1.@PropertySource
@PropertySource:加载指定的配置文件【properties】.
先前我们通过@ConfifigurationProperties加载全局配置文件[appliaction.properties]中的值到javabean中,但是我们在具体使用的时候不会把所用的配置都保存在全局配置文件中的,可能会将
不同的配置保存在不同的配置文件中,那么这时我们就需要@PropertySource注解为指定的javabean类加载指定的配置文件。
例如:
1. @PropertySource
studentbean.properties文件
student.stuid=1001
student.stuname="zhangsan"
student.stusex=false
student.stuheight=168.5package com.wangxing.springboot.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:studentbean.properties")
public class StudentBean {
@Value("${student.stuid}")
private int stuid;
@Value("${student.stuname}")
private String stuname;
@Value("${student.stusex}")
private boolean stusex;
@Value("${student.stuheight}")
private double stuheight;
public int getStuid() {
return stuid;
}
public void setStuid(int stuid) {
this.stuid = stuid;
}
public String getStuname() {
return stuname;
}
public void setStuname(String stuname) {
this.stuname = stuname;
}
public boolean isStusex() {
return stusex;
}
public void setStusex(boolean stusex) {
this.stusex = stusex;
}
public double getStuheight() {
return stuheight;
}
public void setStuheight(double stuheight) {
this.stuheight = stuheight;
}
}package com.wangxing.springboot.controller;
import com.wangxing.springboot.bean.StudentBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/student")
public class StudentController {
@Autowired
private StudentBean studentBean;
@RequestMapping("/testPropertySource.do")
public void testPropertySource(){
int stuid=studentBean.getStuid();
String stuname=studentBean.getStuname();
boolean stusex=studentBean.isStusex();
double stuheight=studentBean.getStuheight();
System.out.println(stuid+","+stuname+","+stusex+","+stuheight);
}
}2.@ConfigurationProperties
personbean.properties文件
person.perid=1002
person.pername="lisisi"
person.persex=true
person.perheight=179.8package com.wangxing.springboot.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:personbean.properties")
public class PersonBean {
private int perid;
private String pername;
private boolean persex;
private double perheight;
public int getPerid() {
return perid;
}
public void setPerid(int perid) {
this.perid = perid;
}
public String getPername() {
return pername;
}
public void setPername(String pername) {
this.pername = pername;
}
public boolean isPersex() {
return persex;
}
public void setPersex(boolean persex) {
this.persex = persex;
}
public double getPerheight() {
return perheight;
}
public void setPerheight(double perheight) {
this.perheight = perheight;
}
}package com.wangxing.springboot.controller;
import com.wangxing.springboot.bean.PersonBean;
import com.wangxing.springboot.bean.StudentBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/person")
public class PersonController {
@Autowired
private PersonBean personBean;
@RequestMapping("/testPropertySource.do")
public void testPropertySource(){
int perid=personBean.getPerid();
String pername=personBean.getPername();
boolean persex=personBean.isPersex();
double perheight=personBean.getPerheight();
System.out.println(perid+","+pername+","+persex+","+perheight);
}
}区别:
| 名称 | 用途 |
| @PropertySource(value = "classpath:studentbean.properties") | 标注在类上,指定的配置文件【properties】,可以引入多个配置文件,例如 @PropertySource({ "classpath:studentbean.properties", "classpath:person.properties"}) |
| @Value("${xxxx}") | 标注在成员变量上,设置当前成员变量的初始值,可以直接设值@Value("zhangsan"),也可以从@PropertySource指定的配置文件【properties】中取值设置给成员变量@Value("${xxxx}") |
| @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person") | 标注在类上,表示设置当前类在配置文件【properties】的配置名称【prefix = "person"】 |
2.@ImportResource
@ImportResource:导入基于XML的Spring的配置文件,让配置文件里面的内容生效;
@ImportResource标注在一个主类上
package com.wangxing.springboot.bean;
public class UserBean {
private int userid;
private String username;
private boolean usersex;
private double userheight;
public int getUserid() {
return userid;
}
public void setUserid(int userid) {
this.userid = userid;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public boolean isUsersex() {
return usersex;
}
public void setUsersex(boolean usersex) {
this.usersex = usersex;
}
public double getUserheight() {
return userheight;
}
public void setUserheight(double userheight) {
this.userheight = userheight;
}
}userbean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userBean" class="com.wangxing.springboot.bean.UserBean">
<property name="userid" value="1003"></property>
<property name="username" value="wangwu"></property>
<property name="usersex" value="true"></property>
<property name="userheight" value="168.9"></property>
</bean>
</beans>package com.wangxing.springboot.controller;
import com.wangxing.springboot.bean.UserBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserBean userBean;
@RequestMapping("/testPropertySource.do")
public void testPropertySource(){
int userid=userBean.getUserid();
String username=userBean.getUsername();
boolean usersex=userBean.isUsersex();
double userheight=userBean.getUserheight();
System.out.println(userid+","+username+","+usersex+","+userheight);
}
}package com.wangxing.springboot.springbootdemo6;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ImportResource;
@SpringBootApplication
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.wangxing.springboot")
@ImportResource(value = "classpath:userbean.xml")
public class Springbootdemo6Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Springbootdemo6Application.class, args);
}
}Spring Boot里面没有Spring的配置文件,我们自己编写的配置文件,也不能自动识别;
想让Spring的配置文件生效,加载进来.
3.@Configuration @Bean @Import
package com.wangxing.springboot.bean;
public class UserBean {
private int userid;
private String username;
private double userdouble;
private boolean usersex;
public int getUserid() {
return userid;
}
public void setUserid(int userid) {
this.userid = userid;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public double getUserdouble() {
return userdouble;
}
public void setUserdouble(double userdouble) {
this.userdouble = userdouble;
}
public boolean isUsersex() {
return usersex;
}
public void setUsersex(boolean usersex) {
this.usersex = usersex;
}
}package com.wangxing.springboot.config;
import com.wangxing.springboot.bean.UserBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;=
@Configuration
public class UserConfig {
@Bean
public UserBean getBean(){
UserBean userBean= new UserBean();
userBean.setUserid(1001);
userBean.setUsername("zhangsan");
userBean.setUserdouble(168.9);
userBean.setUsersex(true);
return userBean;
}
}package com.wangxing.springboot.controller;
import com.wangxing.springboot.bean.UserBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserBean userBean;
@RequestMapping("/testUserBean.do")
public void testUserBean(){
int userid= userBean.getUserid();
String username= userBean.getUsername();
double userdouble= userBean.getUserdouble();
boolean usersex= userBean.isUsersex();
System.out.println(userid+","+username+","+userdouble+","+usersex);
}
}package com.wangxing.springboot.springbootdemo7;
import com.wangxing.springboot.config.UserConfig;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScans;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
@SpringBootApplication
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.wangxing.springboot")
@Import(UserConfig.class)
public class Springbootdemo7Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Springbootdemo7Application.class, args);
}
}| 名称 | 用途 |
| @Configuration | 标注在类上,表示当前类是一个java Config形式的配置类,可以代替基于xml的配置文件 |
| @Bean | 标注在方法上,告诉springIOC容器创建javabean类对象 相当于在基于xml配置文件中的 <bean id=”” class=””></bean> |
| @Import(xxxConfig.class) | 标注在主类上,表示导入xxxConfig.class【java Config形式的配置类】 |
4.Profiles
1.Profifile文件就是用来配置在不同环境下的配置数据。
2.因为在不同的环境下配置文件中配置的运行环境的数据是不同的,所以我们就需要灵活的在不同的运行环境下切换成对应的运行环境的数据,此时我们将不同的运行环境数据,配置到不同的
配置文件中,通过在主配置文件application.properties中的spring.profiles.active属性完成切换。
测试.properties配置
application-dev.properties【开发环境配置】
server.port=8080
application-prod.properties【生产环境配置】
server.port=9090
application.properties 【主配置】
spring.profiles.active=prod 【指定使用生产环境配置】
http://localhost:9090/testInfo
或者
spring.profiles.active=dev 【指定使用开发环境配置】
http://localhost:8080/testInfo测试.yml配置
application-devyml.yml【开发环境配置】
server:
port: 8080
application-prodyml.yml【生产环境配置】
server:
port: 9090
application.yml 【主配置】
spring:
profiles:
active: prodyml 【指定使用生产环境配置】
http://localhost:9090/testInfo
或者
spring:
profiles:
active: devyml 【指定使用开发环境配置】
http://localhost:8080/testInfo上面是通过在1.主配置文件中切换运行环境配置
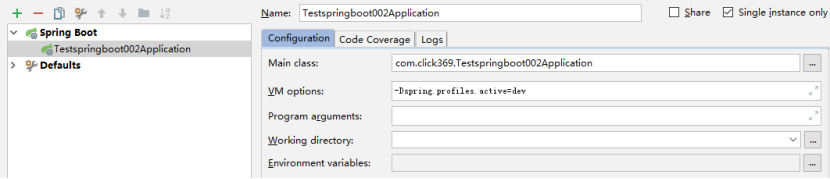
还可以通过配置2.运行环境参数配置视图窗口来指定具体使用哪一个运行环境 “--spring.profiles.active=dev“

还可以通过3.命令行运行jar的时候指定具体使用哪一个运行环境
java -jar testspringboot002-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --spring.profiles.active=dev;
还可以通过4.配置虚拟机参数指定具体使用哪一个运行环境;
“-Dspring.profiles.active=dev”
注意:运行环境配置文件的名称 application-{profiles}.properties/yml
5.主配置文件加载位置
spring boot 启动会扫描以下位置的application.properties或者 application.yml文件作为Spring boot的默认配置文件。
– 项目根目录/config/
– 项目根目录/
– resource/config/
– resource:/
以上是按照优先级从高到低的顺序,所有位置的文件都会被加载,高优先级配置内容会覆盖低优先级配置内容。
SpringBoot会从这四个位置全部加载主配置文件;互补配置。
我们也可以通过配置spring.config.location来改变默认配置,项目打包好以后,我们可以使用命令行参数的形式,启动项目的时候来指定配置文件的新位置;指定配置文件和默认加载的这些
配置文件共同起作用形成互补配置; java -jar testspringboot02-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --spring.confifig.location=F:/application.properties
外部配置加载顺序:
Spring Boot 支持多种外部配置方式
1. 命令行参数
2. 来自java:comp/env的JNDI属性
3. Java系统属性(System.getProperties())
4. 操作系统环境变量
5. RandomValuePropertySource配置的random.*属性值
6. jar包外部的application-{profile}.properties或application.yml(带spring.profile)配置文件
7. jar包内部的application-{profile}.properties或application.yml(带spring.profile)配置文件
8. jar包外部的application.properties或application.yml(不带spring.profile)配置文件
9. jar包内部的application.properties或application.yml(不带spring.profile)配置文件
优先加载带profifile,再来加载不带profifile,由jar包外向jar包内进行寻找
10. @Configuration注解类上的@PropertySource
11. 通过SpringApplication.setDefaultProperties指定的默认属性





















 504
504











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








