masterless
应用场景
- master 与 minion 网络不通或通信有延迟,即网络不稳定
- 想在 minion 端直接执行状态
传统的 SaltStack 是需要通过 master 来执行状态控制 minion 从而实现状态的管理,但是当网络不稳定的时候,当想在minion本地执行状态的时候,当在只有一台主机的时候,想执行状态该怎么办呢?这就需要用到 masterless 了。
有了masterless,即使你只有一台主机,也能玩saltstack,而不需要你有N台主机架构。
masterless配置
修改minion配置文件
- 注释master行
- 取消注释file_client并设其值为local
- 设置file_roots
- 设置pillar_roots
[root@node1 ~]# vim /etc/salt/minion
···
#master: 192.168.111.141
···
file_client: local
···
file_roots:
base:
- /srv/salt
关闭salt-minion服务
使用 masterless 模式时是不需要启动任何服务的,包括salt-master和salt-minion。
[root@node1 ~]# systemctl stop salt-minion
[root@node1 ~]# systemctl disable salt-minion
Removed /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/salt-minion.service.
salt-call
masterless模式执行模块或状态时需要使用salt-call命令,而不再是salt或者salt-ssh。需要注意的是要使用salt-call的–local选项。
[root@node1 ~]# salt-call --local cmd.run "date"
local:
Mon Nov 29 19:33:47 CST 2021
[root@node1 ~]# salt-call --local pkg.install 'httpd'
local:
----------
apr:
----------
new:
1.6.3-12.el8
old:
apr-util:
----------
new:
1.6.1-6.el8
old:
apr-util-bdb:
----------
new:
1.6.1-6.el8
old:
apr-util-openssl:
----------
new:
1.6.1-6.el8
old:
centos-logos-httpd:
----------
new:
85.8-2.el8
old:
httpd:
----------
new:
2.4.37-43.module_el8.5.0+1022+b541f3b1
old:
httpd-filesystem:
----------
new:
2.4.37-43.module_el8.5.0+1022+b541f3b1
old:
httpd-tools:
----------
new:
2.4.37-43.module_el8.5.0+1022+b541f3b1
old:
mailcap:
----------
new:
2.1.48-3.el8
old:
mod_http2:
----------
new:
1.15.7-3.module_el8.4.0+778+c970deab
old:
salt-master高可用
salt-master高可用之数据同步
涉及到高可用时,数据的同步是个永恒的话题,我们必须保证高可用的2个master间使用的数据是一致的,包括:
- /etc/salt/master配置文件
- /etc/salt/pki目录下的所有key
- /srv/下的salt和pillar目录下的所有文件
保障这些数据同步的方案有:
- nfs挂载
- rsync同步
- 使用gitlab进行版本控制
安全相关: 为保证数据的同步与防止丢失,可将状态文件通过gitlab进行版本控制管理。
salt-master高可用配置
# 同步master配置文件和所有的key
[root@master ~]# scp /etc/salt/master 192.168.111.142:/etc/salt/master
root@192.168.111.142's password:
master 100% 52KB 19.6MB/s 00:00
[root@node1 ~]# tree /etc/salt/pki/
/etc/salt/pki/
├── master
└── minion
├── minion_master.pub
├── minion.pem
└── minion.pub
[root@master ~]# tree /etc/salt/pki/
/etc/salt/pki/
├── master
│ ├── master.pem
│ ├── master.pub
│ ├── minions
│ │ └── node1
│ ├── minions_autosign
│ ├── minions_denied
│ ├── minions_pre
│ ├── minions_rejected
│ └── ssh
│ ├── salt-ssh.rsa
│ └── salt-ssh.rsa.pub
└── minion
[root@master ~]# scp /etc/salt/pki/master/master.p* 192.168.111.142:/etc/salt/pki/master/
root@192.168.111.142's password:
master.pem 100% 1679 1.0MB/s 00:00
master.pub 100% 451 183.0KB/s 00:00
[root@node1 ~]# tree /etc/salt/pki/
/etc/salt/pki/
├── master
│ ├── master.pem
│ ├── master.pub
│ ├── minions
│ ├── minions_autosign
│ ├── minions_denied
│ ├── minions_pre
│ └── minions_rejected
└── minion
├── minion_master.pub
├── minion.pem
└── minion.pub
7 directories, 5 files
# 配置minion连接备机master
[root@node2 ~]# vim /etc/salt/minion
master: 192.168.111.142
[root@node1 ~]# salt-key -L
Accepted Keys:
Denied Keys:
Unaccepted Keys:
node2
Rejected Keys:
[root@node1 ~]# salt-key -ya node2
The following keys are going to be accepted:
Unaccepted Keys:
node2
Key for minion node2 accepted.
[root@node1 ~]# salt node2 test.ping
node2:
True
# 修改minion配置文件实现高可用
[root@node2 ~]# vim /etc/salt/minion
···
master_type: failover
···
master_alive_interval: 3
···
master:
- 192.168.111.141
- 192.168.111.142
[root@node2 ~]# systemctl restart salt-minion.service
[root@master ~]# salt node2 test.ping
node1:
True
[root@node1 ~]# salt node2 test.ping
node1:
Minion did not return. [No response]
The minions may not have all finished running and any remaining minions will return upon completion. To look up the return data for this job later, run the following command:
salt-run jobs.lookup_jid 20211129072727657662
# 关闭主节点salt-master
[root@master ~]# systemctl stop salt-master.service
[root@node1 ~]# salt node2 test.ping
node2:
True
salt-syndic分布式架构
salt-syndic架构图
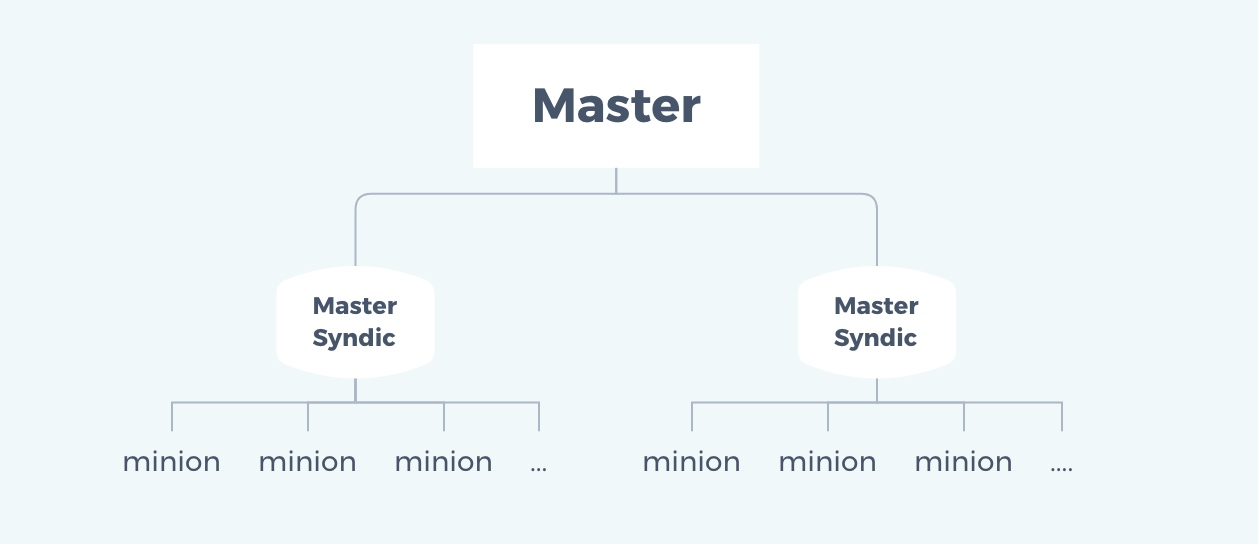
salt-syndic的优劣势
优势:
- 可以通过syndic实现更复杂的salt架构
- 减轻master的负担
劣势:
- syndic的/srv目录下的salt和pillar目录内容要与最顶层的master下的一致,所以要进行数据同步,同步方案同salt-master高可用
- 最顶层的master不知道自己有几个syndic,它只知道自己有多少个minion,并不知道这些minion是由哪些syndic来管理的
salt-syndic部署
环境:
| ip | 主机 | 应用 |
|---|---|---|
| 192.168.111.141 | master | salt-master |
| 192.168.111.142 | syndic | salt-master salt-syndic |
| 192.168.111.145 | node1 | salt-minion |
# 在syndic主机上安装salt-master和salt-synidc
[root@syndic ~]# dnf -y install salt-master salt-syndic
# 修改master配置
[root@master ~]# vim /etc/salt/master
order_masters: True
[root@master ~]# systemctl restart salt-master.service
# 配置syndic
[root@syndic ~]# vim /etc/salt/master
syndic_master: 192.168.111.141 # master的IP
......
file_roots:
base:
- /srv/salt/base
prod:
- /srv/salt/prod
......
pillar_roots:
base:
- /srv/pillar/base
prod:
- /srv/pillar/prod
[root@syndic ~]# systemctl enable --now salt-master.service
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/salt-master.service → /usr/lib/systemd/system/salt-master.service.
[root@syndic ~]# systemctl enable --now salt-syndic.service
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/salt-syndic.service → /usr/lib/systemd/system/salt-syndic.service.
# 配置minion
[root@node1 ~]# vim /etc/salt/minion
master: 192.168.111.142 # syndic的IP
[root@node1 ~]# systemctl enable --now salt-minion.service
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/salt-minion.service → /usr/lib/systemd/system/salt-minion.service.
# 同步master和syndic的/srv目录
[root@master ~]# scp -r /srv/* 192.168.111.142:/srv/.
root@192.168.111.142's password:
# 在syndic上接受minion的key
[root@syndic ~]# salt-key -L
Accepted Keys:
Denied Keys:
Unaccepted Keys:
node1
Rejected Keys:
[root@syndic ~]# salt-key -ya node1
The following keys are going to be accepted:
Unaccepted Keys:
node1
Key for minion node1 accepted.
[root@syndic ~]# salt-key -L
Accepted Keys:
node1
Denied Keys:
Unaccepted Keys:
Rejected Keys:
# 在master上接受syndic主机的key
[root@master ~]# salt-key -L
Accepted Keys:
Denied Keys:
Unaccepted Keys:
syndic
Rejected Keys:
[root@master ~]# salt-key -ya syndic
The following keys are going to be accepted:
Unaccepted Keys:
syndic
Key for minion syndic accepted.
[root@master ~]# salt-key -L
Accepted Keys:
syndic
Denied Keys:
Unaccepted Keys:
Rejected Keys:
# 在master上执行模块
[root@master ~]# salt '*' test.ping
node1:
True
[root@master init]# salt '*' state.sls init.history.main
node1:
----------
ID: /etc/profile
Function: file.line
Result: True
Comment: Changes were made
Started: 19:23:12.723117
Duration: 14.84 ms
Changes:
----------
diff:
---
+++
@@ -1,5 +1,6 @@
# /etc/profile
+export HISTTIMEFORMAT="%F %T `whoami` "
# System wide environment and startup programs, for login setup
# Functions and aliases go in /etc/bashrc
Summary for node1
------------
Succeeded: 1 (changed=1)
Failed: 0
------------
Total states run: 1
Total run time: 14.840 ms





















 93
93











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








