在计算机科学中,AVL树是最先发明的自平衡二叉查找树。AVL树得名于它的发明者 G.M. Adelson-Velsky 和 E.M. Landis,他们在 1962 年的论文《An algorithm for the organization of information》中发表了它。
平衡因子:节点x的平衡因子是x的左子树的高度减去x的右子树的高度。一颗AVL树的所有节点的平衡因子都是 0 或者 +1/-1 。
1 插入的旋转操作
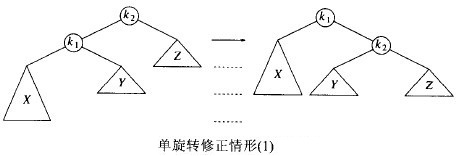
1.1 简单右旋
当插入项位于最近的平衡因子为+2 的祖先节点的左孩子的左子树中时使用。(左-左)
首先,我来解释一下上图的含义。x子树的height比y子树的高1,y和z的height一样,这样就看懂了吧:k1的balanceFactor是+1,k2的balanceFactor是+2。原本平衡树的结构应该是x子树的高度也和z一样的,但是我们往x子树插入了一个值,使x子树的height加一了。【我强调一点是,y的高度其实不那么重要,有两种情况:y的高度与 x 和 z 的高度相等,或是小1】认识到到这一点才能在后面编程的时候考虑周全。
最简单的例子是:
k2
/
k1这个时候,往k1的左侧插入一个值,使得k2的balanceFactor变为+2,从而不平衡。但是这个例子并不典型,如果依照这个例子去写代码,往往会因为考虑不周而出错。下面给一个更典型的例子:
8
/ \
4 13
/ \
1 5这个时候然后要插入0的话,就是插入到1的左侧,从而使8这里变得不平衡。
8 <-------k2
/ \
k1-----> 4 13
/ \
1 5
/
0先不考虑编程,大家可以思考一下怎么样旋转可以让这颗树变得平衡?
4
/ \
1 8
/ / \
0 5 13之所以这样旋转是因为既要让树平衡,也要保持BST的性质。所以,代码为:
private AVLNode rotateRight(AVLNode theRoot) {
AVLNode theLeft = theRoot.left;
theRoot.left = theLeft.right;
theLeft.right = theRoot;
theRoot.height = Math.max(height(theRoot.left), height(theRoot.right)) + 1;
theLeft.height = Math.max(height(theLeft.left), theRoot.height) + 1;
return theLeft;
}上述代码并没有完全使用前面分析的结论,而是用更简单的逻辑在处理。
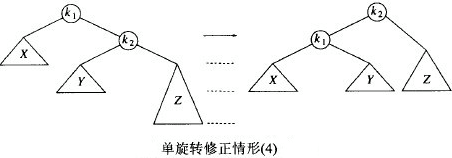
1.2 简单左旋
当插入项位于最近的平衡因子为-2的祖先节点的右孩子的右子树中时使用(右-右)。
由于简单左旋与简单右旋是类似和对称的,所以这里直接给出代码:
private AVLNode rotateLeft(AVLNode theRoot) {
AVLNode theRight = theRoot.right;
theRoot.right = theRight.left;
theRight.left = theRoot;
theRoot.height = Math.max(height(theRoot.left), height(theRoot.right)) + 1;
theRight.height = Math.max(height(theRight.right), theRoot.height) + 1;
return theRight;
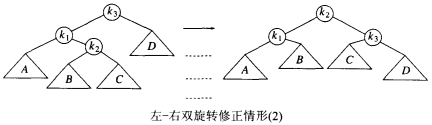
}1.3 左-右旋
当插入项位于最近的平衡因子为 +2 的祖先节点的左孩子的右子树中时使用(左-右)。
最简单的例子是:
12
/
6
\
81旋为:
12
/
8
/
62旋为:
8
/ \
6 12典型的例子是:
20
/ \
15 23
/ \
6 18
/
171旋(对15子树进行一次简单左旋):
20
/ \
18 23
/
15
/ \
6 172旋(对20子树进行一次简单右旋):
18
/ \
15 20
/ \ \
6 17 23所以在理解了单旋操作之后,双旋也就不难了,无非就是两次单旋的组合:
private AVLNode rotateLeftRight(AVLNode theRoot) {
theRoot.left = rotateLeft(theRoot.left);
return rotateRight(theRoot);
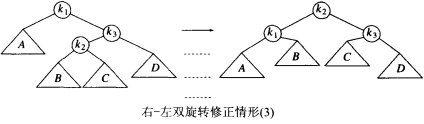
}1.4 右-左旋
当插入项位于最近的平衡因子为-2 的祖先节点的右孩子的左子树中时使用。
private AVLNode rotateRightLeft(AVLNode theRoot) {
theRoot.right = rotateRight(theRoot.right);
return rotateLeft(theRoot);
}2 插入操作的实现
public boolean insert(int data) {
return insert(root, data) != null;
}
private AVLNode insert(AVLNode root, int data) {
if (root == null) {
root = new AVLNode(data);
return root;
}
// 要插入的值比root的值小,所以插入位置在其左子树中
// 每次插入完,就要判断一下,树是否还平衡,如果不平衡,则调整
if (data - root.data < 0) {
root.left = insert(root.left, data);
// 由于是插入在左子树,所以造成的破坏只可能是 +2
if (height(root.left) - height(root.right) == 2) {
// 第一种情况,左-左,需要rotateRight
// 插入到+2祖先节点的左孩子的左子树中
if (data - root.left.data < 0) {
root = rotateRight(root);
}
// 第二种情况,左-右,需要rotateLeftRight
// 插入到+2 祖先节点的左孩子的右子树中
else {
root = rotateLeftRight(root);
}
// 因为已经造成了不平衡,所以肯定不是‘待插值已存在’的情况,所以不用考虑相等
}
}
else if (data - root.data > 0) {
root.right = insert(root.right, data);
if (height(root.left) - height(root.right) == -2) {
// 第三种情况, 右-右,需要rotateLeft
// 插入到 -2 祖先节点的右孩子的右子树中
if (data - root.right.data > 0) {
root = rotateLeft(root);
}
// 第四种情况,右-左,需要rotateRightLeft
// 插入到 -2 祖先节点的右孩子的左子树中
else {
root = rotateRightLeft(root);
}
}
} else {
return null;
}
root.height = Math.max(height(root.left), height(root.right)) + 1;
return root;
}AVL的remove操作很复杂,所以在这里就不分析。
3 完整代码及测试结果
(1) AVLNode.java
package AVL;
public class AVLNode {
public int data;
public int height;
public AVLNode left;
public AVLNode right;
public AVLNode() {
this.data = 0;
this.height = 0;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
public AVLNode(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.height = 0;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
public AVLNode(int data, AVLNode left, AVLNode right) {
super();
this.data = data;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}(2) AVLTree.java
package AVL;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class AVLTree {
private AVLNode root;
// 之所以要写这个函数,是为了处理节点为空的情况
private int height(AVLNode n) {
return n == null ? -1 : n.height;
}
private AVLNode rotateRight(AVLNode theRoot) {
AVLNode theLeft = theRoot.left;
theRoot.left = theLeft.right;
theLeft.right = theRoot;
theRoot.height = Math.max(height(theRoot.left), height(theRoot.right)) + 1;
theLeft.height = Math.max(height(theLeft.left), theRoot.height) + 1;
return theLeft;
}
private AVLNode rotateLeft(AVLNode theRoot) {
AVLNode theRight = theRoot.right;
theRoot.right = theRight.left;
theRight.left = theRoot;
theRoot.height = Math.max(height(theRoot.left), height(theRoot.right)) + 1;
theRight.height = Math.max(height(theRight.right), theRoot.height) + 1;
return theRight;
}
private AVLNode rotateLeftRight(AVLNode theRoot) {
theRoot.left = rotateLeft(theRoot.left);
return rotateRight(theRoot);
}
private AVLNode rotateRightLeft(AVLNode theRoot) {
theRoot.right = rotateRight(theRoot.right);
return rotateLeft(theRoot);
}
public boolean insert(int data) {
return insert(getRoot(), data) != null;
}
private AVLNode insert(AVLNode root, int data) {
if (root == null) {
root = new AVLNode(data);
return root;
}
// 要插入的值比root的值小,所以插入位置在其左子树中
// 每次插入完,就要判断一下,树是否还平衡,如果不平衡,则调整
if (data - root.data < 0) {
root.left = insert(root.left, data);
// 由于是插入在左子树,所以造成的破坏只可能是 +2
if (height(root.left) - height(root.right) == 2) {
// 第一种情况,左-左,需要rotateRight
// 插入到+2祖先节点的左孩子的左子树中
if (data - root.left.data < 0) {
root = rotateRight(root);
}
// 第二种情况,左-右,需要rotateLeftRight
// 插入到+2 祖先节点的左孩子的右子树中
else {
root = rotateLeftRight(root);
}
// 因为已经造成了不平衡,所以肯定不是‘待插值已存在’的情况,所以不用考虑相等
}
}
else if (data - root.data > 0) {
root.right = insert(root.right, data);
if (height(root.left) - height(root.right) == -2) {
// 第三种情况, 右-右,需要rotateLeft
// 插入到 -2 祖先节点的右孩子的右子树中
if (data - root.right.data > 0) {
root = rotateLeft(root);
}
// 第四种情况,右-左,需要rotateRightLeft
// 插入到 -2 祖先节点的右孩子的左子树中
else {
root = rotateRightLeft(root);
}
}
} else {
return null;
}
root.height = Math.max(height(root.left), height(root.right)) + 1;
return root;
}
/**
* 新建一颗树,用于测试
* 5
* / \
* 4 8
* / / \
* 2 6 13
* **/
public void buildAVLTree() {
AVLNode rl = new AVLNode(6);
AVLNode rr = new AVLNode(13);
AVLNode ll = new AVLNode(2);
AVLNode l = new AVLNode(4, ll, null);
l.height = 1;
AVLNode r = new AVLNode(8, rl, rr);
r.height = 1;
setRoot(new AVLNode(5, l, r));
getRoot().height = 3;
this.setRoot(root);
}
// 按层次打印
public void display() {
if (getRoot() == null) {
return;
}
System.out.println("****** The AVLTree ******");
LinkedList<AVLNode> queue = new LinkedList<AVLNode>();
queue.addLast(getRoot());
int parentCount = 1;
int childrenCount = 0;
AVLNode node;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
node = queue.removeFirst();
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
parentCount--;
if (node.left != null) {
queue.addLast(node.left);
childrenCount++;
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.addLast(node.right);
childrenCount++;
}
if (parentCount == 0) {
System.out.println();
parentCount = childrenCount;
childrenCount = 0;
}
}
System.out.println("****** ----------- ******");
}
public AVLNode getRoot() {
return root;
}
public void setRoot(AVLNode root) {
this.root = root;
}
}(3) Main.java
package AVL;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AVLTree avlTree = new AVLTree();
/**
* 新建一颗树,用于测试
* 5
* / \
* 4 8
* / / \
* 2 6 13
* **/
avlTree.buildAVLTree();
avlTree.display();
//应当触发【简单右旋】:
/***
* 5
* / \
* 2 8
* / \ / \
* 1 4 6 13
* */
System.out.println("\n插入1:");
avlTree.insert(1);
avlTree.display();
//在原BST上插入3,应当触发【左-右旋】:
/***
* 5
* / \
* 3 8
* / \ / \
* 2 4 6 13
* */
avlTree.buildAVLTree();
System.out.println("\n插入3:");
avlTree.insert(3);
avlTree.display();
}
}output:
****** The AVLTree ******
5
4 8
2 6 13
****** ----------- ******
插入1:
****** The AVLTree ******
5
2 8
1 4 6 13
****** ----------- ******
插入3:
****** The AVLTree ******
5
3 8
2 4 6 13
****** ----------- ******






















 844
844

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








