In an infinite chess board with coordinates from -infinity to +infinity, you have a knight at square [0, 0].
A knight has 8 possible moves it can make, as illustrated below. Each move is two squares in a cardinal direction, then one square in an orthogonal direction.
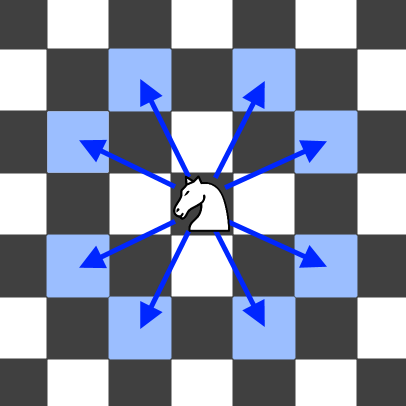
Return the minimum number of steps needed to move the knight to the square [x, y]. It is guaranteed the answer exists.
Example 1:
Input: x = 2, y = 1 Output: 1 Explanation: [0, 0] → [2, 1]
Example 2:
Input: x = 5, y = 5 Output: 4 Explanation: [0, 0] → [2, 1] → [4, 2] → [3, 4] → [5, 5]
Constraints:
|x| + |y| <= 300
Because x and y are constrained to be in range[-300, 300], we can use BFS to find the minimum steps needed to reach target(x, y). Furthermore, we can only consider the case that x >=0 && y >=0 since the chess board is symmetric. The bfs implementation is pretty straightforward. There are two important points you need to be careful with.
1. Pruning. We can limit the search dimension within 310 * 310. Any moves that lead to a position that is outside this box will not yield an optimal result.
2. Initially, you used a Set of type int[] to track visited positions. This caused TLE because you didn't overwrite the hashCode and equals methods for int[]. As a result, Set uses the default hashCode and equals method when checking if an element is already in the set. For equals(), The default implementation provided by the JDK is based on memory location — two objects are equal if and only if they are stored in the same memory address. For a comprehensive reading, refer to https://dzone.com/articles/working-with-hashcode-and-equals-in-java
O(x * y) runtime and space
class Solution { public int minKnightMoves(int x, int y) { x = Math.abs(x); y = Math.abs(y); int MAXN = 310, steps = 0; int[] dx = {-2,-1,1,2,2,1,-1,-2}; int[] dy = {1,2,2,1,-1,-2,-2,-1}; Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>(); boolean[][] visited = new boolean[MAXN][MAXN]; q.add(new int[]{0,0}); visited[0][0] = true; while(q.size() > 0) { int sz = q.size(); for(int i = 0; i < sz; i++) { int[] curr = q.poll(); if(curr[0] == x && curr[1] == y) { return steps; } for(int j = 0; j < 8; j++) { int x1 = curr[0] + dx[j]; int y1 = curr[1] + dy[j]; if(x1 < 0 || y1 < 0 || x1 >= MAXN || y1 >= MAXN) { continue; } if(!visited[x1][y1]) { visited[x1][y1] = true; q.add(new int[]{x1, y1}); } } } steps++; } return -1; } }
BFS with overriden hashCode() and equals(). The asymptotic runtime complexity is the same with using 2D boolean array to track visited positions. But it is slower due to all the Point objects creation overhead.
class Solution { class Point { int x, y; Point(int x, int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (this == o) return true; if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false; Point point = (Point) o; return x == point.x && y == point.y; } @Override public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(x, y); } } public int minKnightMoves(int x, int y) { x = Math.abs(x); y = Math.abs(y); int MAXN = 310, steps = 0; int[] dx = {-2,-1,1,2,2,1,-1,-2}; int[] dy = {1,2,2,1,-1,-2,-2,-1}; Queue<Point> q = new LinkedList<>(); Set<Point> visited = new HashSet<>(); Point sp = new Point(0, 0); q.add(sp); visited.add(sp); while(q.size() > 0) { int sz = q.size(); for(int i = 0; i < sz; i++) { Point curr = q.poll(); if(curr.x == x && curr.y == y) { return steps; } for(int j = 0; j < 8; j++) { int x1 = curr.x + dx[j]; int y1 = curr.y + dy[j]; if(x1 < 0 || y1 < 0 || x1 >= MAXN || y1 >= MAXN) { continue; } Point p = new Point(x1, y1); if(!visited.contains(p)) { visited.add(p); q.add(p); } } } steps++; } return -1; } }





















 370
370











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








