A.电路维修
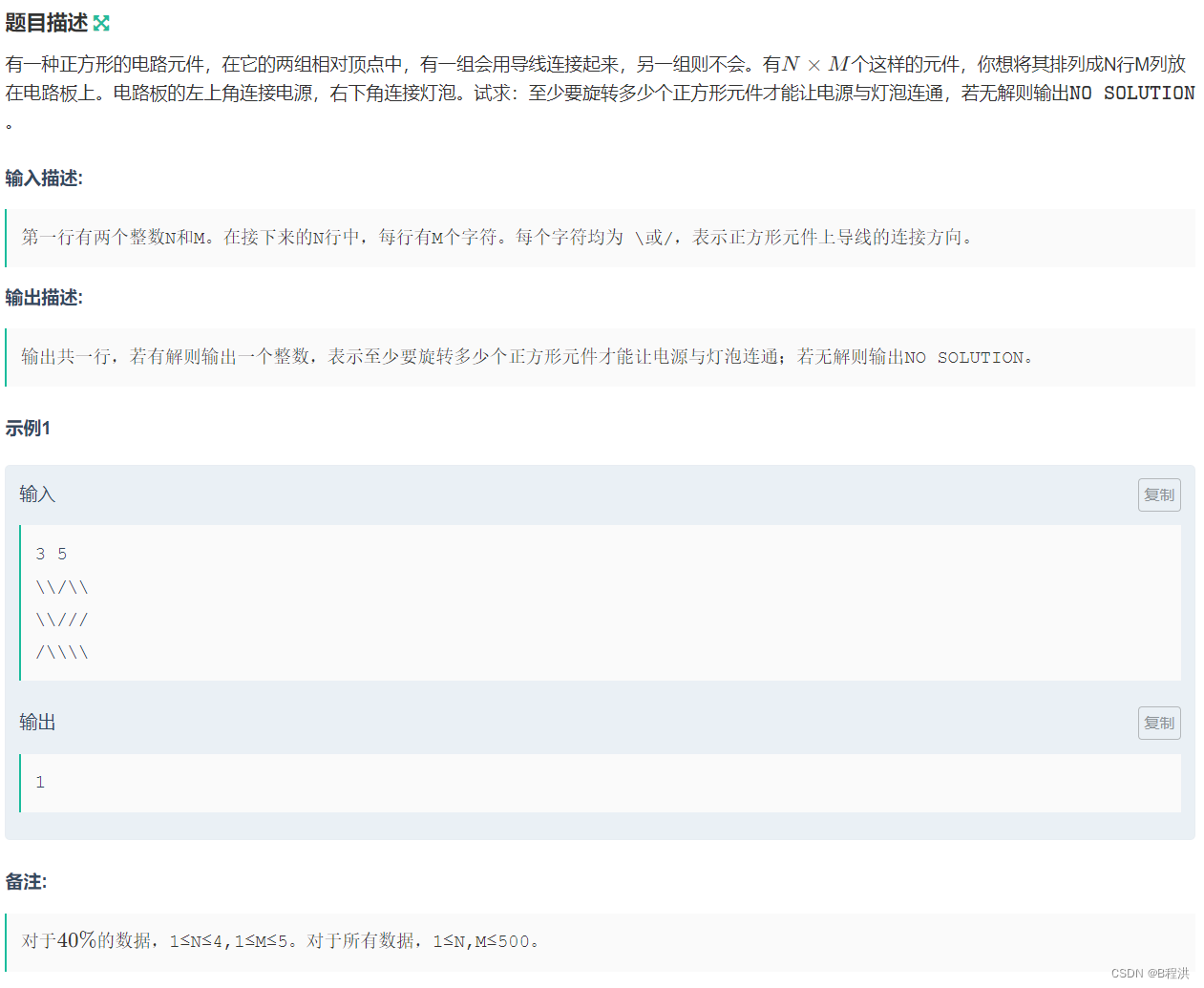
这道题我们对于每一个点都有四个方向,分别为
char op[]={"\\/\\/"};如果我们当前点到下一个点的方向不是对应的方向时我们的distance就加1,因为我们要求最优距离,所以我们采取一个小贪心的法则,每一次我们将距离为0(此处意思就是不需要改变就可以到达)放在队首,我们将距离为1的放在队尾(此处就是需要改变才可以到达)。所以我们用到了双端队列。我们对于每一次的判别只需要将其对应字符串判断是否相等即可。
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int n,m; int maps[1000][1000]; int visits[1000][1000]; char str[500][500]; int dx[4]={-1, -1, 1, 1}, dy[4]={-1, 1, 1, -1};//下一个走到的位置 int ix[4]={-1, -1, 0, 0}, iy[4]={-1, 0, 0, -1};//下一方向的判定位置 char op[]={"\\/\\/"}; int bfs() { deque<pair<int,int>>que; memset(maps,0x3f,sizeof(maps)); memset(visits,0,sizeof(visits)); que.push_back({0,0}); maps[0][0]=0; while(que.size()) { auto top=que.front(); que.pop_front(); //cout<<top.first<<" "<<top.second<<endl; if(visits[top.first][top.second]==1)continue; visits[top.first][top.second]=1; for(int i=0;i<4;i++) { int a=top.first+dx[i]; int b=top.second+dy[i]; if(a<0||a>n||b<0||b>m) continue; int zx=top.first+ix[i]; int zy=top.second+iy[i]; int d=maps[top.first][top.second]+(str[zx][zy]!=op[i]); if(d<maps[a][b]) { maps[a][b]=d; if(str[zx][zy]!=op[i]) { que.push_back({a,b}); } else if(str[zx][zy]==op[i]) { que.push_front({a,b}); } } } } return maps[n][m]; } int main() { scanf("%d%d", &n, &m); for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) scanf("%s", str[i]); if((n+m)&1) { cout<<"NO SOLUTION"<<endl; } else { cout<<bfs(); } }
B.魔板
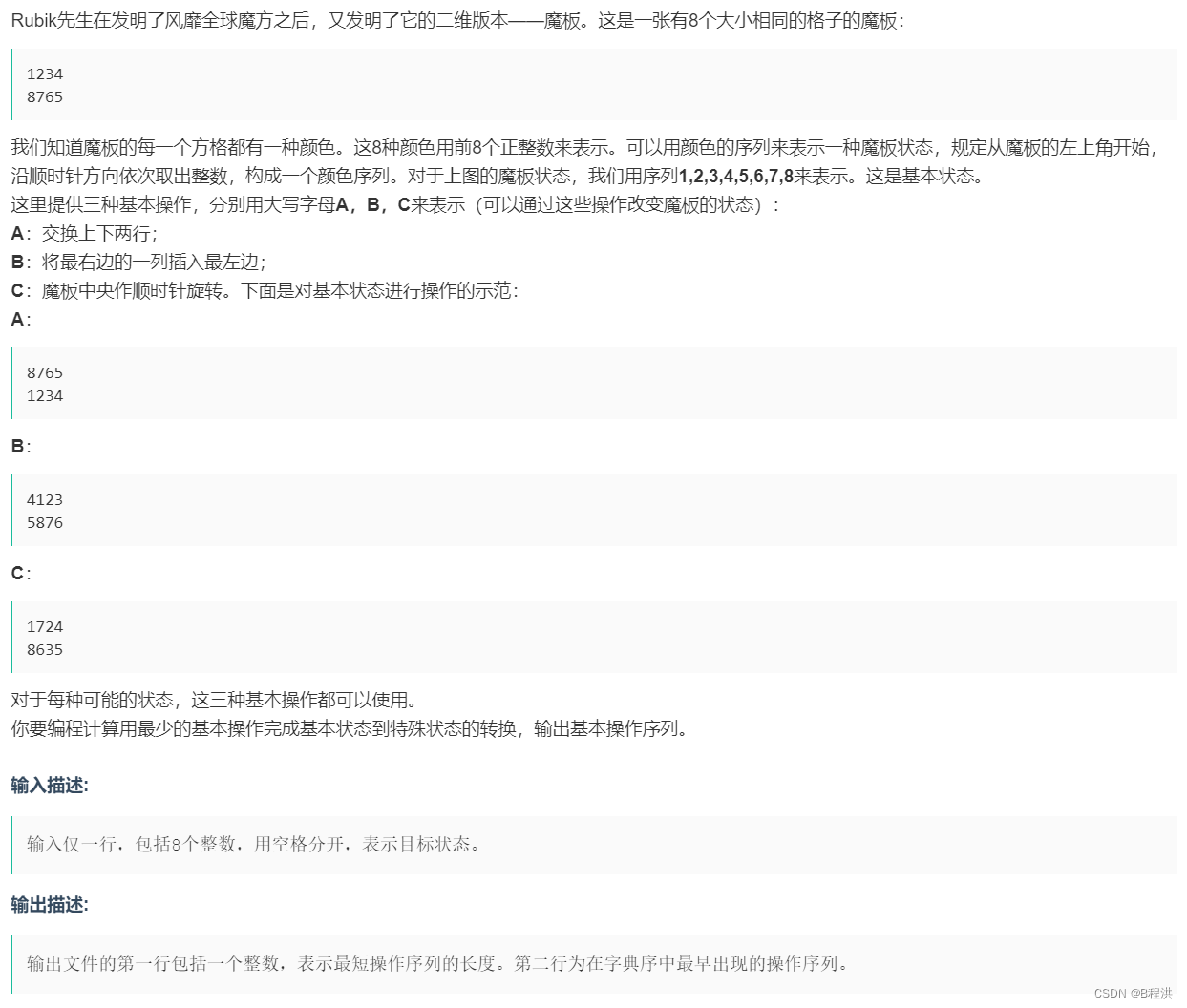
这道题我们采取了状态压缩BFS,我们把我们要更改的两个序列合成一个大字符串,之后我们对于每一步我们都要进行状态的改变进行BFS遍历直到满足情况后退出即可。我们在这里建议用map用来储存当前字符串的状态。
并且我们要想好对应状态改变的方法。
string move0(string t) { for(int i = 0; i < 4; i ++ ) swap(t[i], t[7-i]); return t; } string move1(string t) { for(int i = 0; i < 3; i ++ ) swap(t[i], t[3]); for(int i = 7; i >= 5; i -- ) swap(t[i], t[4]); return t; } string move2(string t) { swap(t[1], t[2]), swap(t[5], t[6]), swap(t[1], t[5]); return t; }之后我们按BFS遍历即可。
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; unordered_map<string, int> dist; unordered_map<string, pair<char, string>> pre;//这里我们存我们对应字符串的改变方法 string start, ed, res; string move0(string t) { for(int i = 0; i < 4; i ++ ) swap(t[i], t[7-i]); return t; } string move1(string t) { for(int i = 0; i < 3; i ++ ) swap(t[i], t[3]); for(int i = 7; i >= 5; i -- ) swap(t[i], t[4]); return t; } string move2(string t) { swap(t[1], t[2]), swap(t[5], t[6]), swap(t[1], t[5]); return t; } void bfs() { dist[start] = 0; queue<string> q; q.push(start); while (q.size()) { auto t = q.front(); q.pop(); string m[3]; m[0] = move0(t); m[1] = move1(t); m[2] = move2(t); for (int i = 0; i < 3; i ++ ) { if(!dist.count(m[i])) { q.push(m[i]); dist[m[i]]=dist[t]+1; pre[m[i]]={'A'+i,t}; } } } } int main() { for (int i = 0; i < 8; i ++ ) { char x; cin >> x; ed += x; start += char(i + '1'); } bfs(); cout << dist[ed] << endl; if (dist[ed]) { while (ed != start) { res = pre[ed].first + res; ed = pre[ed].second; } cout << res << endl; } return 0; }
C.Knight Moves

简单BFS,BFS能使其值最优DFS会超时也会使值不为最优,这道题恰恰体现了广搜与深搜的不同。和广搜的优点。这道题的具体实现过程就是简单的BFS,移动到终点时返回其最优值即可。
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef pair<int,int>pi; int vaule[310][310]; const int dx[8]={2,1,-1,-2,-2,-1, 1, 2}; const int dy[8]={1,2,2 ,1, -1,-2,-2,-1}; void bfs() { memset(vaule,0,sizeof(vaule)); int id;cin>>id; int bex,bey;cin>>bex>>bey; int enx,eny;cin>>enx>>eny; queue<pi>que; que.push({bex,bey}); vaule[bex][bey]=0; while(!que.empty()) { pi top=que.front(); que.pop(); int tx=top.first; int ty=top.second; if(tx==enx&&ty==eny)//到终点直接返回即可 { cout<<vaule[enx][eny]<<endl; return ; } for(int i=0;i<8;i++) { int mx=tx+dx[i]; int my=ty+dy[i]; if(mx<0||mx>=id||my<0||my>=id||vaule[mx][my])continue; vaule[mx][my]=vaule[tx][ty]+1; que.push({mx,my}); } } } int main() { int num;cin>>num; while(num--) { bfs(); } }
D.棋盘游戏
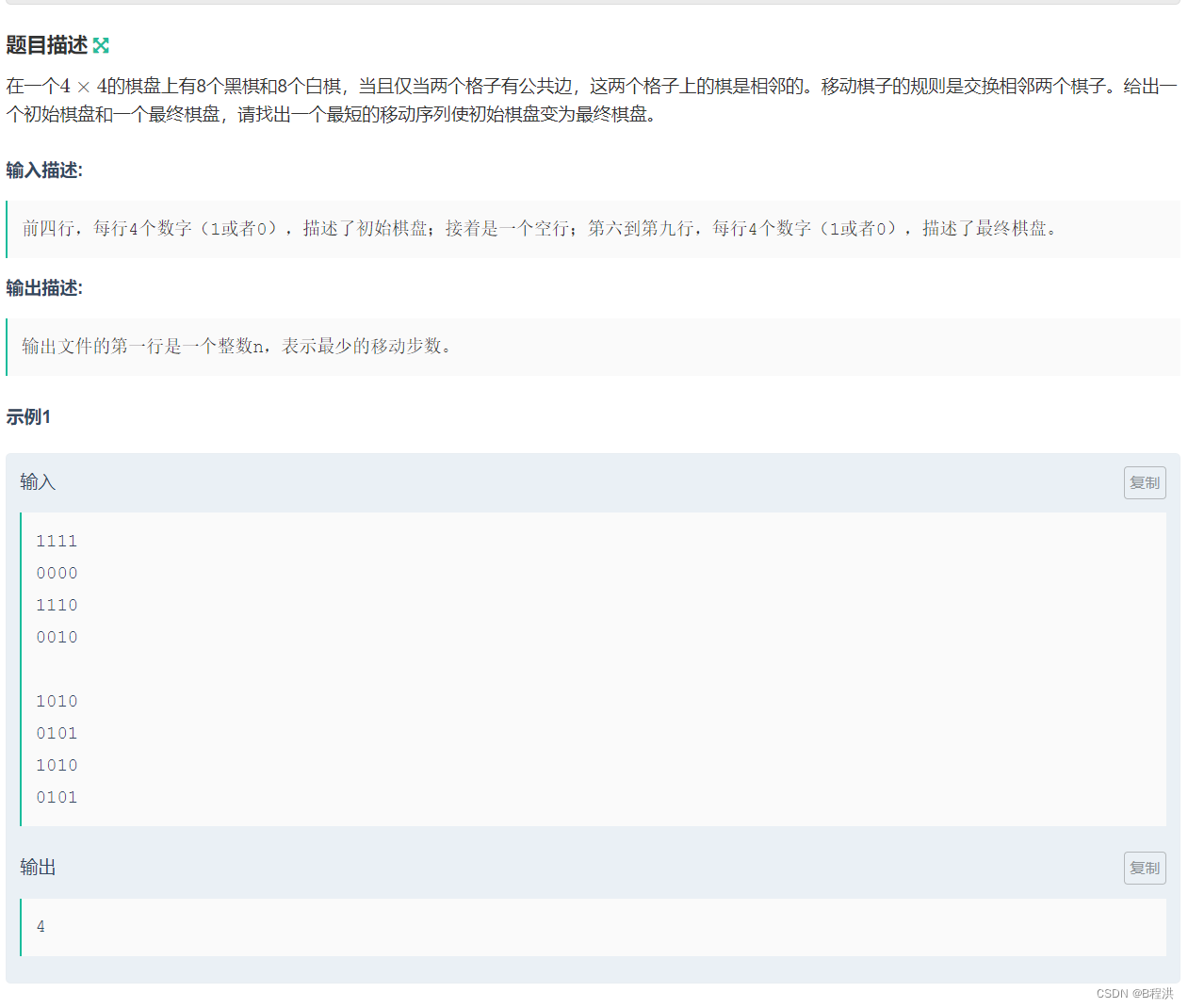
题目类似于上面第二个题也是对其进行状态压缩,然后进行广搜,充分的体现了广搜的优势,在这道题中如果要移动的棋子是相同的我们就continue;之后就是简单的BFS了。
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; map<string,int>maps; typedef pair<int,int>pi; pi p[4]={{0,1},{1,0},{0,-1},{-1,0}};//棋子交换位置 string be; string en; int bfs() { queue<string>que; que.push(be); while(!que.empty()) { string t=que.front(); if(t==en)return maps[en];//依旧如此,到达终点直接返回最优值。 que.pop(); for(int i=0;i<t.size();i++) { for(int i1=0;i1<4;i1++) { int x=i/4+p[i1].first; int y=i%4+p[i1].second; if(x<0||x>3||y<0||y>3||t[i]==t[4*x+y])continue; string xs=t; char l=xs[i]; xs[i]=xs[4*x+y]; xs[4*x+y]=l; if(maps[xs]==0) { maps[xs]=maps[t]+1; que.push(xs); } } } } return -1; } int main() { for(int i=0;i<4;i++)//状态压缩 { string h;cin>>h; be.append(h); } for(int i=0;i<4;i++) { string h;cin>>h; en.append(h); } cout<<bfs(); }
E.Keyboarding
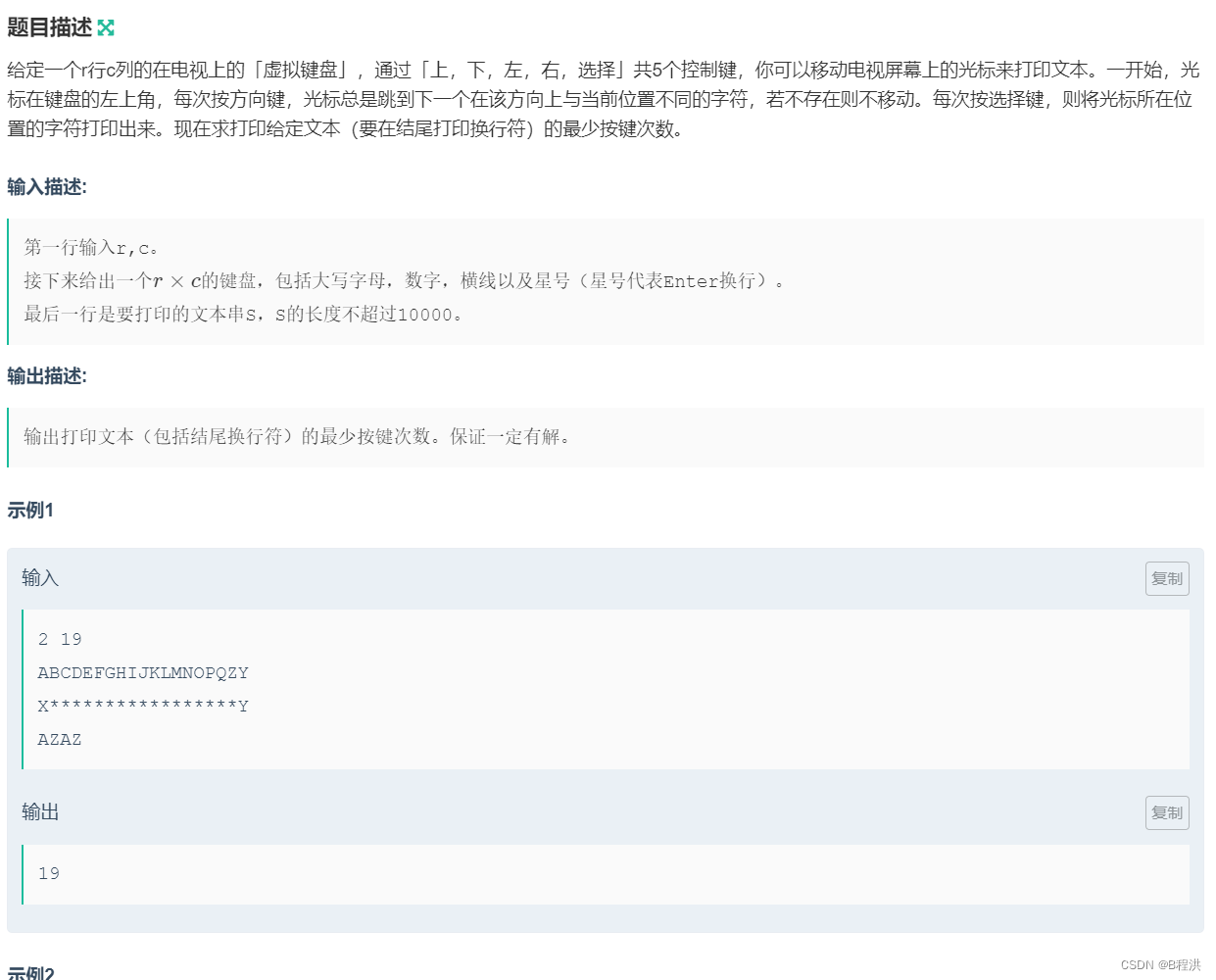
该合集中最抽象的一个题,对于这道题我们要采取预处理的方式进行,我们对于每一个预处理就是对应的每一个方向能到达不同的字符位置处为一个标记。
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { for(int i1=1;i1<=m;i1++) { for(int k=0;k<4;k++) { int x=i+dx[k]; int y=i1+dy[k]; while(kw[i][i1]==kw[x][y])//移动到不同的字符位置处 { x+=dx[k];y+=dy[k]; } if(x<=0||x>n||y<=0||y>m)//越界情况 { n1[i][i1][k]={i,i1}; } else { n1[i][i1][k]={x,y};//我们可以移动到不同字符的位置处 } } } }然后就进行BFS遍历过程,我们对于每一层我们都要保留最优的情况当我们遍历到当前字符时我们一定是在之前就将最优的保留下来,之后当再次遍历到那个位置出同样也保留最优情况。
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; char kw[100][100],en[10010]; int n,m; int len; int dx[]={0,0,1,-1}; int dy[]={1,-1,0,0}; struct node { int x,y,dis,stp;//dis为移动步数//stp为按键盘次数,每一次遍历到指定位置进行按键 }; typedef pair<int,int>pi; pi n1[100][100][4]; int v[100][100];//保留移动最优解 int bfs() { queue<node>que; que.push({1,1,0,0});//最初步 while(!que.empty()) { node top=que.front(); que.pop(); if(kw[top.x][top.y]==en[top.stp])//是否按下按键 { if(top.stp==len)//最后按键次数直接返回 { return top.dis+1; } top.dis++;//移动次数加一 top.stp++;//按键次数加一 v[top.x][top.y]=top.stp;//更新按键次数 que.push(top); continue; } for(int i=0;i<4;i++) { int x=n1[top.x][top.y][i].first;//该方向能移动到不同的位置 int y=n1[top.x][top.y][i].second; if(v[x][y]<top.stp)//只针对按键数小的情况 { v[x][y]=top.stp; que.push({x,y,top.dis+1,top.stp}); } } } return 0; } int main() { memset(v,-1,sizeof v); cin>>n>>m; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { scanf("%s",kw[i]+1); } scanf("%s",en); len=strlen(en); en[len]='*'; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { for(int i1=1;i1<=m;i1++) { for(int k=0;k<4;k++) { int x=i+dx[k]; int y=i1+dy[k]; while(kw[i][i1]==kw[x][y]) { x+=dx[k];y+=dy[k]; } if(x<=0||x>n||y<=0||y>m) { n1[i][i1][k]={i,i1}; } else { n1[i][i1][k]={x,y}; } } } } cout<<bfs(); }
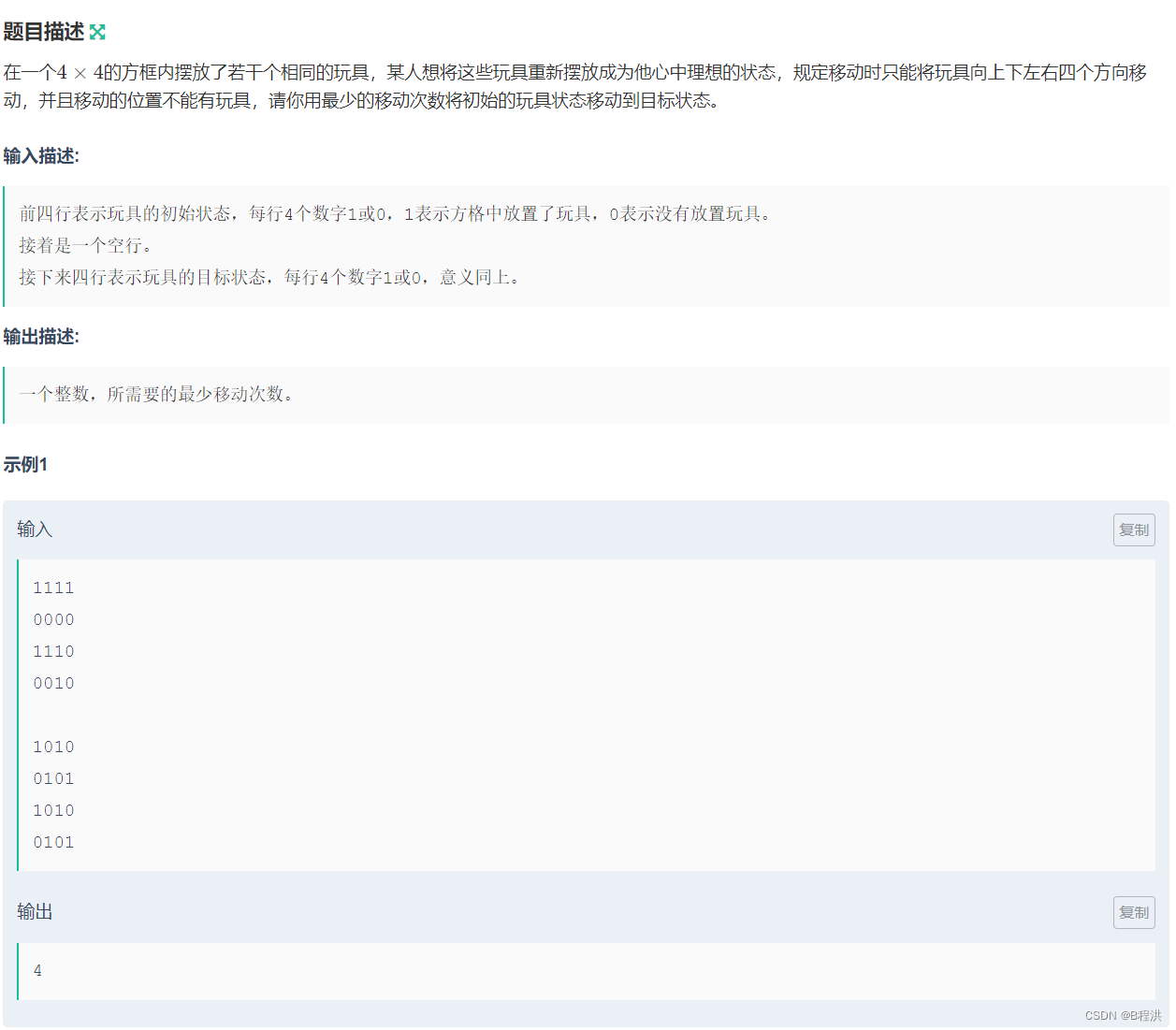
F.移动玩具
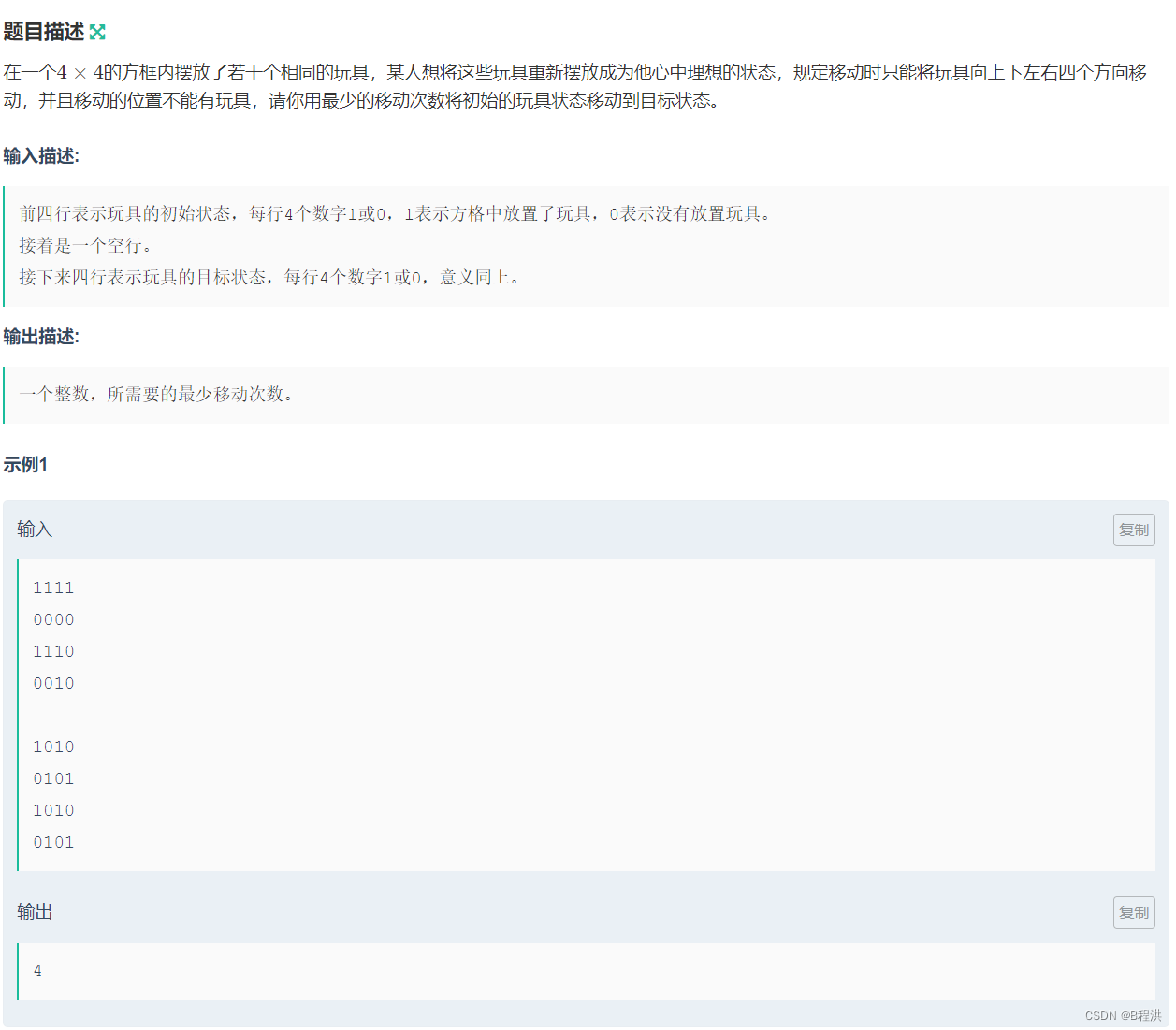
依旧是状态压缩BFS与前面那几个题一个思路与方法。
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; string begins; string endx; int dx[]={1,-1,0,0}; int dy[]={0,0,1,-1}; map<string,int>dis; int main() { for(int i=1;i<=4;i++) { string a;cin>>a; begins.append(a); } for(int i=1;i<=4;i++) { string a;cin>>a; endx.append(a); } queue<string>que; que.push(begins); dis[begins]=0; if(begins==endx) { cout<<0<<endl; return 0; } while(!que.empty()) { string z=que.front(); que.pop(); for(int i=0;i<z.size();i++) { for(int i1=0;i1<4;i1++) { string h=z; int x1=i/4+dx[i1]; int y1=i%4+dy[i1]; if(x1<0||x1>3||y1<0||y1>3||h[i]==h[x1*4+y1])continue; swap(h[i],h[x1*4+y1]); if(dis[h]==0) { que.push(h); dis[h]=dis[z]+1; } if(h==endx) { cout<<dis[h]<<endl; return 0; } } } } }
G.山峰和山谷
此题出的很有趣,就是在搜索过程中如果出现边界值同时大于和小于该遍历值的情况就是 既不是山峰也不是山谷,而当边界值大于我们当前遍历的值时我们当前遍历的值是山谷,反之则是山峰,我们要利用BFS的边界覆盖性质对其进行广搜,然后判断其边界的情况。
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std; int visit[1010][1010]; int maps[1010][1010]; int dx[]={0,0,1,-1,-1,1,1,-1}; int dy[]={1,-1,0,0,1,-1,1,-1}; int p,v; int n; int res1=0,res2=0; typedef pair<int,int>pi; void bfs(int x,int y) { queue<pi>que; que.push({x,y}); visit[x][y]=1; while(!que.empty()) { pi top=que.front(); que.pop(); int px=top.first; int py=top.second; for(int i=0;i<8;i++) { int tx=px+dx[i]; int ty=py+dy[i]; if(tx<0||tx>=n||ty<0||ty>=n)continue; if(maps[x][y]!=maps[tx][ty])//如果不同的话就进行山峰山谷的判定,同时不同的情况不用接着遍历了。 { if(maps[x][y]<maps[tx][ty]) { p=1; } else v=1; } else if(!visit[tx][ty]&&maps[x][y]==maps[tx][ty])//只遍历相同的值 { que.push({tx,ty}); visit[tx][ty]=1; } } } } signed main() { cin>>n; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { for(int i1=0;i1<n;i1++)cin>>maps[i][i1]; } for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { for(int i1=0;i1<n;i1++) { if(visit[i][i1]==0) { p=0;v=0; bfs(i,i1); if(p==v&&p==0) res1=res2=1;//如果全遍历完了,没有边界 else if(p*v==1)continue;//如果全为1,则既是山峰也是山谷,直接跳过 res1+=v;//反之 res2+=p; } } } cout<<res1<<" "<<res2<<endl; }























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










