1. image loading 框架:
1.1 Glide
1.2 Picasso
1.3
2.网络框架:
2.1 xUtil3
1.1Glide:
一、Glide-Getting Started
Glide:
Glide就像Picasso,能从许多资源上加载和显示图片,也照顾了缓存和做图片操作的时候保持一个低的内存影响,它已经被官方谷歌应用程序(如Google I / O的应用程序2015)和Picasso一样受欢迎,在本系列中,我们将探索Glide在Picasso的差异和优势。
Why Use Glide?
经验丰富的Android开发人员可以跳过这一节,但对于初学者来说:你可能会问自己为什么要使用Glide代替自己的实现。
在处理图像时Android是非常细致的,因为它会逐个像素加载到内存。手机照相机中的相片平均大小是2592*1936像素(5百万像素)大约占19MB内存。如果你有一个复杂的网络请求去缓存和处理图片,自己写你将花费大量的时间,甚至安全问题会使你头疼,但是如果你使用一个测试好的框架像Glide变将变得安全方便.
Gradle
如同大多数依赖关系一样你的Gradler project的build.gradle增加一行:
compile 'com.github.bumptech.glide:glide:3.7.0'
Maven
Glide也支持Maven projects
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.bumptech.glide</groupId>
<artifactId>glide</artifactId>
<version>3.7.0</version>
<type>aar</type>
</dependency>
First Loading Image from a URL
就像Picasso,Glide库使用一个连贯接口。Glide的builder至少需要三个参数作为一个完整的方法请求:
-
with(Context context) :许多Android API调用上下文是必要的。Glide没有区别。Glide很方便因为它还可以传入Activity和Fragment对象
-
load(String imageUrl) :在这里你指定图像应该被加载。通常这里传入的是一个URL的字符串去加载网络图片
-
into(ImageView targetImageView) :目标ImageView,你想要显示的ImageView
理论解释总是难以把握,让我们看一个实际的例子:
ImageView targetImageView = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.imageView)
String internetUrl = "http://i.imgur.com/DvpvklR.png"
Glide
.with(context)
.load(internetUrl)
.into(targetImageView)
二、Glide-Advanced Loading
Loading from Resources
从Android加载资源。而不是给一个字符串URL指向一个互联网,给定int类型资源。
int resourceId = R.mipmap.ic_launcher
Glide
.with(context)
.load(resourceId)
.into(imageViewResource)
如果你对R.mipmap困惑,它是Android图标处理的新方法。
当然上述你可以直接给ImageView指定一个资源,但是使用Glide是否更加有趣
Loading from File
从文件加载图片
// this file probably does not exist on your device. However, you can use any file path, which points to an image file
File file = new File(Environment.getExternalStoragePublicDirectory(Environment.DIRECTORY_PICTURES), "Running.jpg");
Glide
.with(context)
.load(file)
.into(imageViewFile);
Loading from Uri
最后,您还可以加载图像定义为一个Uri。这个请求不同于前面的操作:
// this could be any Uri. for demonstration purposes we're just creating an Uri pointing to a launcher icon
Uri uri = resourceIdToUri(context, R.mipmap.future_studio_launcher);
Glide
.with(context)
.load(uri)
.into(imageViewUri);
这个帮助函数是一个简单的从resourceId到一个Uri的转变,它可以是任何的Uri
public static final String ANDROID_RESOURCE = "android.resource://";
public static final String FOREWARD_SLASH = "/";
private static Uri resourceIdToUri(Context context, int resourceId) {
return Uri.parse(ANDROID_RESOURCE + context.getPackageName() + FOREWARD_SLASH + resourceId);
}
三、Glide-Sample Gallery Implementation: ListView
效果图:
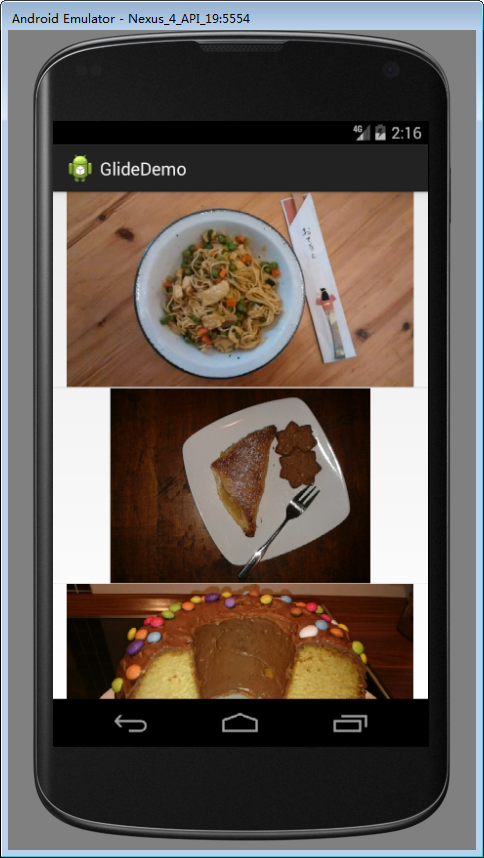
首先添加网络权限:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>
activity_main:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="${relativePackage}.${activityClass}" >
<ListView
android:id="@+id/listView"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
listview_item_image:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<ImageView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="200dp"/>
MainActivity:
import com.bumptech.glide.Glide;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.MenuItem;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.ArrayAdapter;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.ListView;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
ListView listView;
public static String[] eatFoodyImages = {
"http://i.imgur.com/rFLNqWI.jpg",
"http://i.imgur.com/C9pBVt7.jpg",
"http://i.imgur.com/rT5vXE1.jpg",
"http://i.imgur.com/aIy5R2k.jpg",
"http://i.imgur.com/MoJs9pT.jpg",
"http://i.imgur.com/S963yEM.jpg",
"http://i.imgur.com/rLR2cyc.jpg",
"http://i.imgur.com/SEPdUIx.jpg",
"http://i.imgur.com/aC9OjaM.jpg",
"http://i.imgur.com/76Jfv9b.jpg",
"http://i.imgur.com/fUX7EIB.jpg",
"http://i.imgur.com/syELajx.jpg",
"http://i.imgur.com/COzBnru.jpg",
"http://i.imgur.com/Z3QjilA.jpg",
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
listView=(ListView) findViewById(R.id.listView);
listView.setAdapter(new ImageListAdapter(MainActivity.this, eatFoodyImages));
}
public class ImageListAdapter extends ArrayAdapter {
private Context context;
private LayoutInflater inflater;
private String[] imageUrls;
public ImageListAdapter(Context context, String[] imageUrls) {
super(context, R.layout.listview_item_image, imageUrls);
this.context = context;
this.imageUrls = imageUrls;
inflater = LayoutInflater.from(context);
}
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
if (null == convertView) {
convertView = inflater.inflate(R.layout.listview_item_image, parent, false);
}
Glide
.with(context)
.load(imageUrls[position])
.into((ImageView) convertView);
return convertView;
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
总结:其实不论你加载一张还是多张图片Glide的调用还是一样的
四、Glide-Placeholder & Fade Animations
我们可能甚至不需要解释或讨论:空imageview在任何界面不好看。如果你使用Glide,你最有可能是通过一个网络连接加载图像。根据用户的环境中,这可能要花费大量的时间。一个应用程序的预期行为是显示一个占位符(就是还未加载图片前显示给用户的图片),直到图像加载和处理占位符消失,这样就可以给用户留给一个很好的体验效果。
Glide的封装使得这个很容易做到!只要调用.placeHolder()和一个引用(资源)和,作为一个占位符,直到你的实际图像已经准备好了。
Glide
.with(context)
.load(UsageExampleListViewAdapter.eatFoodyImages[0])
.placeholder(R.mipmap.ic_launcher) // can also be a drawable
.into(imageViewPlaceholder)
很明显,你不能设置一个互联网url作为占位符,因为那个需要加载。应用resources和drawable是保证是可用的和可访问。
Error Placeholder: .error()
目前,让我们假设我们的程序试图加载一个图像从一个网站,。Glide返回给我们一个错误的回调 ,这时候我们可以使用Glide的连贯接口是与前面的示例相同pre-display占位符,只是用不同的函数调用error():
Glide
.with(context)
.load("http://futurestud.io/non_existing_imag e.png")
.placeholder(R.mipmap.ic_launcher) // can also be a drawable
.error(R.mipmap.future_studio_launcher) // will be displayed if the image cannot be loaded
.into(imageViewError)
当我们定义的图片不能加载时,Glide将展示R.mipmap.future_studio_launcher替代,error()参数必定是已经存在的resources和drawable
Use of crossFade()
无论如果你加载图片之前还是错误加载显示一个占位符,改变图像的ImageView UI是一个非常重要的变化。一个简单的选择使这种变化更顺利和容易映入眼帘,是使用crossfase(淡入淡出)动画。Glide附带标准crossfade(淡入淡出)动画,这是默认(当前版本3.6.1)活动。如果你想Glide显示crossfase(淡入淡出)动画,你所要做的就是调用crossFade()方法;
Glide
.with(context)
.load(UsageExampleListViewAdapter.eatFoodyImages[0])
.placeholder(R.mipmap.ic_launcher) // can also be a drawable
.error(R.mipmap.future_studio_launcher) // will be displayed if the image cannot be loaded
.crossFade()
.into(imageViewFade)
crossFade()方法还有另一个重载函数crossFase(int duration),如果你想加速或减速这个动画,你可以通过这个函数添加一个时间,默认是300毫秒
Use of dontAnimate()
使用这个方法表示是没有crossfase(淡入淡出)动画的,直接展现imageView给用户。
Glide
.with(context)
.load(UsageExampleListViewAdapter.eatFoodyImages[0])
.placeholder(R.mipmap.ic_launcher) // can also be a drawable
.error(R.mipmap.future_studio_launcher) // will be displayed if the image cannot be loaded
.dontAnimate()
.into(imageViewFade)
总结:以上的每个函数都是不相关的,比如你可以调用error()而不调用placeholder()等等。
五、Glide-Image Resizing & Scaling
在你的服务器或这API需要合适的尺寸这将是一个完美的解决方式,
相比Picasso,Glide在memory-wise更有效率,Glide自定图像大小范围在缓存和内存中,Picasso有相同的能力,但是需要调用fit().对于Glide,如果图像没有显示在合适的大小,调用override(horizontalSize, verticalSize),之后将重置大小后显示给用户
Glide
.with(context)
.load(UsageExampleListViewAdapter.eatFoodyImages[0])
.override(600, 200) // resizes the image to these dimensions (in pixel). does not respect aspect ratio
.into(imageViewResize);
Scaling Images
- CenterCrop : 一种尺度图像的裁剪技术,填补了ImageView的要求范围,然后裁减了多余的。ImageView将被完全填满,但图像可能显示不全。
Glide
.with(context)
.load(UsageExampleListViewAdapter.eatFoodyImages[0])
.override(600, 200) // resizes the image to these dimensions (in pixel)
.centerCrop() // this cropping technique scales the image so that it fills the requested bounds and then crops the extra.
.into(imageViewResizeCenterCrop)
- FitCenter :fitCenter()是一种尺度图像的裁剪技术,这样两个尺寸等于或小于请求的ImageView的界限,图像将显示完全,但可能不会填满整个ImageView。
Glide
.with(context)
.load(UsageExampleListViewAdapter.eatFoodyImages[0])
.override(600, 200)
.fitCenter()
.into(imageViewResizeFitCenter)
六、Glide — Displaying Gifs & Videos
Displaying Gifs
大多数的图片加载框架只支持加载和显示图片,在Glide中Gif将是一个特殊的功能
String gifUrl = "http://i.kinja-img.com/gawker-media/image/upload/s
Glide
.with( context )
.load( gifUrl )
.into( imageViewGif );
在这里你仍然可以调用error()当GIF不能加载时,和placeholder()GIF加载之前
Glide
.with( context )
.load( gifUrl )
.placeholder( R.drawable.cupcake )
.error( R.drawable.full_cake )
.into( imageViewGif )
Gif Check
上面的代码存在一个潜在问题,就是如果你的Url不是一个Gif的话,可能就是一个普通的图像,Glide不能自动识别它,所以如果我们期望加载一个GIF还必须做一个声明:
Glide
.with( context )
.load( gifUrl )
.asGif()//声明
.error( R.drawable.full_cake )
.into( imageViewGif )
如果gifUrl是gif,没有什么变化。然而,与之前不同的是,如果gifUrl不是一个Gif,Glide会理解加载失败。Glide有优势,error()方法被调用和错误占位符显示,即使gifUrl是一个正确的Url图像(但不是一个Gif)。
Display Gif as Bitmap
在某些情况下可能我们只想显示GIF图像的第一帧,你可以调用asBitmap()方法
Glide
.with( context )
.load( gifUrl )
.asBitmap()
.into( imageViewGifAsBitmap )
Display of Local Videos
如果gif是视频。Glide也能够显示视频的缩略图,只要他们存储在手机。让我们假设你得到文件路径,让用户选择一个视频:
String filePath = "/storage/emulated/0/Pictures/example_video.mp4";
Glide
.with( context )
.load( Uri.fromFile( new File( filePath ) ) )
.into( imageViewGifAsBitmap );
然而这适用于本地视频,而且只能显示第一帧,如果是网络或者其他的视频将不能显示,你应该使用VideoView
七、Glide — Caching Basics
Using Cache Strategies
Memory Cache:
让我们想象它从一个非常简单的要求:从互联网ImageView加载一张图片:
Glide
.with( context )
.load( eatFoodyImages[0] )
.skipMemoryCache( true )
.into( imageViewInternet );
你已经注意到我们。skipMemoryCache(true)专门告诉Glide跳过内存缓存。这意味着Glide不会把图像在内存缓存中。重要的是要理解,这只会影响内存缓存!Glide仍将利用磁盘高速缓存,以避免另一个网络请求。
还好知道Glide将所有图像资源默认缓存到内存中。因此,一个特定的调用skipMemoryCache(false)不是必需的。
提示:如果你请求相同的Url和调用.skipMemoryCache( true )方法,资源将会放在内存中缓存,确保你的所有调用相同的资源,当你想要调整缓存行为!
Skipping Disk Cache
当你学到的在上面的部分中,即使你关闭内存缓存,请求图像仍将存储在设备上的磁盘存储。如果你一个图像,在相同的URL,但正在迅速改变,你可能希望禁用磁盘缓存。 你可以改变Glide的磁盘缓存.diskCacheStrategy()方法。与.skipMemoryCache()方法不同的是它接受一个enum,而不是一个简单的布尔。如果你想禁用磁盘缓存请求时,使用DiskCacheStrategy枚举值DiskCacheStrategy.NONE作为参数
Glide
.with( context )
.load( eatFoodyImages[0] )
.diskCacheStrategy( DiskCacheStrategy.NONE )
.into( imageViewInternet )
这个代码片段的图像将不会保存在磁盘高速缓存。然而,默认情况下它仍然会使用内存缓存!以禁用缓存,将方法调用:
Glide
.with( context )
.load( eatFoodyImages[0] )
.diskCacheStrategy( DiskCacheStrategy.NONE )
.skipMemoryCache( true )
.into( imageViewInternet )
Customize Disk Cache Behavior
Glide缓存原始,完全解决图像和另外小版本的图片。举个例子,如果你请求与1000 x1000像素,和500 x500像素两个图像,Glide将两个版本的图像缓存。
. diskCacheStrategy()参数:
-
DiskCacheStrategy.NONE:禁止缓存
-
DiskCacheStrategy.SOURCE :缓存只有原来的全分辨率图像。
-
DiskCacheStrategy.RESULT: 缓存只有最终的图像,在降低分辨率(也可能是转换)(默认行为)
-
DiskCacheStrategy.ALL :缓存所有版本的图像
八、Glide — Request Priorities
通常我们会从网络加载多个图片,加入我们顶部的是一个大的好看的图片,底部是两张小图片,这时候用户很可能想优先加载大的图片,Glide完美解决了这一个问题,通过调用.priority()传入Priority enum。
Getting to know the Priority enum
enum给你四个不同的选项。这是优先级增加的命令列表
- Priority.LOW
- Priority.NORMAL
- Priority.HIGH
- Priority.IMMEDIATE
Usage Example: Hero Element with Child Images
刚才那个例子,理论上讲我们将大图片的优先级设置为HIGH就应该足够了,但是我们这里还将小图片的优先级设为LOW;
private void loadImageWithHighPriority() {
Glide
.with( context )
.load( UsageExampleListViewAdapter.eatFoodyImages[0] )
.priority( Priority.HIGH )
.into( imageViewHero )
}
private void loadImagesWithLowPriority() {
Glide
.with( context )
.load( UsageExampleListViewAdapter.eatFoodyImages[1] )
.priority( Priority.LOW )
.into( imageViewLowPrioLeft )
Glide
.with( context )
.load( UsageExampleListViewAdapter.eatFoodyImages[2] )
.priority( Priority.LOW )
.into( imageViewLowPrioRight )
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
运行的话大图片将第一显示,但是这也会增加显示时间。
九、Glide — Thumbnails
Advantages of Thumbnails
操作缩略图之前,确保你理解和笑话所有选项缓存和请求的优先级。如果你前面你懂了,然后使用了解缩略图可以帮助你进一步提高你的Android应用程序。
缩略图是不同的比之前的占位符。占位符必须附带的应用程序作为一个捆绑的资源。缩略图是一个动态的占位符,也可以从互联网上加载。缩略图会在显示实际的请求之前加载并处理。如果缩略图,不管出于什么原因,到达原始图像后,它不替换原来的形象。它只是将被销毁。
Simple Thumbnails
Glide为缩略图提供了两种不同的方式。首先是简单的选择,使用原始图像,只是在一个更小的分辨率。这个方法特别有用的组合ListView和detail Views。如果你已经在ListView显示图像,我们假设,在250 x250像素,图像将需要一个更大的分辨率detail Views。然而,从用户的角度来看,他已经看到了一个小版本的形象,为什么会有几秒钟的占位符,直到同样的图像显示(高分辨率)?
在这种情况下,它更多的意义继续显示250 x250像素版本细节视图,在后台加载完整的分辨率。Glide使之成为可能,调用.thumbnail()方法。在这种情况下,参数是一个浮点数大小:
Glide
.with( context )
.load( UsageExampleGifAndVideos.gifUrl )
.thumbnail( 0.1f )
.into( imageView2 )
例如,如果你通过0.1 f作为参数,Glide将显示原始图像大小的10%。如果原始图像1000 x1000像素,缩略图100 x100像素。自比ImageView图像会小的多,你需要确保ScaleType正确设置。 注意所有请求设置应用到原始请求也应用于缩略图。例如,如果您使用一个转换图像灰度,都会发生同样的缩略图。
Advanced Thumbnails with Complete Different Requests
使用.thumbnail()与一个浮点参数是容易设置,可以非常有效的,它并不总是有意义。如果缩略图需要负载相同的全分辨率图像通过网络,它可能不是更快。因此,Glide提供了另一种选择加载和显示缩略图。 第二个方式是通过一个完整的新的Glide请求参数。让我们来看一个例子:
private void loadImageThumbnailRequest() {
DrawableRequestBuilder<String> thumbnailRequest = Glide
.with( context )
.load( eatFoodyImages[2] );
Glide
.with( context )
.load( UsageExampleGifAndVideos.gifUrl )
.thumbnail( thumbnailRequest )
.into( imageView3 );
}
所不同的是,第一个缩略图请求完全独立于第二原始请求。缩略图可以是不同的资源或图像的URL,您可以应用不同的转换,等等。
提示,如果你想要更加疯狂,你可以使用递归和应用请求额外的缩略图请求到缩略图…
十、Glide — Callbacks: SimpleTarget and ViewTarget for Custom View Classes
这篇文章中我们将使用Bitmap作为我们的image,而不是ImageView
Callbacks in Glide: Targets:
如果我们想使用Bitmap来显示Image,Glide提供了一个简单的方法来与Targets图像的位图资源的访问。Targets只不是一个回调,用来处理Glide加载完成后结果。Glide提供各种各样的Targets,而每个都有一个明确的target。我们从SimpleTarget开始。
SimpleTarget:
代码:
private SimpleTarget target = new SimpleTarget<Bitmap>() {
@Override
public void onResourceReady(Bitmap bitmap, GlideAnimation glideAnimation) {
imageView1.setImageBitmap( bitmap );
}
};
private void loadImageSimpleTarget() {
Glide
.with( context )
.load( eatFoodyImages[0] )
.asBitmap()
.into( target );
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
代码第一部分是声明一个域对象,给图片设置Bitmap,
第二部分是和之前一样将target传入into(),不同的是,这里需要声明asBitmap(),防止URL加载的图片可能是GIF或者Viedo
Pay Attention with Targets
除了知道怎么实现Glide的Taegts之后,你还必须知道两点:
- 首先我们知道Android和java中我们可以直接在into(new
SimpleTarget((){});,但是这也是一个缺陷这可能当加载完图片缺未加载回调时SimpleTarget就被回收了,所以我们必须和我们如上一样,定义成一个域对象
解决办法是:.with( context.getApplicationContext() ),这样仅仅当application停止时Glide请求才会停
止,请记住这一点。最后,如果你的请求需要以外的activity生命周期,使用以下代码片段:
private void loadImageSimpleTargetApplicationContext() {
Glide
.with( context.getApplicationContext() )
.load( eatFoodyImages[1]
.asBitmap()
.into( target2 );
}
Target with Specific Size
target另一个潜在的问题是他们没有一个特定的大小。如果你通过ImageView .into的参数(),Glide的大小将使用ImageView限制图像的大小。例如,如果加载图片是1000 x1000像素,但是ImageView只有250 x250像素,Glide将使用size较小的图像保存进内存。很明显,target并不能这样做,因为没有已知的大小。然而,如果你有一个特定的大小,您可以增加回调。如果你知道图像应该多大,你应该指定它以便节省内存:
private SimpleTarget target2 = new SimpleTarget<Bitmap>( 250, 250 ) {
@Override
public void onResourceReady(Bitmap bitmap, GlideAnimation glideAnimation) {
imageView2.setImageBitmap( bitmap );
}
};
private void loadImageSimpleTargetApplicationContext() {
Glide
.with( context.getApplicationContext() )
.load( eatFoodyImages[1] )
.asBitmap()
.into( target2 );
}
ViewTarget
我们知道Glide不支持加载自定义View的ImageVeiw,但是Glide提供了ViewTarget很好的帮我们解决了这类问题:
public class FutureStudioView extends FrameLayout {
ImageView iv;
TextView tv;
public void initialize(Context context) {
inflate( context, R.layout.custom_view_futurestudio, this );
iv = (ImageView) findViewById( R.id.custom_view_image );
tv = (TextView) findViewById( R.id.custom_view_text );
}
public FutureStudioView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super( context, attrs );
initialize( context );
}
public FutureStudioView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super( context, attrs, defStyleAttr );
initialize( context );
}
public void setImage(Drawable drawable) {
iv = (ImageView) findViewById( R.id.custom_view_image );
iv.setImageDrawable( drawable );
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
因为自定义View不是继承ImageView,所以我们不能直接将它传入.into()中,现在我们去创建一个ViewTarget:
private void loadImageViewTarget() {
FutureStudioView customView = (FutureStudioView) findViewById( R.id.custom_view );
viewTarget = new ViewTarget<FutureStudioView, GlideDrawable>( customView ) {
@Override
public void onResourceReady(GlideDrawable resource, GlideAnimation<? super GlideDrawable> glideAnimation) {
this.view.setImage( resource.getCurrent() );
}
};
Glide
.with( context.getApplicationContext() )
.load( eatFoodyImages[2] )
.into( viewTarget );
}
在target的回调方法,我们使用函数setImage(Drawable drawable)给自定义View的ImageView设置图片。
同时,确保看到ViewTarget的构造函数:new ViewTarget < FutureStudioView GlideDrawable >(customView)。 这个应该覆盖所有你需要自定义视图。你也可以在回调函数中做额外的事情。例如,我们可以分析传入的位图的主要颜色和设置TextView的值。
从以上我们看到是一个NotificationCompat.Builder,我们可以看到通知是有icon的,如果ico是本地的我们可以直接加载,然而如果icon来自网络呢,没关系,Glide提供了一个方便的NotificationTarget.
NotificationTarget
代码:
activity_main:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@android:color/white"
android:orientation="vertical">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:padding="2dp">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/remoteview_notification_icon"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_marginRight="2dp"
android:layout_weight="0"
android:scaleType="centerCrop"/>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/remoteview_notification_headline"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:ellipsize="end"
android:singleLine="true"
android:textSize="12sp"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/remoteview_notification_short_message"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:ellipsize="end"
android:paddingBottom="2dp"
android:singleLine="true"
android:textSize="14sp"
android:textStyle="bold"/>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
MainActivity:
import com.bumptech.glide.Glide
import com.bumptech.glide.request.target.NotificationTarget
import android.app.Activity
import android.app.Notification
import android.app.NotificationManager
import android.content.Context
import android.os.Bundle
import android.support.v4.app.NotificationCompat
import android.widget.RemoteViews
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
Context context
private final int NOTIFICATION_ID=1
private NotificationTarget notificationTarget
public static String[] eatFoodyImages = {
"http://i.imgur.com/rFLNqWI.jpg",
"http://i.imgur.com/C9pBVt7.jpg",
"http://i.imgur.com/rT5vXE1.jpg",
"http://i.imgur.com/aIy5R2k.jpg",
"http://i.imgur.com/MoJs9pT.jpg",
"http://i.imgur.com/S963yEM.jpg",
"http://i.imgur.com/rLR2cyc.jpg",
"http://i.imgur.com/SEPdUIx.jpg",
"http://i.imgur.com/aC9OjaM.jpg",
"http://i.imgur.com/76Jfv9b.jpg",
"http://i.imgur.com/fUX7EIB.jpg",
"http://i.imgur.com/syELajx.jpg",
"http://i.imgur.com/COzBnru.jpg",
"http://i.imgur.com/Z3QjilA.jpg",
}
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
context=this
final RemoteViews rv = new RemoteViews(context.getPackageName(), R.layout.activity_main)
rv.setImageViewResource(R.id.remoteview_notification_icon, R.drawable.ic_launcher)
rv.setTextViewText(R.id.remoteview_notification_headline, "Headline")
rv.setTextViewText(R.id.remoteview_notification_short_message, "Short Message")
// build notification
NotificationCompat.Builder mBuilder =
new NotificationCompat.Builder(context)
.setSmallIcon(R.drawable.ic_launcher)
.setContentTitle("Content Title")
.setContentText("Content Text")
.setContent(rv)
.setPriority( NotificationCompat.PRIORITY_MIN)
final Notification notification = mBuilder.build()
// set big content view for newer androids
if (android.os.Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 16) {
notification.bigContentView = rv
}
NotificationManager mNotificationManager = (NotificationManager) context.getSystemService(Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE)
mNotificationManager.notify(NOTIFICATION_ID, notification)
notificationTarget = new NotificationTarget(
context,
rv,
R.id.remoteview_notification_icon,
notification,
NOTIFICATION_ID)
Glide
.with( context.getApplicationContext() ) // safer!
.load( eatFoodyImages[3] )
.asBitmap()
.into( notificationTarget )
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
步骤:
- 代码中我们首先定义一个RemoteViews 加载和设置值,
- 接着我们自定义了一个notification并将rv作为content传入,
- 接这new NotificationTarget ()将rv,notificaiton传入,
- 最后将配置好的notificationTarget 传入Glide.into()即可
App Widgets
如果你的程序中有widgets并且有图片来自网络,使用AppWidgetTarget将是非常方便的,下面看一个实例;
import com.bumptech.glide.Glide;
import com.bumptech.glide.request.target.AppWidgetTarget;
import android.appwidget.AppWidgetManager;
import android.appwidget.AppWidgetProvider;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Context;
import android.widget.RemoteViews;
public class FSAppWidgetProvider extends AppWidgetProvider {
private AppWidgetTarget appWidgetTarget;
@Override
public void onUpdate(Context context, AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager,
int[] appWidgetIds) {
RemoteViews rv = new RemoteViews(context.getPackageName(), R.layout.activity_main);
appWidgetTarget = new AppWidgetTarget( context, rv,R.id.remoteview_notification_icon, appWidgetIds );
Glide
.with( context.getApplicationContext() )
.load( MainActivity.eatFoodyImages[3] )
.asBitmap()
.into( appWidgetTarget );
pushWidgetUpdate(context, rv);
}
public static void pushWidgetUpdate(Context context, RemoteViews rv) {
ComponentName myWidget = new ComponentName(context, FSAppWidgetProvider.class);
AppWidgetManager manager = AppWidgetManager.getInstance(context);
manager.updateAppWidget(myWidget, rv);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
重要行是声明appWidgetTarget对象和Glide的构建。好消息是AppWidgetTarget你不需要进一步覆盖onResourceReady方法。Glide自动为你做好了。非常好!
十二、Glide — Exceptions: Debugging and Error Handling
Local Debugging
Glide的GeneralRequest类提供了一个方法来设置log级别。不幸的是,你不能容易的使用。然而,有一个非常简单的方法得到Glide的debug log。你所要做的就是通过使用命令行 adb shell 来激活它。打开终端,使用以下命令:
adb shell setprop log.tag.GenericRequest DEBUG
最后一个字段DEBUG是log等级,有如下几种:
- VERBOSE
- DEBUG
- INFO
- WARN
-
ERROR
例如你有一个图片不存在的错误,它会这样输出:
io.futurestud.tutorials.glide D/GenericRequest: load failed
io.futurestud.tutorials.glide D/GenericRequest: java.io.IOException: Request failed 404: Not Found
...
你已经猜到了,上述只能有错误在才能调试测试app,所以下面我们将讲解回调
General Exception Logging
Glide不提供直接访问GenericRequest类设置log记录,但是你可以捕获异常,以防出现错误的请求。例如,如果一个图像不可用,Glide(默默地)会抛出一个异常并会将drawable显示在你指定的. error()中。如果你明确想知道异常信息,你可以创建一个监听器并将其传递给.listener()方法:
为了防止被回收,我们必须将它定义在域字段
private RequestListener<String, GlideDrawable> requestListener = new RequestListener<String, GlideDrawable>() {
@Override
public boolean onException(Exception e, String model, Target<GlideDrawable> target, boolean isFirstResource) {
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean onResourceReady(GlideDrawable resource, String model, Target<GlideDrawable> target, boolean isFromMemoryCache, boolean isFirstResource) {
return false;
}
};
在onException方法()您可以捕获问题,决定你需要做什么,例如需要进行log记录。如果Glide处理结果,如显示一个错误占位符,你应该在onException方法返回false:
Glide
.with( context )
.load(UsageExampleListViewAdapter.eatFoodyImages[0])
.listener( requestListener )
.error( R.drawable.cupcake )
.into( imageViewPlaceholder )
如果你返回false在onException()方法,. error()不需要进行log记录的工作,只会将你设着的drawable显示出来
在前面的十二个博客,您已经了解了所需的所有基础利用Glide的标准功能。从这篇文章开始,我们将深入研究了一些高级的主题。本篇文章,我们将仔细看看Transformations。
Transformations
Transformations可以作为图像处理之前的图像被显示出来。例如,如果您的应用程序需要显示一个图像灰度,但只有获得原始fully-colored版本,您可以使用一个Transformations操作的位图使之从彩色版本变成惨淡的灰色。我们不能理解错了,Transformations并不局限于颜色。你可以改变任何一个图像的大小,颜色,像素,和更多!Glide已经附带两个Transformations,在之前图像调整时候有:fitCenter and centerCrop
Implementing Your Own Transformation
为了应用自己的自定义Transformation,您需要创建一个新类,它实现了Transformation interface。您需要实现的方法很复杂,你得有相当的洞察力,Glide的内部结构使它做得很好。如果你只是想改变常规的位图图像(没有gif /视频!),我们建议使用抽象BitmapTransformation类。它简化了实现不少,应该覆盖95%的用例。 所以,让我们看一个示例BitmapTransformation实现。
public class BlurTransformation extends BitmapTransformation {
public BlurTransformation(Context context) {
super( context );
}
@Override
protected Bitmap transform(BitmapPool pool, Bitmap toTransform, int outWidth, int outHeight) {
return null;
}
@Override
public String getId() {
return null;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
模糊图像渲染脚本:
public class BlurTransformation extends BitmapTransformation {
private RenderScript rs;
public BlurTransformation(Context context) {
super( context );
rs = RenderScript.create( context );
}
@Override
protected Bitmap transform(BitmapPool pool, Bitmap toTransform, int outWidth, int outHeight) {
Bitmap blurredBitmap = toTransform.copy( Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888, true );
Allocation input = Allocation.createFromBitmap(
rs,
blurredBitmap,
Allocation.MipmapControl.MIPMAP_FULL,
Allocation.USAGE_SHARED
);
Allocation output = Allocation.createTyped(rs, input.getType());
ScriptIntrinsicBlur script = ScriptIntrinsicBlur.create(rs, Element.U8_4(rs));
script.setInput(input);
script.setRadius(10);
script.forEach(output);
output.copyTo(blurredBitmap);
toTransform.recycle();
return blurredBitmap;
}
@Override
public String getId() {
return "blur";
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
如果你困惑的代码块transform(),请等待我模糊脚本渲染文章。getId()方法描述了一个独特的标识符对于这个特定的转换。Glide使用缓存系统的关键部分。确保你让它独一无二的以避免意想不到的问题。 在下一节中,我们将学习如何应用我们刚刚创建的转换。
Apply a Single Transformation
Glide有两种应用方式转换。
- 第一是你的类的一个实例作为参数传递给.transform()。可以是任何的Transformation,无论它是一个图像或Gif。
- 另一个选择是使用.bitmapTransform(),它只接受转换为位图。
因为我们实现上面是专为位图,我们可以使用:
Glide
.with( context )
.load( eatFoodyImages[0] )
.transform( new BlurTransformation( context ) )
//.bitmapTransform( new BlurTransformation( context ) ) // this would work too!
.into( imageView1 );
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
Apply Multiple Transformations
通常,Glide的连贯接口允许链接方法。然而Transformations的连贯并非如此。确保你只调用.transform()或.bitmapTransform()一次,或之前的配置将被覆盖!然而,你仍然可以申请多个转换通过多个对象作为参数转变成.transform()(或.bitmapTransform()):
Glide
.with( context )
.load( eatFoodyImages[1] )
.transform( new GreyscaleTransformation( context ), new BlurTransformation( context ) )
.into( imageView2 );
在这个代码片段中,我们应用一个灰度图像,然后模糊。
Glide执行自动转换。太棒了!
提示:当您使用转换,您不能使用.centerCrop()或.fitCenter()
Collection of Glide Transformations
如果你已经有一个想法什么样的Transformations可以使用在你的应用程序,看第二个库:glide-transformations。
它提供了一个各种滑动转换的整和,可能它已经存在你想的转换。 这个library附带两个不同的版本。扩展的版本包括更多的转换,如GPU。他们需要额外的依赖,所以设置为两个版本有点不同。你应该通过转换列表和决定使用哪个版本
Setup for Glide Transformations
配置是很容易的!对于基本的版本你可以添加另一个你当前的build.gradle行:
dependencies {
compile 'jp.wasabeef:glide-transformations:2.0.0'
}
如果你想使用GPU的转换
repositories {
jcenter()
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
compile 'jp.wasabeef:glide-transformations:2.0.0'
compile 'jp.co.cyberagent.android.gpuimage:gpuimage-library:1.3.0'
}
Usage of Glide Transformations
在你同步Android studio与构建build.gradle文件,您可以使用转换集合。使用模式是一样的与你自定义转换一样。
假设我们想模糊集合的模糊图像变换:
Glide
.with( context )
.load( eatFoodyImages[2] )
.bitmapTransform( new jp.wasabeef.glide.transformations.BlurTransformation( context, 25 ) )
.into( imageView3 )
你也可以应用转换列表就像上面我们已经看到.bitmapTransform()方法接受两个,单个转换或者转换列表!
十四、Glide — Custom Animations with
animate()
上篇博客,我们看了之前转换图像显示。本篇博客我们继续与动画图像的显示的操作。
Animation Basics
从图像到图像的平滑过渡它是非常重要的。用户在欣赏app的时候没有很大的改变,这就是Glide动画,Glide附带了一个标准的动画在软化UI的变化。在我们的第4篇中有提到.crossFade()
Glide提供两个选项设置动画。两个版本都是.animate()方法,只是传入不同的参数。
- 我们忽略了第三个动画:animate(Animation animation).
Animation from Resources
Glide
.with( context )
.load( eatFoodyImages[0] )
.animate( android.R.anim.slide_in_left ) // or R.anim.zoom_in
.into( imageView1 )
返回代码:第一个操作是通过一个Android资源id指向一个动画资源。一个简单的例子是Android系统提供的:android.R.anim.slide_in_left。其背后的代码仅仅是一个XML描述动画:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<set xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<translate android:fromXDelta="-50%p" android:toXDelta="0"
android:duration="@android:integer/config_mediumAnimTime"/>
<alpha android:fromAlpha="0.0" android:toAlpha="1.0"
android:duration="@android:integer/config_mediumAnimTime" />
</set>
当然,您可以创建您自己的XML动画。例如,一个从小到大动画,开始图片小,然后扩大到全尺寸:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<set xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:fillAfter="true">
<scale
android:duration="@android:integer/config_longAnimTime"
android:fromXScale="0.1"
android:fromYScale="0.1"
android:pivotX="50%"
android:pivotY="50%"
android:toXScale="1"
android:toYScale="1"/>
</set>
动画在网络请求加载时就已经准备好了
Animation via Custom Class
通过实现ViewPropertyAnimation.Animator接口
接口是简单的事情,你只需要实现void animate(View view)方法。这个View对象是整个target View。如果它是一个自定义View,您可以找到你的view的子元素,并做必要的动画。
让我们看一个简单的例子。假设你想通过编程实现一个fading(衰弱)的动画,你需要创建动画对象:
ViewPropertyAnimation.Animator animationObject = new ViewPropertyAnimation.Animator() {
@Override
public void animate(View view) {
view.setAlpha( 0f );
ObjectAnimator fadeAnim = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat( view, "alpha", 0f, 1f );
fadeAnim.setDuration( 2500 );
fadeAnim.start();
}
};
接下来在Glide中设置请求
Glide
.with( context )
.load( eatFoodyImages[1] )
.animate( animationObject )
.into( imageView2 )
当然,在你的动画对象的animate(View view)的方法,你可以做任何你想做的视图。用你的动画展现创意。
十五、Glide — Integrating Networking
Stacks
一个重要的模块是从网络通过HTTP/HTTPS协议下载图片显示。已经有不少开发人员对于网络提供了框架。每个框架都有自己的优点和缺点。最后,框架的归结为项目和开发人员的个人品味。
从理论上讲,Glide可以处理任何实现,满足基本的网络功能。将网络用在Glide并非完全无缝的。它需要一个接口Glide’s ModelLoader。
为了使你的开发更容易,滑翔提供了实现两个网络库:OkHttp和 Volley。
OkHttp 2
让我们假设你想要集成OkHttp 2作为Glide的网络框架。集成可以通过声明一个GlideModule手动完成。如果你想避免手工实现,只需要打开您的构建。gradle并添加以下两行你的依赖关系:
dependencies {
// your other dependencies
// ...
// Glide
compile 'com.github.bumptech.glide:glide:3.7.0'
// Glide's OkHttp2 Integration
compile 'com.github.bumptech.glide:okhttp-integration:1.4.0@aar'
compile 'com.squareup.okhttp:okhttp:2.7.5'
}
Gradle将自动合并必要的GlideModule 到你的AndroidManifest。清单文件中Glide会认出它的存在和使用OkHttp所有网络连接。
Volley
如果使用Volley,你必须改变build.gradle:
dependencies {
// your other dependencies
// ...
// Glide
compile 'com.github.bumptech.glide:glide:3.7.0'
// Glide's Volley Integration
compile 'com.github.bumptech.glide:volley-integration:1.4.0@aar'
compile 'com.mcxiaoke.volley:library:1.0.8'
}
Volley集成库添加到您的项目。集成库添加GlideModule到你的 AndroidManifest。Glide会自动识别它并使用Volley作为网络框架。不需要进一步配置!
警告:如果你声明两个库在你的build.gradle,都将得到增加。因为Glide不负载在任何特定的顺序,你将会出现一个不稳定的情况,因为Glide不清楚使用哪个网络框架了。确保你只添加一个集成库。
OkHttp 3
如果使用OkHttp3,你必须改变build.gradle:
dependencies {
// your other dependencies
// ...
// Glide
compile 'com.github.bumptech.glide:glide:3.7.0'
// Glide's OkHttp3 Integration
compile 'com.github.bumptech.glide:okhttp3-integration:1.4.0@aar'
compile 'com.squareup.okhttp3:okhttp:3.2.0'
}
Other Networking Libraries
如果你想使用其他的网络框架,那么你是倒霉的,因为Glide不会自动配置除了Volly,OKHttp2&OkHttp3,然而你还是去GitHub上参考实现这Volly还有OkHttp2&OkHtp3
十六、Glide — How to Rotate Images
一段时间前,我们有一个问题关于如何用Glide旋转图像,因为Picasso提供 out-of-the-box的函数。不幸的是,Glide并没有提供一个方法调用,但在这篇文章我们将向您展示如何让它几乎一样容易。
How to Rotate Images with Glide
实际上 android.graphics.Matrix类提供了我们需要的(以及更多)。旋转图像的代码片段非常简单:
Bitmap toTransform = ... // your bitmap source
Matrix matrix = new Matrix();
matrix.postRotate(rotateRotationAngle);
Bitmap.createBitmap(toTransform, 0, 0, toTransform.getWidth(), toTransform.getHeight(), matrix, true);
为了使它更有用,特别是在使用Glide的情况下,我们将包装这个BitmapTransformation:
public class RotateTransformation extends BitmapTransformation {
private float rotateRotationAngle = 0f;
public RotateTransformation(Context context, float rotateRotationAngle) {
super( context );
this.rotateRotationAngle = rotateRotationAngle;
}
@Override
protected Bitmap transform(BitmapPool pool, Bitmap toTransform, int outWidth, int outHeight) {
Matrix matrix = new Matrix();
matrix.postRotate(rotateRotationAngle);
return Bitmap.createBitmap(toTransform, 0, 0, toTransform.getWidth(), toTransform.getHeight(), matrix, true);
}
@Override
public String getId() {
return "rotate" + rotateRotationAngle;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
如果你不确定发生了什么在这个类中,去看我的第13篇,这将给你所有你需要知道的。 最后,让我们看看我们新的转换的几个例子:
private void loadImageOriginal() {
Glide
.with( context )
.load( eatFoodyImages[0] )
.into( imageView1 );
}
private void loadImageRotated() {
Glide
.with( context )
.load( eatFoodyImages[0] )
.transform( new RotateTransformation( context, 90f ))
.into( imageView3 );
}
效果图:
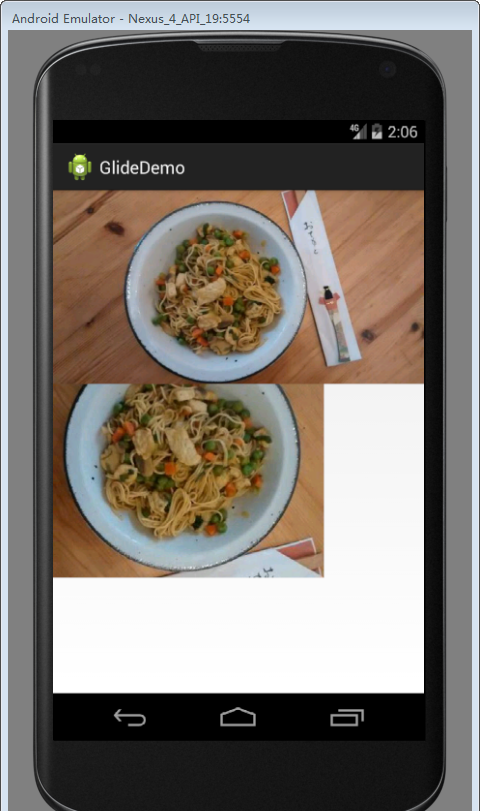
当然,你可以改变第二个参数,表示图像要旋转多少度的,任何你所需要的。
十七、Glide — Customize Glide with Modules
读者可以自行研究下
资料:https://futurestud.io/tutorials/glide-customize-glide-with-modules
*
Glide结语:提升自己的同时希望能帮到大家,谢谢!
*
2.1
xUtil3
一、注解模块
初始化
-
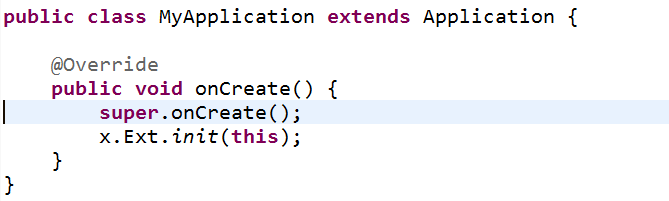
在Application的onCreate()方法中加入下面代码: x.Ext.init(this);
-
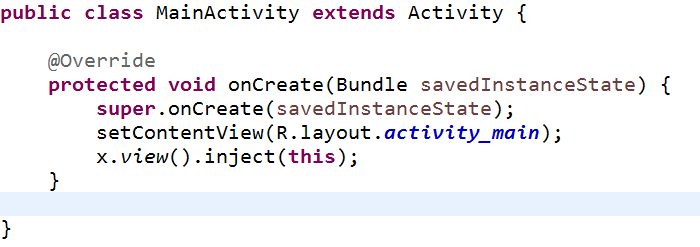
如果当前类是Activity,在Activity的onCreate()方法中加入下面代码: x.view().inject(this);
-
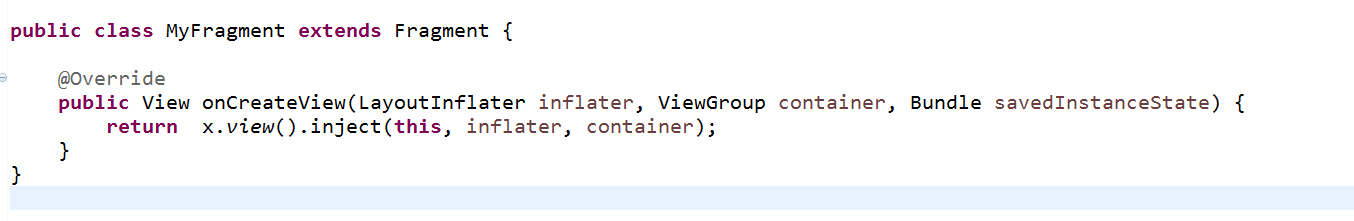
如果当前类是Fragment,在Fragment的onCreateView中return如下代码return
x.view().inject(this, inflater, Container)
加载布局
在activity类上添加@ContentView(布局)
给View初始化ID
使用@InjectView(id)
监听事件
使用@Envent (value={点击的id1,点击的id2}, type=View.OnClickListener.class)
默认type=View.OnClickListener.class
import org.xutils.x
import org.xutils.view.annotation.ContentView
import org.xutils.view.annotation.Event
import org.xutils.view.annotation.ViewInject
import android.app.Activity
import android.os.Bundle
import android.view.View
import android.widget.Button
import android.widget.ImageView
import android.widget.Toast
@ContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@ViewInject(R.id.button)
Button button
@ViewInject(R.id.imageView)
ImageView imageView
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
x.view().inject(this)
button.setText("xutil注解")
}
@Event(value={R.id.button}, type=View.OnClickListener.class)
private void onClick(View view){
switch (view.getId()) {
case R.id.button:
Toast.makeText(this, "点击了我", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
break
default:
break
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
提示:监听时间的方法必须是private修饰
Adapter中的注解
import org.xutils.x;
import org.xutils.view.annotation.ContentView;
import org.xutils.view.annotation.ViewInject;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.BaseAdapter;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.ListView;
@ContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
int[] images={R.drawable.insert_card_004,R.drawable.insert_card_005,R.drawable.insert_card_006,R.drawable.insert_card_007};
@ViewInject(R.id.listView)
ListView listView;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
x.view().inject(this);
MyAdapter adapter=new MyAdapter(this);
listView.setAdapter(adapter);
}
class MyAdapter extends BaseAdapter{
Context context;
public MyAdapter(Context context) {
this.context=context;
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
return images.length;
}
@Override
public Object getItem(int position) {
return images[position];
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int position) {
return position;
}
@SuppressWarnings({ "static-access", "null" })
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
ViewHolder viewHolder;
if (convertView==null) {
convertView=getLayoutInflater().inflate(R.layout.listview_item_image, null);
viewHolder=new ViewHolder();
x.view().inject(viewHolder,convertView);
convertView.setTag(viewHolder);
} else{
viewHolder=(ViewHolder) convertView.getTag();
}
viewHolder.imageView.setImageResource(images[position]);
return convertView;
}
class ViewHolder{
@ViewInject(R.id.imageView)
ImageView imageView;
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
当item中的控件比较多的时候在getView()中会省去大量代码
二、网络模块
发送get请求
String url="";
RequestParams params=new RequestParams(url);
Map<String, String> map=null;
if(null!=map){
for(Map.Entry<String, String> entry : map.entrySet()){
params.addQueryStringParameter(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
}
x.http().get(params, new CommonCallback<String>() {
@Override
public void onCancelled(CancelledException arg0) {
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable arg0, boolean arg1) {
}
@Override
public void onFinished() {
}
@Override
public void onSuccess(String arg0) {
}
});
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
上面的代码我们可以看出首先我们new RequestParams(url)并将url传入,然后判断是否会携带参数,是的话使用addQueryStringParameter(key,value)增加,最后使用 x.http().get()发送请求,其中一个参宿是requestParams对象,另一个是回调函数CommonCallback(),T是一个泛型,表示返回的结果类型,根据需求去定义
第二种GET请求方式:
String url="";
RequestParams params=new RequestParams(url);
Map<String, String> map=null;
if(null!=map){
for(Map.Entry<String, String> entry : map.entrySet()){
params.addQueryStringParameter(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
}
x.http().request(HttpMethod.GET, params, new CommonCallback<String>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(String result) {
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable ex, boolean isOnCallback) {
}
@Override
public void onCancelled(CancelledException cex) {
}
@Override
public void onFinished() {
}
});
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
以上代码其实和第一种get请求方式是大同小异,只是在最后请求的使用x.http().request(),并且使用HttpMethod来声明get还是post
发送Post请求
String url="";
RequestParams params=new RequestParams(url);
Map<String, String> map=null;
if(null!=map){
for(Map.Entry<String, String> entry : map.entrySet()){
params.addParameter(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
}
x.http().post(params, new CommonCallback<String>() {
@Override
public void onCancelled(CancelledException arg0) {
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable arg0, boolean arg1) {
}
@Override
public void onFinished() {
}
@Override
public void onSuccess(String arg0) {
}
});
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
从以上代码可以看出,post请求和get请求的第一种方式基本一样,post参数的方法使用的是
params.addParameter(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
最后调用x.http().post()
最后post第二种方式和get的第二种方式也是大同小异的,这里就不介绍了。
上传文件
String path = Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory() + "/1.docx";
String url = "http://www.omghz.cn/FirstService/FileReceive";
RequestParams params = new RequestParams(url);
params.addHeader("FileName", "1.docx");
File file = new File(path);
params.addBodyParameter("File", file);
x.http().post(params, new Callback.CommonCallback<String>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(String result) {
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable ex, boolean isOnCallback) {
}
@Override
public void onCancelled(CancelledException cex) {
}
@Override
public void onFinished() {
}
});
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
经过以上三篇博客,我们基本可以确定xUtil网络请求的步骤
- new RequestParams(url);
- 如果在网路请求时需要携带数据的,params.addBodyParameter(key, value);
- x.http().后面接你需要的方法
下载文件
String url="";
String filepath="";
RequestParams params=new RequestParams(url);
params.setAutoResume(true);
params.setSaveFilePath(filepath);
x.http().get(params, new Callback.CommonCallback<String>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(String result) {
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable ex, boolean isOnCallback) {
}
@Override
public void onCancelled(CancelledException cex) {
}
@Override
public void onFinished() {
}
});
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
第二种带进度条下载文件:
String url = " ";
RequestParams params = new RequestParams(url);
params.setSaveFilePath(Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory());
params.setAutoRename(true);
x.http().get(params, new Callback.ProgressCallback<File>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(File result) {
}
@Override
public void onLoading(long total, long current, boolean isDownloading) {
seekBar.setMax((int) total);
seekBar.setProgress((int) current);
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable ex, boolean isOnCallback) {
}
@Override
public void onCancelled(CancelledException cex) {
}
@Override
public void onFinished() {
}
@Override
public void onWaiting() {
}
@Override
public void onStarted() {
}
});
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
两种下载文件的方式大同小异,第二种携带了下载进度,使用的ProgressCallback()回调
三、图片加载模块
后续更新……
这足以加载我们从网络获取的模糊算法图片




























 7710
7710

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








