教程:PYNQ DMA(第 1 部分:硬件设计) - 学习 - PYNQ --- Tutorial: PYNQ DMA (Part 1: Hardware design) - Learn - PYNQ
1. 导入PYNQ-Z2 板卡包
https://dpoauwgwqsy2x.cloudfront.net/Download/pynq-z2.zip
解压复制到xilinx的board_files文件夹里面
文件夹为 PYNQ-Z2\pl_test
找到放入板卡里面的三个文件
project_pl_test.runs\impl_1\ system_wapper.bit system_wapper.tcl
project_pl_test.srcs\sources_1\bd\system\hw_handoff\system_wapper.hwh
三个文件一定要相同的名字
Zynq 是一种片上系统。它包括 ARM 处理器、FPGA 逻辑以及内存控制器和外围设备,包括 USB、以太网、SD 卡。Zynq PS 在启动时进行配置。
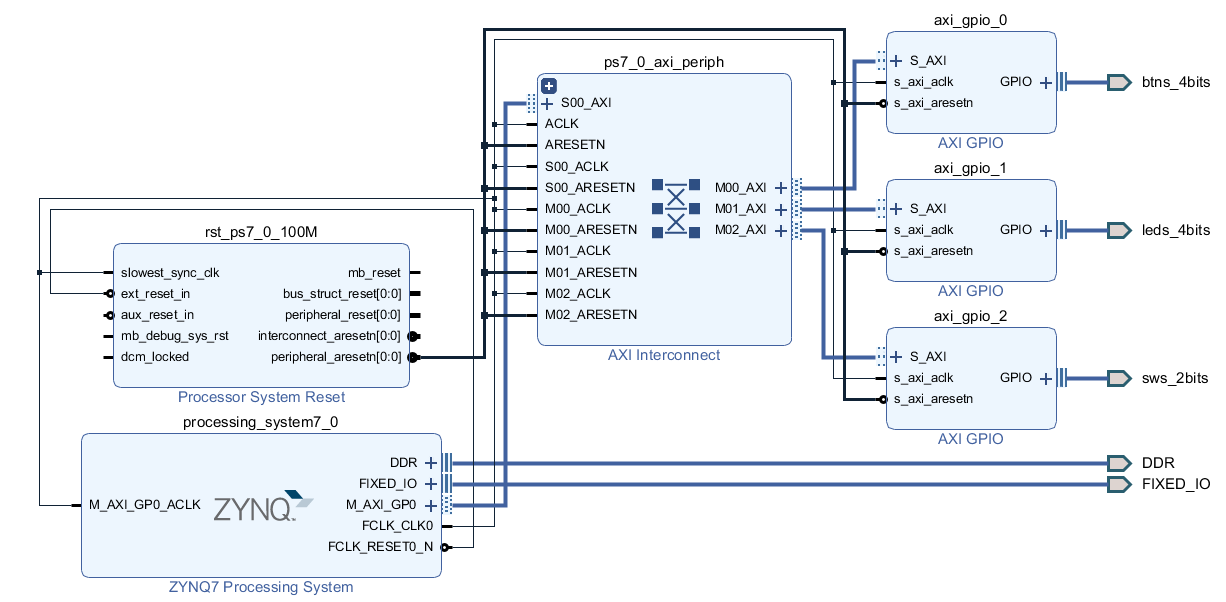
1. GPIO
from pynq import Overlay
from pynq.lib import AxiGPIO
pl_test_design = Overlay("./../bitstreams/pl_test.bit")
buttons_instance = pl_test_design.ip_dict['axi_gpio_0']
buttons = AxiGPIO(buttons_instance).channel1
buttons.read()
switches_instance = pl_test_design.ip_dict['axi_gpio_2']
switches = AxiGPIO(switches_instance).channel1
switches.read()
led_instance = pl_test_design.ip_dict['axi_gpio_1']
led = AxiGPIO(led_instance).channel1
led[0:4].write(0x1)
from time import sleep
# on each 1s
while(1):
led[0:4].write(0x1)
sleep(1)
led[0:4].write(0x3)
sleep(1)
led[0:4].write(0x7)
sleep(1)
led[0:4].write(0xf)
sleep(1)
led[0:4].off()
sleep(1)
led[0:4].off() # off the led 2.BRAM
from pynq import MMIO
RANGE = 0x1000
Baseaddr= 0x40000000
mmio = MMIO(Baseaddr, RANGE)
for i in range(8):
mmio.write(4*i,i) # write
for i in range(8):
r2 = mmio.read(4*i) # read only for 4*i
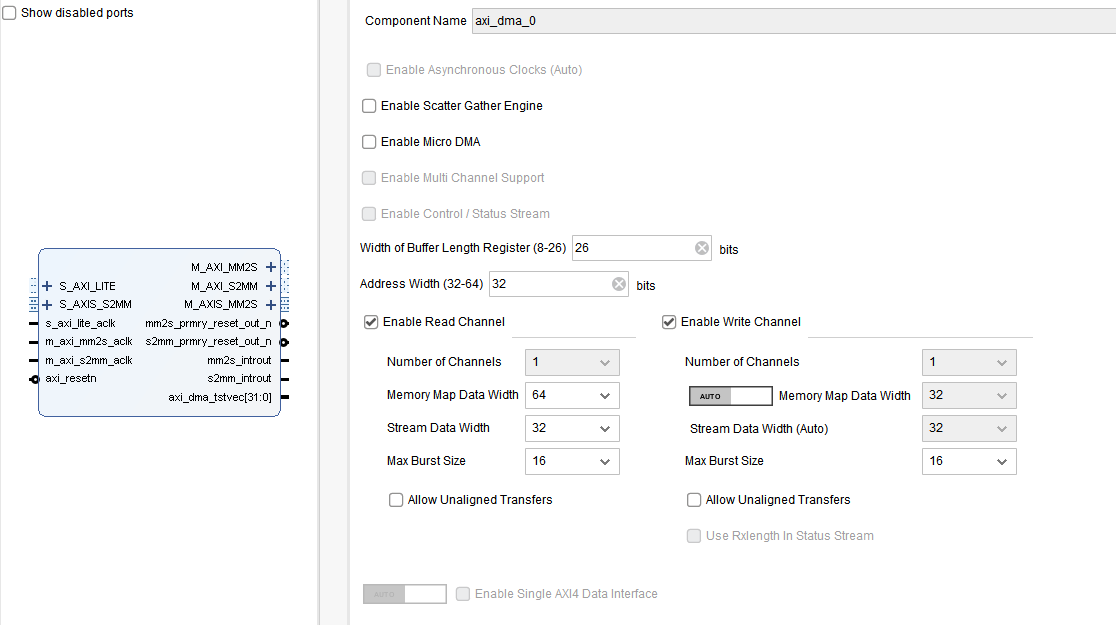
print(f"read {i,r2}")3.DMA 双向
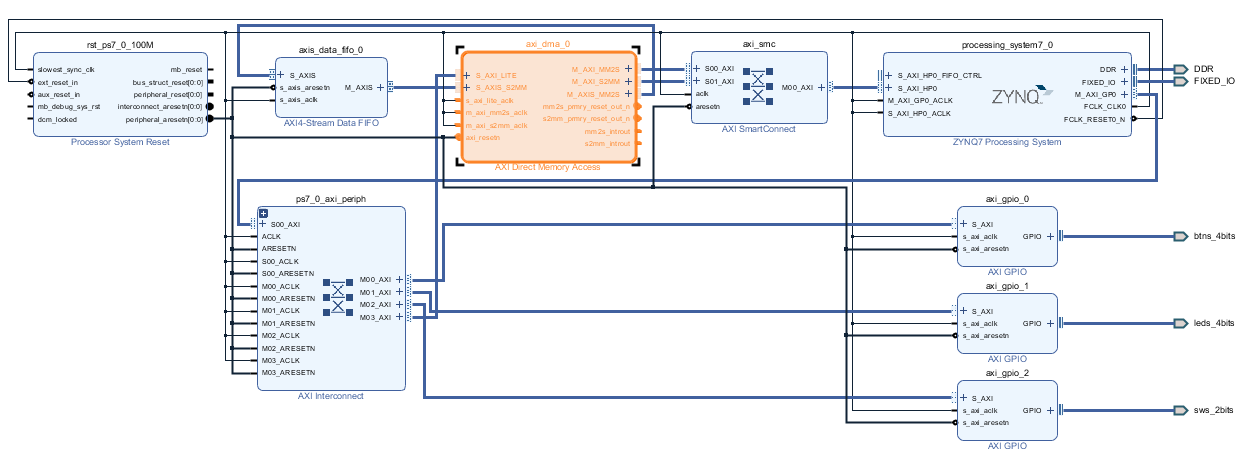
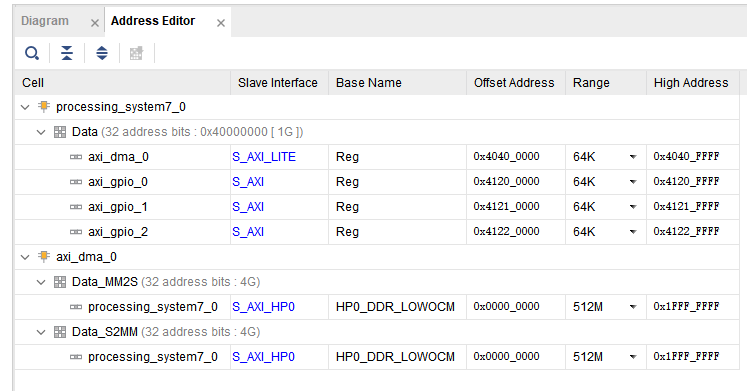
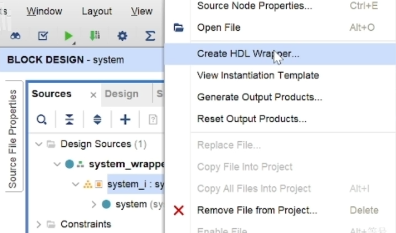
validate 后 create wrapper
导出bit,tcl,hwh
from pynq import Overlay
from pynq import allocate
import numpy as np
import time
import pynq.lib.dma
## load bit
overlay = Overlay("bitstreams/demo_wrapper.bit")
dma_send_recv = overlay.axi_dma_0
length = 1024*1024*10
data_size = int(length/4)
data_size1 = data_size # 10485760/4 = 2621440
data_size2 = data_size
print(f"input buffer size {data_size1} byte output buffer size {data_size2} byte")
input_buffer = allocate(shape=(data_size1,), dtype=np.uint32)
output_buffer = allocate(shape=(data_size2,), dtype=np.uint32)
## write some test data to the array
for i in range(data_size1):
input_buffer[i] = i
## data transmission
start = time.time()
dma_send_recv.sendchannel.transfer(input_buffer)
dma_send_recv.recvchannel.transfer(output_buffer)
dma_send_recv.sendchannel.wait()
dma_send_recv.recvchannel.wait()
end = time.time()
cost = round(end-start,5)
print(f"time cost {cost} s")
## compute the speed
length1 = 1024*1024 # MB
speed = round(length/(cost*length1),5)
print(F"transfer speed {speed} MB/s")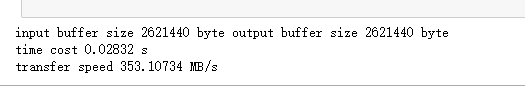




















 454
454

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








