1(1).代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
int a;
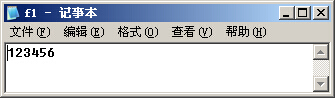
ofstream outfile("f1.dat",ios::out);
if(!outfile)
{
cerr<<"open error!"<<endl;
exit(1);
}
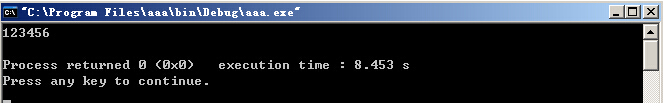
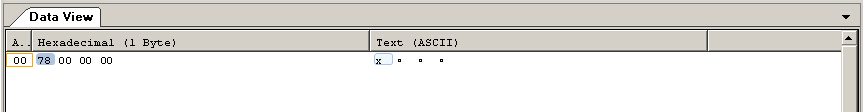
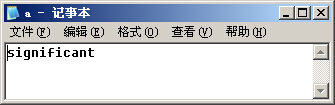
cin>>a;
outfile<<a<<endl;
outfile.close();
return 0;
}
运行结果:
1.(2)代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
int a;
ofstream outfile("f2.dat",ios::out|ios::binary);
if(!outfile)
{
cerr<<"open error!"<<endl;
exit(1);
}
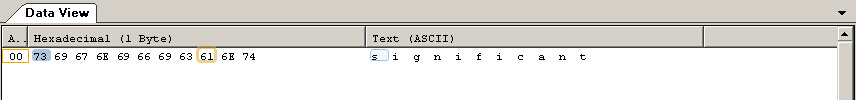
cin>>a;
outfile.write((char*)&a, sizeof(int));
outfile.close();
return 0;
}
运行结果:
学习心得:
(1)是普通的对数据文件的处理,(2)是对二进制文件的操作,用成员函数write写二进制文件,在打开时要用ios::binary指定为以二进制形式传送和储存。
2.代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
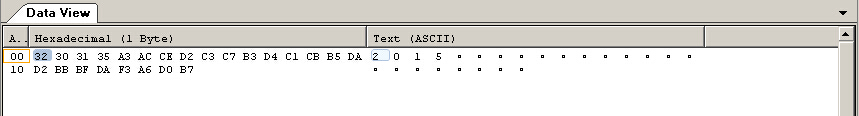
unsigned char a[] = {0x32,0x30,0x31,0x35,0xA3,0xAC,0xCE,0xD2,0xC3,0xC7,0xB3,0xD4,
0xC1,0xCB,0xB5,0xDA,0xD2,0xBB,0xBF,0xDA,0xF3,0xA6,0xD0,0xB7};
ofstream outfile("f3.dat",ios::out|ios::binary);
outfile.write((char*)a, sizeof(a));
outfile.close();
return 0;
}
运行结果:
学习心得:
数组a里是二进制文件。
3(1).代码:
#include<iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
const char * filename = "a.txt";
int main ()
{
long l,m;
ifstream file (filename, ios::in|ios::binary);
l = file.tellg();
file.seekg (0, ios::end);
m = file.tellg();
file.close();
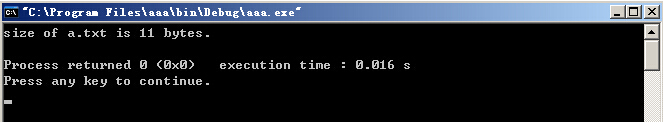
cout << "size of " << filename;
cout << " is " << (m-l) << " bytes.\n";
return 0;
}
运行结果:
3(2).代码:
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
int main (){
long pos;
ofstream outfile;
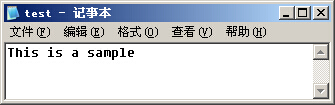
outfile.open ("test.txt");
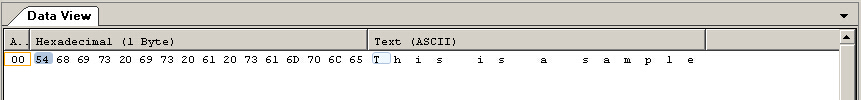
outfile.write ("This is an apple",16);
pos=outfile.tellp();
outfile.seekp (pos-7);
outfile.write (" sam",4);
outfile.close();
return 0;
}
运行结果:
3(3).代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
fstream outfile,infile;
outfile.open("data.txt",ios::out);
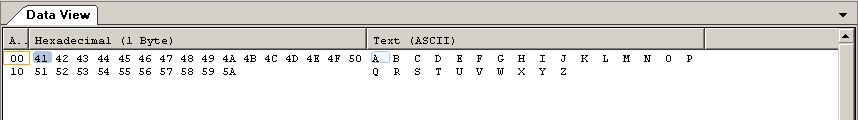
for (int i=0;i<26;i++)
outfile<<(char)('A'+i);
outfile.close();
infile.open("data.txt",ios::in);
char ch;
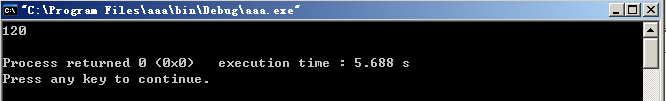
infile.seekg(6,ios::beg);
if(infile.get(ch))
cout<<ch;
infile.seekg(8,ios::beg);
if(infile.get(ch))
cout<<ch;
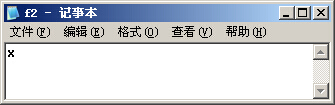
infile.seekg(-8,ios::end);
if(infile.get(ch))
cout<<ch;
cout<<endl;
infile.close();
return 0;
}
运行结果:
学习心得:
tellg()函数,得到输入文件位置标记的当前位置;
tellp()函数,得到输出文件位置标记的当前位置;
seekg(位移量,参照位置)函数,以参照位置为基础移动若干字节;
seekg(文件中的位置)函数,将输入文件标记移到指定位置;
seekp(位移量,参照位置)函数,以参照位置为基础移动若干字节;
seekp(文件中的位置)函数,将输出文件位置标记移到指定位置;
gcount()函数,得到最后一次输入所读入的字节数。
4(1).代码:
#include<iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
struct student
{
int num;
char name[20];
float score;
};
int main( )
{
student stud[5]= {1001,"Li",85,1002,"Fun",97.5,1004,"Wang",54,1006,"Tan",76.5,1010,"ling",96};
fstream iofile("stud.txt",ios::in|ios::out|ios::binary);
//用fstream类定义输入输出二进制文件流对象iofile
if(!iofile)
{
cerr<<"open error!"<<endl;
abort( );
}
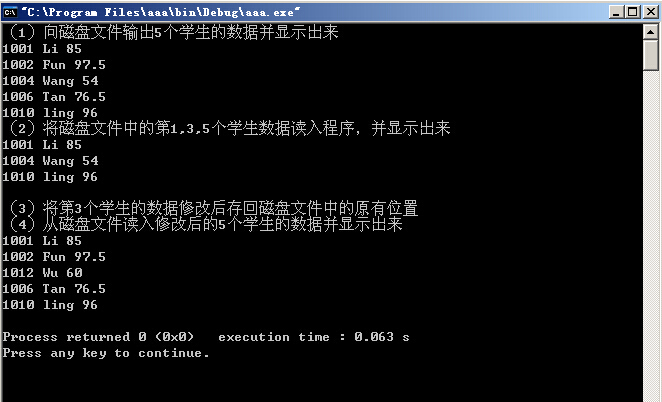
//(1)向磁盘文件输出5个学生的数据并显示出来
cout<<"(1)向磁盘文件输出5个学生的数据并显示出来"<<endl;
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
iofile.write((char *)&stud[i],sizeof(stud[i]));
cout<<stud[i].num<<" "<<stud[i].name<<" "<<stud[i].score<<endl;
}
//(2)将磁盘文件中的第1,3,5个学生数据读入程序,并显示出来;
cout<<"(2)将磁盘文件中的第1,3,5个学生数据读入程序,并显示出来"<<endl;
student stud1[5]; //用来存放从磁盘文件读入的数据
for(int i=0; i<5; i+=2)
{
iofile.seekg(i*sizeof(stud[i]),ios::beg); //定位于第0,2,4学生数据开头
iofile.read((char *)&stud1[i/2],sizeof(stud1[0]));
//先后读入3个学生的数据,存放在stud1[0],stud[1]和stud[2]中
cout<<stud1[i/2].num<<" "<<stud1[i/2].name<<" "<<stud1[i/2].score<<endl;
//输出stud1[0],stud[1]和stud[2]各成员的值
}
cout<<endl;
//(3) 将第3个学生的数据修改后存回磁盘文件中的原有位置。
cout<<"(3)将第3个学生的数据修改后存回磁盘文件中的原有位置"<<endl;
stud[2].num=1012; //修改第3个学生(序号为2)的数据
strcpy(stud[2].name,"Wu");
stud[2].score=60;
iofile.seekp(2*sizeof(stud[0]),ios::beg); //定位于第3个学生数据的开头
iofile.write((char *)&stud[2],sizeof(stud[2])); //更新第3个学生数据
iofile.seekg(0,ios::beg); //重新定位于文件开头
//(4)从磁盘文件读入修改后的5个学生的数据并显示出来。
cout<<"(4)从磁盘文件读入修改后的5个学生的数据并显示出来"<<endl;
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
iofile.read((char *)&stud[i],sizeof(stud[i])); //读入5个学生的数据
cout<<stud[i].num<<" "<<stud[i].name<<" "<<stud[i].score<<endl;
}
iofile.close( );
return 0;
}
运行结果:
4(2).代码:
#include <strstream>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct student
{
int num;
char name[20];
float score;
};
int main( )
{
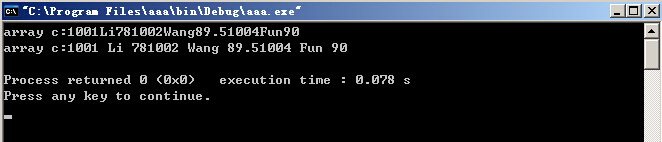
student stud[3]= {1001,"Li",78,1002,"Wang",89.5,1004,"Fun",90};
char c[50]; //用户定义的字符数组
ostrstream strout(c,30); //建立输出字符串流,与数组c建立关联,缓冲区长30
for(int i=0; i<3; i++) //向字符数组c写3个学生的数据
strout<<stud[i].num<<stud[i].name<<stud[i].score;
strout<<ends; //ends是C++的I/O操作符,插入一个′\\0′
cout<<"array c:"<<c<<endl; //显示字符数组c中的字符
ostrstream strout1(c,40); //这时,c将被重写
for(int i=0; i<3; i++)
strout1<<stud[i].num<<" "<<stud[i].name<<" "<<stud[i].score;
strout1<<ends; //ends是C++的I/O操作符,插入一个′\\0′
cout<<"array c:"<<c<<endl; //显示字符数组c中的字符
return 0;
}
运行结果:
4(3).代码:
#include <strstream>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
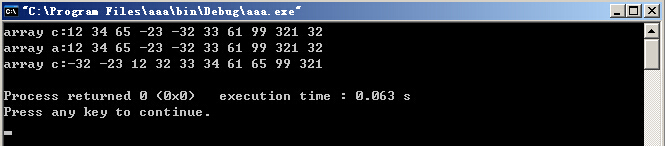
char c[50]="12 34 65 -23 -32 33 61 99 321 32";
int a[10],i,j,t;
cout<<"array c:"<<c<<endl;//显示字符数组中的字符串
istrstream strin(c,sizeof(c)); //建立输入串流对象strin并与字符数组c关联
for(i=0; i<10; i++)
strin>>a[i]; //从字符数组c读入10个整数赋给整型数组a
cout<<"array a:";
for(i=0; i<10; i++)
cout<<a[i]<<" "; //显示整型数组a各元素
cout<<endl;
for(i=0; i<9; i++) //用起泡法对数组a排序
for(j=0; j<9-i; j++)
if(a[j]>a[j+1])
{
t=a[j];
a[j]=a[j+1];
a[j+1]=t;
}
ostrstream strout(c,sizeof(c)); //建立输出串流对象strout并与字符数组c关联
for(i=0; i<10; i++)
strout<<a[i]<<" "; //将10个整数存放在字符数组c
strout<<ends; //加入′\\0′
cout<<"array c:"<<c<<endl; //显示字符数组c
return 0;
}
运行结果:
学习心得:
用字符串流时不需要打开或关闭文件;strin从字符数组中获取数据,strout将数据传送给字符数组;
























 558
558











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








