配置文件内容:
1、hadoop-env.sh
# The java implementation to use.
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-6-sun
# The jsvc implementation to use. Jsvc is required to run secure datanodes.
#export JSVC_HOME=${JSVC_HOME}
export HADOOP_CONF_DIR=${HADOOP_CONF_DIR:-"/etc/hadoop"}
# Extra Java CLASSPATH elements. Automatically insert capacity-scheduler.
for f in $HADOOP_HOME/contrib/capacity-scheduler/*.jar; do
if [ "$HADOOP_CLASSPATH" ]; then
export HADOOP_CLASSPATH=$HADOOP_CLASSPATH:$f
else
export HADOOP_CLASSPATH=$f
fi
done
# The maximum amount of heap to use, in MB. Default is 1000.
#export HADOOP_HEAPSIZE=
#export HADOOP_NAMENODE_INIT_HEAPSIZE=""
# Extra Java runtime options. Empty by default.
export HADOOP_OPTS="$HADOOP_OPTS -Djava.net.preferIPv4Stack=true"
# Command specific options appended to HADOOP_OPTS when specified
export HADOOP_NAMENODE_OPTS="-Dhadoop.security.logger=${HADOOP_SECURITY_LOGGER:-INFO,RFAS} -Dhdfs.audit.logger=${HDFS_AUDIT_LOGGER:-INFO,NullAppender} $HADOOP_NAMENODE_OPTS"
export HADOOP_DATANODE_OPTS="-Dhadoop.security.logger=ERROR,RFAS $HADOOP_DATANODE_OPTS"
export HADOOP_SECONDARYNAMENODE_OPTS="-Dhadoop.security.logger=${HADOOP_SECURITY_LOGGER:-INFO,RFAS} -Dhdfs.audit.logger=${HDFS_AUDIT_LOGGER:-INFO,NullAppender} $HADOOP_SECONDARYNAMENODE_OPTS"
# The following applies to multiple commands (fs, dfs, fsck, distcp etc)
export HADOOP_CLIENT_OPTS="-Xmx512m $HADOOP_CLIENT_OPTS"
#HADOOP_JAVA_PLATFORM_OPTS="-XX:-UsePerfData $HADOOP_JAVA_PLATFORM_OPTS"
# On secure datanodes, user to run the datanode as after dropping privileges
export HADOOP_SECURE_DN_USER=${HADOOP_SECURE_DN_USER}
# Where log files are stored. $HADOOP_HOME/logs by default.
#export HADOOP_LOG_DIR=${HADOOP_LOG_DIR}/$USER
# Where log files are stored in the secure data environment.
export HADOOP_SECURE_DN_LOG_DIR=${HADOOP_LOG_DIR}/${HADOOP_HDFS_USER}
# The directory where pid files are stored. /tmp by default.
# NOTE: this should be set to a directory that can only be written to by
# the user that will run the hadoop daemons. Otherwise there is the
# potential for a symlink attack.
export HADOOP_PID_DIR=${HADOOP_PID_DIR}
export HADOOP_SECURE_DN_PID_DIR=${HADOOP_PID_DIR}
# A string representing this instance of hadoop. $US








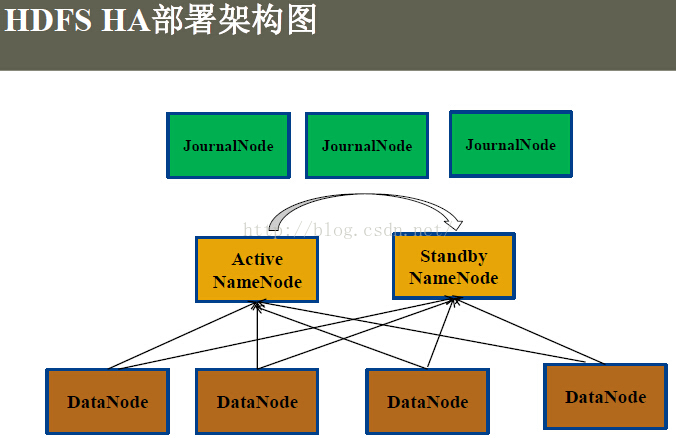
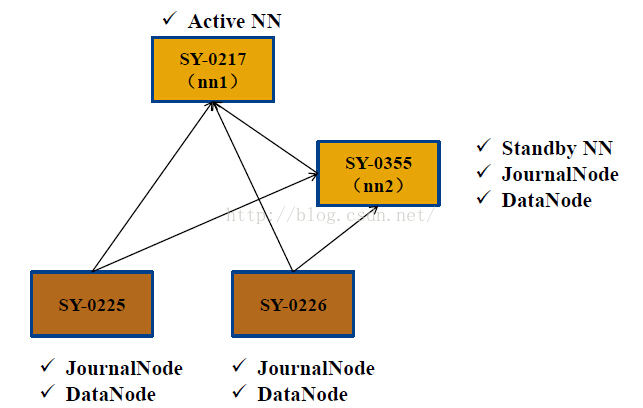
 本文档详细介绍了Hadoop HDFS HA的配置,包括hadoop-env.sh、mapred-site.xml、core-site.xml、hdfs-site.xml、yarn-site.xml等关键配置文件内容。配置涵盖了多个NameNode(nn1, nn2)、JournalNodes、DataNodes以及ResourceManager的相关设置,确保集群的高可用性和稳定性。"
7048226,1209563,ERwin快速导出数据库字典到Excel,"['数据库设计', '数据建模工具', 'Excel导出', 'ERwin教程']
本文档详细介绍了Hadoop HDFS HA的配置,包括hadoop-env.sh、mapred-site.xml、core-site.xml、hdfs-site.xml、yarn-site.xml等关键配置文件内容。配置涵盖了多个NameNode(nn1, nn2)、JournalNodes、DataNodes以及ResourceManager的相关设置,确保集群的高可用性和稳定性。"
7048226,1209563,ERwin快速导出数据库字典到Excel,"['数据库设计', '数据建模工具', 'Excel导出', 'ERwin教程']
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 184
184

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








