Linux内核中创建slab主要由函数cache_grow()实现,从slab的创建中我们可以完整地看到slab与对象、页面的组织方式。
/*
* Grow (by 1) the number of slabs within a cache. This is called by
* kmem_cache_alloc() when there are no active objs left in a cache.
*/
/*使用一个或多个页面创建一个空slab。
objp:页面虚拟地址,为空表示还未申请内存页,不为空
,说明已申请内存页,可直接用来创建slab*/
static int cache_grow(struct kmem_cache *cachep,
gfp_t flags, int nodeid, void *objp)
{
struct slab *slabp;
size_t offset;
gfp_t local_flags;
struct kmem_list3 *l3;
/*
* Be lazy and only check for valid flags here, keeping it out of the
* critical path in kmem_cache_alloc().
*/
BUG_ON(flags & GFP_SLAB_BUG_MASK);
local_flags = flags & (GFP_CONSTRAINT_MASK|GFP_RECLAIM_MASK);
/* Take the l3 list lock to change the colour_next on this node */
check_irq_off();
/* 获得本内存节点的slab三链 */
l3 = cachep->nodelists[nodeid];
spin_lock(&l3->list_lock);
/* Get colour for the slab, and cal the next value. */
/* 获得本slab的着色区偏移 */
offset = l3->colour_next;
/* 更新着色区偏移,使不同slab的着色偏移不同 */
l3->colour_next++;
/* 不能超过着色区的总大小,如果超过了,重置为0。这就是前面分析过的着色循环问题
。事实上,如果slab中浪费的空间很少,那么很快就会循环一次。*/
if (l3->colour_next >= cachep->colour)
l3->colour_next = 0;
spin_unlock(&l3->list_lock);
/* 将着色单位区间的个数转换为着色区大小 */
offset *= cachep->colour_off;
if (local_flags & __GFP_WAIT)
local_irq_enable();
/*
* The test for missing atomic flag is performed here, rather than
* the more obvious place, simply to reduce the critical path length
* in kmem_cache_alloc(). If a caller is seriously mis-behaving they
* will eventually be caught here (where it matters).
*/
kmem_flagcheck(cachep, flags);
/*
* Get mem for the objs. Attempt to allocate a physical page from
* 'nodeid'.
*/
if (!objp)/* 还未分配页面,从本内存节点分配1<<cachep->gfporder个页面
,objp为slab首页面的虚拟地址 */
objp = kmem_getpages(cachep, local_flags, nodeid);
if (!objp)
goto failed;
/* Get slab management. */
/* 分配slab管理对象 */
slabp = alloc_slabmgmt(cachep, objp, offset,
local_flags & ~GFP_CONSTRAINT_MASK, nodeid);
if (!slabp)
goto opps1;
/* 设置page到cache、slab的映射 */
slab_map_pages(cachep, slabp, objp);
/* 初始化slab中的对象 */
cache_init_objs(cachep, slabp);
if (local_flags & __GFP_WAIT)
local_irq_disable();
check_irq_off();
spin_lock(&l3->list_lock);
/* Make slab active. */
list_add_tail(&slabp->list, &(l3->slabs_free));
/* 更新本cache增长计数 */
STATS_INC_GROWN(cachep);
/* 更新slab链表中空闲对象计数 */
l3->free_objects += cachep->num;
spin_unlock(&l3->list_lock);
return 1;
opps1:
kmem_freepages(cachep, objp);
failed:
if (local_flags & __GFP_WAIT)
local_irq_disable();
return 0;
}执行流程:
1,从cache结构中获得并计算着色区偏移量;
2,从伙伴系统中获得1<<cachep->gfporder个页面用于slab;
3,初始化slab中相关变量,如果是外置式slab需要从新申请slab管理区的空间,由函数alloc_slabmgmt()实现。
/*分配slab管理对象*/
static struct slab *alloc_slabmgmt(struct kmem_cache *cachep, void *objp,
int colour_off, gfp_t local_flags,
int nodeid)
{
struct slab *slabp;
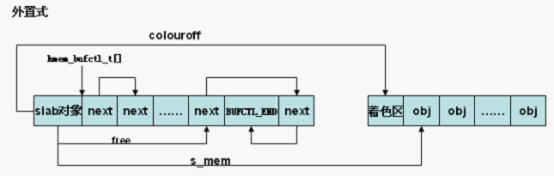
if (OFF_SLAB(cachep)) {
/* Slab management obj is off-slab. */
/* 外置式slab。从general slab cache中分配一个管理对象,
slabp_cache指向保存有struct slab对象的general slab cache。
slab初始化阶段general slab cache可能还未创建,slabp_cache指针为空
,故初始化阶段创建的slab均为内置式slab。*/
slabp = kmem_cache_alloc_node(cachep->slabp_cache,
local_flags, nodeid);
/*
* If the first object in the slab is leaked (it's allocated
* but no one has a reference to it), we want to make sure
* kmemleak does not treat the ->s_mem pointer as a reference
* to the object. Otherwise we will not report the leak.
*//* 对第一个对象做检查 */
kmemleak_scan_area(slabp, offsetof(struct slab, list),
sizeof(struct list_head), local_flags);
if (!slabp)
return NULL;
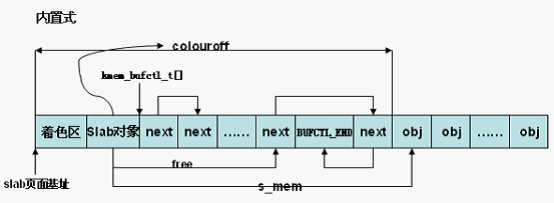
} else {/* 内置式slab。objp为slab首页面的虚拟地址,加上着色偏移
,得到slab管理对象的虚拟地址 */
slabp = objp + colour_off;
/* 计算slab中第一个对象的页内偏移,slab_size保存slab管理对象的大小
,包含struct slab对象和kmem_bufctl_t数组 */
colour_off += cachep->slab_size;
} /* 在用(已分配)对象数为0 */
slabp->inuse = 0;
/* 第一个对象的页内偏移,可见对于内置式slab,colouroff成员不仅包括着色区
,还包括管理对象占用的空间
,外置式slab,colouroff成员只包括着色区。*/
slabp->colouroff = colour_off;
/* 第一个对象的虚拟地址 */
slabp->s_mem = objp + colour_off;
/* 内存节点ID */
slabp->nodeid = nodeid;
/* 第一个空闲对象索引为0,即kmem_bufctl_t数组的第一个元素 */
slabp->free = 0;
return slabp;
}通过初始化,我们画出下面图像。
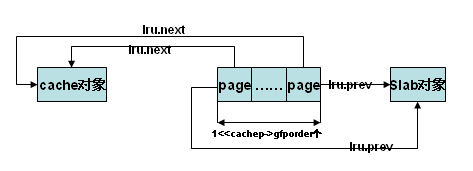
4,设置slab中页面(1<<cachep->gfporder个)到slab、cache的映射。这样,可以通过page的lru链表找到page所属的slab和cache。slab_map_pages()实现
/*设置page到cache、slab的指针,这样就能知道页面所在的cache、slab
addr:slab首页面虚拟地址*/
static void slab_map_pages(struct kmem_cache *cache, struct slab *slab,
void *addr)
{
int nr_pages;
struct page *page;
/* 获得slab首页面*/
page = virt_to_page(addr);
nr_pages = 1;
/* 如果不是大页面(关于大页面请参阅相关文档)
,计算页面的个数 */
if (likely(!PageCompound(page)))
nr_pages <<= cache->gfporder;
do {
/* struct page结构中的lru根据页面的用途有不同的含义
,当页面空闲或用于高速缓存时,
lru成员用于构造双向链表将page串联起来,而当page用于slab时,
next指向page所在的cache,prev指向page所在的slab */
page_set_cache(page, cache);
page_set_slab(page, slab);
page++;
} while (--nr_pages);
}代码实现结果如下图
5,初始化slab中kmem_bufctl_t[]数组,其中kmem_bufctl_t[]数组为一个静态链表,指定了slab对象(obj)的访问顺序。即kmem_bufctl_t[]中存放的是下一个访问的obj。在后面分析中slab_get_obj()函数从slab中提取一个空闲对象,他通过index_to_obj()函数找到空闲对象在kmem_bufctl_t[]数组中的下标,然后通过slab_bufctl(slabp)[slabp->free]获得下一个空闲对象的索引并用它更新静态链表。
/*初始化slab中的对象,主要是通过kmem_bufctl_t数组将对象串联起来*/
static void cache_init_objs(struct kmem_cache *cachep,
struct slab *slabp)
{
int i;
/* 逐一初始化slab中的对象 */
for (i = 0; i < cachep->num; i++) {
/* 获得slab中第i个对象 */
void *objp = index_to_obj(cachep, slabp, i);
#if DEBUG
/* need to poison the objs? */
if (cachep->flags & SLAB_POISON)
poison_obj(cachep, objp, POISON_FREE);
if (cachep->flags & SLAB_STORE_USER)
*dbg_userword(cachep, objp) = NULL;
if (cachep->flags & SLAB_RED_ZONE) {
*dbg_redzone1(cachep, objp) = RED_INACTIVE;
*dbg_redzone2(cachep, objp) = RED_INACTIVE;
}
/*
* Constructors are not allowed to allocate memory from the same
* cache which they are a constructor for. Otherwise, deadlock.
* They must also be threaded.
*/
if (cachep->ctor && !(cachep->flags & SLAB_POISON))
cachep->ctor(objp + obj_offset(cachep));
if (cachep->flags & SLAB_RED_ZONE) {
if (*dbg_redzone2(cachep, objp) != RED_INACTIVE)
slab_error(cachep, "constructor overwrote the"
" end of an object");
if (*dbg_redzone1(cachep, objp) != RED_INACTIVE)
slab_error(cachep, "constructor overwrote the"
" start of an object");
}
if ((cachep->buffer_size % PAGE_SIZE) == 0 &&
OFF_SLAB(cachep) && cachep->flags & SLAB_POISON)
kernel_map_pages(virt_to_page(objp),
cachep->buffer_size / PAGE_SIZE, 0);
#else
/* 调用此对象的构造函数 */
if (cachep->ctor)
cachep->ctor(objp);
#endif /* 初始时所有对象都是空闲的,只需按照数组顺序串起来即可 */
/*相当于静态索引指针*/
slab_bufctl(slabp)[i] = i + 1;
}
/* 最后一个指向BUFCTL_END */
slab_bufctl(slabp)[i - 1] = BUFCTL_END;
}
























 863
863

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








