
来源:信息与反思
作者:伊丽莎白·吉布尼
中国廉价、开放的人工智能模型DeepSeek让科学家们兴奋不已
![]() ,NEWS 23 January 2025
,NEWS 23 January 2025
(中文由原文机器翻译)
DeepSeek-R1执行的推理任务与OpenAI的o1级别相同,并且对研究人员开放。
一个名为DeepSeek-R1的中国制造的大型语言模型让科学家们感到兴奋,它是OpenAI o1等“推理”模型的一个负担得起且开放的竞争对手。
这些模型在类似于人类推理的过程中逐步生成响应。这使得它们比早期的语言模型更擅长解决科学问题,并可能使它们在研究中有用。1月20日发布的R1的初步测试表明,它在化学、数学和编码方面的某些任务上的性能与o1相当,这在OpenAI于9月发布时让研究人员惊叹不已。
“这太疯狂了,完全出乎意料,”人工智能研究员、英国人工智能咨询公司DAIR的联合创始人Elvis Saravia说。AI在X上写道。
R1脱颖而出还有另一个原因。构建该模型的杭州初创公司DeepSeek将其发布为“开放权重”,这意味着研究人员可以研究和构建该算法。根据麻省理工学院的许可证发布,该模型可以自由重用,但由于其训练数据尚未提供,因此不被认为是完全开源的。
德国埃尔兰根马克斯·普朗克光科学研究所人工科学家实验室负责人Mario Krenn说:“DeepSeek的开放性非常显著。”。相比之下,OpenAI在加利福尼亚州旧金山建立的o1和其他模型,包括其最新的o3,“基本上是黑匣子”,他说。
人工智能幻觉无法阻止,但这些技术可以限制它们的伤害。
DeepSeek尚未公布培训R1的全部费用,但它向使用其界面的人收取的费用约为o1运行费用的三十分之一。该公司还创建了R1的迷你“蒸馏”版本,使计算能力有限的研究人员能够使用该模型。Krenn说,“使用o1的实验成本超过300英镑,而使用R1的实验成本不到10美元。”。“这是一个巨大的差异,肯定会在未来的采用中发挥作用。”
R1是中国大型语言模型(LLMs)繁荣的一部分。DeepSeek从一家对冲基金分拆出来,上个月发布了一款名为V3的聊天机器人,该机器人的表现优于主要竞争对手,尽管其预算很小。专家估计,租用训练模型所需的硬件大约需要600万美元,而Meta的Llama 3.1 405B则需要6000万美元,使用了11倍的计算资源。
围绕DeepSeek的部分传言是,尽管美国的出口管制限制了中国公司获得为人工智能处理设计的最佳计算机芯片,但DeepSeek还是成功地制造了R1。华盛顿州西雅图的人工智能研究员François Chollet表示:“它来自中国的事实表明,高效利用资源比单纯的计算规模更重要。”。
华盛顿贝尔维尤的技术专家阿尔文·王·格雷林(Alvin Wang Graylin)在总部位于台湾的沉浸式技术公司HTC工作,他在X上写道,DeepSeek的进展表明,“美国曾经的领先优势已经显著缩小。”
LLMs在数十亿个文本样本上进行训练,将它们剪切成称为“标记”的单词部分,并在数据中学习模式。这些关联使模型能够预测句子中的后续标记。但LLMs倾向于编造事实,这是一种被称为“幻觉”的现象,并且经常难以通过推理解决问题。
与o1一样,R1使用“思维链”方法来提高LLM解决更复杂任务的能力,包括有时回溯和评估其方法。DeepSeek通过使用强化学习“微调”V3来制作R1,强化学习奖励模型达到正确答案并以概述其“思维”的方式解决问题。
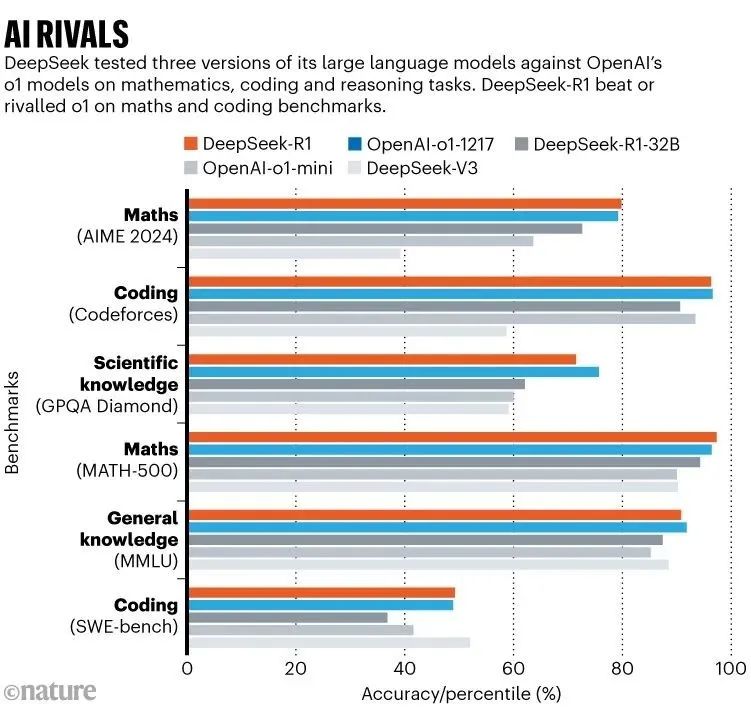
人工智能竞争对手:柱状图显示了DeepSeek进行的测试结果,该测试针对OpenAI的o1模型在数学、编码和推理任务上测试了其大型语言模型的三个版本。DeepSeek-R1在数学和编码基准测试中击败或与o1相媲美。
很难说基准测试是否捕捉到了模型推理或概括的真正能力,或者仅仅是通过这些测试。但剑桥大学计算机科学家Marco Dos Santos表示,由于R1是开放的,研究人员可以访问它的思想链。他说:“这使得模型的推理过程具有更好的可解释性。”。
科学家们已经在测试R1的能力。Krenn挑战了这两个竞争对手的模型,根据它们的有趣程度对3000个研究想法进行排序,并将结果与人工排名进行比较。在这一指标上,R1的表现略低于o1。但Krenn说,在量子光学的某些计算中,R1击败了o1。“这相当令人印象深刻。”
China’s cheap, open AI model DeepSeek thrills scientists
DeepSeek-R1 performs reasoning tasks at the same level as OpenAI’s o1 — and is open for researchers to examine.
By
Elizabeth Gibney

Chinese firm DeepSeek debuted a version of its large language model last year.Credit: Koshiro K/Alamy
A Chinese-built large language model called DeepSeek-R1 is thrilling scientists as an affordable and open rival to ‘reasoning’ models such as OpenAI’s o1.
These models generate responses step-by-step, in a process analogous to human reasoning. This makes them more adept than earlier language models at solving scientific problems and could make them useful in research. Initial tests of R1, released on 20 January, show that its performance on certain tasks in chemistry, mathematics and coding is on par with that of o1 — which wowed researchers when it was released by OpenAI in September.
“This is wild and totally unexpected,” Elvis Saravia, an AI researcher and co-founder of the UK-based AI consulting firm DAIR.AI, wrote on X.
R1 stands out for another reason. DeepSeek, the start-up in Hangzhou that built the model, has released it as ‘open-weight’, meaning that researchers can study and build on the algorithm. Published under an MIT licence, the model can be freely reused but is not considered fully open source, because its training data has not been made available.
“The openness of DeepSeek is quite remarkable,” says Mario Krenn, leader of the Artificial Scientist Lab at the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Light in Erlangen, Germany. By comparison, o1 and other models built by OpenAI in San Francisco, California, including its latest effort o3 are “essentially black boxes”, he says.

AI hallucinations can’t be stopped — but these techniques can limit their damage
DeepSeek hasn’t released the full cost of training R1, but it is charging people using its interface around one-thirtieth of what o1 costs to run. The firm has also created mini ‘distilled’ versions of R1 to allow researchers with limited computing power to play with the model. An “experiment that cost more than £300 with o1, cost less than $10 with R1,” says Krenn. “This is a dramatic difference which will certainly play a role its future adoption.”
Challenge models
R1 is the part of a boom in Chinese large language models (LLMs). Spun out of a hedge fund, DeepSeek emerged from relative obscurity last month when it released a chatbot called V3, which outperformed major rivals, despite being built on a shoestring budget. Experts estimate that it cost around $6 million to rent the hardware needed to train the model, compared with upwards of $60 million for Meta’s Llama 3.1 405B, which used 11 times the computing resources.
Part of the buzz around DeepSeek is that it has succeeded in making R1 despite US export controls that limit Chinese firms’ access to the best computer chips designed for AI processing. “The fact that it comes out of China shows that being efficient with your resources matters more than compute scale alone,” says François Chollet, an AI researcher in Seattle, Washington.
DeepSeek’s progress suggests that “the perceived lead [the] US once had has narrowed significantly,” wrote Alvin Wang Graylin, a technology expert in Bellevue, Washington, who works at the Taiwan-based immersive technology firm HTC, on X. “The two countries need to pursue a collaborative approach to building advanced AI vs continuing on the current no-win arms race approach.”
Chain of thought
LLMs train on billions of samples of text, snipping them into word-parts called ‘tokens’ and learning patterns in the data. These associations allow the model to predict subsequent tokens in a sentence. But LLMs are prone to inventing facts, a phenomenon called ‘hallucination’, and often struggle to reason through problems.
Like o1, R1 uses a ‘chain of thought’ method to improve an LLM’s ability to solve more complex tasks, including sometimes backtracking and evaluating its approach. DeepSeek made R1 by ‘fine-tuning’ V3 using reinforcement learning, which rewarded the model for reaching a correct answer and for working through problems in a way that outlined its ‘thinking’.
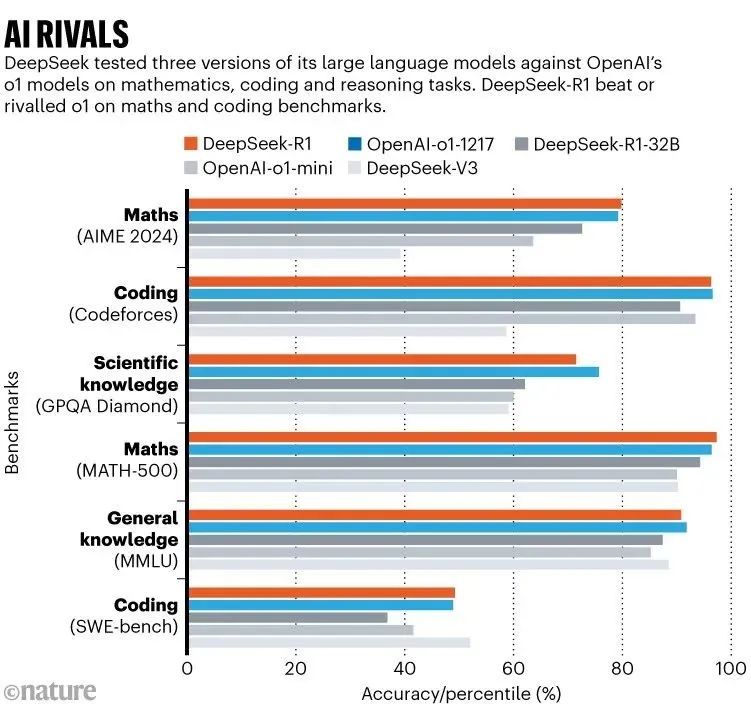
Source: DeepSeek
Having limited computing power drove the firm to “innovate algorithmically”, says Wenda Li, an AI researcher at the University of Edinburgh, UK. During reinforcement learning the team estimated the model’s progress at each stage, rather evaluating it using a separate network. This helped to reduce training and running costs, says Mateja Jamnik, a computer scientist at the University of Cambridge, UK. The researchers also used a ‘mixture-of-experts’ architecture, which allows the model to activate only the parts of itself that are relevant for each task.
In benchmark tests, reported in a technical paper accompanying the model, DeepSeek-R1 scored 97.3% on the MATH-500 set of mathematics problems created by researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, and outperformed 96.3% of human participants in the Codeforces competition. These are on on par with o1’s abilities; o3 was not included in the comparisons (see ‘AI rivals’).
It is hard to tell whether benchmarks capture a model’s true ability to reason or generalize, or merely to pass such tests. But because R1 is open, its chain-of-thought is accessible to researchers, says Marco Dos Santos, a computer scientist at the University of Cambridge. “This allows better interpretability of the model’s reasoning processes,” he says.
Already, scientists are testing R1’s abilities. Krenn challenged both rival models to sort 3,000 research ideas by how interesting they are and compared the results with human-made rankings. On this measure, R1 slightly underperformed compared with o1. But R1 beat o1 on certain computations in quantum optics, says Krenn. “This is quite impressive.”
https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-025-00229-6
阅读最新前沿科技趋势报告,请访问欧米伽研究所的“未来知识库”
https://wx.zsxq.com/group/454854145828

未来知识库是“欧米伽未来研究所”建立的在线知识库平台,收藏的资料范围包括人工智能、脑科学、互联网、超级智能,数智大脑、能源、军事、经济、人类风险等等领域的前沿进展与未来趋势。目前拥有超过8000篇重要资料。每周更新不少于100篇世界范围最新研究资料。欢迎扫描二维码或访问https://wx.zsxq.com/group/454854145828 进入。

截止到12月25日 ”未来知识库”精选的100部前沿科技趋势报告
2024 美国众议院人工智能报告:指导原则、前瞻性建议和政策提案
未来今日研究所:2024 技术趋势报告 - 移动性,机器人与无人机篇
Deepmind:AI 加速科学创新发现的黄金时代报告
Continental 大陆集团:2024 未来出行趋势调研报告
埃森哲:未来生活趋势 2025
国际原子能机构 2024 聚变关键要素报告 - 聚变能发展的共同愿景
哈尔滨工业大学:2024 具身大模型关键技术与应用报告
爱思唯尔(Elsevier):洞察 2024:科研人员对人工智能的态度报告
李飞飞、谢赛宁新作「空间智能」 等探索多模态大模型性能
欧洲议会:2024 欧盟人工智能伦理指南:背景和实施
通往人工超智能的道路:超级对齐的全面综述
清华大学:理解世界还是预测未来?世界模型综合综述
Transformer 发明人最新论文:利用基础模型自动搜索人工生命
兰德公司:新兴技术监督框架发展的现状和未来趋势的技术监督报告
麦肯锡全球研究院:2024 年全球前沿动态(数据)图表呈现
兰德公司:新兴技术领域的全球态势综述
前瞻:2025 年人形机器人产业发展蓝皮书 - 人形机器人量产及商业化关键挑战
美国国家标准技术研究院(NIST):2024 年度美国制造业统计数据报告(英文版)
罗戈研究:2024 决策智能:值得关注的决策革命研究报告
美国航空航天专家委员会:2024 十字路口的 NASA 研究报告
中国电子技术标准化研究院 2024 扩展现实 XR 产业和标准化研究报告
GenAI 引领全球科技变革关注 AI 应用的持续探索
国家低空经济融创中心中国上市及新三板挂牌公司低空经济发展报告
2025 年计算机行业年度策略从 Infra 到 AgentAI 创新的无尽前沿
多模态可解释人工智能综述:过去、现在与未来
【斯坦福博士论文】探索自监督学习中对比学习的理论基础
《机器智能体的混合认知模型》最新 128 页
Open AI 管理 AI 智能体的实践
未来生命研究院 FLI2024 年 AI 安全指数报告 英文版
兰德公司 2024 人工智能项目失败的五大根本原因及其成功之道 - 避免 AI 的反模式 英文版
Linux 基金会 2024 去中心化与人工智能报告 英文版
脑机接口报告脑机接口机器人中的人机交换
联合国贸发会议 2024 年全球科技创新合作促发展研究报告 英文版
Linux 基金会 2024 年世界开源大会报告塑造人工智能安全和数字公共产品合作的未来 英文版
Gartner2025 年重要战略技术趋势报告 英文版
Fastdata 极数 2024 全球人工智能简史
中电科:低空航行系统白皮书,拥抱低空经济
迈向科学发现的生成式人工智能研究报告:进展、机遇与挑战
哈佛博士论文:构建深度学习的理论基础:实证研究方法
Science 论文:面对 “镜像生物” 的风险
镜面细菌技术报告:可行性和风险
Neurocomputing 不受限制地超越人类智能的人工智能可能性
166 页 - 麦肯锡:中国与世界 - 理解变化中的经济联系(完整版)
未来生命研究所:《2024 人工智能安全指数报告》
德勤:2025 技术趋势报告 空间计算、人工智能、IT 升级。
2024 世界智能产业大脑演化趋势报告(12 月上)公开版
联邦学习中的成员推断攻击与防御:综述
兰德公司 2024 人工智能和机器学习在太空领域感知中的应用 - 基于两项人工智能案例英文版
Wavestone2024 年法国工业 4.0 晴雨表市场趋势与经验反馈 英文版
Salesforce2024 年制造业趋势报告 - 来自全球 800 多位行业决策者对运营和数字化转型的洞察 英文版
MicrosoftAzure2024 推动应用创新的九大 AI 趋势报告
DeepMind:Gemini,一个高性能多模态模型家族分析报告
模仿、探索和自我提升:慢思维推理系统的复现报告
自我发现:大型语言模型自我组成推理结构
2025 年 101 项将 (或不会) 塑造未来的技术趋势白皮书
《自然杂志》2024 年 10 大科学人物推荐报告
量子位智库:2024 年度 AI 十大趋势报告
华为:鸿蒙 2030 愿景白皮书(更新版)
电子行业专题报告:2025 年万物 AI 面临的十大待解难题 - 241209
中国信通院《人工智能发展报告(2024 年)》
美国安全与新兴技术中心:《追踪美国人工智能并购案》报告
Nature 研究报告:AI 革命的数据正在枯竭,研究人员该怎么办?
NeurIPS 2024 论文:智能体不够聪明怎么办?让它像学徒一样持续学习
LangChain 人工智能代理(AI agent)现状报告
普华永道:2024 半导体行业状况报告发展趋势与驱动因素
觅途咨询:2024 全球人形机器人企业画像与能力评估报告
美国化学会 (ACS):2024 年纳米材料领域新兴趋势与研发进展报告
GWEC:2024 年全球风能报告英文版
Chainalysis:2024 年加密货币地理报告加密货币采用的区域趋势分析
2024 光刻机产业竞争格局国产替代空间及产业链相关公司分析报告
世界经济论坛:智能时代,各国对未来制造业和供应链的准备程度
兰德:《保护人工智能模型权重:防止盗窃和滥用前沿模型》-128 页报告
经合组织 成年人是否具备在不断变化的世界中生存所需的技能 199 页报告
医学应用中的可解释人工智能:综述
复旦最新《智能体模拟社会》综述
《全球导航卫星系统(GNSS)软件定义无线电:历史、当前发展和标准化工作》最新综述
《基础研究,致命影响:军事人工智能研究资助》报告
欧洲科学的未来 - 100 亿地平线研究计划
Nature:欧盟正在形成一项科学大型计划
Nature 欧洲科学的未来
欧盟科学 —— 下一个 1000 亿欧元
欧盟向世界呼吁 加入我们价值 1000 亿欧元的研究计划
DARPA 主动社会工程防御计划(ASED)《防止删除信息和捕捉有害行为者(PIRANHA)》技术报告
兰德《人工智能和机器学习用于太空域感知》72 页报告
构建通用机器人生成范式:基础设施、扩展性与策略学习(CMU 博士论文)
世界贸易组织 2024 智能贸易报告 AI 和贸易活动如何双向塑造 英文版
人工智能行业应用建设发展参考架构
波士顿咨询 2024 年欧洲天使投资状况报告 英文版
2024 美国制造业计划战略规划
【新书】大规模语言模型的隐私与安全
人工智能行业海外市场寻找 2025 爆款 AI 应用 - 241204
美国环保署 EPA2024 年版汽车趋势报告英文版
经济学人智库 EIU2025 年行业展望报告 6 大行业的挑战机遇与发展趋势 英文版
华为 2024 迈向智能世界系列工业网络全连接研究报告
华为迈向智能世界白皮书 2024 - 计算
华为迈向智能世界白皮书 2024 - 全光网络
华为迈向智能世界白皮书 2024 - 数据通信
华为迈向智能世界白皮书 2024 - 无线网络
安全牛 AI 时代深度伪造和合成媒体的安全威胁与对策 2024 版
2024 人形机器人在工业领域发展机遇行业壁垒及国产替代空间分析报告
《2024 年 AI 现状分析报告》2-1-3 页.zip
万物智能演化理论,智能科学基础理论的新探索 - newv2
世界经济论坛 智能时代的食物和水系统研究报告
生成式 AI 时代的深伪媒体生成与检测:综述与展望
科尔尼 2024 年全球人工智能评估 AIA 报告追求更高层次的成熟度规模化和影响力英文版
计算机行业专题报告 AI 操作系统时代已至 - 241201
Nature 人工智能距离人类水平智能有多近?
Nature 开放的人工智能系统实际上是封闭的
斯坦福《统计学与信息论》讲义,668 页 pdf
国家信息中心华为城市一张网 2.0 研究报告 2024 年
国际清算银行 2024 生成式 AI 的崛起对美国劳动力市场的影响分析报告 渗透度替代效应及对不平等状况英文版
大模型如何判决?从生成到判决:大型语言模型作为裁判的机遇与挑战
毕马威 2024 年全球半导体行业展望报告
MR 行业专题报告 AIMR 空间计算定义新一代超级个人终端 - 241119
DeepMind 36 页 AI4Science 报告:全球实验室被「AI 科学家」指数级接管
《人工智能和机器学习对网络安全的影响》最新 273 页
2024 量子计算与人工智能无声的革命报告
未来今日研究所:2024 技术趋势报告 - 广义计算篇
科睿唯安中国科学院 2024 研究前沿热度指数报告
文本到图像合成:十年回顾
《以人为中心的大型语言模型(LLM)研究综述》
经合组织 2024 年数字经济展望报告加强连通性创新与信任第二版
波士顿咨询 2024 全球经济体 AI 成熟度矩阵报告 英文版
理解世界还是预测未来?世界模型的综合综述
GoogleCloudCSA2024AI 与安全状况调研报告 英文版
英国制造商组织 MakeUK2024 英国工业战略愿景报告从概念到实施
花旗银行 CitiGPS2024 自然环境可持续发展新前沿研究报告
国际可再生能源署 IRENA2024 年全球气候行动报告
Cell: 物理学和化学 、人工智能知识领域的融合
智次方 2025 中国 5G 产业全景图谱报告
上下滑动查看更多
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








