For both AIX 5 and AIX 6, increase the number of aioserver processes from the default value. The recommended value for aio_maxreqs is 64k (65536). Confirm this value for both AIX 5 and AIX 6.
Confirm the aio_maxreqs value using the procedure for your release:
AIX 6.1
# ioo -o aio_maxreqs aio_maxreqs = 65536
AIX 5.3
# lsattr -El aio0 -a maxreqs maxreqs 65536 Maximum number of REQUESTS True
When performing an asynchronous I/O to a file system, note that each asynchronous I/O operation is tied to an asynchronous I/O server. Thus, the number of asynchronous I/O servers limits the number of concurrent asynchronous I/O operations in the system.
The initial number of servers that are started during a system restart is determined by the minservers parameter. As concurrent asynchronous I/O operations occur, additional asynchronous I/O servers are started, up to a maximum of the value set in the maxservers parameter.
每一个异步io操作都需要一个aioserver,当系统启动的时候启动aioserver的数量=minservers,随着异步操作的需求增大,aioserver会陆续启动更多个,直到数量=maxservers。
On AIX 5.3, if you are using Oracle Database with data files on a file system, then increase the default values for minservers and maxservers, as the default values for these parameters are too small. Increase the minservers and maxservers values based on I/O kprocs for each processor.
In general, to set the number of asynchronous I/O servers, complete the following procedure:
Adjust the initial value of maxservers to 10 times the number of disks that are to be used concurrently but no more than 80.(初始的maxservers设置为10倍的磁盘个数,但是不要超过80个)
Monitor the performance effects on the system during periods of high I/O activity. If all AIO server processes are started, then increase the maxservers value. Also, continue to monitor the system performance during peak I/O activity to determine if there was a benefit from the additional AIO servers. Too many asynchronous I/O servers increase memory and processor overload of additional processes, but this disadvantage is small.(在磁盘使用高峰期观察aioserver的数量,如果所有的aioserver都启动了,那就需要再扩大aioserver的数量了,不过不建议设置太多的aioserver,因为这会增加内存和cpu的消耗)
To monitor the number of AIO server processes that have started, enter the following command:
# ps -ek|grep -v grep|grep -v posix_aioserver|grep -c aioserver
下面转一篇专门介绍aix异步io的文章:http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/aix/library/1212_weixy_aixiaio/
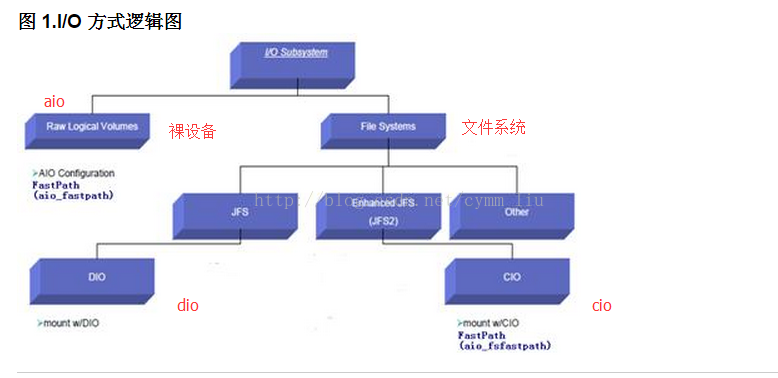
几种 I/O 类型概念的介绍
AIO
AIO 的全称为 Asynchronous I/O,即异步 I/O。在 AIO 的工作模式下,应用程序向操作系统发起 I/O 请求(读 / 写)以后,不必等 I/O 完成,即可发起新的 I/O 请求。通过这种方法,可以提示提升 I/O 吞吐量和性能。从 AIX5L 起,AIX 支持两种 AIO:legacy AIO 和 POSIX AIO。AIO 既支持文件系统也支持裸设备。
DIO
AIO 的全称为 Direct I/O,即直接 I/O。在 DIO 的工作模式下,数据直接从磁盘传送到应用的缓存,而不经过文件的 buffer cache。DIO 是 JFS 文件系统的一个选项,对于一些应用,如 Oracle 数据库,它本身有自己的缓存,如果再使用文件系统缓存,反而会造成性能的下降,在这种情况下,使用 DIO 会提升一定的性能。但是,当应用有大量的顺序读 I/O 的时候,使用 DIO 的方式由于缺少读缓存,会造成一定的性能下降。
CIO
CIO 的全称为 Concurrent I/O 即并发 I/O。CIO 的工作模式是建立在 DIO 模式基础之上的。在 JFS2 的环境下,如果应用需要绕过文件系统缓存,经常会使用 CIO 模式来替代 DIO 模式。在 CIO 的工作模式下,数据会从磁盘直接传递到应用的缓存。从 AIX 5.2.10 开始,JFS2 支持 CIO 选项。
我们知道,在文件系统中,为了保证数据和文件系统的一致性,需要使用 inode lock。Inode lock 保证一个文件在某一时刻,只有一个写 I/O,并且为了避免读到 stale 的数据,写的时候并发读也是不被允许的。
而在 CIO 的工作模式下,JFS2 会绕过 inode lock,从而实现多个线程可以同时读写一个共享文件。而在这种情况下,数据的一致性就需要应用或数据库来提供,如 DB2 Pure Scale、Oracle RAC。
AIO、DIO、CIO 的区别
AIO 在 AIX6.1 中默认是打开的,它既支持文件系统,也支持裸设备。而 DIO 和 CIO 是文件系统的一个选项。我们可以在 mount 文件系统的时候,进行设置,执行命令如下 :
#mount -o dio /weixinyu #mount -o cio /weixinyu
对于已经挂载的文件系统,也可以修改其 I/O 方式 :
# chfs -a options=rw,dio /weixinyu # chfs -a options=rw,aio /weixinyu
DIO 与 CIO 本质上并不矛盾,均属于“绕过文件系统缓存”的 I/O 方式。不同的是,在 DIO 的工作模式下,文件系统中的数据一致性是通过 inode lock 来实现的;而 CIO 为了提高文件的并发读写性,会绕过 inode lock,让应用来提供文件一致性锁。
AIO 对于裸设备的支持与 CIO 对文件系统支持的方式类似,都是通过“FastPath”来实现。前者受内核参数 fastpath 控制,后者受内核参数 fsfastpath 控制。在 AIX6.1 中,这两个参数默认都是设置为 1。
# ioo -F -a |grep -i path
aio_fastpath = 1aio_fsfastpath = 1
三种 I/O 方式的逻辑关系如下图:
AIO 的参数设置与调优
AIO 的两种支持方式
在上文中我们已经提到过,AIO 既支持文件系统,也支持裸设备。在文件系统模式下,AIO 通过文件系统缓存来实现异步 I/O。在裸设备的模式下,AIO 通过“FastPath”来实现,它的作用是将原始逻辑卷直接传递到磁盘层的 AIO 请求。在 AIX6.1 中,这个参数是默认打开,设置为 1。
# ioo -F -a |grep -i path
aio_fastpath = 1
AIO 对文件系统的支持逻辑图如下(通过 Kproc 即 AIO Server 处理 I/O)。在这种工作模式下,将会由 kproc 进程来控制 I/O 请求,而 kproc 的数量(即 AIO Server 的数量)将会决定系统处理的最多 AIO 请求的数量。
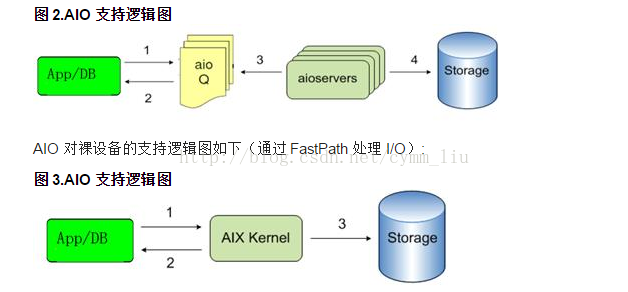
Fastpath 不需要 AIO Server 来处理 I/O 请求,它可以减少 CPU 上下文切换,降低 CPU 开销。
AIO 的主要内核参数
在 AIX6.1 中,使用 ioo 命令可以查看与 AIO 相关的内核参数。
# ioo -F -a |grep -i aio aio_maxreqs = 131072 aio_maxservers = 30 aio_minservers = 3
kproc 的最小值由系统参数 minservers 决定,最大值由系统参数 maxservers 决定。如果异步 I/O 请求的数量很多,就需要将 maxservers 的数值增大。由于 AIX 内核可以自动生成额外的 kproc,因此在大多数情况下,minservers 的数值不需要手动调整。需要注意的是,minservers 和 maxservers 两个参数只对文件系统有效,对于 AIO 的裸设备模式以及 CIO 的模式是无效的,这两种 I/O 由 FastPath 来处理,而不是 kproc。
在 AIX6.1 中,aio_maxservers 和 aio_minservers 的默认数值分别为 30 和 3,一般认为这两个数值是每个 CPU 的 AIO Server 数量设置。
AIX6.1 中的 maxreqs 参数决定 AIO 系统里可以处理最多并发 I/O 请求的数量。这个参数对于 fast path 的 I/O 类型是不起作用的。我们在调整 minservers 和 maxservers 参数时,也需要监控 maxreqs 数值。
在 AIX6.1 中,可以用如下命令查看运行的 AIO Server 的数量:
# pstat -a |grep -c aios |wc -l 1 # ioo -F -a |grep -i aio_minservers aio_minservers = 3
# pstat -a |grep -c kproc |wc -l 1
从上面结果可以看出,目前系统中的 AIO 请求很少,只有一个 AIO server 在运行。而 AIO server 的数量与 kproc 的数量,是一致的。
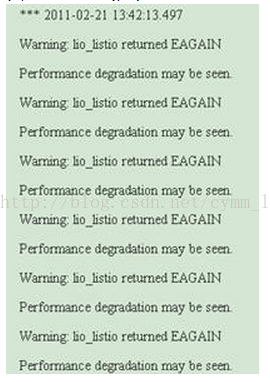
在系统中,如果 maxreqs 和 maxservers 设置的太低低,可能会造成数据库报错或者宕机,查看 Oracle 的 bdump 文件可以发现如下报错:
图 4.Oracle 报错
aio_server_inactivity 参数控制的是 AIO Server 的退出时间:即当 AIO server 空闲的时间超过 aio_server_inactivit 设置的数值时,AIO server 将会退出,默认这个数值默认为 300 秒。
一般情况下,运行的 AIO Server 数量不会低于 aio_minservers 参数的设置,在上面的例子中,之所以出现 AIO Server 的数量低于 aio_minservers 参数设置的数值,是因为该系统是一个空闲的系统,没有任何负载和 AIO 请求。aio_server_inactivity 在 AIX6.1 中一般不需要设置。
aio_active 参数不需要设置,默认为 0。只有当 AIO kernel extensors 被使用时,才会变成 1。
# ioo -a | grep active aio_active = 0 posix_aio_active = 0 # ioo -o aio_active=1 ioo: 1485-114 Static tunable aio_active cannot be changed
如何判断 AIO 性能问题
在 AIX 操作系统中,可以通过系统命令查看 AIO 是否存在性能问题 :
# iostat -A 1 3 |grep -v hdisk
图 5.AIO 性能监控

在上面的命令中,我采用的监控时间是 1 秒,因此下面几个数值的描述都是“每秒”。
用红框标注的几个数值需要关注:
avgc: 每秒全局非 FastPath AIO 平均请求数量。如果 iostat 命令时间间隔为 3 秒,那么此项描述应为:3 秒内全局非 FastPath AIO 请求的平均数量,下不赘述。
avfc: 每秒裸设备(不包括 CIO FastPath IOs)FastPath AIO 平均请求数量。
maxgc:1 秒内,非 FastPath AIO 达到的最大值。
maxfc: 1 秒内,FastPath AIO 达到的最大值。
maxreqs: 参数设定的系统最大允许的 AIO 请求数量。
在命令的输出结果中,如果 maxgc 或 maxfc 的数值接近 maxreqs 或 maxservers 的数值,那么就需要增大系统中 maxreqs 或 maxservers 设置。
AIO 内核参数设置的方法
在 AIX6.1 中,可以用 ioo 命令设置相关的参数。例如我们将 AIO Server 最大值设置为 40,最小值设置为 10:
# ioo -p -o aio_maxservers=40 -o aio_minservers=10 ioo: 1485-110 Invalid tunable name aix_maxservers Setting aio_minservers to 10 in nextboot file Setting aio_minservers to 10
我们将 maxreqs 的数值设置为 666666
# ioo -p -o aio_maxreqs=666666 Setting aio_maxreqs to 666666 in nextboot file Setting aio_maxreqs to 666666
设置 fast path 参数,1 为打开,设置为 0 则关闭:
# ioo -o aio_fastpath=1 Setting aio_fastpath to 1 Warning: a restricted tunable has been modified # ioo -o aio_fsfastpath=1 Setting aio_fsfastpath to 1 Warning: a restricted tunable has been modified
一般情况下,对于常见的应用,主要参数建议设置的数值为:
表 1. 参数设置建议值
| 默认值 | OLTP | SAP | |
|---|---|---|---|
| aio_minservers | 3 | 200 | 400 |
| aio_maxservers | 10 | 800 | 1200 |
| maxreqs | 4096 | 16384 | 16384 |
总结
AIO 在 AIX6.1 及 AIX7.1 中已默认开启,不需要手动开启。AIO 对于数据库而言是很重要的,如果参数设置的不对,将会造成性能大幅下降。因此,在规划数据库或者进行数据库调优时,应充分考虑到 I/O 的方式以及相关参数的设置。






















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








