文章目录
第二节:SpringSecurity(二):SpringSecurity入门
第三节:Spring Security(三):Security中重要的几个类
第四节:Spring Security(四):Security的第一次资源访问流程
第五节:Spring Security(五):Security登陆的超简单例子
第六节:Spring Security(六):Security登录的用户名和密码的校验逻辑
上一节中,我们写了超简单的登录例子,但是所有的代码都指向了如何根据用户名获取用户,但是没有看到密码的校验逻辑,这一节,我们将介绍登录的逻辑。
前言
登录其实也是一个请求,当请求登录逻辑时,Spring Security会走过滤器,而用户名和密码校验的逻辑刚好是UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter过滤器处理的,那么我们从这个类来分析整个流程的逻辑。
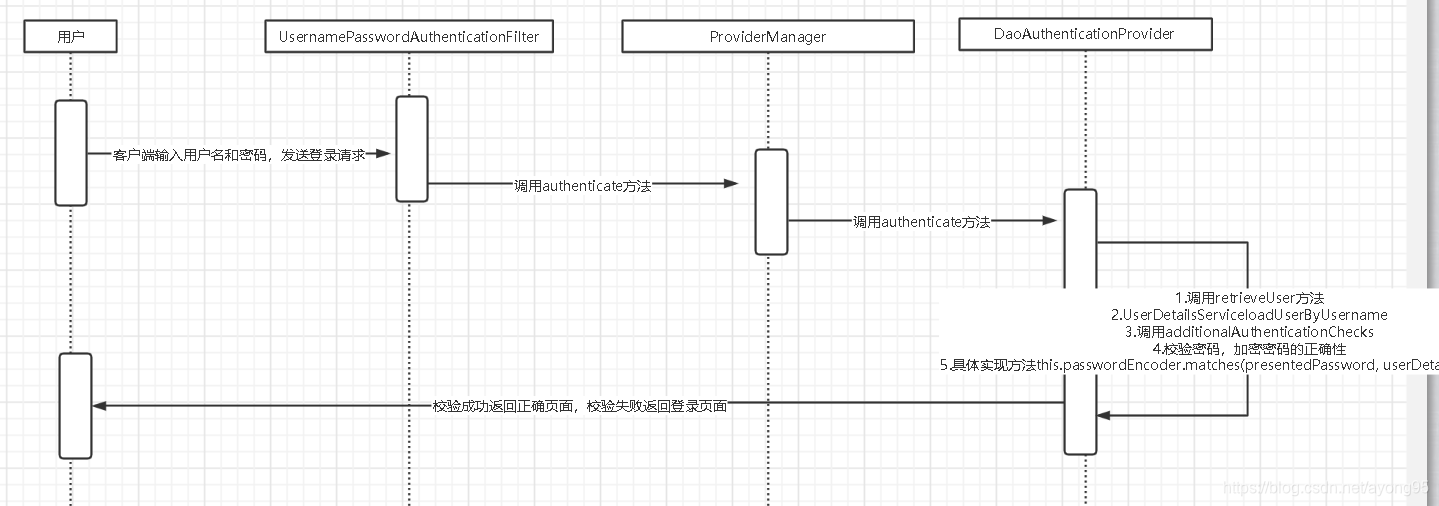
一、用户名和密码的Filter逻辑校验流程
先看下面的流程图:用户发送请求,经过UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter过滤器,调用父类的doFilter方法后执行authenticate方法,此方法调用ProviderManager类中的authenticate方法,该方法中会调用DaoAuthenticationProvider父类AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider中的authenticate方法,这个方法就会调用DaoAuthenticationProvider类中的retrieveUser方法,此时这里本质就是调用UserDetailsService.loadUserByUsername方法,正好和上一节对上,也是为什么我们要实现该接口,重新loadUserByUsername方法,获取到该方法返回接口后,和request中的password进行校验,通过PasswordEncoder.match方法进行校验,下面会具体详解。
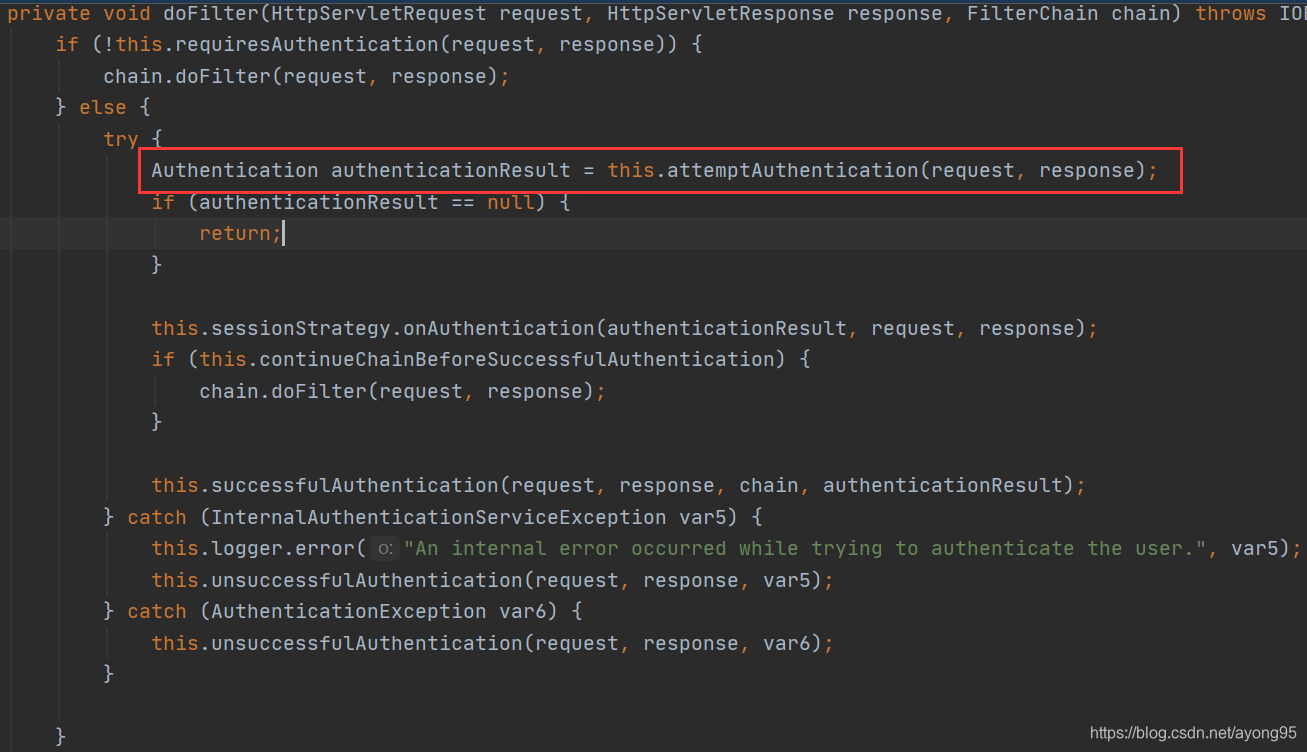
我们走进UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter类,发现doFilter方法在其父类AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter继承过来的。
具体的逻辑在UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter类中,找到这个类的代码
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException {
if (this.postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException("Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
} else {
String username = this.obtainUsername(request);
username = username != null ? username : "";
username = username.trim();
String password = this.obtainPassword(request);
password = password != null ? password : "";
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(username, password);
this.setDetails(request, authRequest);
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}
}this.getAuthenticationManager()方法返回的是ProviderManager对象,调用了authenticate方法,我们继续往下走。
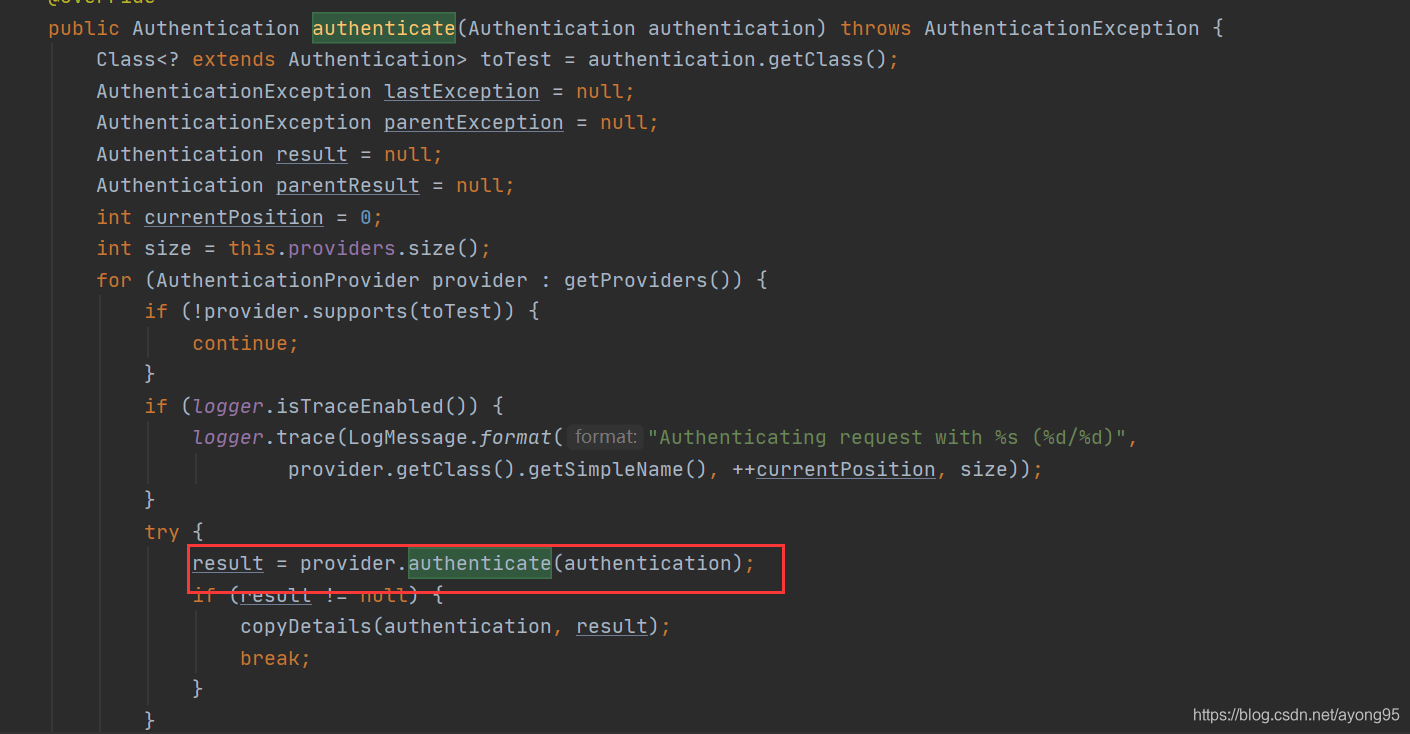
如上图,走到红框的地方,可以看到,provider默认是DaoAuthenticationProvider的实例对象,这里调用的是父类中继承的方法,如下图。
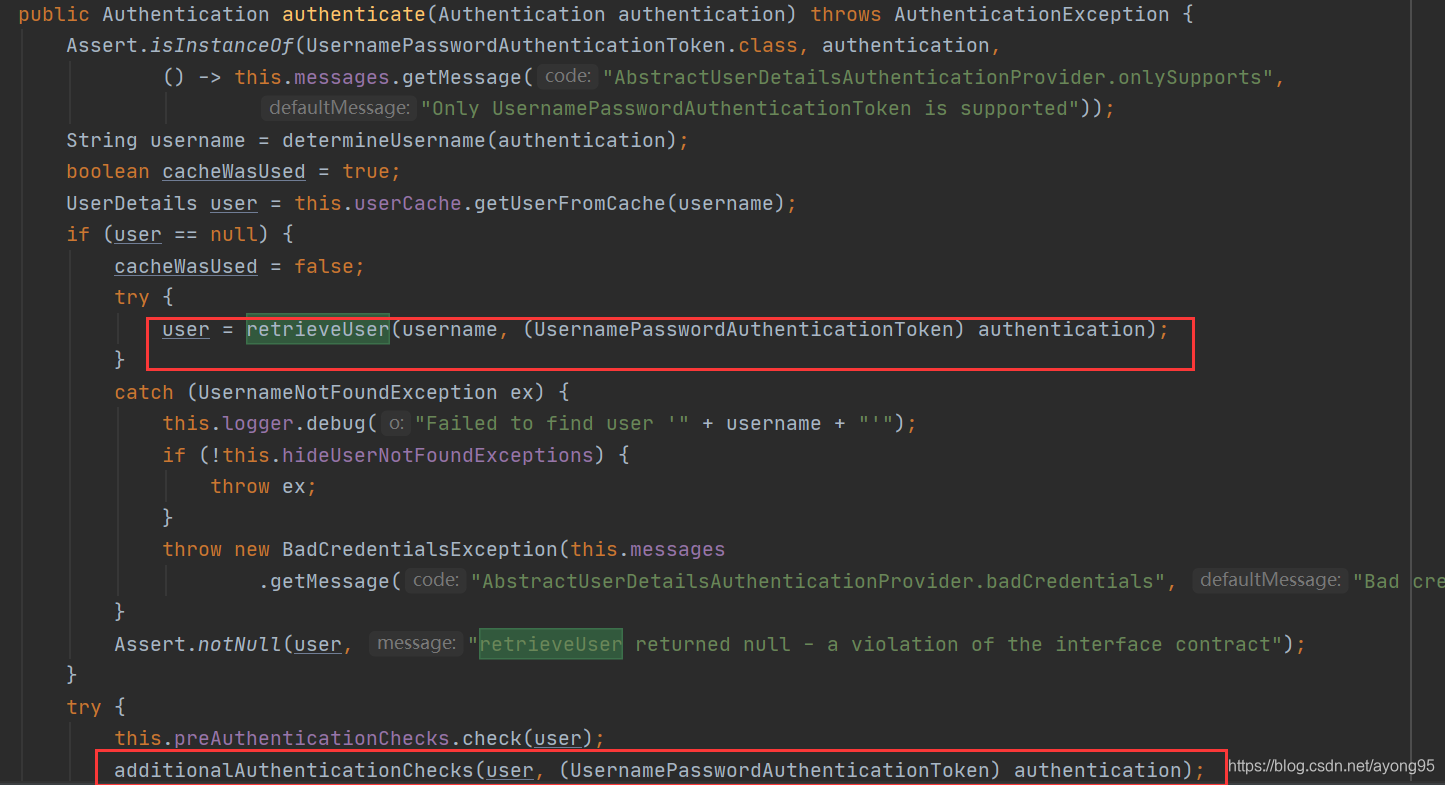
上图中,我们看到重要的两个部分,一个是retrieveUser方法,另外一个是additionalAuthenticationChecks方法;先看retrieveUser方法,底层调用的就是UserDetailsService.loadUserByUsername方法,其实就是上一节中重写的UserDetailsService接口的loadUserByUsername方法,如下图:
protected final UserDetails retrieveUser(String username, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
prepareTimingAttackProtection();
try {
UserDetails loadedUser = this.getUserDetailsService().loadUserByUsername(username);
if (loadedUser == null) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException(
"UserDetailsService returned null, which is an interface contract violation");
}
return loadedUser;
}
catch (UsernameNotFoundException ex) {
mitigateAgainstTimingAttack(authentication);
throw ex;
}
catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException(ex.getMessage(), ex);
}
}第二个红框的方法如下,其实调用的就是下图红框中的密码校验规则,所以其实就是调用了PasswordEncoder类中的match方法,该方法校验的是loadUserByUsername返回的用户对象(该对象可以是内存对象,数据库对象等)中的加密密码和页面表单请求传递过来的明文密码进行校验,校验规则可以看BCryptPasswordEncoder类的源码。
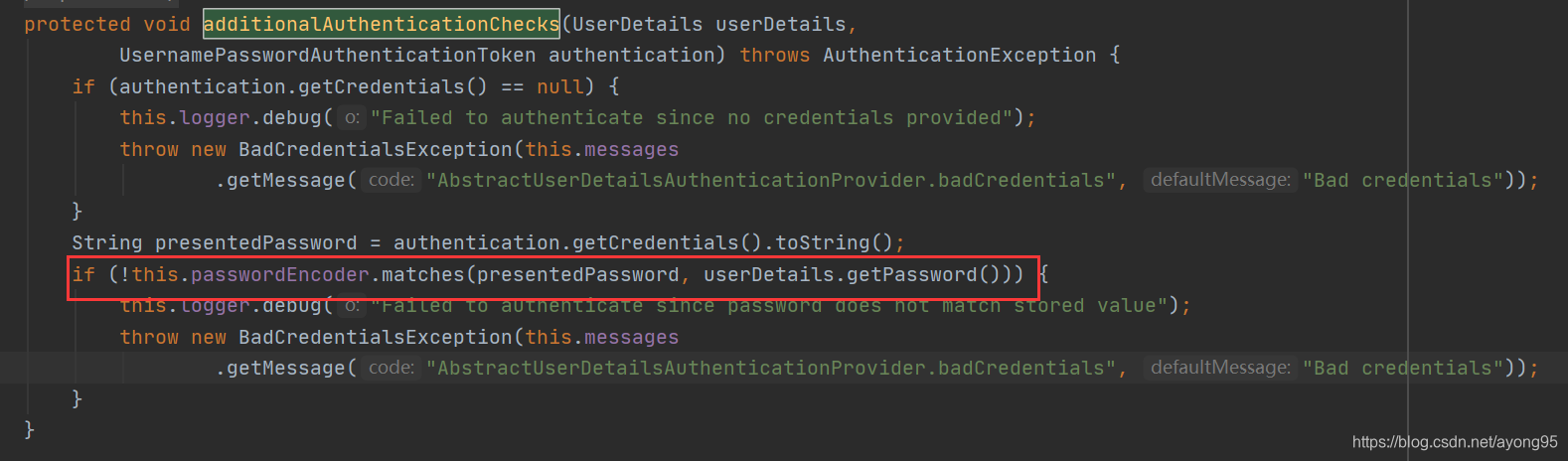
看到这里,其实我们已经弄清楚了,用户登录的用户名和密码的校验过程,其实就是过滤器来做的。如果校验失败,就会抛异常,最后跳转到登录页面,如果校验成功,就会将用户信息缓存起来,并跳转到指定的访问资源。
总结
用户发送请求--》UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter过滤器--》调用UserDetailsService.loadUserByUsername方法--》将获得的结果通过PasswordEncoder.match方法来进行校验密码的正确性。最终我们在写代码的时候,只需要考虑重新UserDetailsService接口,在Spring的IOC容器中注入PasswordEncoder实例对象。





 本文详细解析了Spring Security中登录时的用户名和密码校验流程,从UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter过滤器开始,经过ProviderManager的authenticate方法,再到DaoAuthenticationProvider的retrieveUser方法,最终使用PasswordEncoder进行密码匹配。理解这一流程对于自定义认证逻辑至关重要。
本文详细解析了Spring Security中登录时的用户名和密码校验流程,从UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter过滤器开始,经过ProviderManager的authenticate方法,再到DaoAuthenticationProvider的retrieveUser方法,最终使用PasswordEncoder进行密码匹配。理解这一流程对于自定义认证逻辑至关重要。

















 1802
1802

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








