selectAll('.lines line').style('stroke', '#cbc7c7'); 
4-2.创建白色方块
// 画圆和线条
const g = svg.append('g');
const line = g
.append('line')
.attr('x1', margin.left)
.attr('y1', height - margin.bottom)
.attr('x2', margin.left)
.attr('y2', height)
.attr('stroke', '#11a6e9')
.attr('stroke-width', 2)
.attr('fill', '#11a6e9');
// ====用圆形==
// g.append('circle')
// .attr('class', 'drag')
// .attr('cx', margin.left)
// .attr('cy', margin.bottom)
// .attr('r', 10)
// .attr('stroke', 'pink')
// .attr('fill', 'pink')
// ==end===
const x = 20;
const y = height - margin.bottom - 18;
g.append('polygon')
.attr('class', 'drag')
.attr('points', `${x},${y} ${x + 20},${y} ${x + 20},${y + 10} ${x + 10},${y + 20} ${x},${y + 10}`)
.attr('stroke', '#11a6e9')
.attr('fill', 'white'); 
4-3.白色方块可拖动
const _this = this;
function started(event) {
const circle = d3.select(this).classed('dragging', true);
const dragged = event => {
// 限制可拖动时间范围
let min = event.x < margin.left ? margin.left : event.x;
min = min + margin.left > _this.width ? _this.width - margin.left - 1 : min;
// ====用圆形==
// circle
// .raise()
// .attr('cx', (this.x = min))
// .attr('cy', 50);
// ==end===
const x = min - 10; //减去滑块自身宽度
circle.attr('points', `${x},${y} ${x + 20},${y} ${x + 20},${y + 10} ${x + 10},${y + 20} ${x},${y + 10}`);
_this.time = moment(scale.invert(min)).format('HH:mm:ss');
// 精度不准确,加上粗略显示时间
if (moment(scale.invert(min)).format('HH:mm') == '23:59') {
_this.time = '23:59:59';
}
// 设置线条移动
line.attr('x1', min).attr('x2', min);
};
const ended = () => circle.classed('dragging', false);
event.on('drag', dragged).on('end', ended);
}
g.select('polygon').call(d3.drag().on('start', started));5.模拟时间段数据情况,比如9-12点人流量大显示蓝色,下午13-14人少是橙色
用数组表示,主要是获取初始值和最终值,中间那些值不重要
const blue = ['2023-12-29 01:00:00', '2023-12-29 12:30:30'];
const yellow = ['2023-12-29 17:30:00', '2023-12-29 19:30:15'];
5-1.获取初始值的第一点
// 获取第一个点
const first = parseInt(scale(new Date('2023-12-29 00:00:00')));
5-2.根据时间画两条时间段
svg
.append('line')
.attr('x1', parseInt(scale(new Date(blue[0]))) - first)
.attr('y1', height - margin.bottom)
.attr('x2', parseInt(scale(new Date(blue[1]))) - first)
.attr('y2', height - margin.bottom)
.attr('stroke', '#8688dd')
.attr('stroke-width', 3)
.attr('fill', '#8688dd');
svg
.append('line')
.attr('x1', parseInt(scale(new Date(yellow[0]))) - first)
.attr('y1', height - margin.bottom)
.attr('x2', parseInt(scale(new Date(yellow[1]))) - first)
.attr('y2', height - margin.bottom)
.attr('stroke', '#dfab11')
.attr('stroke-width', 3)
.attr('fill', '#dfab11');以上就是整体的代码过程,完整版组件可看下方
<template>
<div :class="$style.root">
<!-- <svg width="200" height="200">
<polygon points="50,50 150,50 150,100 95,150 50,100" stroke="black" fill="none" />
<polygon points="30,50 40,50 40,55 35,60 30,55" stroke="black" fill="none" />
</svg> -->
<div :class="$style.time">时间{{ time }}</div>
<div ref="rulerRef" :class="$style.ruler"></div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import * as d3 from "https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/d3@7/+esm";
import moment from 'moment';
export default {
data() {
return {
x: null,
svg: null,
g: null,
list: [],
width: 1920,
time: '00:00:00'
};
},
mounted() {
for (let index = 0; index <= 24; index++) {
this.list.push({
time: `2023-12-26 ${index.toString().padStart(2, '0')}:00:00`
});
}
this.init();
},
methods: {
init() {
const height = 100;
const margin = { top: 10, right: 30, left: 30, bottom: 30 };
const svg = d3.create('svg').attr('viewBox', [0, 0, this.width, height]).attr('font-size', 16);
const scale = d3
.scaleTime()
.domain(d3.extent(this.list, d => new Date(d.time)))
.range([margin.left, this.width - margin.left]);
const xAxis = d3
.axisBottom(scale)
.ticks(d3.timeHour.every(2))
.tickSize(20)
.tickSizeOuter(0)
.tickFormat((d, i) => {
return i == 12 ? '23:59:59' : d3.timeFormat('%H:%M:%S')(d);
})
.tickPadding(-50);
const axis = d3
.axisBottom(scale)
.ticks(80)
.tickSize(10)
.tickFormat(() => null);
svg
.append('g')
.attr('class', 'lines')
.attr('transform', `translate(0,${height - margin.bottom})`)
.call(axis)
.select('.domain')
.remove();
svg
.append('g')
.attr('class', 'base')
.attr('transform', `translate(0,${height - margin.bottom})`)
.call(xAxis)
.selectAll('path')
.style('stroke', '#a19d9d')
.style('stroke-width', 3);
// 画颜色线条(模拟数据)===start===
const blue = ['2023-12-29 01:00:00', '2023-12-29 12:30:30'];
const yellow = ['2023-12-29 17:30:00', '2023-12-29 19:30:15'];
// 获取第一个点
const first = parseInt(scale(new Date('2023-12-29 00:00:00')));
svg
.append('line')
.attr('x1', parseInt(scale(new Date(blue[0]))) - first)
.attr('y1', height - margin.bottom)
.attr('x2', parseInt(scale(new Date(blue[1]))) - first)
.attr('y2', height - margin.bottom)
.attr('stroke', '#8688dd')
.attr('stroke-width', 3)
.attr('fill', '#8688dd');
svg
.append('line')
.attr('x1', parseInt(scale(new Date(yellow[0]))) - first)
.attr('y1', height - margin.bottom)
.attr('x2', parseInt(scale(new Date(yellow[1]))) - first)
.attr('y2', height - margin.bottom)
.attr('stroke', '#dfab11')
.attr('stroke-width', 3)
.attr('fill', '#dfab11');
// =====end==========
// 画圆和线条
const g = svg.append('g');
const line = g
.append('line')
.attr('x1', margin.left)
.attr('y1', height - margin.bottom)
.attr('x2', margin.left)
.attr('y2', height)
.attr('stroke', '#11a6e9')
.attr('stroke-width', 2)
.attr('fill', '#11a6e9');
// ====用圆形==
// g.append('circle')
// .attr('class', 'drag')
// .attr('cx', margin.left)
// .attr('cy', margin.bottom)
// .attr('r', 10)
// .attr('stroke', 'pink')
// .attr('fill', 'pink')
// ==end===
const x = 20;
const y = height - margin.bottom - 18;
g.append('polygon')
.attr('class', 'drag')
.attr('points', `${x},${y} ${x + 20},${y} ${x + 20},${y + 10} ${x + 10},${y + 20} ${x},${y + 10}`)
.attr('stroke', '#11a6e9')
.attr('fill', 'white');
const _this = this;
function started(event) {
const circle = d3.select(this).classed('dragging', true);
const dragged = event => {
// 限制可拖动时间范围
let min = event.x < margin.left ? margin.left : event.x;
min = min + margin.left > _this.width ? _this.width - margin.left - 1 : min;
// ====用圆形==
// circle
// .raise()
// .attr('cx', (this.x = min))
// .attr('cy', 50);
// ==end===
const x = min - 10; //减去滑块自身宽度
circle.attr('points', `${x},${y} ${x + 20},${y} ${x + 20},${y + 10} ${x + 10},${y + 20} ${x},${y + 10}`);
_this.time = moment(scale.invert(min)).format('HH:mm:ss');
// 精度不准确,加上粗略显示时间
if (moment(scale.invert(min)).format('HH:mm') == '23:59') {
_this.time = '23:59:59';
}
// 设置线条移动
line.attr('x1', min).attr('x2', min);
};
const ended = () => circle.classed('dragging', false);
event.on('drag', dragged).on('end', ended);
}
g.select('polygon').call(d3.drag().on('start', started));
// 更改线段颜色
svg.selectAll('.base line').style('stroke', '#999');
svg.selectAll('.lines line').style('stroke', '#cbc7c7');
this.$refs.rulerRef.appendChild(svg.node());
}
}
};
</script>
<style lang="scss" module>
.root {
padding-top: 30px;
width: 100%;
.time {
text-align: center;
width: 100%;
}
.ruler {
width: 100%;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid pink;
box-sizing: border-box;
background: beige;
}
}
</style>

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








