新建一张表,把旧表的内容插入到新表中,
语法:
INSERTINTOtable_name [(column [, column ...])] SELECT ...

聚合查询(MySQL中的内置函数)
聚合查询的本质是针对数据库中的行和行进行运算。
注:之前学的表达式查询,是列与列之间的计算
聚合函数
| 函数 | 说明 |
|
COUNT([DISTINCT] expr)
|
返回查询到的数据的数量
|
|
SUM([DISTINCT] expr)
|
返回查询到的数据的总和,不是数字没有意义
|
|
AVG([DISTINCT] expr)
|
返回查询到的数据的平均值,不是数字没有意义
|
|
MAX([DISTINCT] expr)
|
返回查询到的数据的最大值,不是数字没有意义
|
|
MIN([DISTINCT] expr)
|
返回查询到的数据的最小值,不是数字没有意义
|
注:这些操作都是针对列进行的
COUNT()
统计所有的行

常量也可以用来统计
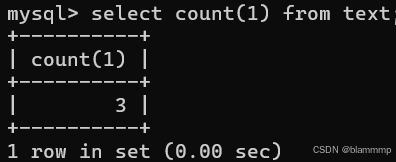
也可以指定某一个列

注:NULL不参与统计
SUM()
求和
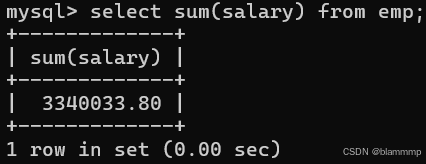
查询英语成绩

查询语文成绩

注:
1.在后面可以跟where 约束
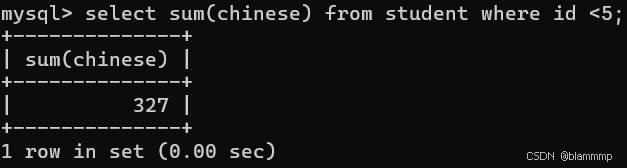
2.非数值运算会报警告

AVG()
求平均值
求英语的平均值

求总分的平均值

并且可以在后面跟别名
MAX() MIN()
求最大值,求最小值
求数学的最小值,英语的最大值

可以使用别名

同一列可以使用不同的聚合函数(求数学的最高分和最低分)

GROUP BY子句
SELECT 中使用 GROUP BY 子句可以对指定列进行分组查询。需要满足:使用 GROUP BY 进行分组查询时,SELECT 指定的字段必须是“分组依据字段”,其他字段若想出现在SELECT 中则必须包含在聚合函数中。
语法:
select column1, sum(column2), .. fromtable groupby column1,column3; 
drop table if exists emp;
create table emp (
id bigint primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20) not null,
role varchar(20) not null,
salary decimal(10, 2) not null
);
insert into emp values (null, '大马', '老板', 1500000.00);
insert into emp values (null, '小马', '老板', 1800000.00);
insert into emp values (null, '小王', '老师', 100000.00);
insert into emp values (null, '小李', '老师', 120000.00);
insert into emp values (null, '小熊', '经理', 90000.00);
insert into emp values (null, '小花', '经理', 80000.00);
insert into emp values (null, '猪悟能', '游戏角色', 700.5);
insert into emp values (null, '沙和尚', '游戏角色', 333.3);
select * from emp; 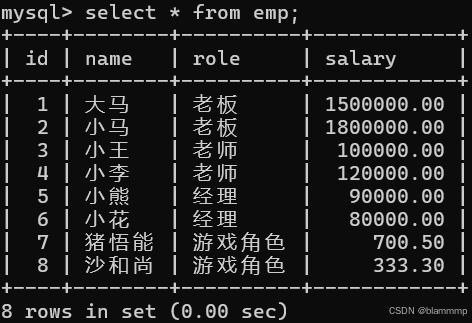
练习:
计算不同角色工资的平均值
select role,avg(salary) from emp group by role;
ROUND(数值,小数点后的位数)
select role,round(avg(salary),2) from emp group by role;
后面可以跟ORDER BY 语句进行排序
select role,round(avg(salary),2) from emp group by role order by round(avg(salary),2) asc;
使用别名后:
select role,round(avg(salary),2) 平均工资 from emp group by role order by 平均工资 asc;
HAVING
GROUP BY字句在分组之后,需要对分组的结果进行条件过滤时,不能使用where语句,而是需要HAVING
因为where是对表中的每一行真实数据进行过滤的
having是对group by之后,计算出来的结果进行过滤的
找出平均工资大于50000小于200000的角色
having可以把这个结果集中的数据进行过滤操作,平均工资并不是表中真正的记录,而是通过聚合函数计算得来的。
select role,round(avg(salary),2) from emp group by role having round(avg(salary),2)>50000 and round(avg(salary),2)<200000;
查询每个角色的最高工资,最低工资,平均工资
select role,max(salary),min(salary),avg(salary) from emp group by role;
使用别名后
select role,max(salary) 最大工资,min(salary) 最少工资,avg(salary) 平均工资 from emp group by role;
显示平均工资低于100000的角色和他的平均工资
select role,avg(salary) from emp group by role having avg(salary)<100000; 注:having要跟在group by之后
注:having要跟在group by之后
联合查询( )
)
联合多个表进行查询
1.取多张表的笛卡尔积
语法:select * from 表名,表名

注:大多数的数据都是无效数据
2.通过连接条件过滤掉无效数据
select * from class,student1 where class.class_id=student1.class_id;
3.通过指定的列循环,精简结果集
查询列表中通过表名.列名的方式指定查询字段
select student.id,student.name,class.name from class,student where class.class_id=student1.class_id;
给表名起别名简化SQL语句
select st.id,st.name,cl.name from class cl,student st where cl.class_id=st.class_id;注:
- 首先确定哪几张表要参与查询
- 根据表与表之间的主外键关系,确定过滤的条件
- 精简查询字段,得到想要的结果
内连接
语法:
select字段from表1 别名1 [inner] join表2 别名2 on连接条件and其他条件;
select字段from表1 别名1,表2 别名2 where连接条件and其他条件;先创建几个表
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `score`;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `student`;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `class`;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `course`;
CREATE TABLE `class` (
`class_id` bigint NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(50) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`class_id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 4 CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4 COLLATE = utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
INSERT INTO `class` VALUES (1, '计算机系2019级1班');
INSERT INTO `class` VALUES (2, '中文系2019级3班');
INSERT INTO `class` VALUES (3, '自动化2019级5班');
CREATE TABLE `course` (
`course_id` bigint NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(50) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`course_id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 7 CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4 COLLATE = utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
INSERT INTO `course` VALUES (1, 'Java');
INSERT INTO `course` VALUES (2, '中国传统文化');
INSERT INTO `course` VALUES (3, '计算机原理');
INSERT INTO `course` VALUES (4, '语文');
INSERT INTO `course` VALUES (5, '高阶数学');
INSERT INTO `course` VALUES (6, '英文');
CREATE TABLE `student` (
`student_id` bigint NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`sn` varchar(6) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`name` varchar(50) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci NOT NULL,
`mail` varchar(50) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`class_id` bigint NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`student_id`) USING BTREE,
UNIQUE INDEX `sn`(`sn` ASC) USING BTREE,
INDEX `class_id`(`class_id` ASC) USING BTREE,
CONSTRAINT `student_ibfk_1` FOREIGN KEY (`class_id`) REFERENCES `class` (`class_id`) ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE RESTRICT
) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 9 CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4 COLLATE = utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES (1, '09982', '黑旋风李逵', 'xuanfeng@qq.com', 1);
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES (2, '00835', '菩提老祖', NULL, 1);
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES (3, '00391', '白素贞', NULL, 1);
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES (4, '00031', '许仙', 'xuxian@qq.com', 1);
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES (5, '00054', '不想毕业', NULL, 1);
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES (6, '51234', '好好说话', 'say@qq.com', 2);
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES (7, '83223', 'tellme', NULL, 2);
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES (8, '09527', '老外学中文', 'foreigner@qq.com', 2);
CREATE TABLE `score` (
`score_id` bigint NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`student_id` bigint NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`course_id` bigint NULL DEFAULT NULL,
`score` decimal(5, 2) NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`score_id`) USING BTREE,
INDEX `student_id`(`student_id` ASC) USING BTREE,
INDEX `course_id`(`course_id` ASC) USING BTREE,
CONSTRAINT `score_ibfk_1` FOREIGN KEY (`student_id`) REFERENCES `student` (`student_id`) ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE RESTRICT,
CONSTRAINT `score_ibfk_2` FOREIGN KEY (`course_id`) REFERENCES `course` (`course_id`) ON DELETE RESTRICT ON UPDATE RESTRICT
) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 21 CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4 COLLATE = utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
INSERT INTO `score` VALUES (1, 1, 1, 70.50);
INSERT INTO `score` VALUES (2, 1, 3, 98.50);
INSERT INTO `score` VALUES (3, 1, 5, 33.00);
INSERT INTO `score` VALUES (4, 1, 6, 98.00);
INSERT INTO `score` VALUES (5, 2, 1, 60.00);
INSERT INTO `score` VALUES (6, 2, 5, 59.50);
INSERT INTO `score` VALUES (7, 3, 1, 33.00);
INSERT INTO `score` VALUES (8, 3, 3, 68.00);
INSERT INTO `score` VALUES (9, 3, 5, 99.00);
INSERT INTO `score` VALUES (10, 4, 1, 67.00);
INSERT INTO `score` VALUES (11, 4, 3, 23.00);
INSERT INTO `score` VALUES (12, 4, 5, 56.00);
INSERT INTO `score` VALUES (13, 4, 6, 72.00);
INSERT INTO `score` VALUES (14, 5, 1, 81.00);
INSERT INTO `score` VALUES (15, 5, 5, 37.00);
INSERT INTO `score` VALUES (16, 6, 2, 56.00);
INSERT INTO `score` VALUES (17, 6, 4, 43.00);
INSERT INTO `score` VALUES (18, 6, 6, 79.00);
INSERT INTO `score` VALUES (19, 7, 2, 80.00);
INSERT INTO `score` VALUES (20, 7, 6, 92.00);查询许仙同学的成绩
1.取两张表的笛卡尔积
select * from student,score;
2.通过连接条件过滤掉无效数据
select * from student,score where student.student_id=score.student_id;
确定集的过滤条件
select * from student,score where student.student_id=score.student_id and student.name='许仙';
3.精简字段
select student.name,score.score from student,score where student.student_id=score.student_id and student.name='许仙';
查询所有同学的总成绩及同学的个人信息
1.取两张表的笛卡尔积
select * from student,score;
2.通过连接条件过滤掉无效数据
select * from student,score where student.student_id=score.student_id;
确定集的过滤条件
select stu.student_id,sum(sc.score) 总分 from student stu,score sc where stu.student_id=sc.student_id group by sc.student_id ;
3.精简字段
select stu.student_id,stu.name,sum(sc.score) 总分 from student stu,score sc where stu.student_id=sc.student_id group by sc.student_id ;
希望能对大家有所帮助!!!!























 538
538

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








