Process API
在UNIX系统中,如何创建进程?
UNIX在提供的system calls中,有一对非常奇异的创建新的进程system calls:
fork()
exec()
当然,要用这两个system calls,还要用到wait(),通常是一个进程用来等待另一个进程完成。
关于为什么UNIX给了这么几个奇异的接口来创建一个新的进程呢?
历史证明吧!在构建UNIX shell中,fork()和exec()是至关重要的。它能够实现shell(就是一个user program)在调用fork()之后、在调用exec()之前运行一些代码。
更详细的说,它给你一个提示,然后等待你的输入。
然后你输入进命令(该命令也是一个可执行程序an executable program),再输入一些参数(arguments)。
在通常情况下,shell先在file system中找到可执行程序,然后调用fork()创建一个新的子进程准备执行命令,然后调用exec()的一些变体函数通过fork出来的进程来执行这个命令,然后调用wait()来等待结果。
当子进程完成,shell从wait()返回,然后重新开始,给出提示,等待你输入。
通过下面的例子来体会一下(关于这三个system calls: fork(), exec() and wait(),具体使用暂且不先介绍)。
实现目标
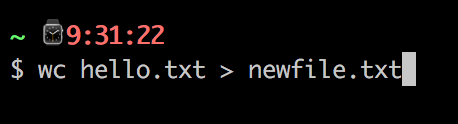
用C语言模拟shell中的该命令wc hello.txt > newfile.txt
在这个例子当中,wc指令/程序的输出被重定向到输出文件newfile.txt中(大于号在这里的意思是重定向)。
用C实现这条语句过程非常有意思:
父进程通过
fork()创建子进程,不过在调用系统调用exec()之前,先进行下面这一行操作父进程关闭
standard output,然后打开newfile.txt文件(这样,在接下来的要运行的程序wc中的任何输出,都会输出到newfile.txt而不是直接到屏幕),其实就是实现重定向>的作用然后调用exec()家族函数
execvp()在新进程中执行wc
文件准备
这两个文件在同一文件夹下
1. hello.txt – 被统计文件大小的文件
1
22
333
44442. process.c – 完成shell命令的程序
#include <stdio.h> // printf; fprintf; stderr
#include <stdlib.h> // exit()
#include <unistd.h> // fork(); getpid(); close(); execvp()
#include <string.h> // strdup()
#include <fcntl.h> // file control options
//#include <sys/wait.h>
int main (int argc, char *argv[]) {
printf("hello world (pid:%d)\n", (int)getpid());
int rc = fork();
if (rc < 0) { // fork failed, exit.
fprintf(stderr, "fork failed\n");
exit(1);
}
else if (rc == 0) { // child: redirect standard output to a file
printf("hello, I am child (pid:%d)\n", (int)getpid());
close(STDOUT_FILENO);
open("./newfile.txt", O_CREAT|O_WRONLY|O_TRUNC, S_IRWXU);
char *myargs[3];
myargs[0] = strdup("wc"); // program: "wc" (word count)
myargs[1] = strdup("hello.txt"); // argument: file to count
myargs[2] = NULL; // marks end of array
execvp(myargs[0], myargs);
printf("this shouldn't print out");
}
else { // parent goes down this path (main)
int wc = wait(NULL);
printf("hello, I am parent of %d (wc:%d) (pid:%d)\n", rc, wc, (int)getpid()); // 这里的返回的rc为子进程ID
}
return 0;
}关于系统调用函数fork(),再多说几句
由fork()创建的新进程被称为子进程(child process)。fork函数被调用一次,但返回两次。两次返回的区别是:
子进程的返回值是0,而父进程的返回值则是新建子进程的进程ID。
所有,在上面的小程序中,rc所处位置不同,返回的结果不同。
结果显示
刚开始,先要用gcc编译一下:
gcc -o process process.c
然后,在shell下运行:
./process
1. 屏幕输出
hello world (pid:9299)
hello, I am child (pid:9300)
hello, I am parent of 9300 (wc:9300) (pid:9299)2. cat output.txt
4 4 14 hello.txt 说明一下
4(行数) 4(单词数,以空格为界) 14(字节数) hello.txt(文件名)





















 2396
2396

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








