Clickhouse:创建和添加数据
ClickHouse 是一款OLAP的工具
OLTP(on-line transaction processing)翻译为联机事务处理, OLAP(On-Line Analytical Processing)翻译为联机分析处理,从字面上来看OLTP是做事务处理,OLAP是做分析处理。从对数据库操作来看,OLTP主要是对数据的增删改,OLAP是对数据的查询。
OLTP主要用来记录某类业务事件的发生,如购买行为,当行为产生后,系统会记录是谁在何时何地做了何事,这样的一行(或多行)数据会以增删改的方式在数据库中进行数据的更新处理操作,要求实时性高、稳定性强、确保数据及时更新成功,像公司常见的业务系统如ERP,CRM,OA等系统都属于OLTP。当数据积累到一定的程度,我们需要对过去发生的事情做一个总结分析时,就需要把过去一段时间内产生的数据拿出来进行统计分析,从中获取我们想要的信息,为公司做决策提供支持,这时候就是在做OLAP了。
下面是OLAP应用场景的主要关注点
- 绝大部分场景都是读操作
- 数据都是一次性大批量更新(一次更新1000 行)
- 数据被添加到数据库后并不修改
- 对于读取操作,大量的行都从数据库里面提取出来,但是只对小量列进行统计
- 数据表里面的属性比较多
- 查询的评率很低,通常每次个服务器只读取数百次
- 对于大量的查询,50毫秒的延时是允许的。
- 列值的长度相对比较短,比如一个URL就60个字节
- 单次查询每秒需要处理非常高的吞吐量(每秒每个服务器可能要处理10亿行数据)
- 不需要考虑事务处理
- 对于数据一致性低要求
- 查询结果的数量远远小于原始数据,其结果能够在单台的机器上用内存储存,换句话说,数据在返回前被过滤或者聚合过了
显而易见,OLAP场景和OLTP或者键值对的场景大大不一样。所以不能用常规的OLTP的数据库区(传统的关系型数据库,文档数据库,键值对数据库,比如,Oracle, MongoDB,Redis)来处理实时联机分析查询的场景;否则其性能会惨不忍睹!
Clickhouse 自带的客户端
安装Clickhouse,其默认会提供一个UI,供大家尝试。比如笔者在阿里云安装好一个Clickhouse之后,就可以通过外网下面类似的外网地址打开。
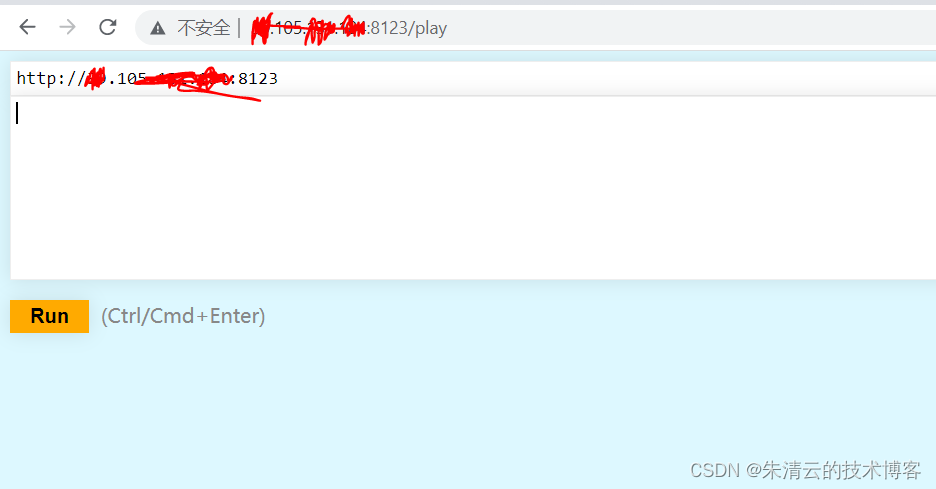
需要注意的是,其默认智能在本地访问,如果要通过互联网访问,则需要修改config.xml
把 被注释的部分"<listen_host>::</listen_host>" 取消注释即可!
其路径如下:
vi /etc/clickhouse-server/config.xml
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<clickhouse>
<logger>
<level>trace</level>
<log>/var/log/clickhouse-server/clickhouse-server.log</log>
<errorlog>/var/log/clickhouse-server/clickhouse-server.err.log</errorlog>
<size>1000M</size>
<count>10</count>
<!--
<levels>
<logger>
<name>ContextAccess (default)</name>
<level>none</level>
</logger>
<logger>
<name>DatabaseOrdinary (test)</name>
<level>none</level>
</logger>
</levels>
</logger>
<http_port>8123</http_port>
<tcp_port>9000</tcp_port>
<mysql_port>9004</mysql_port>
<postgresql_port>9005</postgresql_port>
<interserver_http_port>9009</interserver_http_port>
<listen_host>::</listen_host>
<max_connections>4096</max_connections>
<keep_alive_timeout>3</keep_alive_timeout>
<grpc>
<enable_ssl>false</enable_ssl>
<!-- The following two files are used only if enable_ssl=1 -->
<ssl_cert_file>/path/to/ssl_cert_file</ssl_cert_file>
<ssl_key_file>/path/to/ssl_key_file</ssl_key_file>
<!-- Whether server will request client for a certificate -->
<ssl_require_client_auth>false</ssl_require_client_auth>
<!-- The following file is used only if ssl_require_client_auth=1 -->
<ssl_ca_cert_file>/path/to/ssl_ca_cert_file</ssl_ca_cert_file>
<compression>deflate</compression>
<compression_level>medium</compression_level>
<!-- Send/receive message size limits in bytes. -1 means unlimited -->
<max_send_message_size>-1</max_send_message_size>
<max_receive_message_size>-1</max_receive_message_size>
<!-- Enable if you want very detailed logs -->
<verbose_logs>false</verbose_logs>
</grpc
<openSSL>
<server>
<certificateFile>/etc/clickhouse-server/server.crt</certificateFile>
<privateKeyFile>/etc/clickhouse-server/server.key</privateKeyFile>
<dhParamsFile>/etc/clickhouse-server/dhparam.pem</dhParamsFile>
<verificationMode>none</verificationMode>
<loadDefaultCAFile>true</loadDefaultCAFile>
<cacheSessions>true</cacheSessions>
<disableProtocols>sslv2,sslv3</disableProtocols>
<preferServerCiphers>true</preferServerCiphers>
</server>
<client>
<loadDefaultCAFile>true</loadDefaultCAFile>
<cacheSessions>true</cacheSessions>
<disableProtocols>sslv2,sslv3</disableProtocols>
<preferServerCiphers>true</preferServerCiphers>
<invalidCertificateHandler>
<name>RejectCertificateHandler</name>
</invalidCertificateHandler>
</client>
</openSSL>
<!-- Maximum number of concurrent queries. -->
<max_concurrent_queries>100</max_concurrent_queries>
<max_server_memory_usage>0</max_server_memory_usage>
<max_thread_pool_size>10000</max_thread_pool_size>
<max_server_memory_usage_to_ram_ratio>0.9</max_server_memory_usage_to_ram_ratio>
<total_memory_profiler_step>4194304</total_memory_profiler_step>
<total_memory_tracker_sample_probability>0</total_memory_tracker_sample_probability>
<uncompressed_cache_size>8589934592</uncompressed_cache_size>
<mark_cache_size>5368709120</mark_cache_size>
<mmap_cache_size>1000</mmap_cache_size>
<!-- Cache size in bytes for compiled expressions.-->
<compiled_expression_cache_size>134217728</compiled_expression_cache_size>
<!-- Cache size in elements for compiled expressions.--> <compiled_expression_cache_elements_size>10000</compiled_expression_cache_elements_size>
<!-- Path to data directory, with trailing slash. -->
<path>/var/lib/clickhouse/</path>
<!-- Path to temporary data for processing hard queries. -->
<tmp_path>/var/lib/clickhouse/tmp/</tmp_path>
<!-- Policy from the <storage_configuration> for the temporary files.
If not set <tmp_path> is used, otherwise <tmp_path> is ignored.
Notes:
- move_factor is ignored
- keep_free_space_bytes is ignored
- max_data_part_size_bytes is ignored
- you must have exactly one volume in that policy
-->
<!-- <tmp_policy>tmp</tmp_policy> -->
<!-- Directory with user provided files that are accessible by 'file' table function. -->
<user_files_path>/var/lib/clickhouse/user_files/</user_files_path>
<!-- LDAP server definitions. -->
<ldap_servers>
<!-- List LDAP servers with their connection parameters here to later 1) use them as authenticators for dedicated local users,
who have 'ldap' authentication mechanism specified instead of 'password', or to 2) use them as remote user directories.
Parameters:
host - LDAP server hostname or IP, this parameter is mandatory and cannot be empty.
port - LDAP server port, default is 636 if enable_tls is set to true, 389 otherwise.
bind_dn - template used to construct the DN to bind to.
The resulting DN will be constructed by replacing all '{user_name}' substrings of the template with the actual
user name during each authentication attempt.
user_dn_detection - section with LDAP search parameters for detecting the actual user DN of the bound user.
This is mainly used in search filters for further role mapping when the server is Active Directory. The
resulting user DN will be used when replacing '{user_dn}' substrings wherever they are allowed. By default,
user DN is set equal to bind DN, but once search is performed, it will be updated with to the actual detected
user DN value.
base_dn - template used to construct the base DN for the LDAP search.
The resulting DN will be constructed by replacing all '{user_name}' and '{bind_dn}' substrings
of the template with the actual user name and bind DN during the LDAP search.
scope - scope of the LDAP search.
Accepted values are: 'base', 'one_level', 'children', 'subtree' (the default).
search_filter - template used to construct the search filter for the LDAP search.
The resulting filter will be constructed by replacing all '{user_name}', '{bind_dn}', and '{base_dn}'
substrings of the template with the actual user name, bind DN, and base DN during the LDAP search.
Note, that the special characters must be escaped properly in XML.
verification_cooldown - a period of time, in seconds, after a successful bind attempt, during which a user will be assumed
to be successfully authenticated for all consecutive requests without contacting the LDAP server.
Specify 0 (the default) to disable caching and force contacting the LDAP server for each authentication request.
enable_tls - flag to trigger use of secure connection to the LDAP server.
Specify 'no' for plain text (ldap://) protocol (not recommended).
Specify 'yes' for LDAP over SSL/TLS (ldaps://) protocol (recommended, the default).
Specify 'starttls' for legacy StartTLS protocol (plain text (ldap://) protocol, upgraded to TLS).
tls_minimum_protocol_version - the minimum protocol version of SSL/TLS.
Accepted values are: 'ssl2', 'ssl3', 'tls1.0', 'tls1.1', 'tls1.2' (the default).
tls_require_cert - SSL/TLS peer certificate verification behavior.
Accepted values are: 'never', 'allow', 'try', 'demand' (the default).
tls_cert_file - path to certificate file.
tls_key_file - path to certificate key file.
tls_ca_cert_file - path to CA certificate file.
tls_ca_cert_dir - path to the directory containing CA certificates.
tls_cipher_suite - allowed cipher suite (in OpenSSL notation).
Example:
<my_ldap_server>
<host>localhost</host>
<port>636</port>
<bind_dn>uid={user_name},ou=users,dc=example,dc=com</bind_dn>
<verification_cooldown>300</verification_cooldown>
<enable_tls>yes</enable_tls>
<tls_minimum_protocol_version>tls1.2</tls_minimum_protocol_version>
<tls_require_cert>demand</tls_require_cert>
<tls_cert_file>/path/to/tls_cert_file</tls_cert_file>
<tls_key_file>/path/to/tls_key_file</tls_key_file>
<tls_ca_cert_file>/path/to/tls_ca_cert_file</tls_ca_cert_file>
<tls_ca_cert_dir>/path/to/tls_ca_cert_dir</tls_ca_cert_dir>
<tls_cipher_suite>ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:AES256-GCM-SHA384</tls_cipher_suite>
</my_ldap_server>
Example (typical Active Directory with configured user DN detection for further role mapping):
<my_ad_server>
<host>localhost</host>
<port>389</port>
<bind_dn>EXAMPLE\{user_name}</bind_dn>
<user_dn_detection>
<base_dn>CN=Users,DC=example,DC=com</base_dn>
<search_filter>(&(objectClass=user)(sAMAccountName={user_name}))</search_filter>
</user_dn_detection>
<enable_tls>no</enable_tls>
</my_ad_server>
-->
</ldap_servers>
<!-- To enable Kerberos authentication support for HTTP requests (GSS-SPNEGO), for those users who are explicitly configured
to authenticate via Kerberos, define a single 'kerberos' section here.
Parameters:
principal - canonical service principal name, that will be acquired and used when accepting security contexts.
This parameter is optional, if omitted, the default principal will be used.
This parameter cannot be specified together with 'realm' parameter.
realm - a realm, that will be used to restrict authentication to only those requests whose initiator's realm matches it.
This parameter is optional, if omitted, no additional filtering by realm will be applied.
This parameter cannot be specified together with 'principal' parameter.
Example:
<kerberos />
Example:
<kerberos>
<principal>HTTP/clickhouse.example.com@EXAMPLE.COM</principal>
</kerberos>
Example:
<kerberos>
<realm>EXAMPLE.COM</realm>
</kerberos>
-->
<!-- Sources to read users, roles, access rights, profiles of settings, quotas. -->
<user_directories>
<users_xml>
<!-- Path to configuration file with predefined users. -->
<path>users.xml</path>
</users_xml>
<local_directory>
<!-- Path to folder where users created by SQL commands are stored. -->
<path>/var/lib/clickhouse/access/</path>
</local_directory>
<!-- To add an LDAP server as a remote user directory of users that are not defined locally, define a single 'ldap' section
with the following parameters:
server - one of LDAP server names defined in 'ldap_servers' config section above.
This parameter is mandatory and cannot be empty.
roles - section with a list of locally defined roles that will be assigned to each user retrieved from the LDAP server.
If no roles are specified here or assigned during role mapping (below), user will not be able to perform any
actions after authentication.
role_mapping - section with LDAP search parameters and mapping rules.
When a user authenticates, while still bound to LDAP, an LDAP search is performed using search_filter and the
name of the logged in user. For each entry found during that search, the value of the specified attribute is
extracted. For each attribute value that has the specified prefix, the prefix is removed, and the rest of the
value becomes the name of a local role defined in ClickHouse, which is expected to be created beforehand by
CREATE ROLE command.
There can be multiple 'role_mapping' sections defined inside the same 'ldap' section. All of them will be
applied.
base_dn - template used to construct the base DN for the LDAP search.
The resulting DN will be constructed by replacing all '{user_name}', '{bind_dn}', and '{user_dn}'
substrings of the template with the actual user name, bind DN, and user DN during each LDAP search.
scope - scope of the LDAP search.
Accepted values are: 'base', 'one_level', 'children', 'subtree' (the default).
search_filter - template used to construct the search filter for the LDAP search.
The resulting filter will be constructed by replacing all '{user_name}', '{bind_dn}', '{user_dn}', and
'{base_dn}' substrings of the template with the actual user name, bind DN, user DN, and base DN during
each LDAP search.
Note, that the special characters must be escaped properly in XML.
attribute - attribute name whose values will be returned by the LDAP search. 'cn', by default.
prefix - prefix, that will be expected to be in front of each string in the original list of strings returned by
the LDAP search. Prefix will be removed from the original strings and resulting strings will be treated
as local role names. Empty, by default.
Example:
<ldap>
<server>my_ldap_server</server>
<roles>
<my_local_role1 />
<my_local_role2 />
</roles>
<role_mapping>
<base_dn>ou=groups,dc=example,dc=com</base_dn>
<scope>subtree</scope>
<search_filter>(&(objectClass=groupOfNames)(member={bind_dn}))</search_filter>
<attribute>cn</attribute>
<prefix>clickhouse_</prefix>
</role_mapping>
</ldap>
Example (typical Active Directory with role mapping that relies on the detected user DN):
<ldap>
<server>my_ad_server</server>
<role_mapping>
<base_dn>CN=Users,DC=example,DC=com</base_dn>
<attribute>CN</attribute>
<scope>subtree</scope>
<search_filter>(&(objectClass=group)(member={user_dn}))</search_filter>
<prefix>clickhouse_</prefix>
</role_mapping>
</ldap>
-->
</user_directories>
<!-- Default profile of settings. -->
<default_profile>default</default_profile>
<!-- Comma-separated list of prefixes for user-defined settings. -->
<custom_settings_prefixes></custom_settings_prefixes>
<!-- System profile of settings. This settings are used by internal processes (Distributed DDL worker and so on). -->
<!-- <system_profile>default</system_profile> -->
<!-- Buffer profile of settings.
This settings are used by Buffer storage to flush data to the underlying table.
Default: used from system_profile directive.
-->
<!-- <buffer_profile>default</buffer_profile> -->
<!-- Default database. -->
<default_database>default</default_database>
<!-- Server time zone could be set here.
Time zone is used when converting between String and DateTime types,
when printing DateTime in text formats and parsing DateTime from text,
it is used in date and time related functions, if specific time zone was not passed as an argument.
Time zone is specified as identifier from IANA time zone database, like UTC or Africa/Abidjan.
If not specified, system time zone at server startup is used.
Please note, that server could display time zone alias instead of specified name.
Example: W-SU is an alias for Europe/Moscow and Zulu is an alias for UTC.
-->
<!-- <timezone>Europe/Moscow</timezone> -->
<!-- You can specify umask here (see "man umask"). Server will apply it on startup.
Number is always parsed as octal. Default umask is 027 (other users cannot read logs, data files, etc; group can only read).
-->
<!-- <umask>022</umask> -->
<!-- Perform mlockall after startup to lower first queries latency
and to prevent clickhouse executable from being paged out under high IO load.
Enabling this option is recommended but will lead to increased startup time for up to a few seconds.
-->
<mlock_executable>true</mlock_executable>
<!-- Reallocate memory for machine code ("text") using huge pages. Highly experimental. -->
<remap_executable>false</remap_executable>
<![CDATA[
Uncomment below in order to use JDBC table engine and function.
To install and run JDBC bridge in background:
* [Debian/Ubuntu]
export MVN_URL=https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/ru/yandex/clickhouse/clickhouse-jdbc-bridge
export PKG_VER=$(curl -sL $MVN_URL/maven-metadata.xml | grep '<release>' | sed -e 's|.*>\(.*\)<.*|\1|')
wget https://github.com/ClickHouse/clickhouse-jdbc-bridge/releases/download/v$PKG_VER/clickhouse-jdbc-bridge_$PKG_VER-1_all.deb
apt install --no-install-recommends -f ./clickhouse-jdbc-bridge_$PKG_VER-1_all.deb
clickhouse-jdbc-bridge &
* [CentOS/RHEL]
export MVN_URL=https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/ru/yandex/clickhouse/clickhouse-jdbc-bridge
export PKG_VER=$(curl -sL $MVN_URL/maven-metadata.xml | grep '<release>' | sed -e 's|.*>\(.*\)<.*|\1|')
wget https://github.com/ClickHouse/clickhouse-jdbc-bridge/releases/download/v$PKG_VER/clickhouse-jdbc-bridge-$PKG_VER-1.noarch.rpm
yum localinstall -y clickhouse-jdbc-bridge-$PKG_VER-1.noarch.rpm
clickhouse-jdbc-bridge &
Please refer to https://github.com/ClickHouse/clickhouse-jdbc-bridge#usage for more information.
]]>
<!--
<jdbc_bridge>
<host>127.0.0.1</host>
<port>9019</port>
</jdbc_bridge>
-->
<!-- Configuration of clusters that could be used in Distributed tables.
https://clickhouse.com/docs/en/operations/table_engines/distributed/
-->
<remote_servers>
<!-- Test only shard config for testing distributed storage -->
<test_shard_localhost>
<!-- Inter-server per-cluster secret for Distributed queries
default: no secret (no authentication will be performed)
If set, then Distributed queries will be validated on shards, so at least:
- such cluster should exist on the shard,
- such cluster should have the same secret.
And also (and which is more important), the initial_user will
be used as current user for the query.
Right now the protocol is pretty simple and it only takes into account:
- cluster name
- query
Also it will be nice if the following will be implemented:
- source hostname (see interserver_http_host), but then it will depends from DNS,
it can use IP address instead, but then the you need to get correct on the initiator node.
- target hostname / ip address (same notes as for source hostname)
- time-based security tokens
-->
<!-- <secret></secret> -->
<shard>
<!-- Optional. Whether to write data to just one of the replicas. Default: false (write data to all replicas). -->
<!-- <internal_replication>false</internal_replication> -->
<!-- Optional. Shard weight when writing data. Default: 1. -->
<!-- <weight>1</weight> -->
<replica>
<host>localhost</host>
<port>9000</port>
<!-- Optional. Priority of the replica for load_balancing. Default: 1 (less value has more priority). -->
<!-- <priority>1</priority> -->
</replica>
</shard>
</test_shard_localhost>
<test_cluster_two_shards_localhost>
<shard>
<replica>
<host>localhost</host>
<port>9000</port>
</replica>
</shard>
<shard>
<replica>
<host>localhost</host>
<port>9000</port>
</replica>
</shard>
</test_cluster_two_shards_localhost>
<test_cluster_two_shards>
<shard>
<replica>
<host>127.0.0.1</host>
<port>9000</port>
</replica>
</shard>
<shard>
<replica>
<host>127.0.0.2</host>
<port>9000</port>
</replica>
</shard>
</test_cluster_two_shards>
<test_cluster_two_shards_internal_replication>
<shard>
<internal_replication>true</internal_replication>
<replica>
<host>127.0.0.1</host>
<port>9000</port>
</replica>
</shard>
<shard>
<internal_replication>true</internal_replication>
<replica>
<host>127.0.0.2</host>
<port>9000</port>
</replica>
</shard>
</test_cluster_two_shards_internal_replication>
<test_shard_localhost_secure>
<shard>
<replica>
<host>localhost</host>
<port>9440</port>
<secure>1</secure>
</replica>
</shard>
</test_shard_localhost_secure>
<test_unavailable_shard>
<shard>
<replica>
<host>localhost</host>
<port>9000</port>
</replica>
</shard>
<shard>
<replica>
<host>localhost</host>
<port>1</port>
</replica>
</shard>
</test_unavailable_shard>
</remote_servers>
<!-- The list of hosts allowed to use in URL-related storage engines and table functions.
If this section is not present in configuration, all hosts are allowed.
-->
<!--<remote_url_allow_hosts>-->
<!-- Host should be specified exactly as in URL. The name is checked before DNS resolution.
Example: "yandex.ru", "yandex.ru." and "www.yandex.ru" are different hosts.
If port is explicitly specified in URL, the host:port is checked as a whole.
If host specified here without port, any port with this host allowed.
"yandex.ru" -> "yandex.ru:443", "yandex.ru:80" etc. is allowed, but "yandex.ru:80" -> only "yandex.ru:80" is allowed.
If the host is specified as IP address, it is checked as specified in URL. Example: "[2a02:6b8:a::a]".
If there are redirects and support for redirects is enabled, every redirect (the Location field) is checked.
Host should be specified using the host xml tag:
<host>yandex.ru</host>
-->
<!-- Regular expression can be specified. RE2 engine is used for regexps.
Regexps are not aligned: don't forget to add ^ and $. Also don't forget to escape dot (.) metacharacter
(forgetting to do so is a common source of error).
-->
<!--</remote_url_allow_hosts>-->
<!-- If element has 'incl' attribute, then for it's value will be used corresponding substitution from another file.
By default, path to file with substitutions is /etc/metrika.xml. It could be changed in config in 'include_from' element.
Values for substitutions are specified in /clickhouse/name_of_substitution elements in that file.
-->
<!-- ZooKeeper is used to store metadata about replicas, when using Replicated tables.
Optional. If you don't use replicated tables, you could omit that.
See https://clickhouse.com/docs/en/engines/table-engines/mergetree-family/replication/
-->
<!--
<zookeeper>
<node>
<host>example1</host>
<port>2181</port>
</node>
<node>
<host>example2</host>
<port>2181</port>
</node>
<node>
<host>example3</host>
<port>2181</port>
</node>
</zookeeper>
-->
<!-- Substitutions for parameters of replicated tables.
Optional. If you don't use replicated tables, you could omit that.
See https://clickhouse.com/docs/en/engines/table-engines/mergetree-family/replication/#creating-replicated-tables
-->
<!--
<macros>
<shard>01</shard>
<replica>example01-01-1</replica>
</macros>
-->
<!-- Reloading interval for embedded dictionaries, in seconds. Default: 3600. -->
<builtin_dictionaries_reload_interval>3600</builtin_dictionaries_reload_interval>
<!-- Maximum session timeout, in seconds. Default: 3600. -->
<max_session_timeout>3600</max_session_timeout>
<!-- Default session timeout, in seconds. Default: 60. -->
<default_session_timeout>60</default_session_timeout>
<!-- Sending data to Graphite for monitoring. Several sections can be defined. -->
<!--
interval - send every X second
root_path - prefix for keys
hostname_in_path - append hostname to root_path (default = true)
metrics - send data from table system.metrics
events - send data from table system.events
asynchronous_metrics - send data from table system.asynchronous_metrics
-->
<!--
<graphite>
<host>localhost</host>
<port>42000</port>
<timeout>0.1</timeout>
<interval>60</interval>
<root_path>one_min</root_path>
<hostname_in_path>true</hostname_in_path>
<metrics>true</metrics>
<events>true</events>
<events_cumulative>false</events_cumulative>
<asynchronous_metrics>true</asynchronous_metrics>
</graphite>
<graphite>
<host>localhost</host>
<port>42000</port>
<timeout>0.1</timeout>
<interval>1</interval>
<root_path>one_sec</root_path>
<metrics>true</metrics>
<events>true</events>
<events_cumulative>false</events_cumulative>
<asynchronous_metrics>false</asynchronous_metrics>
</graphite>
-->
<!-- Serve endpoint for Prometheus monitoring. -->
<!--
endpoint - mertics path (relative to root, statring with "/")
port - port to setup server. If not defined or 0 than http_port used
metrics - send data from table system.metrics
events - send data from table system.events
asynchronous_metrics - send data from table system.asynchronous_metrics
status_info - send data from different component from CH, ex: Dictionaries status
-->
<!--
<prometheus>
<endpoint>/metrics</endpoint>
<port>9363</port>
<metrics>true</metrics>
<events>true</events>
<asynchronous_metrics>true</asynchronous_metrics>
<status_info>true</status_info>
</prometheus>
-->
<!-- Query log. Used only for queries with setting log_queries = 1. -->
<query_log>
<!-- What table to insert data. If table is not exist, it will be created.
When query log structure is changed after system update,
then old table will be renamed and new table will be created automatically.
-->
<database>system</database>
<table>query_log</table>
<!--
PARTITION BY expr: https://clickhouse.com/docs/en/table_engines/mergetree-family/custom_partitioning_key/
Example:
event_date
toMonday(event_date)
toYYYYMM(event_date)
toStartOfHour(event_time)
-->
<partition_by>toYYYYMM(event_date)</partition_by>
<!--
Table TTL specification: https://clickhouse.com/docs/en/engines/table-engines/mergetree-family/mergetree/#mergetree-table-ttl
Example:
event_date + INTERVAL 1 WEEK
event_date + INTERVAL 7 DAY DELETE
event_date + INTERVAL 2 WEEK TO DISK 'bbb'
<ttl>event_date + INTERVAL 30 DAY DELETE</ttl>
-->
<!-- Instead of partition_by, you can provide full engine expression (starting with ENGINE = ) with parameters,
Example: <engine>ENGINE = MergeTree PARTITION BY toYYYYMM(event_date) ORDER BY (event_date, event_time) SETTINGS index_granularity = 1024</engine>
-->
<!-- Interval of flushing data. -->
<flush_interval_milliseconds>7500</flush_interval_milliseconds>
</query_log>
<!-- Trace log. Stores stack traces collected by query profilers.
See query_profiler_real_time_period_ns and query_profiler_cpu_time_period_ns settings. -->
<trace_log>
<database>system</database>
<table>trace_log</table>
<partition_by>toYYYYMM(event_date)</partition_by>
<flush_interval_milliseconds>7500</flush_interval_milliseconds>
</trace_log>
<!-- Query thread log. Has information about all threads participated in query execution.
Used only for queries with setting log_query_threads = 1. -->
<query_thread_log>
<database>system</database>
<table>query_thread_log</table>
<partition_by>toYYYYMM(event_date)</partition_by>
<flush_interval_milliseconds>7500</flush_interval_milliseconds>
</query_thread_log>
<!-- Query views log. Has information about all dependent views associated with a query.
Used only for queries with setting log_query_views = 1. -->
<query_views_log>
<database>system</database>
<table>query_views_log</table>
<partition_by>toYYYYMM(event_date)</partition_by>
<flush_interval_milliseconds>7500</flush_interval_milliseconds>
</query_views_log>
<!-- Uncomment if use part log.
Part log contains information about all actions with parts in MergeTree tables (creation, deletion, merges, downloads).-->
<part_log>
<database>system</database>
<table>part_log</table>
<partition_by>toYYYYMM(event_date)</partition_by>
<flush_interval_milliseconds>7500</flush_interval_milliseconds>
</part_log>
<!-- Uncomment to write text log into table.
Text log contains all information from usual server log but stores it in structured and efficient way.
The level of the messages that goes to the table can be limited (<level>), if not specified all messages will go to the table.
<text_log>
<database>system</database>
<table>text_log</table>
<flush_interval_milliseconds>7500</flush_interval_milliseconds>
<level></level>
</text_log>
-->
<!-- Metric log contains rows with current values of ProfileEvents, CurrentMetrics collected with "collect_interval_milliseconds" interval. -->
<metric_log>
<database>system</database>
<table>metric_log</table>
<flush_interval_milliseconds>7500</flush_interval_milliseconds>
<collect_interval_milliseconds>1000</collect_interval_milliseconds>
</metric_log>
<!--
Asynchronous metric log contains values of metrics from
system.asynchronous_metrics.
-->
<asynchronous_metric_log>
<database>system</database>
<table>asynchronous_metric_log</table>
<!--
Asynchronous metrics are updated once a minute, so there is
no need to flush more often.
-->
<flush_interval_milliseconds>7000</flush_interval_milliseconds>
</asynchronous_metric_log>
<!--
OpenTelemetry log contains OpenTelemetry trace spans.
-->
<opentelemetry_span_log>
<!--
The default table creation code is insufficient, this <engine> spec
is a workaround. There is no 'event_time' for this log, but two times,
start and finish. It is sorted by finish time, to avoid inserting
data too far away in the past (probably we can sometimes insert a span
that is seconds earlier than the last span in the table, due to a race
between several spans inserted in parallel). This gives the spans a
global order that we can use to e.g. retry insertion into some external
system.
-->
<engine>
engine MergeTree
partition by toYYYYMM(finish_date)
order by (finish_date, finish_time_us, trace_id)
</engine>
<database>system</database>
<table>opentelemetry_span_log</table>
<flush_interval_milliseconds>7500</flush_interval_milliseconds>
</opentelemetry_span_log>
<!-- Crash log. Stores stack traces for fatal errors.
This table is normally empty. -->
<crash_log>
<database>system</database>
<table>crash_log</table>
<partition_by />
<flush_interval_milliseconds>1000</flush_interval_milliseconds>
</crash_log>
<!-- Session log. Stores user log in (successful or not) and log out events. -->
<session_log>
<database>system</database>
<table>session_log</table>
<partition_by>toYYYYMM(event_date)</partition_by>
<flush_interval_milliseconds>7500</flush_interval_milliseconds>
</session_log>
<!-- Parameters for embedded dictionaries, used in Yandex.Metrica.
See https://clickhouse.com/docs/en/dicts/internal_dicts/
-->
<!-- Path to file with region hierarchy. -->
<!-- <path_to_regions_hierarchy_file>/opt/geo/regions_hierarchy.txt</path_to_regions_hierarchy_file> -->
<!-- Path to directory with files containing names of regions -->
<!-- <path_to_regions_names_files>/opt/geo/</path_to_regions_names_files> -->
<!-- <top_level_domains_path>/var/lib/clickhouse/top_level_domains/</top_level_domains_path> -->
<!-- Custom TLD lists.
Format: <name>/path/to/file</name>
Changes will not be applied w/o server restart.
Path to the list is under top_level_domains_path (see above).
-->
<top_level_domains_lists>
<!--
<public_suffix_list>/path/to/public_suffix_list.dat</public_suffix_list>
-->
</top_level_domains_lists>
<!-- Configuration of external dictionaries. See:
https://clickhouse.com/docs/en/sql-reference/dictionaries/external-dictionaries/external-dicts
-->
<dictionaries_config>*_dictionary.xml</dictionaries_config>
<!-- Configuration of user defined executable functions -->
<user_defined_executable_functions_config>*_function.xml</user_defined_executable_functions_config>
<!-- Uncomment if you want data to be compressed 30-100% better.
Don't do that if you just started using ClickHouse.
-->
<!--
<compression>
<!- - Set of variants. Checked in order. Last matching case wins. If nothing matches, lz4 will be used. - ->
<case>
<!- - Conditions. All must be satisfied. Some conditions may be omitted. - ->
<min_part_size>10000000000</min_part_size> <!- - Min part size in bytes. - ->
<min_part_size_ratio>0.01</min_part_size_ratio> <!- - Min size of part relative to whole table size. - ->
<!- - What compression method to use. - ->
<method>zstd</method>
</case>
</compression>
-->
<!-- Configuration of encryption. The server executes a command to
obtain an encryption key at startup if such a command is
defined, or encryption codecs will be disabled otherwise. The
command is executed through /bin/sh and is expected to write
a Base64-encoded key to the stdout. -->
<encryption_codecs>
<!-- aes_128_gcm_siv -->
<!-- Example of getting hex key from env -->
<!-- the code should use this key and throw an exception if its length is not 16 bytes -->
<!--key_hex from_env="..."></key_hex -->
<!-- Example of multiple hex keys. They can be imported from env or be written down in config-->
<!-- the code should use these keys and throw an exception if their length is not 16 bytes -->
<!-- key_hex id="0">...</key_hex -->
<!-- key_hex id="1" from_env=".."></key_hex -->
<!-- key_hex id="2">...</key_hex -->
<!-- current_key_id>2</current_key_id -->
<!-- Example of getting hex key from config -->
<!-- the code should use this key and throw an exception if its length is not 16 bytes -->
<!-- key>...</key -->
<!-- example of adding nonce -->
<!-- nonce>...</nonce -->
<!-- /aes_128_gcm_siv -->
</encryption_codecs>
<!-- Allow to execute distributed DDL queries (CREATE, DROP, ALTER, RENAME) on cluster.
Works only if ZooKeeper is enabled. Comment it if such functionality isn't required. -->
<distributed_ddl>
<!-- Path in ZooKeeper to queue with DDL queries -->
<path>/clickhouse/task_queue/ddl</path>
<!-- Settings from this profile will be used to execute DDL queries -->
<!-- <profile>default</profile> -->
<!-- Controls how much ON CLUSTER queries can be run simultaneously. -->
<!-- <pool_size>1</pool_size> -->
<!--
Cleanup settings (active tasks will not be removed)
-->
<!-- Controls task TTL (default 1 week) -->
<!-- <task_max_lifetime>604800</task_max_lifetime> -->
<!-- Controls how often cleanup should be performed (in seconds) -->
<!-- <cleanup_delay_period>60</cleanup_delay_period> -->
<!-- Controls how many tasks could be in the queue -->
<!-- <max_tasks_in_queue>1000</max_tasks_in_queue> -->
</distributed_ddl>
<!-- Settings to fine tune MergeTree tables. See documentation in source code, in MergeTreeSettings.h -->
<!--
<merge_tree>
<max_suspicious_broken_parts>5</max_suspicious_broken_parts>
</merge_tree>
-->
<!-- Protection from accidental DROP.
If size of a MergeTree table is greater than max_table_size_to_drop (in bytes) than table could not be dropped with any DROP query.
If you want do delete one table and don't want to change clickhouse-server config, you could create special file <clickhouse-path>/flags/force_drop_table and make DROP once.
By default max_table_size_to_drop is 50GB; max_table_size_to_drop=0 allows to DROP any tables.
The same for max_partition_size_to_drop.
Uncomment to disable protection.
-->
<!-- <max_table_size_to_drop>0</max_table_size_to_drop> -->
<!-- <max_partition_size_to_drop>0</max_partition_size_to_drop> -->
<!-- Example of parameters for GraphiteMergeTree table engine -->
<graphite_rollup_example>
<pattern>
<regexp>click_cost</regexp>
<function>any</function>
<retention>
<age>0</age>
<precision>3600</precision>
</retention>
<retention>
<age>86400</age>
<precision>60</precision>
</retention>
</pattern>
<default>
<function>max</function>
<retention>
<age>0</age>
<precision>60</precision>
</retention>
<retention>
<age>3600</age>
<precision>300</precision>
</retention>
<retention>
<age>86400</age>
<precision>3600</precision>
</retention>
</default>
</graphite_rollup_example>
<!-- Directory in <clickhouse-path> containing schema files for various input formats.
The directory will be created if it doesn't exist.
-->
<format_schema_path>/var/lib/clickhouse/format_schemas/</format_schema_path>
<!-- Default query masking rules, matching lines would be replaced with something else in the logs
(both text logs and system.query_log).
name - name for the rule (optional)
regexp - RE2 compatible regular expression (mandatory)
replace - substitution string for sensitive data (optional, by default - six asterisks)
-->
<query_masking_rules>
<rule>
<name>hide encrypt/decrypt arguments</name>
<regexp>((?:aes_)?(?:encrypt|decrypt)(?:_mysql)?)\s*\(\s*(?:'(?:\\'|.)+'|.*?)\s*\)</regexp>
<!-- or more secure, but also more invasive:
(aes_\w+)\s*\(.*\)
-->
<replace>\1(???)</replace>
</rule>
</query_masking_rules>
<!-- Uncomment to use custom http handlers.
rules are checked from top to bottom, first match runs the handler
url - to match request URL, you can use 'regex:' prefix to use regex match(optional)
methods - to match request method, you can use commas to separate multiple method matches(optional)
headers - to match request headers, match each child element(child element name is header name), you can use 'regex:' prefix to use regex match(optional)
handler is request handler
type - supported types: static, dynamic_query_handler, predefined_query_handler
query - use with predefined_query_handler type, executes query when the handler is called
query_param_name - use with dynamic_query_handler type, extracts and executes the value corresponding to the <query_param_name> value in HTTP request params
status - use with static type, response status code
content_type - use with static type, response content-type
response_content - use with static type, Response content sent to client, when using the prefix 'file://' or 'config://', find the content from the file or configuration send to client.
<http_handlers>
<rule>
<url>/</url>
<methods>POST,GET</methods>
<headers><pragma>no-cache</pragma></headers>
<handler>
<type>dynamic_query_handler</type>
<query_param_name>query</query_param_name>
</handler>
</rule>
<rule>
<url>/predefined_query</url>
<methods>POST,GET</methods>
<handler>
<type>predefined_query_handler</type>
<query>SELECT * FROM system.settings</query>
</handler>
</rule>
<rule>
<handler>
<type>static</type>
<status>200</status>
<content_type>text/plain; charset=UTF-8</content_type>
<response_content>config://http_server_default_response</response_content>
</handler>
</rule>
</http_handlers>
-->
<send_crash_reports>
<!-- Changing <enabled> to true allows sending crash reports to -->
<!-- the ClickHouse core developers team via Sentry https://sentry.io -->
<!-- Doing so at least in pre-production environments is highly appreciated -->
<enabled>false</enabled>
<!-- Change <anonymize> to true if you don't feel comfortable attaching the server hostname to the crash report -->
<anonymize>false</anonymize>
<!-- Default endpoint should be changed to different Sentry DSN only if you have -->
<!-- some in-house engineers or hired consultants who're going to debug ClickHouse issues for you -->
<endpoint>https://6f33034cfe684dd7a3ab9875e57b1c8d@o388870.ingest.sentry.io/5226277</endpoint>
</send_crash_reports>
<!-- Uncomment to disable ClickHouse internal DNS caching. -->
<!-- <disable_internal_dns_cache>1</disable_internal_dns_cache> -->
<!-- You can also configure rocksdb like this: -->
<!--
<rocksdb>
<options>
<max_background_jobs>8</max_background_jobs>
</options>
<column_family_options>
<num_levels>2</num_levels>
</column_family_options>
<tables>
<table>
<name>TABLE</name>
<options>
<max_background_jobs>8</max_background_jobs>
</options>
<column_family_options>
<num_levels>2</num_levels>
</column_family_options>
</table>
</tables>
</rocksdb>
-->
</clickhouse>
Clickhouse 创建数据
- 查看数据库
show databases

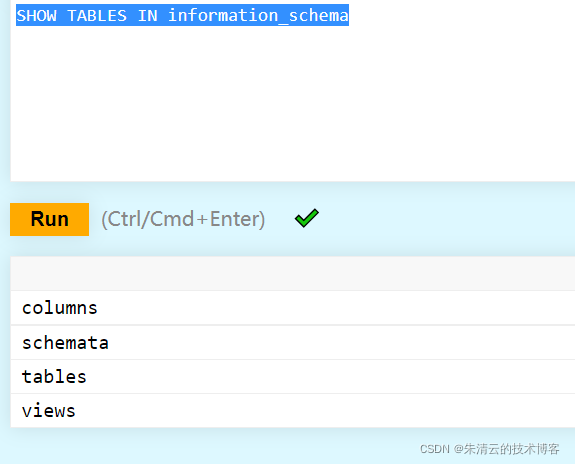
2. 查看数据库里面的表
show tables in information_schema
3. 创建数据和表
CREATE DATABASE gettingstarted
CREATE TABLE gettingstarted.clickstream (
customer_id String,
time_stamp Date,
click_event_type String,
country_code FixedString(2),
source_id UInt64
)
ENGINE = MergeTree()
ORDER BY (time_stamp)
执行完之后可以查看gettingstarted数据库中已经存在表clickstream

4. 查看表结构
desc gettingstarted.clickstream

5. 插入数据
//1.典型的全部字段插入
INSERT INTO gettingstarted.clickstream
VALUES ('customer1', '2021-10-02', 'add_to_cart', 'US', 568239 ) ;
//2. 指定部分字段插入
INSERT INTO gettingstarted.clickstream (customer_id, time_stamp, click_event_type)
VALUES ('customer2', '2021-10-30', 'remove_from_cart' )
//3. 排除特定字段部分插入
INSERT INTO gettingstarted.clickstream (* EXCEPT(country_code))
VALUES ('customer3', '2021-11-07', 'checkout', 307493 )
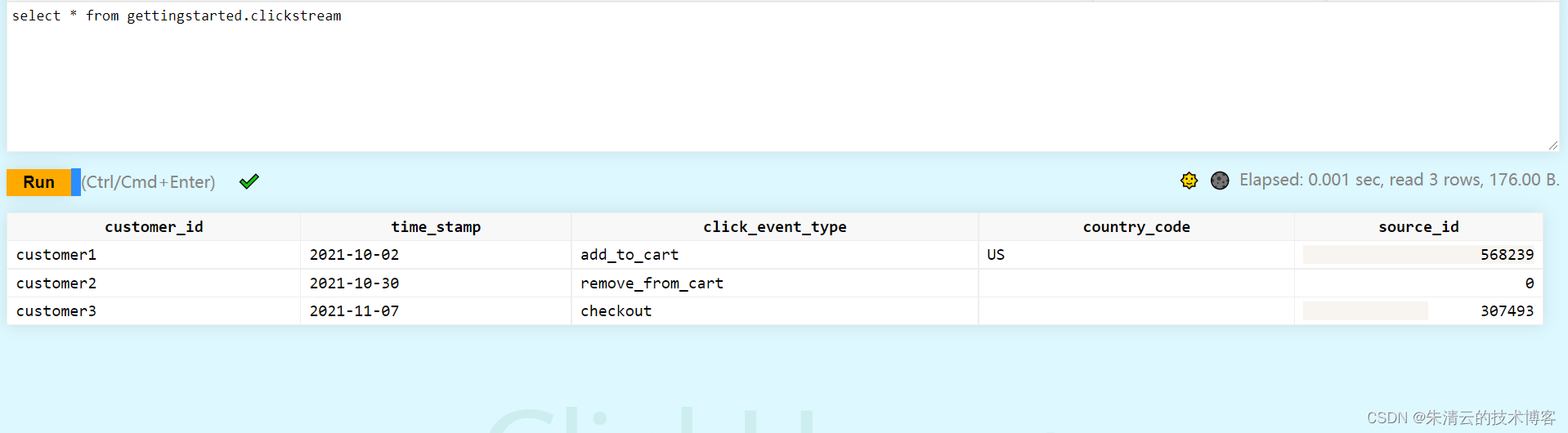
6.查询插入的数据
select * from gettingstarted.clickstream
结束语
本章主要简单介绍了Clickhouse的基本配置和方法。下个章节将看如何利用Clickhouse
来处理数以亿计的数据,而且其查询时间在几十毫秒以内。敬请期待!
参考文献
[1] https://www.zhihu.com/question/24110442/answer/851671343
[2] https://clickhouse.com/learn/lessons/gettingstarted

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








