归并排序是建立在归并操作上的一种有效的排序算法,该算法是采用分治法(Divide and Conquer)的一个非常典型的应用。将已有序的子序列合并,得到完全有序的序列;即先使每个子序列有序,再使子序列段间有序。若将两个有序表合并成一个有序表,称为二路归并。
归并排序的算法思想:
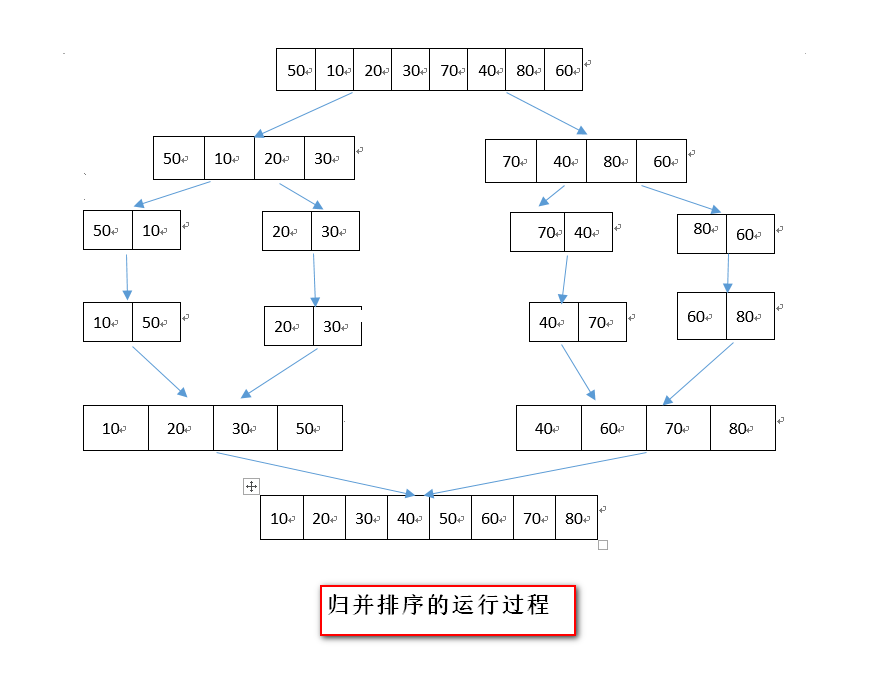
假设初始系列有n个待排序的记录,则可以看成n个有序的子序列,每个子序列长度为1;然后两两归并,得到n/2个长度为2的序列;再两两归并…….如此重复,直到得到一个长度为n的有序序列。
归并排序的时间复杂度:
时间复杂度为O(nlogn) 这是该算法中最好、最坏和平均的时间性能。
归并排序的空间复杂度:
空间复杂度为 O(n);归并排序比较占用内存,但却是一种效率高且稳定的算法。
下面举例子说明:
算法实现:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
void Merge(int sourceArr[],int tempArr[], int startIndex, int midIndex, int endIndex)
{
int i = startIndex, j=midIndex+1, k = startIndex;
for(;i<=midIndex&&j<=endIndex;k++){
if(sourceArr[i]>=sourceArr[j]){
tempArr[k]=sourceArr[j++];
}else{
tempArr[k]=sourceArr[i++];
}
}
while(i<=midIndex){//将剩余的元素直接copy到tempArr中
tempArr[k++]=sourceArr[i++];
}
while(j<=endIndex){
tempArr[k++]=sourceArr[j++];
}
for(i=startIndex;i<=endIndex;i++){
sourceArr[i]=tempArr[i];
}
}
//内部使用递归
void MergeSort(int sourceArr[], int tempArr[], int startIndex, int endIndex)
{
int midIndex;
if(startIndex < endIndex)
{
midIndex = (startIndex + endIndex) / 2;
MergeSort(sourceArr, tempArr, startIndex, midIndex);
MergeSort(sourceArr, tempArr, midIndex+1, endIndex);
Merge(sourceArr, tempArr, startIndex, midIndex, endIndex);
}
}
int main()
{
int a[8] = {50, 10, 20, 30, 70, 40, 80, 60};
int i, b[8];
MergeSort(a, b, 0, 7);
for(i=0; i<8; i++)
printf("%d ", a[i]);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}






















 445
445

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








