控制台输入输出
Scanner
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> arry=new ArrayList<Integer> ();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(sc.hasNextLine())
{
String str=sc.nextLine();
Scanner scc=new Scanner(str);
while(scc.hasNextInt())
{
temp=scc.nextInt();
arry.add(temp);
}
scc.close();
for (int ss : arry) {
System.out.print(ss+" ");
}
arry.clear();
System.out.println();
}
sc.close();
}Byte Streams
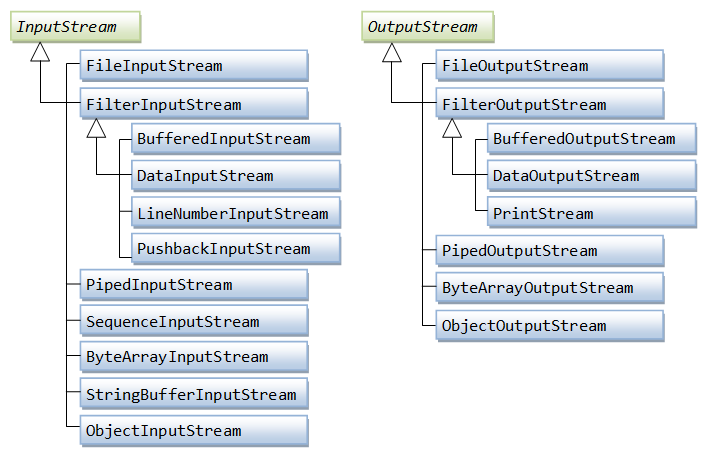
Java byte streams are used to perform input and output of 8-bit bytes. Though there are many classes related to byte streams but the most frequently used classes are , FileInputStream and FileOutputStream.
import java.io.*;
public class CopyFile {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
FileInputStream in = null;
FileOutputStream out = null;
try {
in = new FileInputStream("input.txt");
out = new FileOutputStream("output.txt");
int c;
while ((c = in.read()) != -1) {
out.write(c);
}
}finally {
if (in != null) {
in.close();
}
if (out != null) {
out.close();
}
}
}
}Character Streams
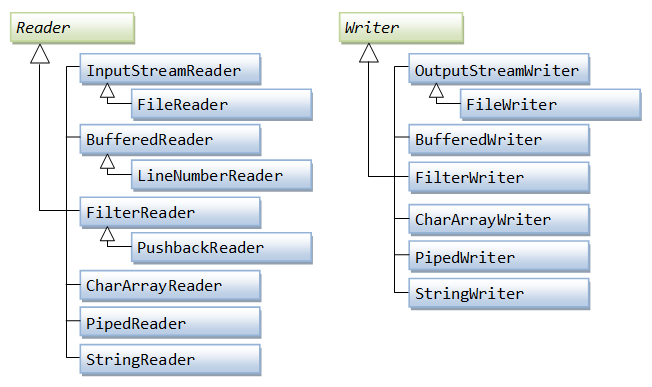
Java Byte streams are used to perform input and output of 8-bit bytes, where as Java Character streams are used to perform input and output for 16-bit unicode. Though there are many classes related to character streams but the most frequently used classes are , FileReader and FileWriter.. Though internally FileReader uses FileInputStream and FileWriter uses FileOutputStream but here major difference is that FileReader reads two bytes at a time and FileWriter writes two bytes at a time.
import java.io.*;
public class CopyFile {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
FileReader in = null;
FileWriter out = null;
try {
in = new FileReader("input.txt");
out = new FileWriter("output.txt");
int c;
while ((c = in.read()) != -1) {
out.write(c);
}
}finally {
if (in != null) {
in.close();
}
if (out != null) {
out.close();
}
}
}
}Standard Streams
All the programming languages provide support for standard I/O where user’s program can take input from a keyboard and then produce output on the computer screen. If you are aware if C or C++ programming languages, then you must be aware of three standard devices STDIN, STDOUT and STDERR. Similar way Java provides following three standard streams
Standard Input: This is used to feed the data to user’s program and usually a keyboard is used as standard input stream and represented as System.in.
Standard Output: This is used to output the data produced by the user’s program and usually a computer screen is used to standard output stream and represented as System.out.
Standard Error: This is used to output the error data produced by the user’s program and usually a computer screen is used to standard error stream and represented as System.err.
import java.io.*;
public class ReadConsole {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
InputStreamReader cin = null;
try {
cin = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter characters, 'q' to quit.");
char c;
do {
c = (char) cin.read();
System.out.print(c);
} while(c != 'q');
}finally {
if (cin != null) {
cin.close();
}
}
}
}FileInputStream
This stream is used for reading data from the files. Objects can be created using the keyword new and there are several types of constructors available.
import java.io.*;
public class fileStreamTest{
public static void main(String args[]){
try{
byte bWrite [] = {11,21,3,40,5};
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("test.txt");
for(int x=0; x < bWrite.length ; x++){
os.write( bWrite[x] ); // writes the bytes
}
os.close();
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("test.txt");
int size = is.available();
for(int i=0; i< size; i++){
System.out.print((char)is.read() + " ");
}
is.close();
}catch(IOException e){
System.out.print("Exception");
}
}
}JAVA I/O Re-direct
//out
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.PrintStream;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
PrintStream ps=new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("work"));
System.setOut(ps);
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
}
//in
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("work");
System.setIn(fis);
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
while(sc.hasNextLine())
{
System.out.println(sc.nextLine());
}
}
}






















 369
369

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








