1 编程方式一
1.1 画状态图
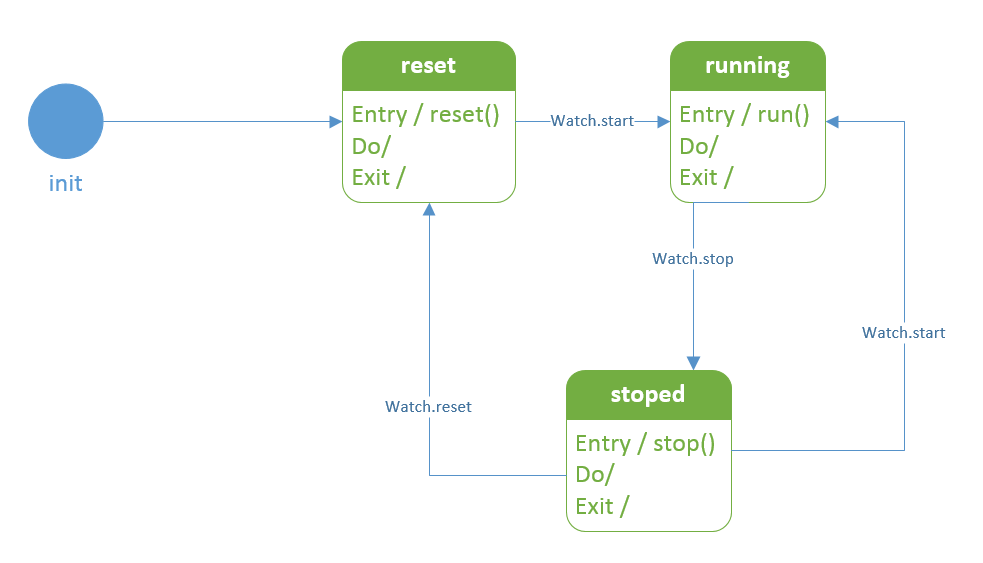
秒表的状态图,其中秒表有:重置,运行中,**已停止**3个状态
1.2 编写xml文件
秒表状态机定义文件:stopwatch1.xml,xml文件分析请看后面
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<scxml xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2005/07/scxml" version="1.0"
initial="reset">
<state id="reset">
<onentry>
<script>
stopWatchEntity.reset()
</script>
</onentry>
<transition event="watch.start" target="running" />
</state>
<state id="running">
<onentry>
<script>
stopWatchEntity.run()
</script>
</onentry>
<transition event="watch.stop" target="stopped" />
</state>
<state id="stopped">
<onentry>
<script>
stopWatchEntity.stop()
</script>
</onentry>
<transition event="watch.start" target="running" >
</transition>
<transition event="watch.reset" target="reset" />
</state>
</scxml>1.3 编写程序控制状态转移
需要操作的实体类,用来约束秒表的行为:StopWatchEntity.java
package stopwatch;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
public class StopWatchEntity implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
//时分秒
private int hr;
private int min;
private int sec;
//100毫秒
private int fract;
private transient Timer timer;
/**
* 重置当前状态机
*/
public synchronized void reset() {
hr = min = sec = fract = 0;
}
/**
* 运行秒表
*/
public synchronized void run() {
if (timer == null) {
timer = new Timer(true);
//使用timer来定时执行,秒表计数,每100毫秒,执行一次increment方法
timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
increment();
}
}, 100, 100);
}
}
/**
* 停止秒表
*/
public synchronized void stop() {
timer.cancel();
timer = null;
}
/**
* 得到当前秒表的时间
* @return
*/
public synchronized String getDisplay() {
return String.format("%d:%02d:%02d,%d", hr, min, sec, fract);
}
/**
* 自增方法
*/
private synchronized void increment() {
if (fract < 9) {
fract++;
} else {
fract = 0;
if (sec < 59) {
sec++;
} else {
sec = 0;
if (min < 59) {
min++;
} else {
min = 0;
hr++;
}
}
}
}
}界面类:StopWatchFrame.java
/**
* Created by zhengshouzi on 2015/11/20.
*/
package stopwatch;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
import javax.swing.*;
import org.apache.commons.scxml2.Context;
import org.apache.commons.scxml2.Evaluator;
import org.apache.commons.scxml2.SCXMLExecutor;
import org.apache.commons.scxml2.TriggerEvent;
import org.apache.commons.scxml2.env.SimpleErrorReporter;
import org.apache.commons.scxml2.env.jexl.JexlEvaluator;
import org.apache.commons.scxml2.io.SCXMLReader;
import org.apache.commons.scxml2.model.ModelException;
import org.apache.commons.scxml2.model.SCXML;
public class StopWatchFrame extends JFrame implements ActionListener {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private JLabel displayLabel;
private JButton startButton;
private JButton stopButton;
private JButton resetButton;
private SCXMLExecutor executor;
private StopWatchEntity stopWatchEntity;
public static void main(String[] args) {
new StopWatchFrame();
}
public StopWatchFrame() {
super("SCXML StopWatch");
//初始化状态机
initStopWatch();
//初始化界面
initUI();
}
/**
* 监听器需要执行的方法,自动调用
* @param event 事件源
*/
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) {
//得到绑定在每个按钮上的命令
String command = event.getActionCommand();
//对各个命令进行判断,在执行相应的内容
try {
if ("START".equals(command)) {
//生成watch.start事件,将转到running状态
executor.triggerEvent(new TriggerEvent("watch.start", TriggerEvent.SIGNAL_EVENT));
//设置一些列按钮的可见性
startButton.setEnabled(false);
stopButton.setEnabled(true);
resetButton.setEnabled(false);
} else if ("STOP".equals(command)) {
//生成watch.stop事件,将转到stoped状态
executor.triggerEvent(new TriggerEvent("watch.stop", TriggerEvent.SIGNAL_EVENT));
startButton.setEnabled(true);
stopButton.setEnabled(false);
resetButton.setEnabled(true);
} else if ("RESET".equals(command)) {
//生成watch.reset事件,将转到reset状态
executor.triggerEvent(new TriggerEvent("watch.reset", TriggerEvent.SIGNAL_EVENT));
startButton.setEnabled(true);
stopButton.setEnabled(false);
resetButton.setEnabled(false);
}
} catch (ModelException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 初始化秒表
*/
private void initStopWatch() {
//得到资源文件路径
final URL STOPWATCH = this.getClass().getResource("stopwatch1.xml");
//实例化数据模型解析器
Evaluator evaluator = new JexlEvaluator();
//实例化引擎
executor = new SCXMLExecutor(evaluator, null, new SimpleErrorReporter());
try {
//加载资源文件,实例化到一个SCXML对象,两者之间一一对应
SCXML scxml = SCXMLReader.read(STOPWATCH);
//将这样的一个SCXML实例,作为状态机对象,传入到引擎里面。
executor.setStateMachine(scxml);
//设置引擎执行的根上下文
Context rootContext = evaluator.newContext(null);
final StopWatchEntity stopWatchEntity = new StopWatchEntity();
rootContext.set("stopWatchEntity", stopWatchEntity);
executor.setRootContext(rootContext);
//设置当前对象
this.stopWatchEntity = stopWatchEntity;
//开始启动流程
executor.go();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 初始化界面
*/
private void initUI() {
JPanel mainPanel = new JPanel();
mainPanel.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
setContentPane(mainPanel);
JPanel contentPanel = new JPanel();
contentPanel.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
displayLabel = new JLabel("0:00:00,000");
displayLabel.setFont(new Font(Font.DIALOG,100,50));
contentPanel.add(displayLabel, BorderLayout.CENTER);
mainPanel.add(contentPanel, BorderLayout.CENTER);
JPanel buttonPanel = new JPanel();
buttonPanel.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
startButton = createButton("START", "Start");
buttonPanel.add(startButton);
stopButton = createButton("STOP", "Stop");
stopButton.setEnabled(false);
buttonPanel.add(stopButton);
resetButton = createButton("RESET", "Reset");
resetButton.setEnabled(false);
buttonPanel.add(resetButton);
mainPanel.add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
setLocation(250,300);
setSize(400,200);
setResizable(true);
setVisible(true);
Timer displayTimer = new Timer();
displayTimer.scheduleAtFixedRate(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
displayLabel.setText(stopWatchEntity.getDisplay());
}
}, 100, 100);
setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
/**
* 创建一个按钮
* @param command 按钮的命令
* @param text 按钮上的文本
* @return 返回一个新建的按钮
*/
private JButton createButton(final String command, final String text) {
JButton button = new JButton(text);
button.setActionCommand(command);
button.addActionListener(this);
return button;
}
}1.4 程序结果分析
程序界面类中的定时器一直在访问 StopWatchEntity的getDisplay属性,来得到秒表的值。我们通过Start,Stop,Reset来控制秒表的状态,在进入某一个状态机的时候,我们调用这个状态机根上下文设置的stopWatcheEntity对象相应的方法,来改变秒表的值。当秒表一直处于某一个状态的时候,我们又通过点击按钮来改变秒表的状态。
2 编程方式2
2.1 画状态图
图和方式一一样
2.2 编写状态图xml文件
stopwatch2.xml,这个类里面没有了srcipt等标签。
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<scxml xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2005/07/scxml"
version="1.0"
initial="reset">
<state id="reset">
<transition event="watch.start" target="running"/>
</state>
<state id="running">
<transition event="watch.stop" target="stopped"/>
</state>
<state id="stopped">
<transition event="watch.start" target="running"/>
<transition event="watch.reset" target="reset"/>
</state>
</scxml>
2.3编写程序控制状态转移
需要操作的实体类(同时也是状态机类),用来约束秒表的行为:StopWatchStateMachine.java。这个类中的方法名字和上面的StopWatchEntity.java名字稍有不同,这个类里面的名字必须要和所对应的xml文件里面的状态名字相同。这是因为当状态发生转移的时候,进入某一个状态的时候,由框架自身根据反射机制去调用对应的方法。
package stopwatch;
import org.apache.commons.scxml2.env.AbstractStateMachine;
import org.apache.commons.scxml2.model.ModelException;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
public class StopWatchStateMachine extends AbstractStateMachine {
public static final String EVENT_START = "watch.start";
public static final String EVENT_STOP = "watch.stop";
public static final String EVENT_RESET = "watch.reset";
private int hr, min, sec, fract;
private Timer timer;
public StopWatchStateMachine() throws ModelException {
super(StopWatchStateMachine.class.
getResource("stopwatch3.xml"));
}
/**
* 重置当前状态机,方法名和所在的状态名相同,又框架自己调用
*/
public void reset() {
hr = min = sec = fract=0;
timer=null;
}
/**
* 运行秒表,方法名和所在的状态名相同,又框架自己调用
*/
public void running() {
if (timer == null) {
timer = new Timer(true);
timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
increment();
}
}, 100, 100);
}
}
/**
* 停止秒表,方法名和所在的状态名相同,又框架自己调用
*/
public void stopped() {
timer.cancel();
timer = null;
}
/**
* 得到当前秒表的时间
* @return
*/
public synchronized String getDisplay() {
return String.format("%d:%02d:%02d,%d", hr, min, sec, fract);
}
//只是做一个演示,不使用这个方法
public String getCurrentState() {
return getEngine().getStatus().getStates().iterator().next().getId();
}
/**
* 自增方法
*/
private synchronized void increment() {
if (fract < 9) {
fract++;
} else {
fract = 0;
if (sec < 59) {
sec++;
} else {
sec = 0;
if (min < 59) {
min++;
} else {
min = 0;
hr++;
}
}
}
}
}StopWatchDisplay.java 界面展现类
package stopwatch;
import org.apache.commons.scxml2.model.ModelException;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
public class StopWatchDisplay extends JFrame
implements ActionListener {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private JLabel displayLabel;
private JButton startButton;
private JButton stopButton;
private JButton resetButton;
private StopWatchStateMachine stopWatchStateMachine;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new StopWatchDisplay();
}
public StopWatchDisplay() throws ModelException {
super("SCXML StopWatch StateMachine");
stopWatchStateMachine = new StopWatchStateMachine();
initUI();
}
/**
* 监听器需要执行的方法,自动调用
* @param event 事件源
*/
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) {
//得到绑定在每个按钮上的命令
String command = event.getActionCommand();
//对各个命令进行判断,在执行相应的内容
if ("START".equals(command)) {
//生成watch.start事件,将转到running状态
stopWatchStateMachine.fireEvent(StopWatchStateMachine.EVENT_START);
//设置一些列按钮的可见性
startButton.setEnabled(false);
stopButton.setEnabled(true);
resetButton.setEnabled(false);
} else if ("STOP".equals(command)) {
//生成watch.stop事件,将转到stoped状态
stopWatchStateMachine.fireEvent(StopWatchStateMachine.EVENT_STOP);
startButton.setEnabled(true);
stopButton.setEnabled(false);
resetButton.setEnabled(true);
} else if ("RESET".equals(command)) {
//生成watch.reset事件,将转到reset状态
stopWatchStateMachine.fireEvent(StopWatchStateMachine.EVENT_RESET);
startButton.setEnabled(true);
stopButton.setEnabled(false);
resetButton.setEnabled(false);
}
}
/**
* 初始化界面
*/
private void initUI() {
JPanel mainPanel = new JPanel();
mainPanel.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
setContentPane(mainPanel);
JPanel contentPanel = new JPanel();
contentPanel.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
displayLabel = new JLabel("0:00:00,000");
displayLabel.setFont(new Font(Font.DIALOG, 100, 50));
contentPanel.add(displayLabel, BorderLayout.CENTER);
mainPanel.add(contentPanel, BorderLayout.CENTER);
JPanel buttonPanel = new JPanel();
buttonPanel.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
startButton = createButton("START", "Start");
buttonPanel.add(startButton);
stopButton = createButton("STOP", "Stop");
stopButton.setEnabled(false);
buttonPanel.add(stopButton);
resetButton = createButton("RESET", "Reset");
resetButton.setEnabled(false);
buttonPanel.add(resetButton);
mainPanel.add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
setLocation(250, 300);
setSize(400,200);
setResizable(true);
setVisible(true);
Timer displayTimer = new Timer();
displayTimer.scheduleAtFixedRate(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
displayLabel.setText(stopWatchStateMachine.getDisplay());
}
}, 100, 100);
setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
/**
* 创建一个按钮
* @param command 按钮的命令
* @param text 按钮上的文本
* @return 返回一个新建的按钮
*/
private JButton createButton(final String command, final String text) {
JButton button = new JButton(text);
button.setActionCommand(command);
button.addActionListener(this);
return button;
}
}2.4 程序结果分析
程序界面类中的定时器一直在访问 StopWatctStateMachine的getDisplay方法,来得到秒表的值。我们通过Start,Stop,Reset来控制秒表的状态,在进入某一个状态机的时候,由框架自动调用对应状态名相同的的函数,来改变秒表的值。当秒表一直处于某一个状态的时候,我们又通过点击按钮来改变秒表的状态。
源代码AbstractStateMachine.java中对应的调用语句如下
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void onEntry(final EnterableState entered) {
invoke(entered.getId());
}
/**
* Invoke the no argument method with the following name.
*
* @param methodName The method to invoke.
* @return Whether the invoke was successful.
*/
public boolean invoke(final String methodName) {
Class<?> clas = this.getClass();
try {
Method method = clas.getDeclaredMethod(methodName, SIGNATURE);
method.invoke(this, PARAMETERS);
} catch (SecurityException se) {
logError(se);
return false;
} catch (NoSuchMethodException nsme) {
logError(nsme);
return false;
} catch (IllegalArgumentException iae) {
logError(iae);
return false;
} catch (IllegalAccessException iae) {
logError(iae);
return false;
} catch (InvocationTargetException ite) {
logError(ite);
return false;
}
return true;
}3 两种方式的总结
其实第二种方式是官网给出的例子里面的,同时也是更贴近状态机对象的思想。但是也有如下缺点(也许)
1、 stopWatchStateMachine.fireEvent(StopWatchStateMachine.EVENT_START);只有这一个触发事件的函数,不能传递数据。而第一种方式里面的executor.triggerEvent(new TriggerEvent("watch.start", TriggerEvent.SIGNAL_EVENT),数据);可以通过触发时间传递数据进入状态机里面。






















 1065
1065

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








