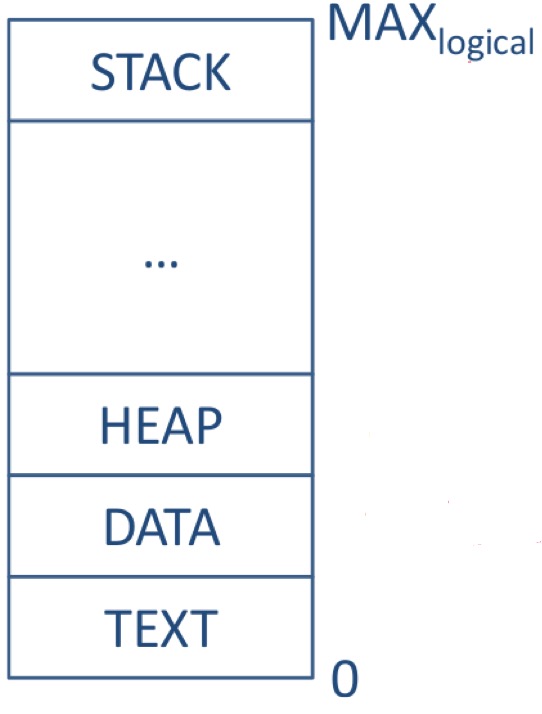
CODE(静态存储区域)
- Also known as the TEXT Segment
- Usually starts at or near address 0 and does not change size during the lifetime of the process
- Contains:
- the machine instructions for the problem
STACK
- Used to pass data between functions, and to store temporary variables local to a given routine
- The stack often starts at a very high address and grows torwards smaller addresses (this may seem to waste a large amount of space. However, it does not, because the use of virtual memory means that unused addresses below the stack do not need to be mapped in memory)
HEAP
- Dynamic memory which allocated by the process at run time(the most complicated type of memory)
- Usually allocated starting just beyond the end of the code segment, and grows up in memory towards the stack
- The end of heap is sometimes called the process break point (usually using malloc()/free() to manage this task)
Stack vs Heap Pros and Cons
Stack
- very fast access
- don’t have to explicitly de-allocate variables
- space is managed efficiently by CPU, memory will not become fragmented
- local variables only
- limit on stack size (OS-dependent)
- variables cannot be resized
Heap
- variables can be accessed globally
- no limit on memory size
- (relatively) slower access
- no guaranteed efficient use of space, memory may become fragmented overtime as blocks of memory are allocated, then freed
- you must manage memory (you’re in charge of allocating and freeing variables)
- variables can be resized using realloc()
























 1310
1310

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








