首先看北京天气网络数据,打开这个网页:
http://www.weather.com.cn/data/sk/101010100.html
{"weatherinfo":{"city":"北京","cityid":"101010100","temp":"22","WD":"东风","WS":"1级","SD":"33%","WSE":"1","time":"21:25","isRadar":"1","Radar":"JC_RADAR_AZ9010_JB"}}新建一个Android工程,添加一个class:JsonUtils.java
package cn.itcast.net.jsonparse;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.StringReader;
import java.net.HttpURLConnection;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.ProtocolException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.json.JSONException;
import org.json.JSONObject;
import com.google.gson.stream.JsonReader;
public class JsonUtils {
public static String getConnection(String path)
throws MalformedURLException, IOException, ProtocolException {
URL url = new URL(path);
try {
// 建立一个http连接
HttpURLConnection cn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
// 5秒超时
cn.setConnectTimeout(5 * 1000);
// 使用Get方法传递数据
cn.setRequestMethod("GET");
InputStreamReader in = new InputStreamReader(cn.getInputStream());
// 流数据读取
BufferedReader buff = new BufferedReader(in);
String data = buff.readLine().toString();
System.out.println("流数据data: " + data);
buff.close();
in.close();
// 返回数据流
return data;
}
catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("查询失败,请检查网络...");
return null;
}
}
public List<Map<String, String>> getWeather(String path) {
List<Map<String, String>> list = new ArrayList<Map<String, String>>();
String json = null;
Map<String, String> map;
try {
// 调用getConnection()获得数据流
String line = getConnection(path);
if (line != null) {
json = new String(line);
// 对象的形式
JSONObject Item = new JSONObject(json);
// 得到对象中的对象
JSONObject item = Item.getJSONObject("weatherinfo");
String city = item.getString("city");
String temp = item.getString("temp");
String time = item.getString("time");
// 添加到map中
map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put("city", city);
map.put("temp", temp);
map.put("time", time);
list.add(map);
}
else {
System.out.println("获取流数据失败!");
}
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ProtocolException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (JSONException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return list;
} 在需要使用的activity调用:
package com.example.weather;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import cn.itcast.net.jsonparse.*;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.AlertDialog;
import android.content.DialogInterface;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class weatherActivity extends Activity {
private TextView textView;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.weather);
// 找到控件
findViews();
}
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
private void findViews() {
textView = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.WeathertextView1);
// json数据解析
JsonUtils jsonUtils = new JsonUtils();
// 北京天气网络数据
String path ="http://www.weather.com.cn/data/sk/101010100.html";
List list= jsonUtils.getWeather(path);
if(!list.isEmpty())
{
Map map =(Map) list.get(0);
if(!map.isEmpty())
{
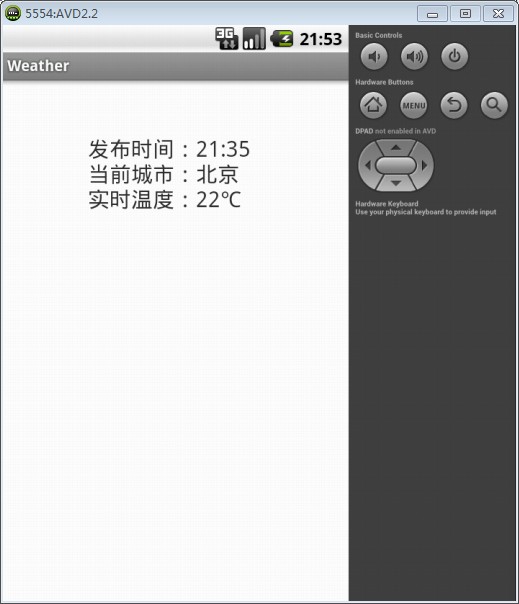
String time="发布时间:" +(String) map.get("time")+"\n";
String city="当前城市:"+(String) map.get("city")+"\n";
String temp="实时温度:"+(String) map.get("temp")+"℃";
String message =time+city+temp;
// 将解析数据放置到textView里显示
textView.setText((CharSequence) message);
}
}
else
{
AlertDialog.Builder build=new AlertDialog.Builder(this);
build.setTitle("提示")
.setMessage("网络出现故障,请稍后重试!")
.setPositiveButton("确定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
}).show();
}
}
}
注意:这里涉及访问网络,那么要在AndroidManifest.xml开启权限,否则会报相关错误!
<!-- 访问internet权限 -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>
顺便指出:我们在向SD卡里写入或读取数据时也要在AndroidManifest.xml开启相应权限:
<!-- 在SDCard中创建与删除文件权限 -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.MOUNT_UNMOUNT_FILESYSTEMS"/>
<!-- 往SDCard写入数据权限 -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE"/>






















 1653
1653











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








