首先声明:这些内容主要是面向C语言的初学者,尤其是正在学习C语言的学生。
学习C语言的字符型数据时,首先需要记住两条重要特性:1.字符型数据存储的是字符的ASCII码值;2. 由于ASCII码值本质上是一个整数,因此字符型数据可以像整数一样做加减运算。光记住这两条只能应付一些简单的考试题,要想利用字符型数据来解决一些实际的应用问题,还需要更多的练习。本文中的例子将结合文本文件的操作来增强对字符型数据的学习。
文本文件中每个英语字符占一个字节,存储的也是字符的ASCII码值,因此对文本文件的操作,完全可以借助字符型数据来处理。从文本文件中读出的一个字符,可以存储在字符型变量里,然后按照应用需求对字符型变量进行处理,最后把该变量写回文本文件中去。
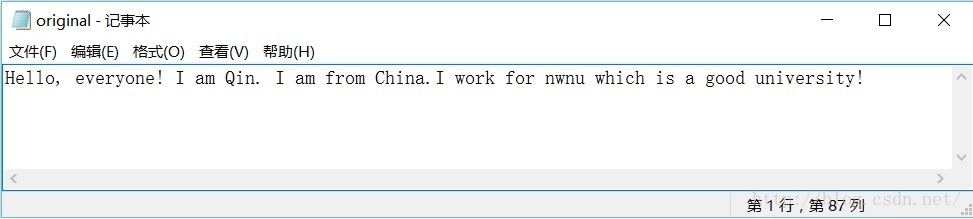
例1:用记事本编辑一个名为“original.txt”的文本文件,其中包含一段英语文本。现在要求编程序对该文件内容按照恺撒密码进行加密,加密后的内容保存到一个新文件 “result.txt” 中。
恺撒密码是一种古老的加密方法,是指把信息中的每一个字母用字母表中的该字母后的第三个字母代替,即a被d替换,b被e替换,…,z被c替换。假设从文件中读出的字符存放在字符型变量ch中,这种替换可以很容易的描述为:ch = ch + 3; 当ch + 3大于‘z’时,需要转回去从a再开始,因此需要减去26。为了简单起见,我们对非字母字符不做任何处理,原样输出。
初学者可能对文件的打开和读写不太熟悉,我们在这里用freopen函数来简化对文件的操作,freopen函数可以将标准输入stdin(对应的是键盘)和标准输出stdout(对应的是显示器)分别重定向到输入文件和输出文件,也就说,本来从键盘输入数据,现在改为从输入文件读取数据,本来是向显示器输出数据,现在改为向输出文件输出数据。这样的好处是,可以直接使用scanf,getchar,printf和putchar函数读写文件数据。这也是程序设计竞赛中常用的读取测试数据的方法。
程序:
#include "stdio.h"
int main()
{
char ch;
freopen("original.txt","r",stdin) ; //输入输出被分别重定向到两个文件。
freopen("result.txt","w",stdout);
ch=getchar();
while(ch!=EOF) //EOF指文件的末尾
{
if(ch>='A'&&ch<='Z'||ch>='a'&&ch<='z')
{
ch=ch+3;
if(ch>'z'||(ch>'Z'&&ch<='Z'+3))
ch= ch-26;
}
printf("%c",ch);
ch = getchar();
}
return 0;
}图1显示的是original.txt文件中的内容,图2显示的是加密处理后的内容。
图1. original.txt文件
图2. result.txt文件
可能很多初学C语言的同学在学习字符型数据时,还没有学习条件语句、循环语句以及文件的读写,因为大多数教材的编排顺序往往先是数据类型,然后才是控制语句,文件通常是放在最后一章的。如果完全按照教材按部就班,学的知识点会比较零散,难以形成一个整体。因此,我建议老师在教前面的知识时,在例子程序中可以适当地将后面的内容加进来一些,对于没学到的知识点,老师稍作讲解,学生大体是可以明白的,有兴趣的同学也可以提前自学后面的内容。这样有利于学生将多个知识点在脑海中串成一个整体。
回到上面的文本文件操作问题,有些学生可能会有疑问,如果文件的内容不是英文,而是汉字呢,能用相同的方法读取并处理汉字吗?下一篇文章中我们将把字符型数据的学习扩充到对汉字的简单处理。























 7628
7628

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








