Comparison
RDBMS
HBase
Overview
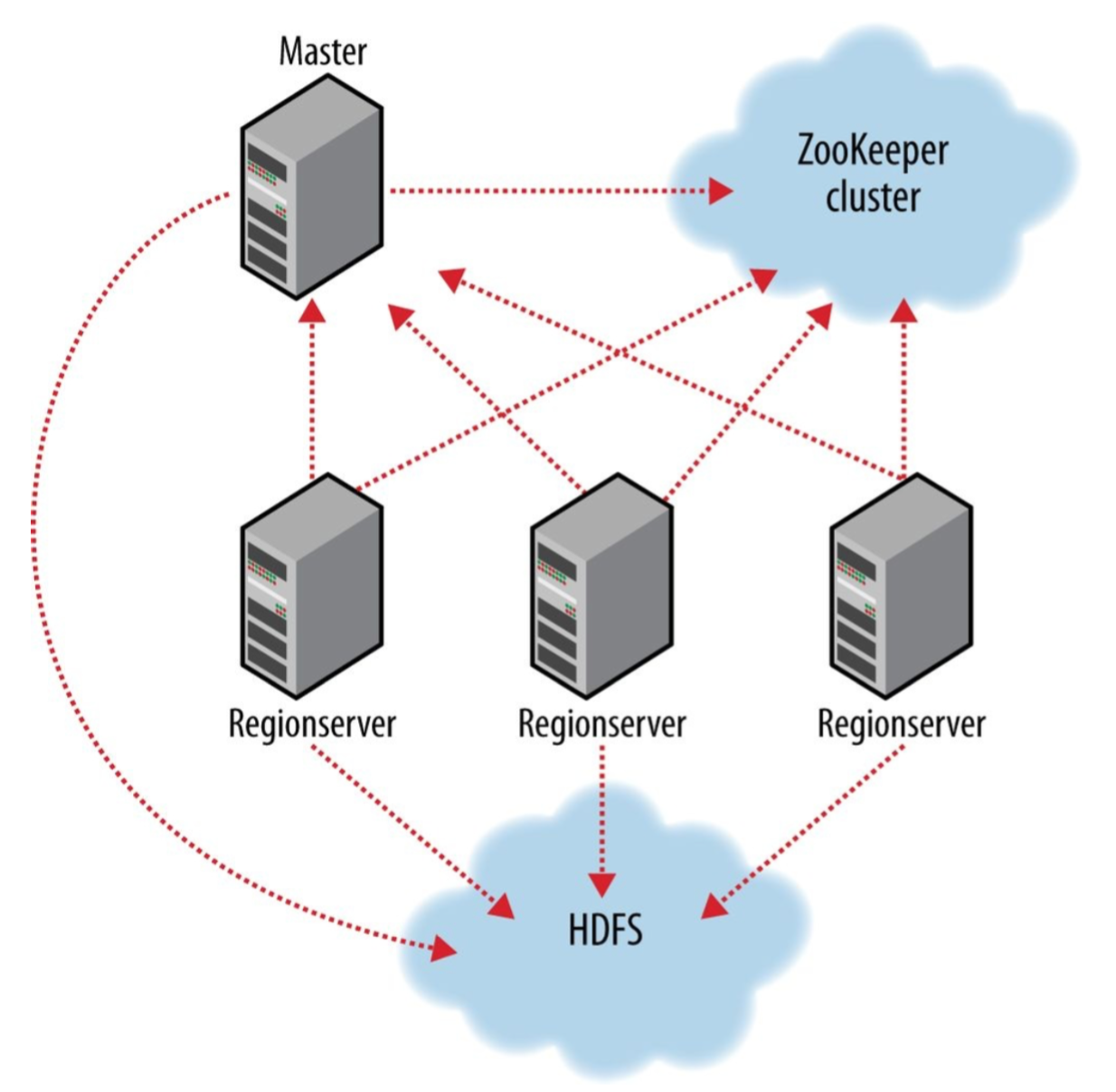

Master
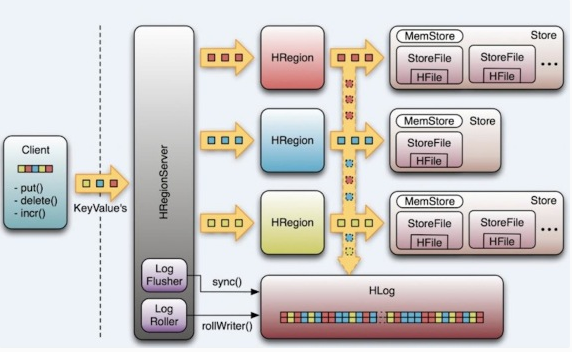
HBase Master Node orchestrates a cluster of one or more Region Servers
- Bootstrap a virgin install
- Assign regions to Region Servers
- Recover Region Server failure
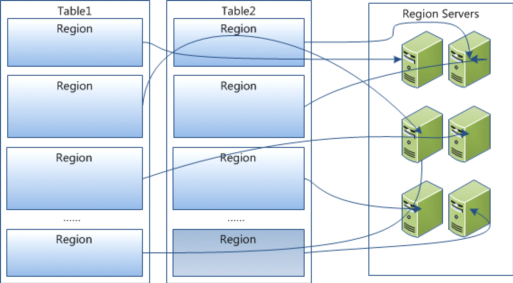
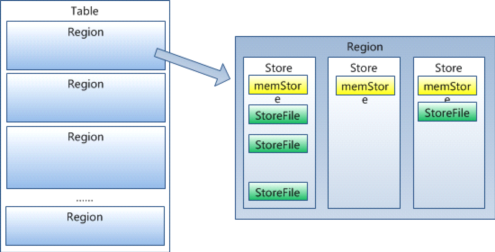
Region Server
- Carry regions
- Respond to client read/write requests
- Inform Master Node the new region
Zookeeper
The authority on cluster state. The Zookeeper ensemble hosts vital:
- Location of the hbase:meta table
- Address of Master
- Host the assignment transaction state (for recovery purpose)
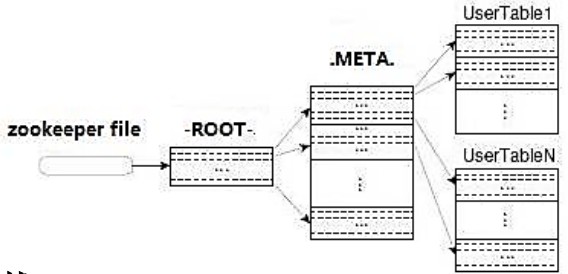
Client
When bootstrapping a client connection to HBase cluster, the client must be passed the location of Zookeeper ensemble. Thereafter, client navigates the ZooKeeper hierarchy to learn about cluster attributes
hbase:meta
HBase keep a special catalog table named hbase:meta, within which it maintains the current list, state and locations of all user-space regions afloat on the cluster. Entries in hbase:meta are keyed by region name, which is
- table_name,start_row,creation_time.MD5(table_namestart_rowcreation_time).
Fresh clients connect to the ZooKeeper cluster first to learn the location of hbase:meta. The client then does a lookup against the appropriate hbase:meta region to figure out the hosting user-space region and its location. Thereafter, the client interacts directly with the hosting region server.
As region transitions - split, disabled, enabled, deleted or redeployed, the catalog table is updated.
HBase Commands
By default, HBase writes to /${java.io.tmpdir}/hbase-${user.name}.${java.io.tmpdir} usually maps to /tmp, but you should configure HBase to use a more permanent location by setting hbase.tmp.dir in hbase-site.xml. In standalone mode, the HBase master, the regionserver, and a Zookeeper instance are all run in the same JVM.
- HBase Shell
%hbase shell
# Create a table with one column family (with default column family attributes)
hbase(main):001:0>create 'table_name', 'column_family_name'
# Display tables
hbase(main):002:0>list
# Insert some data
hbase(main):003:0>put 'table_name' 'row1', 'column_family_name:column_name', 'value1'
hbase(main):004:0>put 'table_name' 'row2', 'column_family_name:column_name', 'value2'
hbase(main):005:0>put 'table_name' 'row3', 'column_family_name:column_name', 'value3'
# Get a particular row with the row key
hbase(main):006:0>get 'table_name' 'row1'
# List the table content
hbase(main):007:0>scan 'table_name'Client
Java Client, REST, Thrift and MapReduce API.
Load Data
For a large dataset, first, copy the raw file into HDFS, and then run a MapReduce job that can read the input and write to HBase.





















 4644
4644

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








