陈拓 2021/11/24-2021/11/25
1. 概述
https://github.com/joltwallet/esp_littlefs
LittleFS是一个用于微控制器的小型故障安全文件系统。我们将LittleFS移植到esp-idf(特别是ESP32),因为SPIFFS速度太慢,“臃肿”且脆弱。
2. 用法
有两种方法可以将此组件添加到项目中。
- 作为ESP-IDF托管组件:在项目目录中运行
idf.py add-dependency joltwallet/littlefs==1.0.0
- 作为子模块:在项目中,将其作为子模块添加到components/目录中
git submodule add https://github.com/joltwallet/esp_littlefs.git

git submodule update --init --recursive

mv esp_littlefs components/

现在就可以在项目中通过idf.py menuconfig下面的 Component config-> LittleFS配置库了。
3. 实例
User@wreyford提供了一份演示报告https://github.com/wreyford/demo_esp_littlefs
展示了esp_littlefs的使用。 在example/目录中有修改后的副本。
- 克隆demo
git clone https://github.com/wreyford/demo_esp_littlefs.git

- 文件夹内容

- 配置
idf.py menuconfig
1) 设置定制分区表文件partitions_demo_esp_littlefs.csv

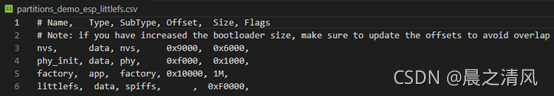
分区表文件partitions_demo_esp_littlefs.csv的内容:
2) 设置LittleFS文件系统


- 编译项目
cd demo_esp_littlefs
idf.py build
如果出现:
![]()
刷新esp-idf环境:
get_idf
再编译。

对比之前的分区表:

- 烧写项目
idf.py -p /dev/ttyS3 -b 115200 flash
- 运行结果
文件操作示范,创建文件,写文件,文件改名,读文件。

程序流程:
- 初始化LittelFS
- 创建文件Opening file -> fopen("/littlefs/hello.txt", "w");
- 向文件写入字符串File written -> fprintf(f, "LittleFS Rocks!\n");
- 改文件名Renaming file -> rename("/littlefs/hello.txt", "/littlefs/foo.txt")
- 读文件Reading file -> fopen("/littlefs/foo.txt", "r");
- 读一行Read from file -> fgets(line, sizeof(line), f);
- 显示读结果 -> ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Read from file: '%s'", line);
- 卸载文件系统 -> esp_vfs_littlefs_unregister(conf.partition_label);
对应的C程序:
printf("Now we are starting the LittleFs Demo ...\n");
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Initializing LittelFS");
esp_vfs_littlefs_conf_t conf = {
.base_path = "/littlefs",
.partition_label = "littlefs",
.format_if_mount_failed = true,
.dont_mount = false,
};
// Use settings defined above to initialize and mount LittleFS filesystem.
// Note: esp_vfs_littlefs_register is an all-in-one convenience function.
esp_err_t ret = esp_vfs_littlefs_register(&conf);
if (ret != ESP_OK)
{
if (ret == ESP_FAIL)
{
ESP_LOGE(TAG, "Failed to mount or format filesystem");
}
else if (ret == ESP_ERR_NOT_FOUND)
{
ESP_LOGE(TAG, "Failed to find LittleFS partition");
}
else
{
ESP_LOGE(TAG, "Failed to initialize LittleFS (%s)", esp_err_to_name(ret));
}
return;
}
size_t total = 0, used = 0;
ret = esp_littlefs_info(conf.partition_label, &total, &used);
if (ret != ESP_OK)
{
ESP_LOGE(TAG, "Failed to get LittleFS partition information (%s)", esp_err_to_name(ret));
}
else
{
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Partition size: total: %d, used: %d", total, used);
}
// Use POSIX and C standard library functions to work with files.
// First create a file.
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Opening file");
FILE *f = fopen("/littlefs/hello.txt", "w");
if (f == NULL)
{
ESP_LOGE(TAG, "Failed to open file for writing");
return;
}
fprintf(f, "LittleFS Rocks!\n");
fclose(f);
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "File written");
// Check if destination file exists before renaming
struct stat st;
if (stat("/littlefs/foo.txt", &st) == 0)
{
// Delete it if it exists
unlink("/littlefs/foo.txt");
}
// Rename original file
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Renaming file");
if (rename("/littlefs/hello.txt", "/littlefs/foo.txt") != 0)
{
ESP_LOGE(TAG, "Rename failed");
return;
}
// Open renamed file for reading
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Reading file");
f = fopen("/littlefs/foo.txt", "r");
if (f == NULL)
{
ESP_LOGE(TAG, "Failed to open file for reading");
return;
}
char line[64];
fgets(line, sizeof(line), f);
fclose(f);
// strip newline
char *pos = strchr(line, '\n');
if (pos)
{
*pos = '\0';
}
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "Read from file: '%s'", line);
// All done, unmount partition and disable LittleFS
esp_vfs_littlefs_unregister(conf.partition_label);
ESP_LOGI(TAG, "LittleFS unmounted");- LittleFS在块上运行,在ESP32上块的大小为4096字节
- 一个新格式化的LittleFS将有2个块在使用中,使它看起来像8KB在使用中。








 本文介绍ESP32上的LittleFS文件系统的使用方法及优势。通过示例代码展示如何进行文件的创建、重命名、读取等操作,并提供配置指南。
本文介绍ESP32上的LittleFS文件系统的使用方法及优势。通过示例代码展示如何进行文件的创建、重命名、读取等操作,并提供配置指南。


















 705
705

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










