service的原理在这里就不在复述了,下面直接介绍service的两种启动方式及生命周期。
首先建立一个serviceDemo,如图所示。

然后修改main.xml布局文件:
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
- <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent"
- android:orientation="vertical" >
- <TextView
- android:id="@+id/text"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="@string/hello" />
- <Button
- android:id="@+id/startservice"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="startService" />
- <Button
- android:id="@+id/stopservice"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="stopService" />
- <Button
- android:id="@+id/bindservice"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="bindService" />
- <Button
- android:id="@+id/unbindservice"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="unbindService" />
- </LinearLayout>
- public class MyService extends Service {
- private static final String TAG = "MyService";
- private MyBinder mBinder=new MyBinder();
- @Override
- public IBinder onBind(Intent arg0) {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- Log.e(TAG, "start IBinder~~~");
- return mBinder;
- }
- @Override
- public void onCreate() {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- Log.e(TAG, "start onCreate~~~");
- super.onCreate();
- }
- @Override
- public void onDestroy() {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- Log.e(TAG, "start onDestroy~~~");
- super.onDestroy();
- }
- @Override
- public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- Log.e(TAG, "start onStartCommand~~~");
- return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
- }
- @Override
- public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- Log.e(TAG, "start onUnbind~~~");
- return super.onUnbind(intent);
- }
- public String getSystemTime(){
- /*Time t=new Time();
- t.setToNow();*/
- SimpleDateFormat format=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
- return format.format(new Date());
- }
- public class MyBinder extends Binder{
- public MyService getService(){
- return MyService.this;
- }
- }
- }
- public class ServiceDemoActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener{
- /** Called when the activity is first created. */
- private MyService mMyService;
- private TextView mTextView;
- private Context mContext;
- private Button startServiceButton;
- private Button stopServiceButton;
- private Button bindServiceButton;
- private Button unbindServiceButton;
- //这里需要用到ServiceConnection在Context.bindService和context.unBindService()里用到
- private ServiceConnection mServiceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
- //当我bindService时,让TextView显示MyService里getSystemTime()方法的返回值
- @Override
- public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- mMyService = ((MyService.MyBinder)service).getService();
- mTextView.setText("I am frome Service :" + mMyService.getSystemTime());
- }
- @Override
- public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- }
- };
- @Override
- public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.main);
- setupViews();
- }
- private void setupViews(){
- mContext=this;
- mTextView=(TextView) this.findViewById(R.id.text);
- startServiceButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.startservice);
- stopServiceButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.stopservice);
- bindServiceButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.bindservice);
- unbindServiceButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.unbindservice);
- startServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
- stopServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
- bindServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
- unbindServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
- }
- @Override
- public void onClick(View v) {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- if(v == startServiceButton){
- Intent i = new Intent();
- i.setClass(ServiceDemoActivity.this, MyService.class);
- mContext.startService(i);
- }else if(v == stopServiceButton){
- Intent i = new Intent();
- i.setClass(ServiceDemoActivity.this, MyService.class);
- mContext.stopService(i);
- }else if(v == bindServiceButton){
- Intent i = new Intent();
- i.setClass(ServiceDemoActivity.this, MyService.class);
- mContext.bindService(i, mServiceConnection, BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
- }else{
- mContext.unbindService(mServiceConnection);
- }
- }
- }
下面看一下运行效果:
点击startService按钮看一下打印的log日志:
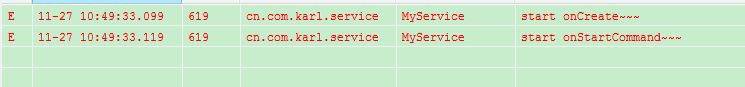
首先开启一个start服务先是执行了onCreate方法和onStartCommand方法,然后点击stopService按钮:

执行了onDestroy方法,知道了这些生命周期方法后我们就可以在这些生命周期方法里做一些相应的事件了。
下面点击一下bindService按钮看会出现什么效果吧:
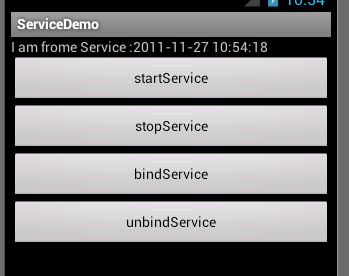
在最上方打印出了系统时间,绑定服务其实就是让服务执行完后,返回一些数据给启动它的组件比如activity。
这是后台打印的log:

最后点击unbindService取消绑定:

绑定服务 生命周期结束 。
下面让我们再看一下官方给出的两种服务的生命周期图:
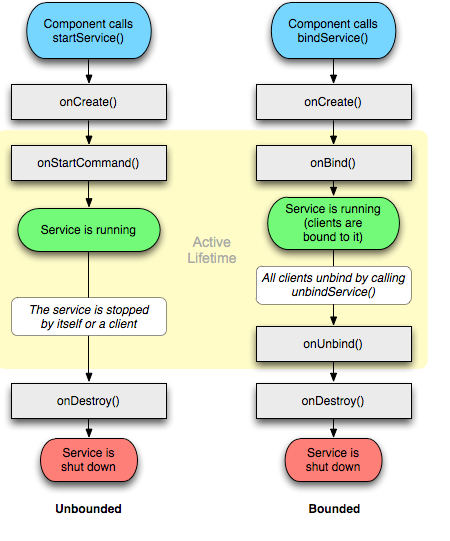
这样是不是一眼就看明白了。






















 269
269

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








