1.关联式容器
我们已经接触过STL中的部分容器,比如:vector、list、deque、forward_list(C++11)等,这些容器统称为序列式容器,因为其底层为线性序列的数据结构,里面存储的是元素本身。那什么是关联式容器?它与序列式容器有什么区别?
关联式容器也是用来存储数据的,与序列式容器不同的是,其里面存储的是<key, value>结构的键值对,在数据检索时比序列式容器效率更高。
2.键值对
用来表示具有一一对应关系的一种结构,该结构中一般只包含两个成员变量key和value,key代表键值,value表示与key对应的信息。比如:现在要建立一个英汉互译的字典,那该字典中必然有英文单词与其对应的中文含义,而且,英文单词与其中文含义是一一对应的关系,即通过该应该单词,在词典中就可以找到与
其对应的中文含义。在SGI-STL中关于键值对的定义如下:

3.树形结构的关联式容器
树型结构的关联式容器主要有四种:map、set、multimap、multiset。这四种容器的共同点是:使用平衡搜索树(即红黑树)作为其底层结果,容器中的元素是一个有序的序列。
4.set
- set是按照一定次序存储元素的容器
- 在set中,元素的value也标识它(value就是key,类型为T),并且每个value必须是唯一的。set中的元素不能在容器中修改(元素总是const),但是可以从容器中插入或删除它们。
- 在内部,set中的元素总是按照其内部比较对象(类型比较)所指示的特定严格弱排序准则进行排序。
- set容器通过key访问单个元素的速度通常比unordered_set容器慢,但它们允许根据顺序对子集进行直接迭代。
- set在底层是用二叉搜索树(红黑树)实现的。
注意:
-
与map/multimap不同,map/multimap中存储的是真正的键值对<key, value>,set中只放value,但在底层实际存放的是由<value, value>构成的键值对。
-
set中插入元素时,只需要插入value即可,不需要构造键值对。
-
set中的元素不可以重复(因此可以使用set进行去重)。
-
使用set的迭代器遍历set中的元素,可以得到有序序列
-
set中的元素默认按照小于来比较
-
set中查找某个元素,时间复杂度为:log2 N
-
set中的元素不允许修改(为什么?)
修改之后可能破坏了二叉搜索树的结构
-
set中的底层使用二叉搜索树(红黑树)来实现。
5.map
- map是关联容器,它按照特定的次序(按照key来比较)存储由键值key和值value组合而成的元素。
- 在map中,键值key通常用于排序和惟一地标识元素,而值value中存储与此键值key关联的内容。键值key和值value的类型可能不同,并且在map的内部,key与value通过成员类型value_type绑定在一起,为其取别名称为pair:typedef pair value_type;
- 在内部,map中的元素总是按照键值key进行比较排序的。
- map中通过键值访问单个元素的速度通常比unordered_map容器慢,但map允许根据顺序对元素进行直接迭代(即对map中的元素进行迭代时,可以得到一个有序的序列)。
- map支持下标访问符,即在[]中放入key,就可以找到与key对应的value。
- map通常被实现为二叉搜索树(更准确的说:平衡二叉搜索树(红黑树))。
- multiset是按照特定顺序存储元素的容器,其中元素是可以重复的。
- 在multiset中,元素的value也会识别它(因为multiset中本身存储的就是<value, value>组成的键值对,因此value本身就是key,key就是value,类型为T). multiset元素的值不能在容器中进行修改(因为元素总是const的),但可以从容器中插入或删除。
- 在内部,multiset中的元素总是按照其内部比较规则(类型比较)所指示的特定严格弱排序准则进行排序。
- multiset容器通过key访问单个元素的速度通常比unordered_multiset容器慢,但当使用迭代器遍历时会得到一个有序序列。
- multiset底层结构为二叉搜索树(红黑树)。
6.map和set的简单运用
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
void test_set1()
{
set<int> s;
s.insert(3);
s.insert(1);
s.insert(2);
s.insert(14);
s.insert(36);
s.insert(4);
s.insert(3);
s.insert(3);
//set中的值都是唯一的,所以可以起到去重的效果
//遍历方式1
set<int>::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
}
cout << endl;
//遍历方式2
for (const auto& e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//检查单词拼写是否正确
//思路:把所有单词都放进set的对象中,把每个写出来的单词去set中查一下在不在
//在就是正确的,否则就是错误的
set<string> strSet;
strSet.insert("hello");
strSet.insert("happy");
strSet.insert("false");
strSet.insert("true");
strSet.insert("left");
strSet.insert("right");
for (auto e : strSet)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//set<string>::iterator ret = strSet.find("happy");
set<string>::iterator ret = strSet.find("happ");
if(ret != strSet.end())
{
cout << "找到了" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找不到了" << endl;
}
}
void test_set2()
{
set<int> s;
s.insert(3);
s.insert(1);
s.insert(2);
s.insert(14);
s.insert(36);
s.insert(4);
s.insert(3);
s.insert(3);
//先查找,找到了就删除
auto pos = s.find(4);
if (pos != s.end())
{
s.erase(pos);
}
如果没找到直接删除就会报错
//pos = s.find(40);
//s.erase(pos);
s.erase(40);//这样写 在就删除,不在就不处理也不会报错
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_set3()
{
//multiset允许键值冗余,使用方法和set基本一致
//就下面的几个地方有差异
multiset<int> s;
s.insert(3);
s.insert(1);
s.insert(2);
s.insert(14);
s.insert(36);
s.insert(4);
s.insert(3);
s.insert(3);
//排序不会去重 允许键值冗余
multiset<int>::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
}
cout << endl;
//find查找val有多个的时候,找到的是中序遍历的第一个
multiset<int>::iterator pos = s.find(3);
while (*pos == 3)
{
cout << *pos << " ";//会将3个3都打印出来
pos++;
}
cout << endl;
cout << s.count(3) << endl;//统计3的个数
cout << s.count(1) << endl;
s.erase(3);//会将所有的3全部删掉
it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
}
}
void test_map1()
{
map<int, double> m;
//插入方式1:调用pair的构造函数,构造一个匿名对象进行插入
m.insert(pair<int, double>(1, 1.1));
m.insert(pair<int, double>(2, 2.2));
m.insert(pair<int, double>(3, 3.3));
m.insert(pair<int, double>(4, 4.4));
m.insert(pair<int, double>(5, 5.5));
//插入方式2 调用函数模板
//好处:不需要声明模板参数,让函数模板自己推演,用起来更方便
m.insert(make_pair(6, 6.6));
//map的遍历
map<int, double>::iterator it = m.begin();
while (it != m.end())
{
//cout << (*it).first << ":" << (*it).second << endl;
cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;
it++;
}
map<string, string> dict;
dict.insert(make_pair("happy", "开心"));
dict.insert(make_pair("good", "好的"));
dict.insert(make_pair("world", "世界"));
dict.insert(make_pair("hello", "你好"));
map<string, string>::iterator dit = dict.begin();
while (dit != dict.end())
{
cout << dit->first << ":" << dit->second << endl;
dit++;
}
}
void test_map2()
{
map<string, string> dict;
dict.insert(make_pair("happy", "开心"));
dict.insert(make_pair("good", "好的"));
dict.insert(make_pair("world", "世界"));
dict.insert(make_pair("hello", "你好"));
map<string, string>::iterator dit = dict.begin();
while (dit != dict.end())
{
dit->second.insert(0, "{");
dit->second += "}";
dit++;
}
dit = dict.begin();
while (dit != dict.end())
{
cout << dit->first << ":" << dit->second << endl;
dit++;
}
//修改map的value数据
auto ret = dict.find("happy");
if (ret != dict.end())
{
string& str = ret->second;
str.insert(str.size()-1,"、快乐的");
}
dit = dict.begin();
while (dit != dict.end())
{
cout << dit->first << ":" << dit->second << endl;
dit++;
}
}
void test_map3()
{
//统计出现次数最多的前3种水果
string arr[] = { "苹果","橘子", "香蕉", "苹果", "橘子", "苹果", "草莓" ,"苹果" ,"橘子" ,"香蕉" ,"草莓" };
//1.统计次数
统计次数的方式1:思路:第一次出现就插入<str,1>,否则就++次数
//map<string, int> countMap;
//for (const auto& str : arr)
//{
// map<string, int>::iterator ret = countMap.find(str);
// if (ret != countMap.end())
// {
// ret->second++;
// }
// else
// {
// countMap.insert(make_pair(str, 1));
// }
//
//}
统计次数的方式2
//map<string, int> countMap;
//for (const auto& str : arr)
//{
// //insert 的返回值是pair<iterator, bool>
// pair<map<string, int>::iterator, bool> ret = countMap.insert(make_pair(str,1));
// if (ret.second == false)
// {
// ret.first->second++;//插入失败,说明不是第一次插入,数量++即可
// }
//}
//统计方式3
map<string, int> countMap;
for (const auto& str : arr)
{
countMap[str]++;
}
for (auto e : countMap)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
}
struct MapItCompare
{
bool operator()(map<string, int>::iterator x, map<string, int>::iterator y)
{
return x->second > y->second;
}
};
void test_map4()
{
//2找出出现次数最多的前三种水果
string arr[] = { "苹果","橘子", "香蕉", "苹果", "橘子", "苹果", "草莓" ,"苹果" ,"橘子" ,"香蕉" ,"草莓" };
map<string, int> countMap;
for (const auto& str : arr)
{
countMap[str]++;
}
//对所有水果次数排序的思路
vector<map<string, int>::iterator> v;
map<string, int>::iterator countMapIt = countMap.begin();
while (countMapIt != countMap.end())
{
v.push_back(countMapIt);
countMapIt++;
}
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), MapItCompare());
//利用map排序 --拷贝pair数据
map<int, string, greater<int>> SortMap;
for (auto e : countMap)
{
SortMap.insert(make_pair(e.second, e.first));
}
//利用set排序--不拷贝pair数据
//set<map<string, int>::iterator, MapItCompare> sortSet;
//countMapIt = countMap.begin();
//while (countMapIt != countMap.end())
//{
// sortSet.insert(countMapIt);
// countMapIt++;
//}
typedef map<string, int>::iterator M_IT;
//利用优先级队列
priority_queue< M_IT, vector<M_IT>, MapItCompare> pq;
countMapIt = countMap.begin();
while (countMapIt != countMap.end())
{
pq.push(countMapIt);
countMapIt++;
}
}
void test_map5()
{
map<string, string> dict;
dict.insert(make_pair("left", "左边"));
dict.insert(make_pair("left", "剩余"));//插入失败,已经有left了
multimap<string, string> mdict;//允许冗余
mdict.insert(make_pair("left", "左边"));
mdict.insert(make_pair("left", "剩余"));
mdict.insert(make_pair("left", "左边"));
}
int main()
{
//test_set1();
//test_set2();
//test_set3();
//test_map1();
//test_map2();
//test_map4();
test_map5();
return 0;
}
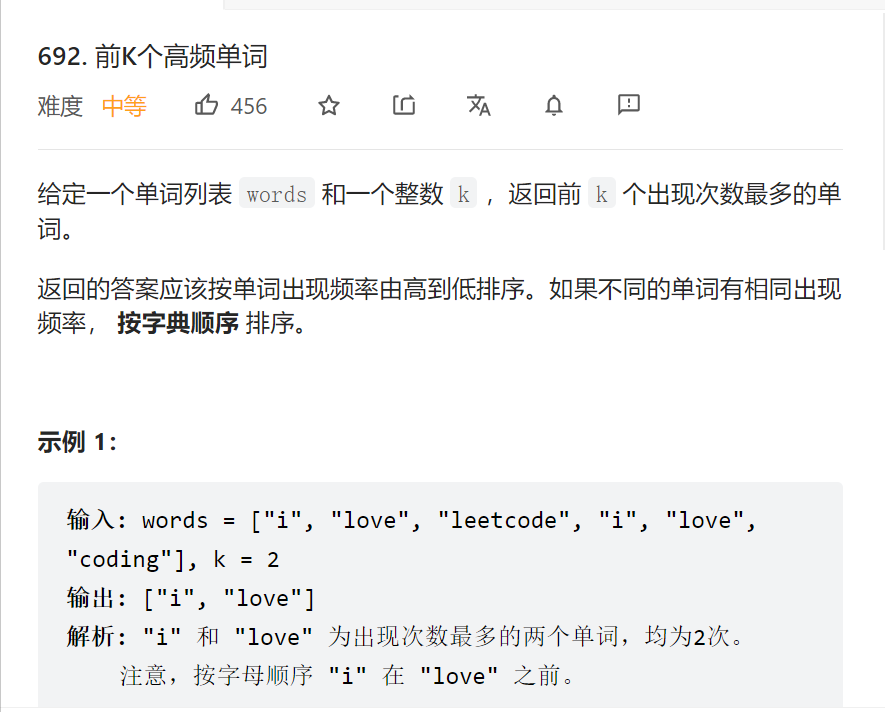
7.求前k个高频单词
[692. 前K个高频单词 - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> topKFrequent(vector<string>& words, int k) {
map<string,int> countMap;//先将数据存到map,此时已经进行了去重并计数
for(auto e:words)
{
countMap[e]++;
}
multimap<int, string,greater<int>> sortMap;//利用multimap允许出现同样次数的单词放进去排序
for(auto e : countMap)
{
sortMap.insert(make_pair(e.second, e.first));
}
vector<string> retV;
auto it = sortMap.begin();
while(k--)//循环k次,取前k个出现次数最多的
{
retV.push_back(it->second);
it++;
}
return retV;
}
};























 3659
3659











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










