概念
哈希函数:
顺序结构以及平衡树中,搜索的效率取决于搜索过程中元素比较的次数
理想的搜索方法:可以不经过任何比较,一次直接从表中得到要搜索的元素。如果构造一种存储结构,通过某种函数(hashFunc)使元素的存储位置与他的关键码之间能够建立一一映射的关系,那么在查找时可以通过该函数可以很快找到该元素
当向该结构中
插入元素 根据待插入元素的关键码,以此函数计算出该函数的存储位置并按此位置存放
搜索元素 对元素的关键码进行同样的计算,在相应的位置找是否有相应的
该方式即为哈希(散列)方法,哈希方法中使用的转换函数为哈希(散列)函数,构造出来的结构称为哈希表(hashTable)(或者散列表)
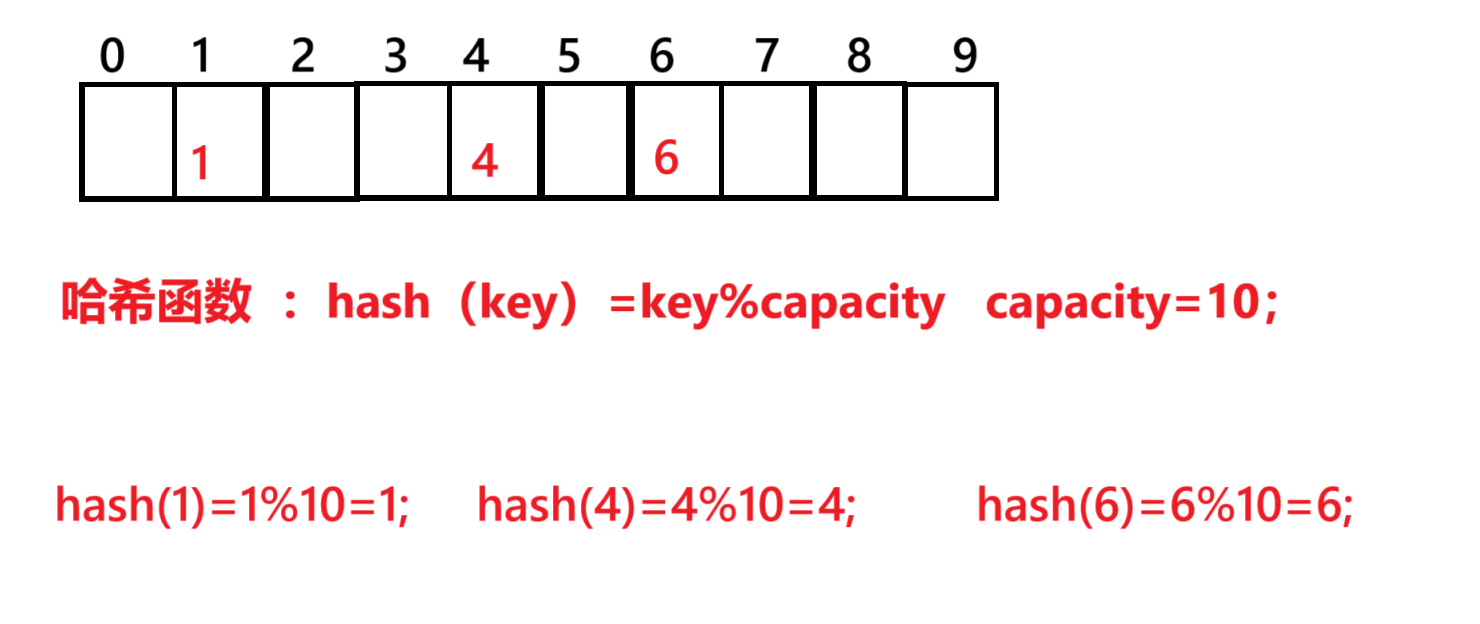
冲突
概念
对于两个数据元素的关键字k1,k2,有k1!=k2,但有hash(k1)==hash(k2),不同关键字通过相同哈希函数计算出相同的哈希地址,该种现象叫做哈希冲突或哈希碰撞
冲突避免
冲突避免
首先我们要明确哈希冲突是必然发生的,我们能做的只有降低冲突率
冲突避免-哈希函数设计
引起哈希冲突的一个原因可能是:哈希函数设计不够合理,哈希函数设计原则:
1.哈希函数的定义域必须包括需要存储的全部关键码,而如果散列表允许有m个地址时,其值域必须在0到m-1之间
2.哈希函数计算出来的地址能够均匀分布在整个空间中
3.哈希函数应该比较简单
常见的哈希函数:
1.直接定制法(常用)
Hash(key)=A*key+B(简单均匀,要事先知道分布情况)
2.除留余数法
Hash(Key)=key%p(p<=m)
3.平方取中法
冲突避免-负载因子调节(重点掌握)
散列表中负载因子的定义为:α=填入表中的元素个数/散列表的长度
对于开放地址法,负载因子是特别重要因素,要控制在0.7-0.8以下,Java中限制为0.75
负载因子和冲突率的关系粗略演示
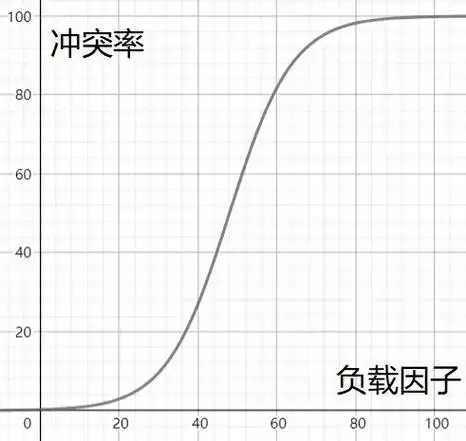
所以当冲突率达到一个无法忍受的程度时,我们要通过降低负载因子来变相降低冲突率
已知哈希表中已有的关键字个数是无法改变的,我们能做的就是扩容
冲突解决
解决哈希冲突两种常见的方法:闭散列和开散列
闭散列
闭散列也叫开放地址法,当发生哈希冲突时,如果哈希表未被装满,说明哈希表中必然还有空位置,那么可以将key存放到冲突位置的下一个位置去
如何寻找下一个位置呢?
1.线性探测:从发生冲突的位置开始,依次向后探测,直到寻到下一个空位置为止
线性探测的缺点是冲突元素堆积在一起
2.二次探测:找下一个位置的方法Hi=(H0+i^2)%m
闭散列的缺点是空间利用率低,这也是哈希的缺陷
开散列
开散列也叫链地址法,即将发生哈希冲突的元素以链表的形式存储在在一起,即开散列采用的方法是数组加链表的方法,认为时间复杂度为0(1)
模拟实现哈希桶
public class HashBucket {
private static class Node {
private int key;
private int value;
Node next;
public Node(int key, int value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
private Node[] array;
private int size; // 当前的数据个数
private static final double LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75;
private static final int DEFAULT_SIZE = 8;//默认桶的大小
public void put(int key, int value) {
// write code here
int index = key % array.length;
Node cur = array[index];
while (cur != null) {
if(cur.key == key) {
cur.key = key;
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
//没有找到当前链表中有这个key的节点
Node node = new Node(key, value);
node.next = array[index];
array[index] = node;
size++;
if(loadFactor() >= LOAD_FACTOR) {
resize();
}
}
private void resize() {
// write code here
Node[] newArray = new Node[2*array.length];
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
Node cur = array[i];
while (cur != null) {
int newIndex = cur.key % newArray.length;
Node curN = cur.next;
cur.next = newArray[newIndex];
newArray[newIndex] = cur;
cur = curN;
}
}
array = newArray;
}
private double loadFactor() {
return size * 1.0 / array.length;
}
public int get(int key) {
// write code here
int index = key % array.length;
Node cur = array[index];
while (cur != null) {
if(cur.key == key) {
return cur.key;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return -1;
}
}
public class HashBuck2 <K,V>{
static class Node<K,V> {
public K key;
public V val;
public Node<K,V> next;
public Node(K key,V val) {
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
}
}
public Node<K,V>[] array = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[10];
public int usedSize;
public static final double DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
public void push(K key,V val) {
int hashcode = key.hashCode();
int index = hashcode % array.length;
Node<K,V> cur = array[index];
while (cur != null) {
if(cur.key.equals(key)) {
cur.val = val;
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
Node<K,V> node = new Node<>(key, val);
node.next = array[index];
array[index] = node;
usedSize++;
}
public V getVal(K key) {
int hashcode = key.hashCode();
int index = hashcode % array.length;
Node<K,V> cur = array[index];
while (cur != null) {
if(cur.key.equals(key)) {
return cur.val;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}
}
性能分析
虽然哈希表一直在和冲突做斗争,但哈希冲突率并不高,冲突个数是可控的,我们认为哈希表的插入/删除/查找的时间复杂度为0(1)
和java类集的关系
1.HashMap和HashSet是java中利用哈希表实现的map和set
2.java中使用的是哈希桶方式来解决冲突的
3.java会在链表长度大于一定值后,将链表转换为搜索树(红黑树)
4.必须要重写hashCode和equals方法





















 3108
3108

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








