常用算术生成算法:
accumulate // 计算容器元素累计总和
fill // 向容器中添加元素
accumulate
计算区间内 容器元素累计总和
需要包含头文件 #include
accumulate(iterator beg, iterator end, value);
// 计算容器元素累计总和
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// value 起始值
#include<iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <numeric>
using namespace std;
void test()
{
vector<int> v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
v1.push_back(i);
}
int sum = accumulate(v1.begin(), v1.end(), 1000); //第三个参数是在v1总和的基础上加上的数值
cout << "sum = " << sum << endl;
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
fill
向容器中填充指定的元素
需要包含头文件#iclude
fill(iterator beg, iterator end, value);
// 向容器中填充元素
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// value 填充的值
//fill
void print(const int& val)
{
cout << val<<" ";
}
void test01()
{
vector<int>v2;
v2.resize(10);
fill(v2.begin(), v2.end(), 100); //指定区间填充100
for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), print);
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
常用集合算法:
set_intersection // 求两个容器的交集
set_union // 求两个容器的并集
set_difference // 求两个容器的差集
set_intersection
求两个容器的交集
set_intersection(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest);
// 求两个集合的交集
// 注意:两个集合必须是有序序列
// beg1 容器1开始迭代器
// end1 容器1结束迭代器
// beg2 容器2开始迭代器
// end2 容器2结束迭代器
// dest 目标容器开始迭代器
//返回的是交集最后一个元素的迭代器
输出交集是最后使用算法返回的迭代器,不然会按照开辟空间的元素个数进行输出;
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void print(int val) {
cout << val << " ";
}
void test()
{
vector<int>v1;
vector<int>v2;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v1.push_back(i);
v2.push_back(i + 5);
}
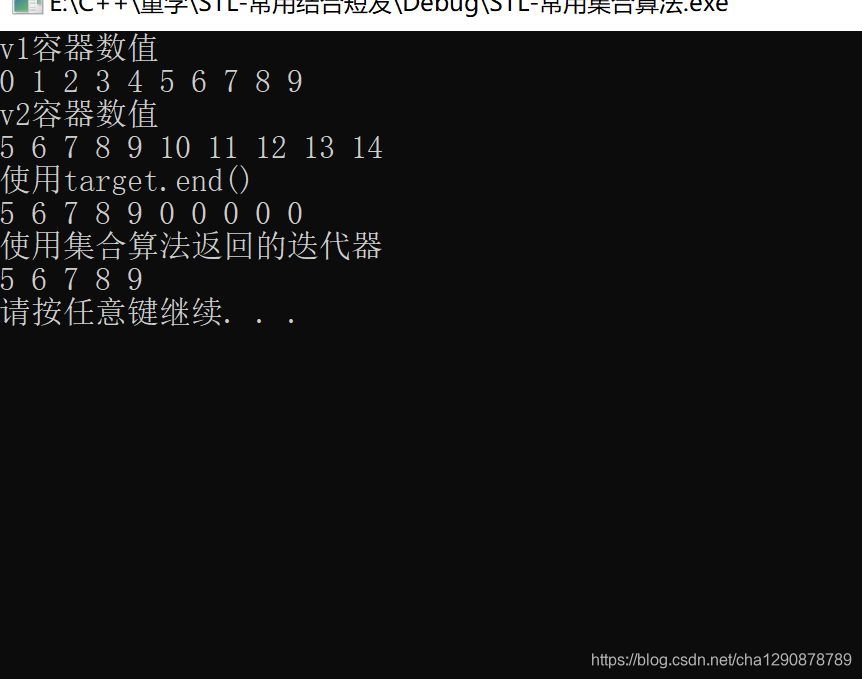
cout << "v1容器数值" << endl;
for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(),print);
cout << endl;
cout << "v2容器数值" << endl;
for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), print);
cout << endl;
vector<int>target;
target.resize(min(v1.size(), v1.size()));
vector<int>::iterator itEnd = set_intersection(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), target.begin());
cout << "使用target.end()" << endl;
for_each(target.begin(), target.end(), print);
cout << endl;
cout << "使用集合算法返回的迭代器" << endl;
for_each(target.begin(), itEnd, print);
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
set_union
求两个集合的并集
set_union(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest);
// 求两个集合的并集
// 注意:两个集合必须是有序序列
// beg1 容器1开始迭代器
// end1 容器1结束迭代器
// beg2 容器2开始迭代器
// end2 容器2结束迭代器
// dest 目标容器开始迭代器
void test02()
{
vector<int>v1;
vector<int>v2;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v1.push_back(i);
v2.push_back(i + 5);
}
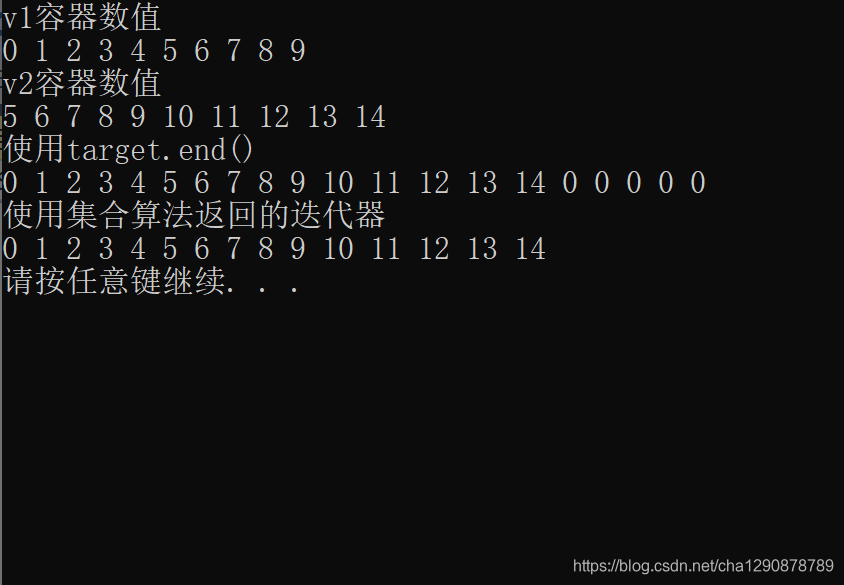
cout << "v1容器数值" << endl;
for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), print);
cout << endl;
cout << "v2容器数值" << endl;
for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), print);
cout << endl;
vector<int>target;
target.resize(v1.size()+v1.size());
vector<int>::iterator itEnd = set_union(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), target.begin());
cout << "使用target.end()" << endl;
for_each(target.begin(), target.end(), print);
cout << endl;
cout << "使用集合算法返回的迭代器" << endl;
for_each(target.begin(), itEnd, print);
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test02();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
set_difference
求两个集合的差集
A:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
B:5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
A和B的差集:1 2 3 4
B和A的差集: 11 12 13 14
set_difference(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest);
// 求两个集合的差集
// 注意:两个集合必须是有序序列
// beg1 容器1开始迭代器
// end1 容器1结束迭代器
// beg2 容器2开始迭代器
// end2 容器2结束迭代器
// dest 目标容器开始迭代器
void test03()
{
vector<int>v1;
vector<int>v2;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v1.push_back(i);
v2.push_back(i + 5);
}
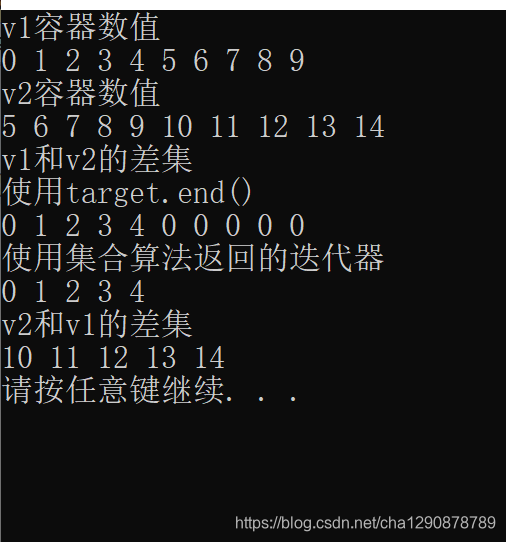
cout << "v1容器数值" << endl;
for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), print);
cout << endl;
cout << "v2容器数值" << endl;
for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), print);
cout << endl;
vector<int>target1;
vector<int>target2;
target1.resize(max(v1.size(), v1.size()));
cout << "v1和v2的差集" << endl;
vector<int>::iterator itEnd1 = set_difference(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), target1.begin());
cout << "使用target.end()" << endl;
for_each(target1.begin(), target1.end(), print);
cout << endl;
cout << "使用集合算法返回的迭代器" << endl;
for_each(target1.begin(), itEnd1, print);
cout << endl;
target2.resize(max(v1.size(), v1.size()));
cout << "v2和v1的差集" << endl;
vector<int>::iterator itEnd2 = set_difference(v2.begin(), v2.end(), v1.begin(), v1.end(), target2.begin());
for_each(target2.begin(), itEnd2, print);
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test03();
system("pause");
return 0;
}





















 435
435











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








