代码:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int fd=-1;
char filename[]="test.txt";
fd=open(filename,O_RDWR);
if(-1==fd)
{
printf("Open file %s failure!,fd:%d\n",filename,fd);
}
else
{
printf("Open file %s succees!,fd:%d\n",filename,fd);
}
return 0;
}
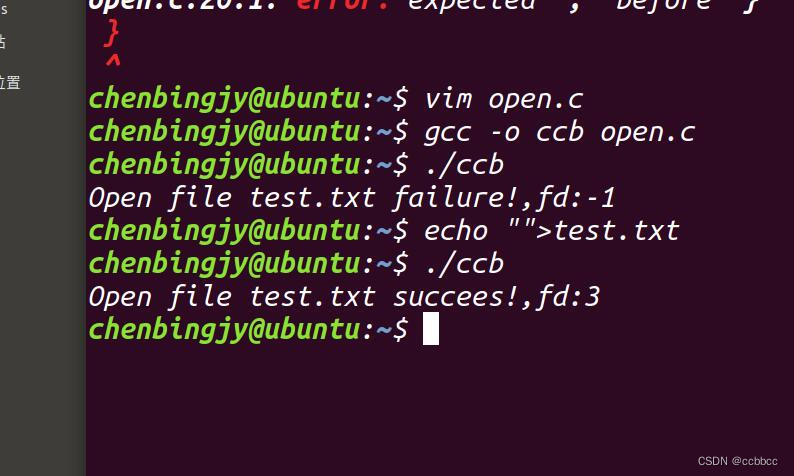
编译运行





















 8万+
8万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








