异常
概念:程序在执行过程中出现意外,叫做异常。
1.异常处理方式
(1).捕获异常
我们用try…cacth…(finally)来捕获异常
public class test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str="123a";
try {
int a=Integer.parseInt(str);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("继续执行");
}
}
运行结果
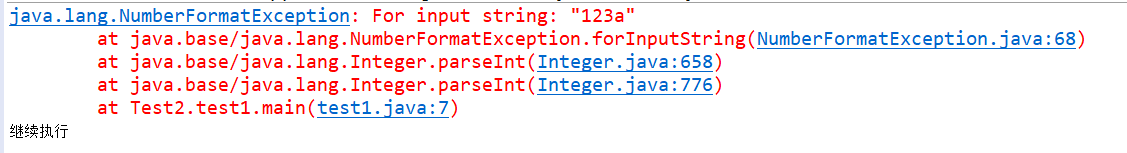
我们发现 虽然报错了 但是程序依然继续执行了
Exception是异常类的老祖宗,在捕获异常的时候,假如我们不确定会抛出什么异常,可以写多个异常捕获
public class test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str="123a";
try{
int a=Integer.parseInt(str);
}catch(NullPointerException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(NumberFormatException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("继续执行");
}
}
注:由上往下的异常 必须范围同级别或者更高;否则编译报错
假如我们有种需求,不管有没有发生异常,都要执行某些代码,这时候用try…cacth…finally
public class test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str="123a";
try {
int a=Integer.parseInt(str);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("exception");
return;
}finally {
System.out.println("finally end");
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
运行结果
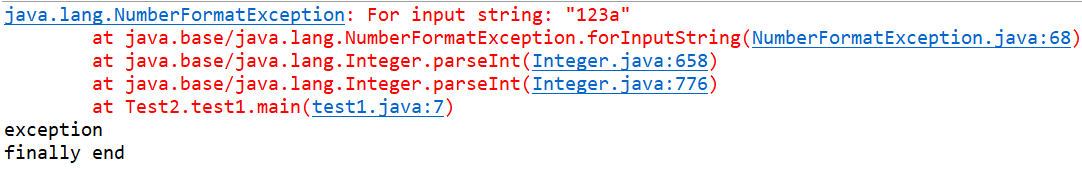
我们发现 finally里面的都会执行 但是try catch后面的代码未必会执行。
(2).抛出异常
throws:表示当前方法不处理异常,而是交给方法的调用出去处理
throw:表示直接抛出一个异常
public class test2 {
//把异常向外面抛
public static void testThrows()throws NumberFormatException{
String str="123a";
int a=Integer.parseInt(str);
System.out.println(a);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
testThrows();
System.out.println("here");
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("我们在这里处理异常");
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("I'm here");
}
}
运行结果

throw表示直接抛出一个异常,我们可以根据业务在代码任何地方抛出异常
public class test3 {
public static void testThrow(int a) throws Exception{
if(a==1){
// 直接抛出一个异常类
throw new Exception("有异常");
}
System.out.println(a);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
testThrow(1);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行结果

2.Exception 和 RuntimeException 的区别
Exception是检查型异常,在程序中必须使用try…catch进行处理(编译时就要处理)
RuntimeException 是运行时异常,如NumberFormatException,可以不使用try…catch进行处理(编译时不要处理),但是如果产生异常,则异常将由JVM进行处理,RuntimeException最好也用try…catch捕获。
3.自定义异常
在业务开发过程中,我们可以自定义一套关于业务性的异常体系,来满足程序的开发需求;自定义异常要继承自Exception
public class MyException extends Exception{
//自定义异常,继承自Exception
public MyException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
写个测试类
public class testMyException {
public static void test()throws MyException{
throw new MyException("自定义异常");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
test();
} catch (MyException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行结果
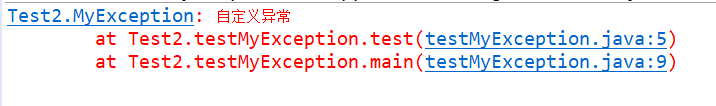





















 2257
2257











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








