The Graphics Pipeline and OpenGL
The synthetic camera model
- Two components of viewing
- Set of geometric objects that form content of the scene
- Viewer through which the scene is imaged
The graphics pipeline
Primitives->Geometry processor->Rasterizer->Fragment processor->Frame buffer
The geometry processor
- Transforms primitves to the camera’s coordinate system, prepares them for rasterization
- Culls primitives facing away from the camera or lying outside the view frustum
The rasterizer
- Generates fragments(proto-pixels)
Fragment processor
- Check if fragments are visible
- Determines color
- All fragments treated identically, irrespective of the original primitive
Frame buffer
- Memory buffer used for the construction of the image.
- Not all data that passes through the frame buffer is displayed. It is like a sandbox in which the image is constructed.
- Used by the window system for display
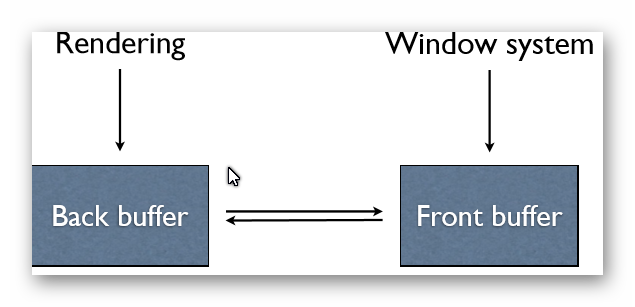
Double buffering
- Render into the back buffer while the window system points to the front buffer. When the next frame is assembled, swap.
- Avoid terrible visual artifacts
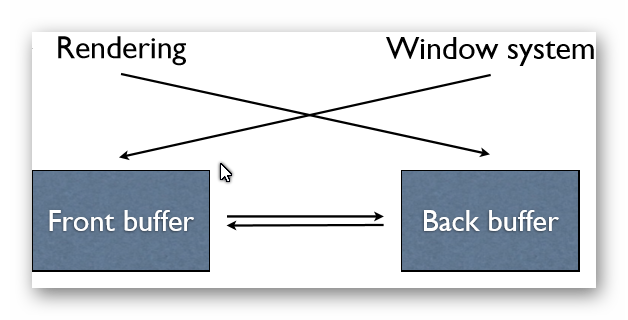
Double buffering
- Render into the back buffer while the window system points to the front buffer. When the next frame is assembled, swap.
- Avoid terrible visual artifacts.
Advantages and disadvantages of pipeline model
- Great fro parallel processing
- Primitives processed independently
- Fragments processed independently
- Does not support interaction between multiple object in the scene
- Global illumination,shadows,reflection,refraction
Global illumination
- Consider indirect illumination that is transmitted by means of other objects
- Primitives are no longer independent
Ray tracing
- Rays are cast from the viewpoint and followed recursivley through the scene
- Whitted ray tracing: Compute direct illumination from light sources at every point hit by traced rays.
Radiosity
- Discretize scene into pathes. Compute strength of interaction between patches.
- Shoot light from source patches, deposit in other patches. iterate until light is absorbed.
Photon mapping
- Stage 1: Trace photons from light sources and deposit onto photon map when photons interact with diffuse surfaces.
- Stage 2: Cast rays from viewpoint and estimate radiance
Design considerations for OpenGL
Separation of content and viewer
- Separates object description from viewer specification
- Two types of function
- Describe objects in the world (the input)
- Specify how the object should be processed for constructing an image (the state)
OpenGL is a state machine
- State machine with input and outputs
- Input is geometric object, output is a set of pixels
- State machine converts a collection of geometric objects in three dimensions to an image. This process is controlled by the state.
- State specifies how objects are projected onto the image plane, how the are colored, etc.

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








