前言
C语言数据结构现在通用来说就有两种存储结构,在上一篇中我们说了栈的链式结构,那么在这一篇中谈谈栈的顺序结构
1.顺序栈的定义
和顺序表一样,顺序栈其实是数组的一种特殊形式,我们也用结构体来定义,把数组第一个下标当作栈顶指针,那么栈空时top = -1;
//定义顺序栈
typedef struct
{
SElemType data[M];
int top;
}SqStack;
2.内容布局
本篇文章所涉及的主要内容有:
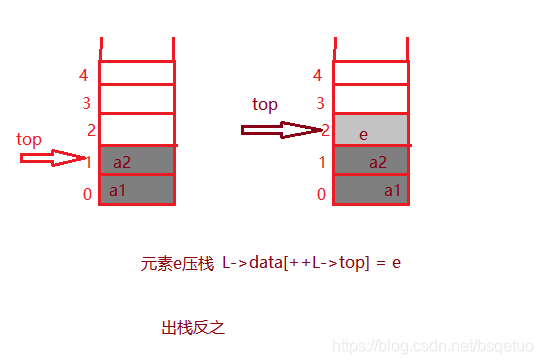
1.压栈:
//压栈
L->data[++L->top] = x;
2.出栈:
//出栈
*e = L->data[L->top--];
3.操作的一些图解
代码如下
/*
程序名称:链栈的建立与基本操作
编译环境:vs2010
最后修改:2019.8.1
作者:许安
*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define M 20
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
typedef int Status;
typedef int SElemType;
//定义顺序栈
typedef struct
{
SElemType data[M];
int top;
}SqStack;
Status InitStack(SqStack *L);//初始化顺序栈
Status Push(SqStack *L);//压栈
Status Pop(SqStack *L,SElemType *e);//出栈
Status Display(SqStack *L);//显示栈
Status ClearSqStack(SqStack *L);//置空栈
int main()
{
SqStack L;
SElemType e;
Status i;
int n=0;
InitStack(&L);
while(n!=4)
{
printf(" \n");
printf(" 1.压栈 2.出栈 3.清空栈 \n");
scanf("%d",&n);
switch(n)
{
case 1:
i = Push(&L);
if(i == ERROR)
printf("失败\n");
else
printf("成功\n");
printf("操作后的顺序栈:\n");
Display(&L);
break;
case 2:
i = Pop(&L,&e);
if(i == ERROR)
printf("失败\n");
else
printf("成功,取出%d \n",e);
printf("操作后的顺序栈:\n");
Display(&L);
break;
case 3:
ClearSqStack(&L);
printf("操作后的顺序栈:\n");
Display(&L);
}
}
return 0;
}
Status InitStack(SqStack *L)
{
L->top = -1;
return OK;
}
Status Push(SqStack *L)
{
int x = 0;
if(L->top == (M-1))//栈满
return ERROR;
printf("请输入数据,为-1时停止\n");
for(int i = 0;x!=-1;)
{
scanf("%d",&x);
if(x!=-1)
L->data[++L->top] = x;
}
return OK;
}
Status Pop(SqStack *L,SElemType *e)
{
if(L->top == -1)
return ERROR;
*e = L->data[L->top--];
return OK;
}
Status Display(SqStack *L)
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<=L->top;i++)
printf("%d ",L->data[i]);
printf("\n");
return OK;
}
Status ClearSqStack(SqStack *L)
{
L->top = -1;
return OK;
}
运行结果
附录
在程杰老师的书中,在顺序栈这一章中,还讨论了两栈共享空间的问题
1.为什么需要共享
对于两种相同类型的栈,我们可以做到最大限度地利用其事先开辟的存储空间操作,关键思路是top都在数组两端,向中间靠拢,只要两个栈顶指针不见面,两个栈就可以一直使用
栈满的情况:top1+1 == top2
2.使用情况
通常用在两个栈的空间有相反关系时,也就是一个栈在增长而另一个栈在缩短的情况,但一定要是相同类型的数据类型。
3.举例
买股票,有人赚钱,就有人亏钱
4.关键代码
//两栈共享空间结构
typedef struct
{
SElemType data[M];
int top1;
int top2;
}SqStack;
//压栈操作
Status Push(SqStack *L,SElemType e,int StackNum)
{
if(L->top1+1 == L->top2)
return ERROR;
if(StackNum == 1)
L->data[++L->top1] = e;
else if(StackNum == 2)
L->data[--L->top2] = e;
return OK;
}
//出栈操作
Status Push(SqStack *L,SElemType *e,int StackNum)
{
if(StackNum == 1)
{
if(L->top1 == -1)
return ERROR;
*e = L->data[L->top1--];
}
else if(StackNum == 2)
{
if(L->top2 == M)
return ERROR;
*e = L->data[L->top2++];
}
}
后记
其实明白链表的一些详细设定之后,顺序表的一些就相比较简单了许多,顺序表你把它当成数组就行了
以上就是顺序栈的表示和各种操作,喜欢的多多支持喔~






















 3863
3863











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








