这个是用来执行计划任务的。
有两个方法
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long period,
TimeUnit unit);
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long delay,
TimeUnit unit);
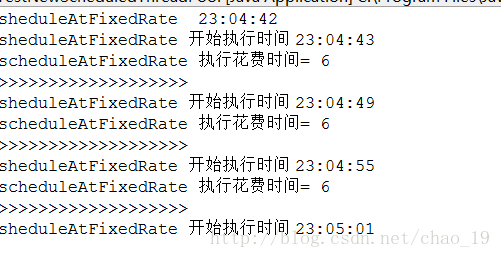
第一个方法scheduleAtFixedRate 以固定的频率执行,首先会延迟 initialDelay开始执行。然后下一次执行,距离上一次开始的执行的时间间隔为 period。 period是计算两个任务开始执行的时间的间隔的。
此时会存在一个情况,就是这个任务执行的时间超过了,period时间,那么下一个任务将会在任务执行完毕后启动。
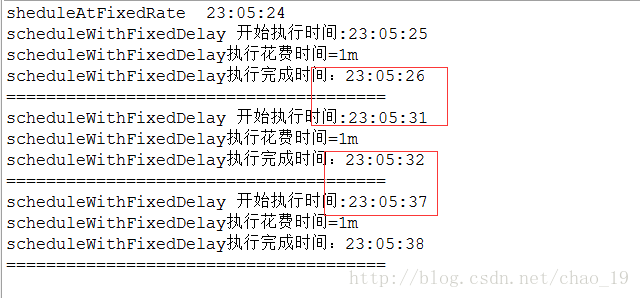
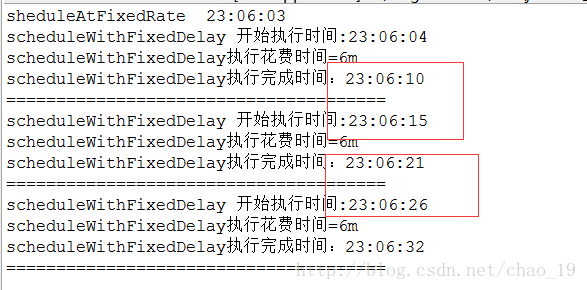
scheduleWithFixedDelay ,它也是首先延迟initialDelay开始执行。然后下一次执行,是距离上一次执行完毕的时间间隔为delay。 delay是计算上一个任务执行完毕的时间和本次任务开始时间的差值,此值和任务的执行时间就没有关系了。
下面是代码:
initialDelay 为1s ,delay 为5s 。 任务执行时间 为 1s 或者6s。
public class TestNewScheduledThreadPool {
public static void main(String args[]) {
ScheduledExecutorService service = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2);
System.out.println("sheduleAtFixedRate " + DateFormat.getTimeInstance().format(new Date()));
//sheduleAtFixedRate(service, 1000);
//sheduleAtFixedRate(service, 6000);
scheduleWithFixedDelay(service, 1000);
//scheduleWithFixedDelay(service, 6000);
}
private static void sheduleAtFixedRate(ScheduledExecutorService service, final int sleepTime) {
service.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
long start = new Date().getTime();
System.out.println("sheduleAtFixedRate 开始执行时间 " + DateFormat.getTimeInstance().format(new Date()));
try {
Thread.sleep(sleepTime);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
// long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
long end = new Date().getTime();
System.out.println("scheduleAtFixedRate 执行花费时间= " + (end - start) / 1000);
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");
}
}, 1000, 5000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
private static void scheduleWithFixedDelay(ScheduledExecutorService service, final int sleepTime) {
service.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
long start = new Date().getTime();
System.out.println("scheduleWithFixedDelay 开始执行时间:" + DateFormat.getTimeInstance().format(new Date()));
try {
Thread.sleep(sleepTime);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
long end = new Date().getTime();
System.out.println("scheduleWithFixedDelay执行花费时间=" + (end - start) / 1000 + "m");
System.out.println("scheduleWithFixedDelay执行完成时间:" + DateFormat.getTimeInstance().format(new Date()));
System.out.println("======================================");
}
}, 1000, 5000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
}






















 5万+
5万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








