这个RISC CPU模型的微结构,其指令集是基于商用RISC处理器和类似MMX的DSP程序指令定义的,由39条之多的指令组成(算术、逻辑、分支、浮点、SIMD(类似MMX))。
本次通过译码和执行单元学习下这些指令的具体含义,取指前面已有学习,这里也会再来看一下波形的过程,下面先看看指令码的组成:32bit
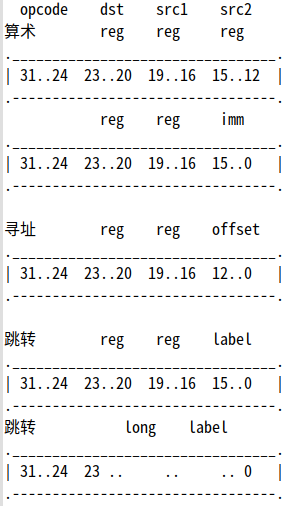
图示了计算alu和数据load上的指令码的格式,分支没有列出来,每一类指令接下来都会从取指、译码、执行的波形中分析一下。
1 汇编器和译码单元
例子里提供了一个perl语言实现的汇编器,就是将汇编语言转换为上面的二进制指令码。不复杂,学习下perl的基本语法(不用花太多时间在这里)就能看得懂。下面图示了一部分,再用字符替代和分割后,就是一对一地转换了:
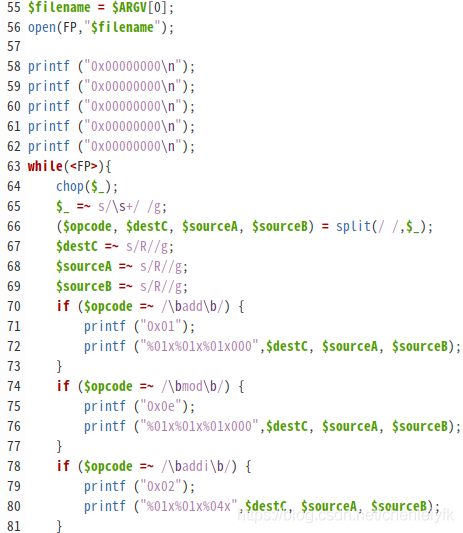
译码单元差不多把上面的意思理解翻译一下,直接上代码吧(部分代码),一看就懂:
struct decode : sc_module {
sc_in<bool> resetin; // input reset
sc_in<unsigned> instruction; // fetched instruction
sc_in<unsigned> pred_instruction; // fetched instruction
sc_in<bool> instruction_valid; // input valid
sc_in<bool> pred_inst_valid; // input valid
sc_in<bool> destreg_write; // register write enable
sc_in<unsigned> destreg_write_src; // which register to write?
sc_in<signed> alu_dataout; // data from ALU
sc_in<signed> dram_dataout; // data from Dcache
sc_in<bool> dram_rd_valid; // Dcache read data valid
sc_in<unsigned> dram_write_src; // Dcache data write to which reg
sc_in<signed> fpu_dout; // data from FPU
sc_in<bool> fpu_valid; // FPU data valid
sc_in<unsigned> fpu_destout; // write to which register
sc_in<bool> clear_branch; // clear outstanding branch
sc_in<bool> display_done; // display to monitor done
sc_in<unsigned > pc; // program counter from IFU
sc_in<bool> pred_on; // branch prediction is on
sc_out<unsigned > br_instruction_address; // branch invoke instruction
sc_out<bool> next_pc; // next pc ++ ?
sc_out<bool> branch_valid; // branch valid signal
sc_out<unsigned > branch_target_address; // branch target address
sc_out<bool> mem_access; // memory access valid
sc_out<unsigned > mem_address; // memory physical address
sc_out<int> alu_op; // ALU/FPU/MMU Opcode
sc_out<bool> mem_write; // memory write enable
sc_out<unsigned> alu_src; // destination register number
sc_out<bool> reg_write; // not implemented
sc_out<signed int> src_A; // operand A
sc_out<signed int> src_B; // operand B
sc_out<bool> forward_A; // data forwarding to operand A
sc_out<bool> forward_B; // data forwarding to operand B
sc_out<bool> stall_fetch; // stall fetch due to branch
sc_out<bool> decode_valid; // decoder output valid
sc_out<bool> float_valid; // enable FPU
sc_out<bool> mmx_valid; // enable MMU
sc_out<bool> pid_valid; // load process ID
sc_out<signed> pid_data; // process ID value
sc_in_clk CLK;
signed int cpu_reg[32]; //CPU register
signed int vcpu_reg[32]; //virtual CPU register
bool cpu_reg_lock[32]; //lock architectural state register
unsigned int pc_reg; //pc register
unsigned int jalpc_reg; //jump back register
//Constructor
SC_CTOR(decode) {
SC_CTHREAD(entry, CLK.pos());
FILE *fp = fopen("register.img","r");
int size=0;
unsigned mem_word;
printf("** ALERT ** ID: initialize Architectural Registers\n");
while (fscanf(fp,"%x", &mem_word) != EOF) {
cpu_reg[size] = mem_word;
size++;
}
pc_reg = 0;
jalpc_reg = 0;
for (int j =0; j<32; j++)
vcpu_reg[j] = 0;
for (int k =0; k<32; k++)
cpu_reg_lock[k] = 0;
}
// Process functionality in member function below
void entry();
};
void decode::entry()
{
unsigned int instr_tmp = 0;
unsigned int opcode_tmp = 0;
unsigned int regA_tmp = 0;
unsigned int regB_tmp = 0;
unsigned int regC_tmp = 0;
unsigned int imm_tmp = 0;
unsigned int offset_tmp = 0;
signed int label_tmp = 0;
unsigned int longlabel_tmp = 0;
signed int srcA_tmp = 0;
signed int srcB_tmp = 0;
signed int srcC_tmp = 0;
int i;
bool branch_direction_tmp = 0;
branch_valid.write(false);
decode_valid.write(false);
float_valid.write(false);
mmx_valid.write(false);
wait(2);
while (true) {
if (destreg_write.read() == true) {
cpu_reg[destreg_write_src.read()] = alu_dataout.read();
}
if (dram_rd_valid.read() == true) {
cpu_reg[dram_write_src.read()] = dram_dataout.read();
}
if (fpu_valid.read() == true) {
cpu_reg[fpu_destout.read()] = fpu_dout.read();
}
if ((instruction_valid.read() == true)) {
pc_reg = pc.read();
if (clear_branch.read() == true) {
branch_valid.write(false);
}
instr_tmp = instruction.read();
opcode_tmp = (instr_tmp & 0xff000000) >> 24;
regC_tmp = (instr_tmp & 0x00f00000) >> 20;
regA_tmp = (instr_tmp & 0x000f0000) >> 16;
regB_tmp = (instr_tmp & 0x0000f000) >> 12;
imm_tmp = (instr_tmp & 0x0000ffff);
offset_tmp = (instr_tmp & 0x00000fff);
label_tmp = (instr_tmp & 0x0000ffff);
longlabel_tmp = (instr_tmp & 0x00ffffff);
branch_direction_tmp = (instr_tmp & 0x00008000) >> 15;
if (branch_direction_tmp) { // handle backward branch
label_tmp = - (0xffff - label_tmp + 1) ;
}
//printf("opcode = %d regC = %d regA = %d regB = %d\n",opcode_tmp, regC_tmp, regA_tmp, regB_tmp);
srcA_tmp = cpu_reg[regA_tmp];
srcB_tmp = cpu_reg[regB_tmp];
srcC_tmp = cpu_reg[regC_tmp];
wait()
switch(opcode_tmp) {
case 0x0: // halt
wait();
wait();
break;
case 0x01: // add R1, R2, R3
src_A.write(srcA_tmp);
src_B.write(srcB_tmp);
alu_src.write(regC_tmp);
alu_op.write(3);
decode_valid.write(true);
wait();
decode_valid.write(false);
wait();
break;
case 0x02: // addi R1, R2, #value
src_A.write(srcA_tmp);
src_B.write(imm_tmp);
alu_src.write(regC_tmp);
alu_op.write(3);
decode_valid.write(true);
wait();
decode_valid.write(false);
wait();
break;
-------------------------------
-------------------------------
case 0x0a: // and R1, R2, R3
src_A.write(srcA_tmp);
src_B.write(srcB_tmp);
alu_src.write(regC_tmp);
alu_op.write(8);
decode_valid.write(true);
wait();
decode_valid.write(false);
wait();
break;
case 0x0b: // or R1, R2, R3
src_A.write(srcA_tmp);
src_B.write(srcB_tmp);
alu_src.write(regC_tmp);
alu_op.write(9);
decode_valid.write(true);
wait();
decode_valid.write(false);
wait();
break;
case 0x0c: // xor R1, R2, R3
src_A.write(srcA_tmp);
src_B.write(srcB_tmp);
alu_src.write(regC_tmp);
alu_op.write(10);
decode_valid.write(true);
wait();
decode_valid.write(false);
wait();
break;
-------------------------------
-------------------------------
case 0x10: // beq R1, R2, label
src_A.write(0);
src_B.write(0);
alu_src.write(0);
alu_op.write(3);
decode_valid.write(true);
if (srcC_tmp == srcA_tmp) {
branch_target_address.write(pc_reg + label_tmp);
br_instruction_address.write(instr_tmp);
branch_valid.write(true);
} else {
regC_tmp, srcC_tmp, regA_tmp, srcA_tmp);
}
wait();
branch_target_address.write(pc_reg + 1);
decode_valid.write(false);
wait();
break;
-------------------------------
-------------------------------
case 0xff: // QUIT
decode_valid.write(false);
float_valid.write(false);
mmx_valid.write(false);
wait();
sc_stop();
wait();
wait();
break;
default :
wait();
break;
}
next_pc.write(true);
wait();
}
else {
next_pc.write(true);
wait();
}
}
} // end of entry function2 算术逻辑操作--加减乘除等
从汇编文件看,从零开始,刚好和PC计数一致,
第17条指令 add R1, R2, R3
第25条指令 addi R1, R3, 14
第31条指令 sub R4, R5, R6
第39条指令 mul R1, R1, R4
第87条指令 div R1, R1, R3
这里着重分析译码的波形和执行单元操作,把寄存器的变化放在move数据里面,另外逻辑的操作也类似,这里不再观察,我们自行观摩代码吧。
struct exec : sc_module {
sc_in<bool> reset; // reset not used.
sc_in<bool> in_valid; // input valid
sc_in<int> opcode; // opcode from ID
sc_in<bool> negate; // not implemented
sc_in<int> add1; // not implemented
sc_in<bool> shift_sel; // not implemented
sc_in<signed int> dina; // operand A
sc_in<signed int> dinb; // operand B
sc_in<bool> forward_A; // data forwarding A valid
sc_in<bool> forward_B; // data forwarding B valid
sc_in<unsigned> dest; // destination register number
sc_out<bool> C; // Carry bit
sc_out<bool> V; // Overflow bit
sc_out<bool> Z; // Zero bit
sc_out<signed int> dout; // output data
sc_out<bool> out_valid; // output valid
sc_out<unsigned> destout; // write to which registers?
sc_in_clk CLK;
SC_CTOR(exec) {
SC_CTHREAD(entry, CLK.pos());
}
void entry();
};
void exec::entry(){
int opcode_tmp = 0;
int add1_tmp = 0;
signed int dina_tmp = 0;
signed int dinb_tmp = 0;
sc_dt::int64 dout_tmp = 0;
unsigned int dest_tmp = 0;
// main loop
// initialization of output
wait(3);
while(1) {
if (in_valid.read() == true) {
dina_tmp = dina.read();
dinb_tmp = dinb.read();
opcode_tmp = opcode.read();
dest_tmp = dest.read();
// output MUX
switch (opcode_tmp) {
case 0: // Stall
// dout_tmp = dout_tmp; // keeps its value
wait();
break;
case 1: // add with carry
dout_tmp = dina_tmp + dinb_tmp + add1_tmp;
wait();
break;
case 2: // sub with carry
dout_tmp = dina_tmp - dinb_tmp - add1_tmp;
wait();
break;
case 3: // add without carry
dout_tmp = dina_tmp + dinb_tmp;
wait();
break;
case 4: // sub without carry
dout_tmp = dina_tmp - dinb_tmp;
wait();
break;
case 5: // multiply assume 2 clock cycle multiplication
dout_tmp = dina_tmp * dinb_tmp;
wait(); // so that BC has something to do
wait();
break;
case 6: // divide assume 2 clock cycle multiplication
if (dinb_tmp == 0) {
printf("Division Exception - Divide by zero \n");
} else {
dout_tmp = dina_tmp / dinb_tmp;
}
wait(); // so that BC has something to do
wait();
break;
case 7: // bitwise NAND
dout_tmp = ~(dina_tmp & dinb_tmp);
wait();
break;
case 8: // bitwise AND
dout_tmp = dina_tmp & dinb_tmp;
wait();
break;
case 9: // bitwise OR
dout_tmp = dina_tmp | dinb_tmp;
wait();
break;
case 10: // bitwise XOR
dout_tmp = dina_tmp ^ dinb_tmp;
wait();
break;
case 11: // bitwise complement
dout_tmp = ~ dina_tmp;
wait();
break;
case 12: // left shift
dout_tmp = dina_tmp << dinb_tmp;
wait();
break;
case 13: // right shift
dout_tmp = dina_tmp >> dinb_tmp;
wait();
break;
case 14: // modulo
dout_tmp = dina_tmp % dinb_tmp;
wait();
break;
default:
printf("ALU: Bad Opcode %d.\n",opcode_tmp);
break;
}
dout.write(static_cast<signed int>(dout_tmp));
out_valid.write(true);
destout.write(dest_tmp);
if (dout_tmp == 0) {
Z.write(true);
} else {
Z.write(false);
}
sc_dt::int64 abs_dout = dout_tmp >= 0 ? dout_tmp : -dout_tmp;
const sc_dt::int64 carry_mask = sc_dt::int64(1) << 32;
if (abs_dout & carry_mask) {
C.write(true);
} else {
C.write(false);
}
if (abs_dout > carry_mask) {
V.write(true);
} else {
V.write(false);
}
wait();
out_valid.write(false);
wait();
} else {
wait();
}
}
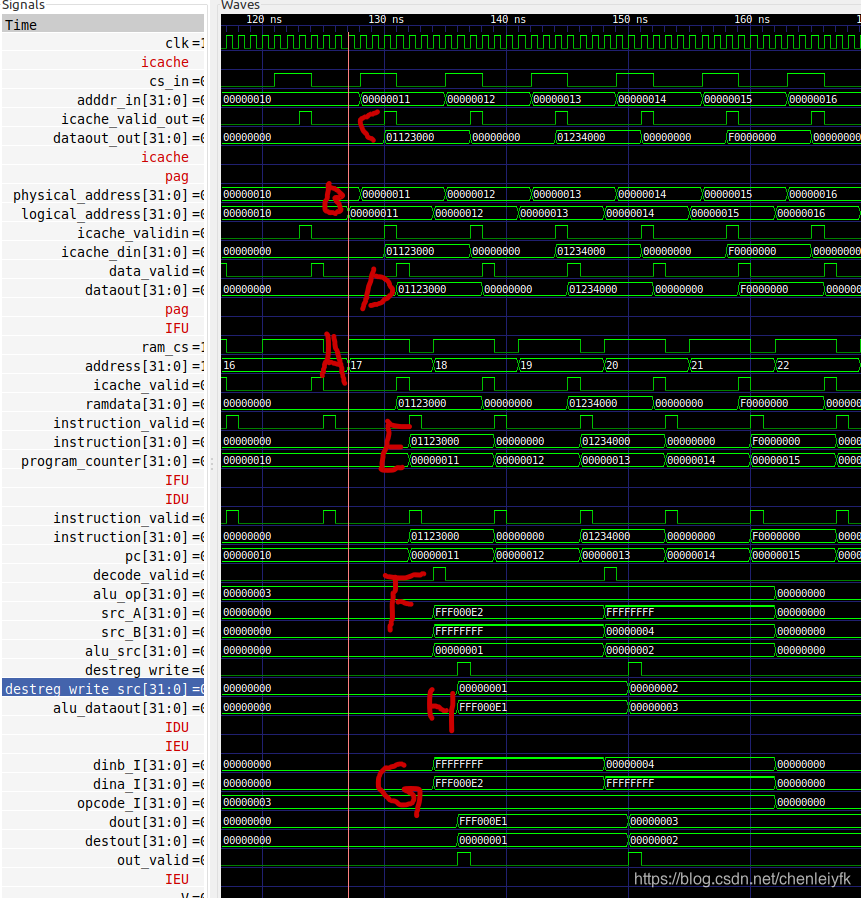
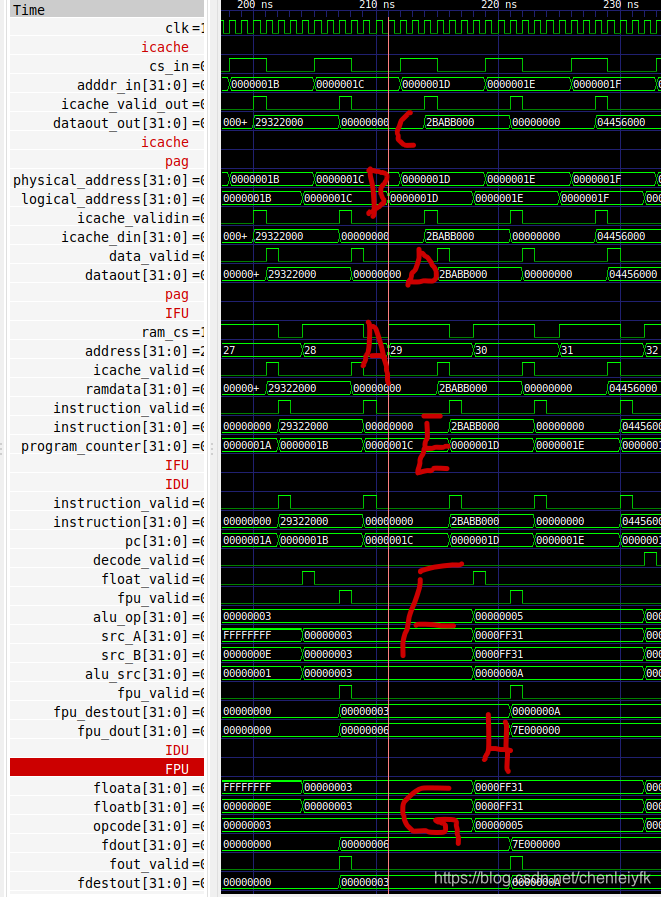
}第17条指令 add R1, R2, R3:A--IFU发起读地址和使能信号,B--pag拿过地址将其转换为物理地址,C--icache获得物理地址开启取指并发出(始终命中)。D--pag待有效信号将获取指令返回给IFU。E--IFU待有效信号将获取指令输出给IDU,F--IDU进行指令译码输出相应的alu和有效指示,G--IEU执行,两拍后返回结果。H--这里IDU执行了R1结果的写回。
第25条指令 addi R1, R3, 14:除了PC计数其他的都一样。
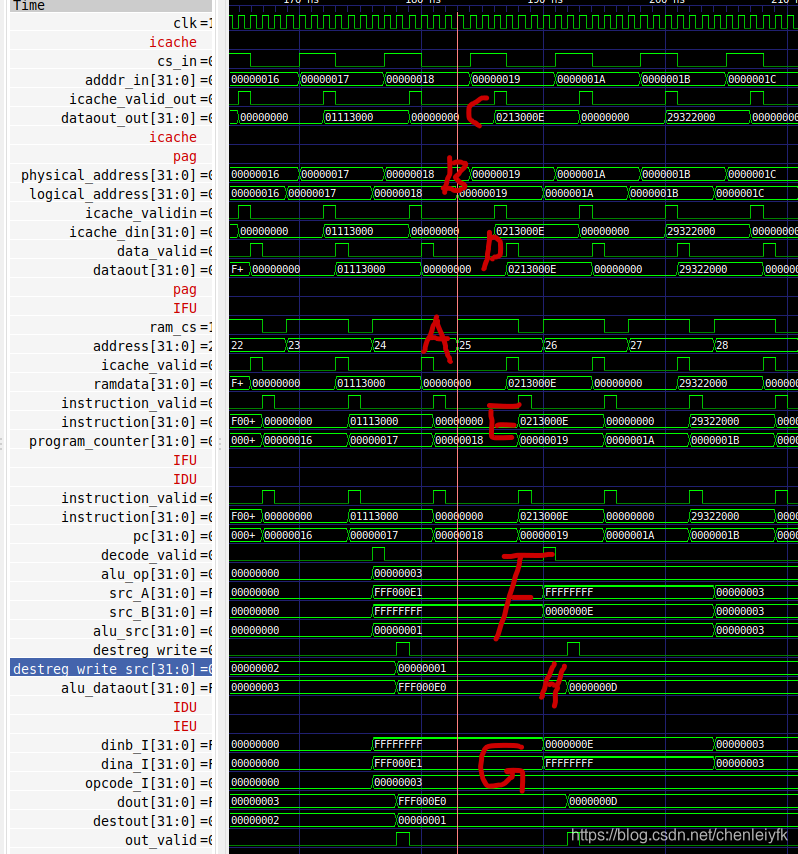
减法就不看了,第39条指令 mul R1, R1, R4:注意操作码和延迟节拍的变化 。除法的和乘法的一样的,不同的就是操作码了。

3 浮点操作
浮点此处是32bit的,其表示方式有相应的标准IEEE可去参考,大致的步骤如下:

struct floating : sc_module {
sc_in<bool> in_valid; // input valid bit
sc_in<int> opcode; // opcode
sc_in<signed int> floata; // operand A
sc_in<signed int> floatb; // operand B
sc_in<unsigned> dest; // write to which register
sc_out<signed int> fdout; // FPU output
sc_out<bool> fout_valid; // output valid
sc_out<unsigned> fdestout; // write to which register
sc_in_clk CLK;
SC_CTOR(floating) {
SC_CTHREAD(entry, CLK.pos());
}
void entry();
};
void floating::entry(){
int opcode_tmp = 0;
signed int dout_tmp = 0;
unsigned int dest_tmp = 0;
unsigned int fpua_sign_tmp;
unsigned int fpua_exponent_tmp;
unsigned int fpua_significand_tmp;
unsigned int fpub_sign_tmp;
unsigned int fpub_exponent_tmp;
unsigned int fpub_significand_tmp;
const char * opcode_encode="";
unsigned int fpua_tmp;
unsigned int fpub_tmp;
int exponent_diff_tmp = 0;
unsigned int significant_result = 0;
unsigned int overflow_sign_tmp = 0;
unsigned int result_exp_tmp = 0;
unsigned int result_sign_tmp = 0;
wait(3);
while(true) {
do { wait(); }
while ( !(in_valid == true) );
dest_tmp = dest.read();
opcode_tmp = opcode.read();
fpua_tmp = floata.read();
fpub_tmp = floatb.read();
fpua_sign_tmp = (fpua_tmp & 0x80000000) >> 31 ;
fpub_sign_tmp = (fpub_tmp & 0x80000000) >> 31 ;
fpua_exponent_tmp = (fpua_tmp & 0x7f800000) >> 23 ;
fpub_exponent_tmp = (fpub_tmp & 0x7f800000) >> 23 ;
fpua_significand_tmp = (fpua_tmp & 0x007fffff) ;
fpub_significand_tmp = (fpub_tmp & 0x007fffff) ;
// 对阶
exponent_diff_tmp = int(fpua_exponent_tmp) - int(fpub_exponent_tmp);
if (exponent_diff_tmp > 0) {
fpub_significand_tmp = fpub_significand_tmp >> exponent_diff_tmp ;
fpub_exponent_tmp = fpua_exponent_tmp;
} else {
fpua_significand_tmp = fpua_significand_tmp >> exponent_diff_tmp ;
fpua_exponent_tmp = fpub_exponent_tmp;
}
wait();
// output MUX
switch (opcode_tmp) {
case 0: // Stall
opcode_encode = "STALL";
// dout_tmp = dout_tmp; // keeps its value
wait();
break;
case 3: // add
opcode_encode = "FADD";
significant_result = int(fpua_significand_tmp) + int(fpub_significand_tmp);
wait();
break;
case 4: // sub
opcode_encode = "FSUB";
significant_result = int(fpua_significand_tmp) - int(fpub_significand_tmp);
wait();
break;
case 5: // mul
opcode_encode = "FMUL";
significant_result = int(fpua_significand_tmp) * int(fpub_significand_tmp);
fpub_exponent_tmp *= 2; // exponent is doubled in value
wait();
break;
case 6: // div
opcode_encode = "FDIV";
significant_result = int(fpua_significand_tmp) / int(fpub_significand_tmp);
wait();
break;
default:
printf("\t\t\t\t\t\t\tFPU: Bad Opcode %d.\n",opcode_tmp);
wait();
break;
}
// 规格化并进行舍入处理
overflow_sign_tmp = (significant_result & 0xff800000) >> 23;
dout_tmp = (significant_result << overflow_sign_tmp) & 0x007fffff ;
result_exp_tmp = fpub_exponent_tmp + overflow_sign_tmp;
dout_tmp = dout_tmp | ((result_exp_tmp << 23) & 0x7f800000) ;
result_sign_tmp = fpua_sign_tmp;
dout_tmp = dout_tmp | ((result_sign_tmp << 31) & 0x80000000) ;
fdout.write(dout_tmp);
fout_valid.write(true);
fdestout.write(dest_tmp);
wait();
fout_valid.write(false);
wait();
}
}第27条指令 fadd R3, R2, R2
第29条指令 fmul R10, R11, R11
第27条指令 fadd R3, R2, R2:A--IFU发起读地址和使能信号,B--pag拿过地址将其转换为物理地址,C--icache获得物理地址开启取指并发出(始终命中)。D--pag待有效信号将获取指令返回给IFU。E--IFU待有效信号将获取指令输出给IDU,F--IDU进行指令译码输出相应的alu和有效指示,G--FPU执行,两拍后返回结果。H--这里IDU执行了R3结果的写回。

第29条指令 fmul R10, R11, R11:时序是一模一样的
4 SIMD
单指令多数据,一条指令下去,操作的是多个源和目的数据,这个例子并没有单独设置这样的寄存器或是存储器,直接使用了32bit的通用寄存取分解使用4个8bit的数据,时序波形就不分析了,且看代码的实现:
struct mmxu : sc_module {
sc_in<bool> mmx_valid; // MMX unit enable
sc_in<int> opcode; // opcode
sc_in<signed int> mmxa; // operand A
sc_in<signed int> mmxb; // operand B
sc_in<unsigned> dest; // Destination register number
sc_out<signed int> mmxdout; // MMX output
sc_out<bool> mmxout_valid; // MMX output valid
sc_out<unsigned> mmxdestout; // destination number
sc_in_clk CLK;
// can make it asynchronous process to speed up simulation
SC_CTOR(mmxu) {
SC_CTHREAD(entry, CLK.pos());
}
void entry();
};
void mmxu::entry(){
int opcode_tmp = 0;
unsigned int dout_tmp = 0;
unsigned int dest_tmp = 0;
const char * opcode_encode;
unsigned int mmxa_tmp = 0;
unsigned int mmxb_tmp = 0;
unsigned int mmxa0_tmp = 0;
unsigned int mmxa1_tmp = 0;
unsigned int mmxa2_tmp = 0;
unsigned int mmxa3_tmp = 0;
unsigned int mmxb0_tmp = 0;
unsigned int mmxb1_tmp = 0;
unsigned int mmxb2_tmp = 0;
unsigned int mmxb3_tmp = 0;
unsigned int mmxc0_tmp = 0;
unsigned int mmxc1_tmp = 0;
unsigned int mmxc2_tmp = 0;
unsigned int mmxc3_tmp = 0;
unsigned int mmxcU_tmp = 0;
unsigned int mmxcL_tmp = 0;
wait(3);
while(1) {
if (mmx_valid.read() == true) {
mmxa_tmp = mmxa.read();
mmxb_tmp = mmxb.read();
mmxa0_tmp = (mmxa_tmp & 0x000000ff) ;
mmxb0_tmp = (mmxb_tmp & 0x000000ff) ;
mmxa1_tmp = (mmxa_tmp & 0x0000ff00) >> 8 ;
mmxb1_tmp = (mmxb_tmp & 0x0000ff00) >> 8 ;
mmxa2_tmp = (mmxa_tmp & 0x00ff0000) >> 16 ;
mmxb2_tmp = (mmxb_tmp & 0x00ff0000) >> 16 ;
mmxa3_tmp = (mmxa_tmp & 0xff000000) >> 24 ;
mmxb3_tmp = (mmxb_tmp & 0xff000000) >> 24 ;
opcode_tmp = opcode.read();
dest_tmp = dest.read();
// output MUX
switch (opcode_tmp) {
case 0: // Stall
opcode_encode = "STALL";
// dout_tmp = dout_tmp; // keeps its value
wait();
break;
case 3: // add
opcode_encode = "PADD";
mmxc3_tmp = mmxa3_tmp + mmxb3_tmp;
mmxc2_tmp = mmxa2_tmp + mmxb2_tmp;
mmxc1_tmp = mmxa1_tmp + mmxb1_tmp;
mmxc0_tmp = mmxa0_tmp + mmxb0_tmp;
mmxc3_tmp = (mmxc3_tmp << 24) & 0xff000000;
mmxc2_tmp = (mmxc2_tmp << 16) & 0x00ff0000;
mmxc1_tmp = (mmxc1_tmp << 8) & 0x0000ff00;
dout_tmp = mmxc0_tmp | mmxc1_tmp | mmxc2_tmp | mmxc3_tmp;
wait();
break;
case 4: // add with saturation
opcode_encode = "PADDS";
mmxc3_tmp = mmxa3_tmp + mmxb3_tmp;
mmxc2_tmp = mmxa2_tmp + mmxb2_tmp;
mmxc1_tmp = mmxa1_tmp + mmxb1_tmp;
mmxc0_tmp = mmxa0_tmp + mmxb0_tmp;
if (mmxc3_tmp >= 256) mmxc3_tmp = 0xff;
if (mmxc2_tmp >= 256) mmxc2_tmp = 0xff;
if (mmxc1_tmp >= 256) mmxc1_tmp = 0xff;
if (mmxc0_tmp >= 256) mmxc0_tmp = 0xff;
mmxc3_tmp = (mmxc3_tmp << 24) & 0xff000000;
mmxc2_tmp = (mmxc2_tmp << 16) & 0x00ff0000;
mmxc1_tmp = (mmxc1_tmp << 8) & 0x0000ff00;
dout_tmp = mmxc0_tmp | mmxc1_tmp | mmxc2_tmp | mmxc3_tmp;
wait();
break;
case 5: // sub
opcode_encode = "PSUB";
mmxc3_tmp = mmxa3_tmp - mmxb3_tmp;
mmxc2_tmp = mmxa2_tmp - mmxb2_tmp;
mmxc1_tmp = mmxa1_tmp - mmxb1_tmp;
mmxc0_tmp = mmxa0_tmp - mmxb0_tmp;
mmxc3_tmp = (mmxc3_tmp << 24) & 0xff000000;
mmxc2_tmp = (mmxc2_tmp << 16) & 0x00ff0000;
mmxc1_tmp = (mmxc1_tmp << 8) & 0x0000ff00;
dout_tmp = mmxc0_tmp | mmxc1_tmp | mmxc2_tmp | mmxc3_tmp;
wait();
break;
case 6: // sub with saturation
opcode_encode = "PSUBS";
mmxc3_tmp = mmxa3_tmp - mmxb3_tmp;
mmxc2_tmp = mmxa2_tmp - mmxb2_tmp;
mmxc1_tmp = mmxa1_tmp - mmxb1_tmp;
mmxc0_tmp = mmxa0_tmp - mmxb0_tmp;
if (mmxb3_tmp > mmxa3_tmp) mmxc3_tmp = 0x00;
if (mmxb2_tmp > mmxa2_tmp) mmxc2_tmp = 0x00;
if (mmxb1_tmp > mmxa1_tmp) mmxc1_tmp = 0x00;
if (mmxb0_tmp > mmxa0_tmp) mmxc0_tmp = 0x00;
mmxc3_tmp = (mmxc3_tmp << 24) & 0xff000000;
mmxc2_tmp = (mmxc2_tmp << 16) & 0x00ff0000;
mmxc1_tmp = (mmxc1_tmp << 8) & 0x0000ff00;
dout_tmp = mmxc0_tmp | mmxc1_tmp | mmxc2_tmp | mmxc3_tmp;
wait();
break;
case 7: // packed multiply add with saturation
// a3*b3+a2*b2 , a1*b1+a0*b0
opcode_encode = "PMADD";
mmxc3_tmp = mmxa3_tmp * mmxb3_tmp;
mmxc2_tmp = mmxa2_tmp * mmxb2_tmp;
mmxc1_tmp = mmxa1_tmp * mmxb1_tmp;
mmxc0_tmp = mmxa0_tmp * mmxb0_tmp;
if (mmxc3_tmp >= 256) mmxc3_tmp = 0xff;
if (mmxc2_tmp >= 256) mmxc2_tmp = 0xff;
if (mmxc1_tmp >= 256) mmxc1_tmp = 0xff;
if (mmxc0_tmp >= 256) mmxc0_tmp = 0xff;
mmxcU_tmp = mmxc3_tmp + mmxc2_tmp;
mmxcL_tmp = mmxc1_tmp + mmxc0_tmp;
if (mmxcU_tmp >= 256) mmxcU_tmp = 0xff;
if (mmxcL_tmp >= 256) mmxcL_tmp = 0xff;
mmxcU_tmp = (mmxcU_tmp << 16) ;
dout_tmp = mmxcU_tmp | mmxcL_tmp;
wait();
break;
case 8: // packed b1 (16bit) b0(16bit) and a1(16 bit) a0(16 bit)
// to B1(8bit) B0(8bit) A1(8bit) A0(8bit)
opcode_encode = "PACK";
mmxc3_tmp = mmxb2_tmp << 24;
mmxc2_tmp = mmxb0_tmp << 16;
mmxc1_tmp = mmxa2_tmp << 8;
mmxc0_tmp = mmxa0_tmp ;
dout_tmp = mmxc3_tmp | mmxc2_tmp | mmxc1_tmp | mmxc0_tmp;
wait();
break;
case 9: // mmx chroma keying
// A =green != green green !=green
// B =green green green green
//Res=0xff 00 ff 00
opcode_encode = "MMXCK";
if (mmxa3_tmp == mmxb3_tmp)
mmxc3_tmp = 0xff;
else
mmxc3_tmp = 0x00;
if (mmxa2_tmp == mmxb2_tmp)
mmxc2_tmp = 0xff;
else
mmxc2_tmp = 0x00;
if (mmxa1_tmp == mmxb1_tmp)
mmxc1_tmp = 0xff;
else
mmxc1_tmp = 0x00;
if (mmxa0_tmp == mmxb0_tmp)
mmxc0_tmp = 0xff;
else
mmxc0_tmp = 0x00;
mmxc3_tmp = mmxc3_tmp << 24;
mmxc2_tmp = mmxc2_tmp << 16;
mmxc1_tmp = mmxc1_tmp << 8;
// mmxc0_tmp = mmxc0_tmp ; // keeps its value
dout_tmp = mmxc3_tmp | mmxc2_tmp | mmxc1_tmp | mmxc0_tmp;
wait();
break;
default:
opcode_encode = "INVALID";
printf("MMX: Bad Opcode %d.\n",opcode_tmp);
wait();
break;
}
mmxdout.write(dout_tmp);
mmxout_valid.write(true);
mmxdestout.write(dest_tmp);
wait();
mmxout_valid.write(false);
wait();
} else {
wait();
}
}
}5 分支等其余指令
仔细地研习了代码,分支指令的实现似乎不正确,波形看分支目标地址并未真正地传出,代码也没有作出该地值的取指:下面是IFU代码的片段和波形截图
if (branch_valid.read() == true) {
printf("IFU ALERT: **BRANCH**\n");
lock_tmp ++;
ram_cs.write(true);
addr_tmp = branch_address.read();
ram_we.write(false);
wait(memory_latency);
do { wait(); } while ( !((bios_valid == true) || (icache_valid == true)) );
datai_tmp = ramdata.read()
instruction_valid.write(true);
instruction.write(datai_tmp);
ram_cs.write(false);
if (next_pc.read() == true) { addr_tmp++; }
wait();
instruction_valid.write(false);
wait();
} 
除了分支指令的代码和端口波形不对外,代码对数据的转移和访存也并未找到支持。对CPU的研习基本就到此了,剩下再有一篇文章把数据cache等剩余的代码分析下,SystemC的编程认识和学习就告一段落了。
























 1270
1270











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










