本文主要的内容就是用自己的代码实现spring下面的代码功能:
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("bean.xml");
XmlBeanFactory factory = new XmlBeanFactory(is);
Action action = (Action) factory.getBean("TheAction");
具体流程如下图:
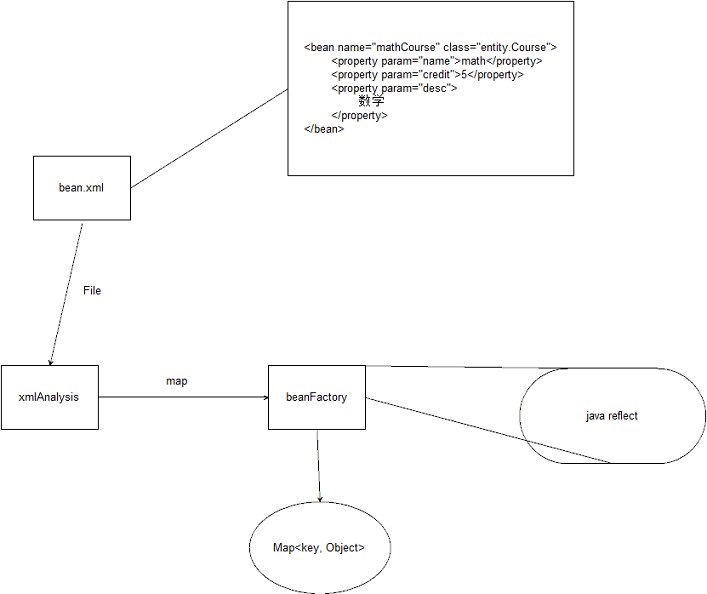
1. 确定有两个类,一个是Course,一个是Student,Course由名称、学分、描述组成。Student由学号、名字、课程组成。现在要先建一个Course然后把这个类作为Student的Course属性。

1. 确定有两个类,一个是Course,一个是Student,Course由名称、学分、描述组成。Student由学号、名字、课程组成。现在要先建一个Course然后把这个类作为Student的Course属性。
Course.java
package entity;
public class Course {
private String name;
private long credit;
private String desc;
public Course() {
super();
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public long getCredit() {
return credit;
}
public void setCredit(long credit) {
this.credit = credit;
}
public String getDesc() {
return desc;
}
public void setDesc(String desc) {
this.desc = desc;
}
}package entity;
public class Student {
private String NO;
private String name;
private Course course;
public String getNO() {
return NO;
}
public void setNO(String nO) {
NO = nO;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Course getCourse() {
return course;
}
public void setCourse(Course course) {
this.course = course;
}
}
2 在bean.xml中写上bean的信息,我改了一下xml的名字,现在是conf.xml,name和class都是必要的,而children节点的property就是这个bean的一些属性。property中的param指这个属性的名字,text的部分是value。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans>
<bean id="mathCourse" class="entity.Course">
<property param="name">math</property>
<property param="credit">5</property>
<property param="desc">
数学
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="stud0" class="entity.Student">
<property param="NO">000</property>
<property param="name">stud0</property>
<property param="course" ref="mathCourse">mathCourse</property>
</bean>
</beans>
xml里面的信息要和上面的类的属性相互对应,在property上写有ref的节点说明是根据上上面已经定义的bean注入进来的。
3.用一个Property类作为存放每个<property/>节点的信息,因为比较的简单,所以这个类只有几个属性
package entity;
public class Property {
private String name;
private boolean ref;
private String value;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public boolean isRef() {
return ref;
}
public void setRef(boolean ref) {
this.ref = ref;
}
public String getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(String value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
4.通过解析这个xml获得写在里面的信息。这里使用dom4j
public static Map<String, Property> getBeanParams(Element bean) {
Map<String, Property> map = new HashMap<String, Property>();
for (Iterator<Element> beanIt = bean.elementIterator(); beanIt
.hasNext();) {
Element property = beanIt.next();
Property p = new Property();
p.setName(property.attribute("param").getStringValue());
p.setRef(property.attribute("ref") == null ? false : true);
p.setValue(property.getTextTrim());
map.put(property.attribute("param").getStringValue(), p);
}
return map;
}
5.使用java的反射对对象的属性进行赋值。可以通过两种方法,一种是直接通过访问属性,另一种就是使用方法就是setXXX(value),当然也可以用构造函数,用起来不是一般的麻烦。
package reflect;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class ClassHelper {
// 通过类方法获取属性值
public static Map<String, Object> getMethods(Object obj)
throws IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException,
InvocationTargetException {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
Method[] method = obj.getClass().getDeclaredMethods();
for (int i = 0; i < method.length; i++) {
String methodName = method[i].getName().toString();
if (methodName.startsWith("get")) {
map.put(method[i].getName().toString(),
method[i].invoke(obj, null));
}
}
return map;
}
// 通过类方法对属性赋值
public static String[] setMethods(Object obj,
Map<String, Property> propertyMap, Map<String, Object> objMap)
throws NumberFormatException, IllegalAccessException,
IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException {
Method[] method = obj.getClass().getDeclaredMethods();
String[] methods = new String[method.length];
for (int i = 0; i < method.length; i++) {
String methodName = method[i].getName().toString();
if (methodName.startsWith("set")) {
for (Class<?> c : method[i].getParameterTypes()) {
String paramType = c.getSimpleName().toString();// 获取方法中变量的类型
String name = method[i].getName().toString()
.substring(3, methodName.length()).toLowerCase();// 记得要转换为小写,截取后得到的string开头字母是大写
// System.out.println(name);
Property property = propertyMap.get(name);
String val = property.getValue();
if (property.isRef()) {
Object o = objMap.get(val);
method[i].invoke(obj, o);
} else if (paramType.toLowerCase().equals("long")) {
method[i].invoke(obj, Long.parseLong(val));
} else if (paramType.toLowerCase().equals("int")
|| paramType.equals("Integer")) {
method[i].invoke(obj, Integer.valueOf(val));
} else if (paramType.toLowerCase().equals("float")) {
method[i].invoke(obj, Float.valueOf(val));
} else if (paramType.toLowerCase().equals("short")) {
method[i].invoke(obj, Short.valueOf(val));
} else if (paramType.toLowerCase().equals("double")) {
method[i].invoke(obj, Double.valueOf(val));
} else if (paramType.toLowerCase().equals("char")) {
method[i].invoke(obj, val.charAt(0));
} else if (paramType.toLowerCase().equals("boolean")) {
method[i].invoke(obj, Boolean.valueOf(val));
} else if (paramType.toLowerCase().equals("byte")) {
method[i].invoke(obj, val.getBytes()[0]);
} else {
method[i].invoke(obj, val);
}
}
}
}
return methods;
}
// 获取类属性的值
public static Map<String, Object> getFieldsValues(Object obj)
throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {
Field[] field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
for (int i = 0; i < field.length; i++) {
field[i].setAccessible(true); // 允许访问私有属性
map.put(field[i].getName(), field[i].get(obj));// 使用属性的名称作为key
// ,属性的值作为value
}
return map;
}
// 通过属性直接赋值
public static String[] setFields(Object obj,
Map<String, Property> propertyMap, Map<String, Object> objMap)
throws NumberFormatException, IllegalArgumentException,
IllegalAccessException {
Field[] field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
String[] fields = new String[field.length];
for (int i = 0; i < field.length; i++) {
field[i].setAccessible(true); // 允许访问私有属性
String name = field[i].getName();
fields[i] = name;
String type = field[i].getType().getSimpleName();
// System.out.println("name:" + name + " type:" + type);
Property property = propertyMap.get(name);
String val = property.getValue();
if (property.isRef()) {
Object o = objMap.get(val);
field[i].set(obj, o);
} else if (type.toLowerCase().equals("long")) {
field[i].setLong(obj, Long.parseLong(val));
} else if (type.toLowerCase().equals("int")
|| type.equals("Integer")) {
field[i].setInt(obj, Integer.valueOf(val));
} else if (type.toLowerCase().equals("float")) {
field[i].setFloat(obj, Float.valueOf(val));
} else if (type.toLowerCase().equals("short")) {
field[i].setShort(obj, Short.valueOf(val));
} else if (type.toLowerCase().equals("double")) {
field[i].setDouble(obj, Double.valueOf(val));
} else if (type.toLowerCase().equals("char")) {
field[i].setChar(obj, val.charAt(0));
} else if (type.toLowerCase().equals("boolean")) {
field[i].setBoolean(obj, Boolean.valueOf(val));
} else if (type.toLowerCase().equals("byte")) {
field[i].setByte(obj, val.getBytes()[0]);
} else {
// System.out.println(val);
field[i].set(obj, val);
}
}
return fields;
}
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
}
6.利用上面的方法构建BeanFactory;
public class BeanFactory {
/**
* @param args
*/
private String path;
public static Map<String, Object> map;
public BeanFactory() {
this("src/bean.xml");
}
public BeanFactory(String path) {
super();
this.path = path;
init();
}
private void init() {
Document doc = null;
map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
try {
doc = reader.read(new File(path));
Element root = doc.getRootElement();
for (Iterator<Element> beans = root.elementIterator(); beans
.hasNext();) {
Element bean = beans.next();
Map<String, String> beanParams = XmlHelper.getBeanParams(bean);
Class cla = Class.forName(bean.attributeValue("class"));
Object obj = cla.newInstance();
// set value
ClassHelper.setFields(obj, beanParams, map);
// ClassHelper.setMethods(obj, beanParams, map);
map.put(bean.attributeValue("name"), obj);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
// System.out.println(System.getProperty("user.dir"));
}
public static <T> T getBean(String key, Class<T> classOf) {
return (T) map.get(key);
}
public String getPath() {
return path;
}
public void setPath(String path) {
this.path = path;
}
}
本次实现是通过直接访问类的属性进行赋值的。
7.写个main函数作为测试;
public class Main {
/**
* @param args
* @throws InvocationTargetException
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* @throws IllegalAccessException
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IllegalAccessException,
IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
BeanFactory beanFactory = new BeanFactory("src/conf.xml");
Student stud0 = BeanFactory.getBean("stud0", Student.class);
Course mathCourse = BeanFactory.getBean("mathCourse", Course.class);
System.out.println("stud name:" + stud0.getName());
System.out.println("stud NO.:" + stud0.getNO());
Course testMathCourse = stud0.getCourse();
System.out.println("the same ?:"
+ (mathCourse == testMathCourse ? true : false));
System.out.println("math name:" + mathCourse.getName());
System.out.println("math credit:" + mathCourse.getCredit());
System.out.println("math desc:" + mathCourse.getDesc());
Map<String, Object> vals = ClassHelper.getMethods(stud0);
for (Iterator<String> it = vals.keySet().iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
String key=it.next();
System.out.println(key+":"+vals.get(key));
}
}
}
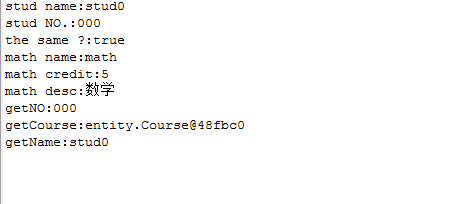
8.运行结果;

通过第三行的输出可以看出来,stud0的Course和从BeanFactory拿出来的是同一个对象。其他的值和xml设置的值是一个样的
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("bean.xml");
XmlBeanFactory factory =new XmlBeanFactory(is);
BeanFactorybeanFactory = new BeanFactory("src/conf.xml");和上面的两句功能一样
Action action = (Action) factory.getBean("TheAction");
Student stud0 = BeanFactory.getBean("stud0", Student.class);
这两句的功能一样,但此目的达成
done
source code url:






















 7503
7503

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








