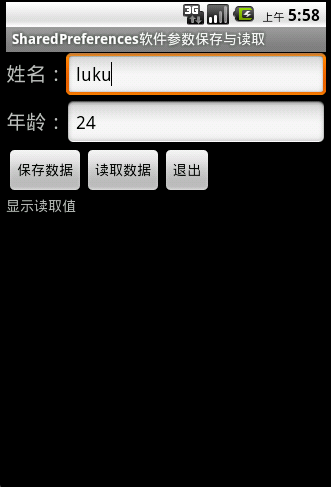
很多时候我们开发软件需要向用户提供软件参数设置功能,如电子书软件的背景颜色设置,喜好设置等。在Android的应用的使用SharedPreferences类来
保存软件设置参数非常方便。
使用SharedPreferences类保存数据,其实是将这些参数保存在xml文件中,文件存放在/data/data/包名/shared_prefs目录下:

点击保存后,

将test.xml导出,打开

即为我们保存的数据。
点击读取按钮:

读取正确。
代码:
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.SharedPreferences;
import android.content.SharedPreferences.Editor;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class SharedPreferencesActivity extends Activity
{
private EditText nameEditText;
private EditText ageEditText;
private Button save;
private Button read;
private Button exit;
private TextView resulTextView;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
nameEditText=(EditText)findViewById(R.id.name);
ageEditText=(EditText)findViewById(R.id.age);
save=(Button)findViewById(R.id.save);
read=(Button)findViewById(R.id.read);
exit=(Button)findViewById(R.id.exit);
resulTextView=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.result);
save.setOnClickListener(listener);
read.setOnClickListener(listener);
exit.setOnClickListener(listener);
}
private OnClickListener listener=new OnClickListener()
{
@Override
public void onClick(View v)
{
Button button=(Button)v;
SharedPreferences sharedPreferences=SharedPreferencesActivity.
this.getSharedPreferences("test", Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
switch (button.getId())
{
case R.id.save:
String name=nameEditText.getText().toString();
String age=ageEditText.getText().toString();
Editor editor=sharedPreferences.edit();
editor.putString("name", name);
editor.putInt("age", Integer.parseInt(age));
editor.commit(); //内容提交
Toast.makeText(SharedPreferencesActivity.this, "保存成功",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
case R.id.read:
String namevalue= sharedPreferences.getString("name", "");//如果存在name返回name的值,如果不存在该元素,返回“”
int agevalue= sharedPreferences.getInt("age", -1);
resulTextView.setText("姓名是:"+namevalue+"\n"+"年龄是:"+agevalue);
Toast.makeText(SharedPreferencesActivity.this, "读取成功",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
case R.id.exit:
android.os.Process.killProcess(android.os.Process.myPid());
break;
default:
break;
}
}
};
}布局文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:id="@+id/linearLayout1"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView
android:text="姓名:"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"></TextView>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/name"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"></EditText>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:id="@+id/linearLayout2"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView
android:text="年龄:"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"></TextView>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/age"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"></EditText>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:id="@+id/linearLayout3"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<Button
android:text="保存数据"
android:id="@+id/save"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"></Button>
<Button
android:text="读取数据"
android:id="@+id/read"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"></Button>
<Button
android:text="退出"
android:id="@+id/exit"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"></Button>
</LinearLayout>
<TextView
android:text="显示读取值"
android:id="@+id/result"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"></TextView>
</LinearLayout>每次启动程序时,自动读取参数,只要做简单改动:
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.SharedPreferences;
import android.content.SharedPreferences.Editor;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class SharedPreferencesActivity extends Activity
{
private EditText nameEditText;
private EditText ageEditText;
private Button save;
private Button read;
private Button exit;
private TextView resulTextView;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
nameEditText=(EditText)findViewById(R.id.name);
ageEditText=(EditText)findViewById(R.id.age);
save=(Button)findViewById(R.id.save);
read=(Button)findViewById(R.id.read);
exit=(Button)findViewById(R.id.exit);
resulTextView=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.result);
save.setOnClickListener(listener);
read.setOnClickListener(listener);
exit.setOnClickListener(listener);
SharedPreferences sharedPreferences=SharedPreferencesActivity.
this.getSharedPreferences("test", Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
String namevalue= sharedPreferences.getString("name", "");
int agevalue= sharedPreferences.getInt("age", -1);
nameEditText.setText(namevalue);
ageEditText.setText(String.valueOf(agevalue));
}
private OnClickListener listener=new OnClickListener()
{
@Override
public void onClick(View v)
{
Button button=(Button)v;
SharedPreferences sharedPreferences=SharedPreferencesActivity.
this.getSharedPreferences("test", Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
switch (button.getId())
{
case R.id.save:
String name=nameEditText.getText().toString();
String age=ageEditText.getText().toString();
Editor editor=sharedPreferences.edit();
editor.putString("name", name);
editor.putInt("age", Integer.parseInt(age));
editor.commit(); //内容提交
Toast.makeText(SharedPreferencesActivity.this, "保存成功",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
case R.id.read:
String namevalue= sharedPreferences.getString("name", "");
int agevalue= sharedPreferences.getInt("age", -1);
resulTextView.setText("姓名是:"+namevalue+"\n"+"年龄是:"+agevalue);
Toast.makeText(SharedPreferencesActivity.this, "读取成功",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
case R.id.exit:
android.os.Process.killProcess(android.os.Process.myPid());
break;
default:
break;
}
}
};
}
若想保存的xml文件被其他文件访问,应修改:
SharedPreferences sharedPreferences=SharedPreferencesActivity.
this.getSharedPreferences("test", Context.MODE_WORLD_READABLE+Context.MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE);
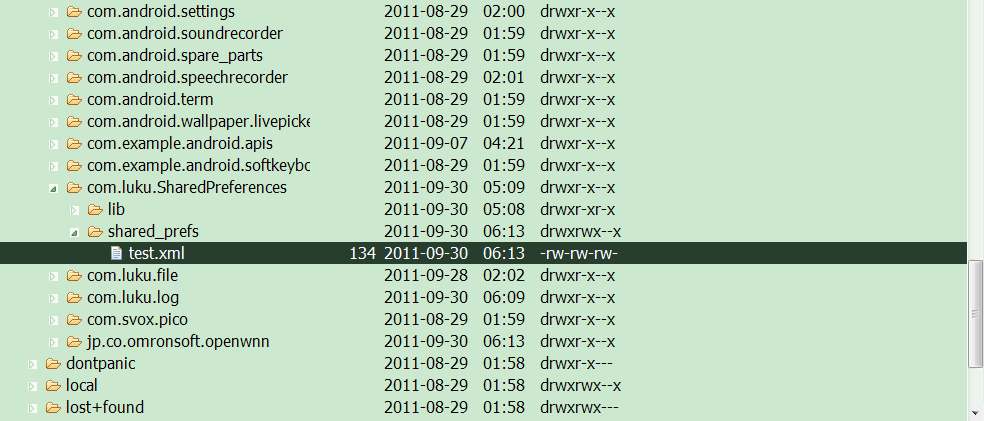
可以看到其读写权限发生变化
测试的其他Activity
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.SharedPreferences;
import android.content.pm.PackageManager.NameNotFoundException;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
public class LogActivity extends Activity
{
private static final String TAG="LogActivity";
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
//Log.i(TAG, "TAG打印测试");
try
{
Context context=this.createPackageContext("com.luku.SharedPreferences",
Context.CONTEXT_IGNORE_SECURITY);
SharedPreferences sharedPreferences=context.getSharedPreferences
("test", Context.MODE_WORLD_READABLE+Context.MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE);
String namevalue= sharedPreferences.getString("name", "");
int agevalue= sharedPreferences.getInt("age", -1);
Log.i(TAG, "名字是:"+namevalue+","+"年龄为:"+agevalue);
} catch (NameNotFoundException e)
{
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
由其他程序访问成功!
原文链接: http://blog.csdn.net/yf210yf/article/details/6837137




















 2248
2248











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








