=====================================================
H.264源代码分析文章列表:
【编码 - x264】
x264源代码简单分析:x264命令行工具(x264.exe)
x264源代码简单分析:x264_slice_write()
x264源代码简单分析:宏块分析(Analysis)部分-帧内宏块(Intra)
x264源代码简单分析:宏块分析(Analysis)部分-帧间宏块(Inter)
x264源代码简单分析:熵编码(Entropy Encoding)部分
【解码 - libavcodec H.264 解码器】
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:解析器(Parser)部分
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:解码器主干部分
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:熵解码(EntropyDecoding)部分
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:宏块解码(Decode)部分-帧内宏块(Intra)
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:宏块解码(Decode)部分-帧间宏块(Inter)
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:环路滤波(Loop Filter)部分
=====================================================
本文简单分析x264的x264_slice_write()的源代码。x264_slice_write()是x264项目的核心,它完成了编码了一个Slice的工作。根据功能的不同,该函数可以分为滤波(Filter),分析(Analysis),宏块编码(Encode)和熵编码(Entropy Encoding)几个子模块。本文首先对x264_slice_write()进行总体的概括,在后续文章中将会对上述几个子模块展开进行分析。
函数调用关系图
x264_slice_write()的源代码在整个x264中的位置如下图所示。
x264_slice_write()的函数调用关系如下图所示。

从图中可以看出,x264_slice_write()调用了如下函数:
x264_nal_start():开始写一个NALU。本文将会对上述函数进行分析。其中x264_fdec_filter_row(),x264_macroblock_analyse(),x264_macroblock_encode(),x264_macroblock_write_cabac()/x264_macroblock_write_cavlc()只做概述,后续文章中再做分析。
x264_macroblock_thread_init():初始化宏块重建数据缓存fdec_buf[]和编码数据缓存fenc_buf[]。
x264_slice_header_write():输出 Slice Header。
x264_fdec_filter_row():滤波模块。该模块包含了环路滤波,半像素插值,SSIM/PSNR的计算。
x264_macroblock_cache_load():将要编码的宏块的周围的宏块的信息读进来。
x264_macroblock_analyse():分析模块。该模块包含了帧内预测模式分析以及帧间运动估计等。
x264_macroblock_encode():宏块编码模块。该模块通过对残差的DCT变换、量化等方式对宏块进行编码。
x264_macroblock_write_cabac():CABAC熵编码模块。
x264_macroblock_write_cavlc():CAVLC熵编码模块。
x264_macroblock_cache_save():保存当前宏块的信息。
x264_ratecontrol_mb():码率控制。
x264_nal_end():结束写一个NALU。
x264_slice_write()
x264_slice_write()用于编码一个Slice。该函数的定义位于encoder\encoder.c,如下所示。/****************************************************************************
* 真正的编码——编码1个Slice
* 注释和处理:雷霄骅
* http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020
* leixiaohua1020@126.com
****************************************************************************/
static intptr_t x264_slice_write( x264_t *h )
{
int i_skip;
//宏块的序号,以及序号对应的x,y坐标
int mb_xy, i_mb_x, i_mb_y;
/* NALUs other than the first use a 3-byte startcode.
* Add one extra byte for the rbsp, and one more for the final CABAC putbyte.
* Then add an extra 5 bytes just in case, to account for random NAL escapes and
* other inaccuracies. */
int overhead_guess = (NALU_OVERHEAD - (h->param.b_annexb && h->out.i_nal)) + 1 + h->param.b_cabac + 5;
int slice_max_size = h->param.i_slice_max_size > 0 ? (h->param.i_slice_max_size-overhead_guess)*8 : 0;
int back_up_bitstream_cavlc = !h->param.b_cabac && h->sps->i_profile_idc < PROFILE_HIGH;
int back_up_bitstream = slice_max_size || back_up_bitstream_cavlc;
int starting_bits = bs_pos(&h->out.bs);
int b_deblock = h->sh.i_disable_deblocking_filter_idc != 1;
int b_hpel = h->fdec->b_kept_as_ref;
int orig_last_mb = h->sh.i_last_mb;
int thread_last_mb = h->i_threadslice_end * h->mb.i_mb_width - 1;
uint8_t *last_emu_check;
#define BS_BAK_SLICE_MAX_SIZE 0
#define BS_BAK_CAVLC_OVERFLOW 1
#define BS_BAK_SLICE_MIN_MBS 2
#define BS_BAK_ROW_VBV 3
x264_bs_bak_t bs_bak[4];
b_deblock &= b_hpel || h->param.b_full_recon || h->param.psz_dump_yuv;
bs_realign( &h->out.bs );
/* Slice */
//开始输出一个NAL
//后面对应着x264_nal_end()
x264_nal_start( h, h->i_nal_type, h->i_nal_ref_idc );
h->out.nal[h->out.i_nal].i_first_mb = h->sh.i_first_mb;
/* Slice header */
//存储宏块像素的缓存fdec_buf和fenc_buf的初始化
//宏块编码缓存p_fenc[0],p_fenc[1],p_fenc[2]
//宏块重建缓存p_fdec[0],p_fdec[1],p_fdec[2]
//[0]存Y,[1]存U,[2]存V
x264_macroblock_thread_init( h );
/* Set the QP equal to the first QP in the slice for more accurate CABAC initialization. */
h->mb.i_mb_xy = h->sh.i_first_mb;
h->sh.i_qp = x264_ratecontrol_mb_qp( h );
h->sh.i_qp = SPEC_QP( h->sh.i_qp );
h->sh.i_qp_delta = h->sh.i_qp - h->pps->i_pic_init_qp;
//输出 slice header
x264_slice_header_write( &h->out.bs, &h->sh, h->i_nal_ref_idc );
//如果使用CABAC,需要初始化
if( h->param.b_cabac )
{
/* alignment needed */
bs_align_1( &h->out.bs );
/* init cabac */
x264_cabac_context_init( h, &h->cabac, h->sh.i_type, x264_clip3( h->sh.i_qp-QP_BD_OFFSET, 0, 51 ), h->sh.i_cabac_init_idc );
x264_cabac_encode_init ( &h->cabac, h->out.bs.p, h->out.bs.p_end );
last_emu_check = h->cabac.p;
}
else
last_emu_check = h->out.bs.p;
h->mb.i_last_qp = h->sh.i_qp;
h->mb.i_last_dqp = 0;
h->mb.field_decoding_flag = 0;
//宏块位置-纵坐标(初始值)
i_mb_y = h->sh.i_first_mb / h->mb.i_mb_width;
//宏块位置-横坐标(初始值)
i_mb_x = h->sh.i_first_mb % h->mb.i_mb_width;
i_skip = 0;
//一个大循环
//对一个slice中每个宏块进行编码
while( 1 )
{
//宏块序号。由i_mb_x和i_mb_y计算而来。
mb_xy = i_mb_x + i_mb_y * h->mb.i_mb_width;
int mb_spos = bs_pos(&h->out.bs) + x264_cabac_pos(&h->cabac);
//一行的开始
if( i_mb_x == 0 )
{
if( x264_bitstream_check_buffer( h ) )
return -1;
if( !(i_mb_y & SLICE_MBAFF) && h->param.rc.i_vbv_buffer_size )
x264_bitstream_backup( h, &bs_bak[BS_BAK_ROW_VBV], i_skip, 1 );
//去块效应滤波、半像素插值、SSIM/PSNR计算等
//一次处理一行宏块
if( !h->mb.b_reencode_mb )
x264_fdec_filter_row( h, i_mb_y, 0 );
}
if( back_up_bitstream )
{
if( back_up_bitstream_cavlc )
x264_bitstream_backup( h, &bs_bak[BS_BAK_CAVLC_OVERFLOW], i_skip, 0 );
if( slice_max_size && !(i_mb_y & SLICE_MBAFF) )
{
x264_bitstream_backup( h, &bs_bak[BS_BAK_SLICE_MAX_SIZE], i_skip, 0 );
if( (thread_last_mb+1-mb_xy) == h->param.i_slice_min_mbs )
x264_bitstream_backup( h, &bs_bak[BS_BAK_SLICE_MIN_MBS], i_skip, 0 );
}
}
if( PARAM_INTERLACED )
{
if( h->mb.b_adaptive_mbaff )
{
if( !(i_mb_y&1) )
{
/* FIXME: VSAD is fast but fairly poor at choosing the best interlace type. */
h->mb.b_interlaced = x264_field_vsad( h, i_mb_x, i_mb_y );
memcpy( &h->zigzagf, MB_INTERLACED ? &h->zigzagf_interlaced : &h->zigzagf_progressive, sizeof(h->zigzagf) );
if( !MB_INTERLACED && (i_mb_y+2) == h->mb.i_mb_height )
x264_expand_border_mbpair( h, i_mb_x, i_mb_y );
}
}
h->mb.field[mb_xy] = MB_INTERLACED;
}
/* load cache */
//将要编码的宏块的周围的宏块的值读进来
//主要是上面、左边块的值
if( SLICE_MBAFF )
x264_macroblock_cache_load_interlaced( h, i_mb_x, i_mb_y );
else
x264_macroblock_cache_load_progressive( h, i_mb_x, i_mb_y );
//分析-帧内预测模式选择、帧间运动估计等
x264_macroblock_analyse( h );
/* encode this macroblock -> be careful it can change the mb type to P_SKIP if needed */
reencode:
//编码-残差DCT变换、量化
x264_macroblock_encode( h );
//输出CABAC
if( h->param.b_cabac )
{
if( mb_xy > h->sh.i_first_mb && !(SLICE_MBAFF && (i_mb_y&1)) )
x264_cabac_encode_terminal( &h->cabac );
if( IS_SKIP( h->mb.i_type ) )
x264_cabac_mb_skip( h, 1 );
else
{
if( h->sh.i_type != SLICE_TYPE_I )
x264_cabac_mb_skip( h, 0 );
//输出
x264_macroblock_write_cabac( h, &h->cabac );
}
}
else
{
//输出CAVLC
if( IS_SKIP( h->mb.i_type ) )
i_skip++;
else
{
if( h->sh.i_type != SLICE_TYPE_I )
{
bs_write_ue( &h->out.bs, i_skip ); /* skip run */
i_skip = 0;
}
//输出
x264_macroblock_write_cavlc( h );
/* If there was a CAVLC level code overflow, try again at a higher QP. */
if( h->mb.b_overflow )
{
h->mb.i_chroma_qp = h->chroma_qp_table[++h->mb.i_qp];
h->mb.i_skip_intra = 0;
h->mb.b_skip_mc = 0;
h->mb.b_overflow = 0;
x264_bitstream_restore( h, &bs_bak[BS_BAK_CAVLC_OVERFLOW], &i_skip, 0 );
goto reencode;
}
}
}
int total_bits = bs_pos(&h->out.bs) + x264_cabac_pos(&h->cabac);
int mb_size = total_bits - mb_spos;
if( slice_max_size && (!SLICE_MBAFF || (i_mb_y&1)) )
{
/* Count the skip run, just in case. */
if( !h->param.b_cabac )
total_bits += bs_size_ue_big( i_skip );
/* Check for escape bytes. */
uint8_t *end = h->param.b_cabac ? h->cabac.p : h->out.bs.p;
for( ; last_emu_check < end - 2; last_emu_check++ )
if( last_emu_check[0] == 0 && last_emu_check[1] == 0 && last_emu_check[2] <= 3 )
{
slice_max_size -= 8;
last_emu_check++;
}
/* We'll just re-encode this last macroblock if we go over the max slice size. */
if( total_bits - starting_bits > slice_max_size && !h->mb.b_reencode_mb )
{
if( !x264_frame_new_slice( h, h->fdec ) )
{
/* Handle the most obnoxious slice-min-mbs edge case: we need to end the slice
* because it's gone over the maximum size, but doing so would violate slice-min-mbs.
* If possible, roll back to the last checkpoint and try again.
* We could try raising QP, but that would break in the case where a slice spans multiple
* rows, which the re-encoding infrastructure can't currently handle. */
if( mb_xy <= thread_last_mb && (thread_last_mb+1-mb_xy) < h->param.i_slice_min_mbs )
{
if( thread_last_mb-h->param.i_slice_min_mbs < h->sh.i_first_mb+h->param.i_slice_min_mbs )
{
x264_log( h, X264_LOG_WARNING, "slice-max-size violated (frame %d, cause: slice-min-mbs)\n", h->i_frame );
slice_max_size = 0;
goto cont;
}
x264_bitstream_restore( h, &bs_bak[BS_BAK_SLICE_MIN_MBS], &i_skip, 0 );
h->mb.b_reencode_mb = 1;
h->sh.i_last_mb = thread_last_mb-h->param.i_slice_min_mbs;
break;
}
if( mb_xy-SLICE_MBAFF*h->mb.i_mb_stride != h->sh.i_first_mb )
{
x264_bitstream_restore( h, &bs_bak[BS_BAK_SLICE_MAX_SIZE], &i_skip, 0 );
h->mb.b_reencode_mb = 1;
if( SLICE_MBAFF )
{
// set to bottom of previous mbpair
if( i_mb_x )
h->sh.i_last_mb = mb_xy-1+h->mb.i_mb_stride*(!(i_mb_y&1));
else
h->sh.i_last_mb = (i_mb_y-2+!(i_mb_y&1))*h->mb.i_mb_stride + h->mb.i_mb_width - 1;
}
else
h->sh.i_last_mb = mb_xy-1;
break;
}
else
h->sh.i_last_mb = mb_xy;
}
else
slice_max_size = 0;
}
}
cont:
h->mb.b_reencode_mb = 0;
/* save cache */
//保存当前宏块的的值,用于以后的宏块的编码
//包括Intra4x4宏块帧内预测模式,DCT非零系数,运动矢量,参考帧序号等等
x264_macroblock_cache_save( h );
//码率控制
if( x264_ratecontrol_mb( h, mb_size ) < 0 )
{
x264_bitstream_restore( h, &bs_bak[BS_BAK_ROW_VBV], &i_skip, 1 );
h->mb.b_reencode_mb = 1;
i_mb_x = 0;
i_mb_y = i_mb_y - SLICE_MBAFF;
h->mb.i_mb_prev_xy = i_mb_y * h->mb.i_mb_stride - 1;
h->sh.i_last_mb = orig_last_mb;
continue;
}
/* accumulate mb stats */
//后面很大一段代码都是对stat结构体中的统计信息进行赋值================================
h->stat.frame.i_mb_count[h->mb.i_type]++;
int b_intra = IS_INTRA( h->mb.i_type );
int b_skip = IS_SKIP( h->mb.i_type );
if( h->param.i_log_level >= X264_LOG_INFO || h->param.rc.b_stat_write )
{
if( !b_intra && !b_skip && !IS_DIRECT( h->mb.i_type ) )
{
if( h->mb.i_partition != D_8x8 )
h->stat.frame.i_mb_partition[h->mb.i_partition] += 4;
else
for( int i = 0; i < 4; i++ )
h->stat.frame.i_mb_partition[h->mb.i_sub_partition[i]] ++;
if( h->param.i_frame_reference > 1 )
for( int i_list = 0; i_list <= (h->sh.i_type == SLICE_TYPE_B); i_list++ )
for( int i = 0; i < 4; i++ )
{
int i_ref = h->mb.cache.ref[i_list][ x264_scan8[4*i] ];
if( i_ref >= 0 )
h->stat.frame.i_mb_count_ref[i_list][i_ref] ++;
}
}
}
if( h->param.i_log_level >= X264_LOG_INFO )
{
if( h->mb.i_cbp_luma | h->mb.i_cbp_chroma )
{
if( CHROMA444 )
{
for( int i = 0; i < 4; i++ )
if( h->mb.i_cbp_luma & (1 << i) )
for( int p = 0; p < 3; p++ )
{
int s8 = i*4+p*16;
int nnz8x8 = M16( &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[s8]+0] )
| M16( &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[s8]+8] );
h->stat.frame.i_mb_cbp[!b_intra + p*2] += !!nnz8x8;
}
}
else
{
int cbpsum = (h->mb.i_cbp_luma&1) + ((h->mb.i_cbp_luma>>1)&1)
+ ((h->mb.i_cbp_luma>>2)&1) + (h->mb.i_cbp_luma>>3);
h->stat.frame.i_mb_cbp[!b_intra + 0] += cbpsum;
h->stat.frame.i_mb_cbp[!b_intra + 2] += !!h->mb.i_cbp_chroma;
h->stat.frame.i_mb_cbp[!b_intra + 4] += h->mb.i_cbp_chroma >> 1;
}
}
if( h->mb.i_cbp_luma && !b_intra )
{
h->stat.frame.i_mb_count_8x8dct[0] ++;
h->stat.frame.i_mb_count_8x8dct[1] += h->mb.b_transform_8x8;
}
if( b_intra && h->mb.i_type != I_PCM )
{
if( h->mb.i_type == I_16x16 )
h->stat.frame.i_mb_pred_mode[0][h->mb.i_intra16x16_pred_mode]++;
else if( h->mb.i_type == I_8x8 )
for( int i = 0; i < 16; i += 4 )
h->stat.frame.i_mb_pred_mode[1][h->mb.cache.intra4x4_pred_mode[x264_scan8[i]]]++;
else //if( h->mb.i_type == I_4x4 )
for( int i = 0; i < 16; i++ )
h->stat.frame.i_mb_pred_mode[2][h->mb.cache.intra4x4_pred_mode[x264_scan8[i]]]++;
h->stat.frame.i_mb_pred_mode[3][x264_mb_chroma_pred_mode_fix[h->mb.i_chroma_pred_mode]]++;
}
h->stat.frame.i_mb_field[b_intra?0:b_skip?2:1] += MB_INTERLACED;
}
//===========================================================
/* calculate deblock strength values (actual deblocking is done per-row along with hpel) */
//计算去块效应滤波器强度Bs
//这里没有滤波
if( b_deblock )
x264_macroblock_deblock_strength( h );
//如果处理完最后一个宏块,就跳出大循环
if( mb_xy == h->sh.i_last_mb )
break;
if( SLICE_MBAFF )
{
i_mb_x += i_mb_y & 1;
i_mb_y ^= i_mb_x < h->mb.i_mb_width;
}
else
i_mb_x++;//宏块序号x加1
//处理完一行宏块
if( i_mb_x == h->mb.i_mb_width )
{
//该处理下一行了
i_mb_y++;//宏块序号y加1
i_mb_x = 0;//宏块序号x设置为0
}
}
if( h->sh.i_last_mb < h->sh.i_first_mb )
return 0;
h->out.nal[h->out.i_nal].i_last_mb = h->sh.i_last_mb;
//熵编码的收尾工作
if( h->param.b_cabac )
{
x264_cabac_encode_flush( h, &h->cabac );
h->out.bs.p = h->cabac.p;
}
else
{
if( i_skip > 0 )
bs_write_ue( &h->out.bs, i_skip ); /* last skip run */
/* rbsp_slice_trailing_bits */
bs_rbsp_trailing( &h->out.bs );
bs_flush( &h->out.bs );
}
//结束输出一个NAL
//前面对应着x264_nal_start()
if( x264_nal_end( h ) )
return -1;
//多线程并行处理?
if( h->sh.i_last_mb == (h->i_threadslice_end * h->mb.i_mb_width - 1) )
{
h->stat.frame.i_misc_bits = bs_pos( &h->out.bs )
+ (h->out.i_nal*NALU_OVERHEAD * 8)
- h->stat.frame.i_tex_bits
- h->stat.frame.i_mv_bits;
x264_fdec_filter_row( h, h->i_threadslice_end, 0 );
if( h->param.b_sliced_threads )
{
/* Tell the main thread we're done. */
x264_threadslice_cond_broadcast( h, 1 );
/* Do hpel now */
for( int mb_y = h->i_threadslice_start; mb_y <= h->i_threadslice_end; mb_y++ )
x264_fdec_filter_row( h, mb_y, 1 );
x264_threadslice_cond_broadcast( h, 2 );
/* Do the first row of hpel, now that the previous slice is done */
if( h->i_thread_idx > 0 )
{
x264_threadslice_cond_wait( h->thread[h->i_thread_idx-1], 2 );
x264_fdec_filter_row( h, h->i_threadslice_start + (1 << SLICE_MBAFF), 2 );
}
}
/* Free mb info after the last thread's done using it */
if( h->fdec->mb_info_free && (!h->param.b_sliced_threads || h->i_thread_idx == (h->param.i_threads-1)) )
{
h->fdec->mb_info_free( h->fdec->mb_info );
h->fdec->mb_info = NULL;
h->fdec->mb_info_free = NULL;
}
}
return 0;
}根据源代码简单梳理了x264_slice_write()的流程,如下所示:
(1)调用x264_nal_start()开始输出一个NALU。
(2)x264_macroblock_thread_init():初始化宏块重建像素缓存fdec_buf[]和编码像素缓存fenc_buf[]。
(3)调用x264_slice_header_write()输出 Slice Header。
(4)进入一个循环,该循环每执行一遍编码一个宏块:
a) 每处理一行宏块,调用一次x264_fdec_filter_row()执行滤波模块。b) 调用x264_macroblock_cache_load_progressive()将要编码的宏块的周围的宏块的信息读进来。c) 调用x264_macroblock_analyse()执行分析模块。d) 调用x264_macroblock_encode()执行宏块编码模块。e) 调用x264_macroblock_write_cabac()/x264_macroblock_write_cavlc()执行熵编码模块。f) 调用x264_macroblock_cache_save()保存当前宏块的信息。g) 调用x264_ratecontrol_mb()执行码率控制。h) 准备处理下一个宏块。
(5)调用x264_nal_end()结束输出一个NALU。
下文分别从数据结构和函数两个方面分析x264_slice_write()的源代码。
重要的数据结构
X264在宏块编码方面涉及到下面几个比较重要的结构体:宏块像素存储缓存fenc_buf[]和fdec_buf[]——位于x264_t.mb.pic中,用于存储宏块的亮度和色度像素。
宏块各种信息的缓存Cache——位于x264_t.mb.pic中,用于存储宏块的信息例如4x4帧内预测模式、DCT的非0系数个数、运动矢量、参考帧序号等。
图像半像素点存储空间filtered[]——位于x264_frame_t中,用于存储半像素插值后的点。
宏块像素存储缓存fenc_buf[]和fdec_buf[]
fenc_buf[]和fdec_buf[]为x264_t.mb.cache中的结构体,用于存储一个宏块的像素数据。其中fenc_buf[]用于存储宏块编码像素数据,而fdec_buf[]用于存储宏块重建像素数据。他们的定义如下所示。/* space for p_fenc and p_fdec */
#define FENC_STRIDE 16
#define FDEC_STRIDE 32
//存储编码宏块fenc和重建宏块fdec的内存
uint8_t fenc_buf[48*FENC_STRIDE]
uint8_t fdec_buf[52*FDEC_STRIDE]

从图中可以看出,fdec_buf[]和fenc_buf[]主要的区别在于fdec_buf[]像素块的左边和上边包含了左上方相邻块用于预测的像素。
宏块各种信息的缓存Cache
在x264中x264_t.mb.cache结构体中包含了存储宏块信息的各种各样的缓存Cache。例如:intra4x4_pred_mode:Intra4x4帧内预测模式的缓存这几个Cache的定义如下所示。
non_zero_count:DCT的非0系数个数的缓存
mv:运动矢量缓存
ref:运动矢量参考帧的缓存
/* 宏块信息缓存cache */
struct
{
/* real intra4x4_pred_mode if I_4X4 or I_8X8, I_PRED_4x4_DC if mb available, -1 if not */
/*
* mb.cache.intra4x4_pred_mode[]格式如下
* |
* --+--------------
* | 0 0 0 y y y y y
* | 0 0 0 y Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 y Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 y Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 y Y Y Y Y
*/
ALIGNED_8( int8_t intra4x4_pred_mode[X264_SCAN8_LUMA_SIZE] );
/* i_non_zero_count if available else 0x80 */
/*
* mb.cache.non_zero_count[]格式如下
* |
* --+--------------
* | 0 0 0 y y y y y
* | 0 0 0 y Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 y Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 y Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 y Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 u u u u u
* | 0 0 0 u U U U U
* | 0 0 0 u U U U U
* | 0 0 0 u U U U U
* | 0 0 0 u U U U U
* | 0 0 0 v v v v v
* | 0 0 0 v V V V V
* | 0 0 0 v V V V V
* | 0 0 0 v V V V V
* | 0 0 0 v V V V V
*/
ALIGNED_16( uint8_t non_zero_count[X264_SCAN8_SIZE] );
/* -1 if unused, -2 if unavailable */
/*
* mb.cache.ref[0][]格式如下
* |
* --+--------------
* | 0 0 0 y y y y y
* | 0 0 0 y Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 y Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 y Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 y Y Y Y Y
*/
ALIGNED_4( int8_t ref[2][X264_SCAN8_LUMA_SIZE] );
/* 0 if not available */
/*
* mb.cache.mv[0][]格式如下
* |
* --+--------------
* | 0 0 0 y y y y y
* | 0 0 0 y Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 y Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 y Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 y Y Y Y Y
*/
ALIGNED_16( int16_t mv[2][X264_SCAN8_LUMA_SIZE][2] );
ALIGNED_8( uint8_t mvd[2][X264_SCAN8_LUMA_SIZE][2] );
/* 1 if SKIP or DIRECT. set only for B-frames + CABAC */
ALIGNED_4( int8_t skip[X264_SCAN8_LUMA_SIZE] );
ALIGNED_4( int16_t direct_mv[2][4][2] );
ALIGNED_4( int8_t direct_ref[2][4] );
int direct_partition;
ALIGNED_4( int16_t pskip_mv[2] );
/* number of neighbors (top and left) that used 8x8 dct */
int i_neighbour_transform_size;
int i_neighbour_skip;
/* neighbor CBPs */
int i_cbp_top;
int i_cbp_left;
/* extra data required for mbaff in mv prediction */
int16_t topright_mv[2][3][2];
int8_t topright_ref[2][3];
/* current mb deblock strength */
uint8_t (*deblock_strength)[8][4];
} cache;通过观察上面的定义,会发现Cache都是一个包含x*8个元素的一维数组(x取15或者5)。Cache使用一维数组比较形象的存储了二维图像的信息。从上面的代码可以看出Cache中存储有效数据的地方是一个位于右下角的“方形区域”,这一部分实际上对应一维数组中第12-15,20-23,28-31,36-39的元素。这个“方形区域”代表了一个宏块的亮度相关的信息,其中一共包含16个元素。由于1个宏块的亮度数据是1个16x16的块,所以这个“方形区域”里面1个元素实际上代表了一个4x4的块的信息(“4x4”的亮度块应该也是H.264压缩编码中最小的处理单元)。
如果我们使用12-15,20-23,28-31,36-39这些范围内的下标引用Cache中的元素,实在是不太方便。由此也引出了x264中另一个关键的变量——scan8[]数组。scan8[]
scan8[]存储的是缓存的序号值,它一般情况下是与前面提到的Cache配合使用的。scan8[]的定义位于libavcodec\h264.h,如下所示。/* Scan8 organization:
* 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
* 0 DY y y y y y
* 1 y Y Y Y Y
* 2 y Y Y Y Y
* 3 y Y Y Y Y
* 4 y Y Y Y Y
* 5 DU u u u u u
* 6 u U U U U
* 7 u U U U U
* 8 u U U U U
* 9 u U U U U
* 10 DV v v v v v
* 11 v V V V V
* 12 v V V V V
* 13 v V V V V
* 14 v V V V V
* DY/DU/DV are for luma/chroma DC.
*/
/*
* 扫描方式:
* o-o o-o
* / / /
* o-o o-o
* ,---'
* o-o o-o
* / / /
* o-o o-o
*/
/*
* 关于多次出现的scan8
*
* cache是一个表格。表格中存储了一整个宏块的信息,每一个元素代表了一个“4x4块”(H.264中最小的处理单位)。
* scan8[]则存储了宏块信息在cache中的索引值
*
* scan8[]中的“8”,意思应该是按照8x8为单元来扫描?
* 因此可以理解为“按照8x8为单元来扫描4x4的块”?
*
* scan8中按照顺序分别存储了Y,U,V的索引值。具体的存储还是在相应的cache中。
*
* cache中首先存储Y,然后存储U和V。cache中的存储方式如下所示。
* 其中数字代表了scan8[]中元素的索引值
*
* +---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+
* | | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
* +---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+
* | 0 | 48| | | | y| y| y| y|
* | 1 | | | | y| 0| 1| 4| 5|
* | 2 | | | | y| 2| 3| 6| 7|
* | 3 | | | | y| 8| 9| 12| 13|
* | 4 | | | | y| 10| 11| 14| 15|
* | 5 | 49| | | | u| u| u| u|
* | 6 | | | | u| 16| 17| 20| 21|
* | 7 | | | | u| 18| 19| 22| 23|
* | 8 | | | | u| 24| 25| 28| 29|
* | 9 | | | | u| 26| 27| 30| 31|
* |10 | 50| | | | v| v| v| v|
* |11 | | | | v| 32| 33| 36| 37|
* |12 | | | | v| 34| 35| 38| 39|
* |13 | | | | v| 40| 41| 44| 45|
* |14 | | | | v| 42| 43| 46| 47|
* |---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+
* | |
*
*/
#define LUMA_DC 48
#define CHROMA_DC 49
static const uint8_t x264_scan8[16*3 + 3] =
{
4+ 1*8, 5+ 1*8, 4+ 2*8, 5+ 2*8,
6+ 1*8, 7+ 1*8, 6+ 2*8, 7+ 2*8,
4+ 3*8, 5+ 3*8, 4+ 4*8, 5+ 4*8,
6+ 3*8, 7+ 3*8, 6+ 4*8, 7+ 4*8,
4+ 6*8, 5+ 6*8, 4+ 7*8, 5+ 7*8,
6+ 6*8, 7+ 6*8, 6+ 7*8, 7+ 7*8,
4+ 8*8, 5+ 8*8, 4+ 9*8, 5+ 9*8,
6+ 8*8, 7+ 8*8, 6+ 9*8, 7+ 9*8,
4+11*8, 5+11*8, 4+12*8, 5+12*8,
6+11*8, 7+11*8, 6+12*8, 7+12*8,
4+13*8, 5+13*8, 4+14*8, 5+14*8,
6+13*8, 7+13*8, 6+14*8, 7+14*8,
0+ 0*8, 0+ 5*8, 0+10*8
};可以看出scan8[]数组中元素的值都是以“a+b*8”的形式写的,我们不妨计算一下前面16个元素的值:
scan8[0]=12
scan8[1]= 13
scan8[2]= 20
scan8[3]= 21
scan8[4]= 14
scan8[5]= 15
scan8[6]= 22
scan8[7]= 23
scan8[8]= 28
scan8[9]= 29
scan8[10]= 36
scan8[11]= 37
scan8[12]= 30
scan8[13]= 31
scan8[14]= 38
scan8[15]= 39
如果把scan8[]数组这些元素的值,作为Cache(例如mv[],ref[]等)的序号,会发现他们的在Cache中代表的元素的位置如下图所示。

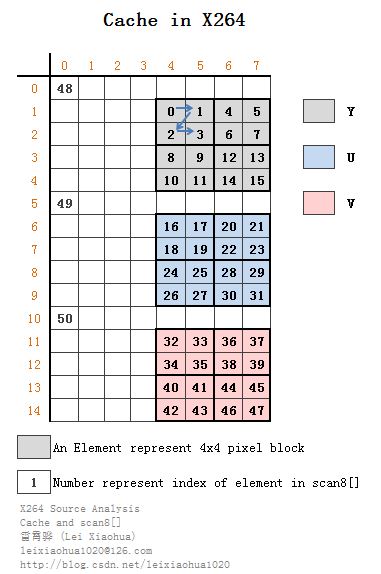
PS:有关scan8[]数组在网上能查到一点资料。但是经过源代码比对之后,我发现网上的资料已经过时了。旧版本scan8[]代表的Cache的存储方式如下所示。

图像半像素点存储缓存filtered[]
X264中在图像运动搜索的过程中,需要使用1/4像素精度的运动补偿。其中半像素点的内插工作是提前完成的。每一帧的半像素点存储在x264_frame_t的filtered[3][4]变量中。其中前面的“[3]”代表Y,U,V三个分量,后面的“[4]”分别存储了整像素, H半像素, V半像素, C(对角线)半像素的数据。
下面的图以4x4图像块为例演示了filtered[][4]中几种半像素点与整像素点之间的位置关系。图中灰色的点为整像素点,黄色的点为半像素点。filtered[][0]存储了整像素点数据,filtered[][1]存储了H半像素点数据,filtered[][2]存储了V半像素点数据,filtered[][3]存储了C(对角线)半像素点数据。
重要的函数
下文简单记录x264_slice_write()中调用的几个函数:x264_macroblock_thread_init():初始化宏块重建数据缓存fdec_buf[]和编码数据缓存fenc_buf[]。另外还有一些关键模块对应的函数将会在后续文章中进行分析:
x264_slice_header_write():输出 Slice Header。
x264_macroblock_cache_load():将要编码的宏块的周围的宏块的信息读进来。x264_macroblock_cache_save():保存当前宏块的信息。
x264_fdec_filter_row():滤波模块。该模块包含了环路滤波,半像素插值,SSIM/PSNR的计算。
x264_macroblock_analyse():分析模块。该模块包含了帧内预测模式分析以及帧间运动估计等。
x264_macroblock_encode():宏块编码模块。该模块通过对残差的DCT变换、量化等方式对宏块进行编码。
x264_macroblock_write_cabac():CABAC熵编码模块。
x264_macroblock_write_cavlc():CAVLC熵编码模块。
x264_macroblock_thread_init()
x264_macroblock_thread_init()用于初始化宏块重建数据缓存fdec_buf[]和编码数据缓存fenc_buf[]。该函数的定义位于common\macroblock.c,如下所示。//存储宏块像素的缓存fdec_buf和fenc_buf的初始化
//设定宏块编码缓存p_fenc[0],p_fenc[1],p_fenc[2]
//设定宏块重建缓存p_fdec[0],p_fdec[1],p_fdec[2]
//[0]存Y,[1]存U,[2]存V
void x264_macroblock_thread_init( x264_t *h )
{
h->mb.i_me_method = h->param.analyse.i_me_method;
h->mb.i_subpel_refine = h->param.analyse.i_subpel_refine;
if( h->sh.i_type == SLICE_TYPE_B && (h->mb.i_subpel_refine == 6 || h->mb.i_subpel_refine == 8) )
h->mb.i_subpel_refine--;
h->mb.b_chroma_me = h->param.analyse.b_chroma_me &&
((h->sh.i_type == SLICE_TYPE_P && h->mb.i_subpel_refine >= 5) ||
(h->sh.i_type == SLICE_TYPE_B && h->mb.i_subpel_refine >= 9));
h->mb.b_dct_decimate = h->sh.i_type == SLICE_TYPE_B ||
(h->param.analyse.b_dct_decimate && h->sh.i_type != SLICE_TYPE_I);
h->mb.i_mb_prev_xy = -1;
/*
* fdec_buf和fenc_buf简易存储图
* fdec_buf用于存储重建帧
* fenc_buf用于存储编码帧
*
* 存储结果如图所示
* fdec_buf用于存储数据;fdec[0],fdec[1],fdec[2]指向fdec_buf的不同位置
* 4:2:0 4:2:2 4:4:4
* fdec fenc fdec fenc fdec fenc
* y y y y y y y Y Y Y Y y y y y y y y Y Y Y Y y y y y y y y Y Y Y Y
* y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
* y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
* y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
* y Y Y Y Y U U V V y Y Y Y Y U U V V y Y Y Y Y U U U U
* u u u v v v U U V V u u u v v v U U V V u u u u u u u U U U U
* u U U v V V u U U v V V U U V V u U U U U U U U U
* u U U v V V u U U v V V U U V V u U U U U U U U U
* u U U v V V u U U U U V V V V
* u U U v V V u U U U U V V V V
* v v v v v v v V V V V
* v V V V V V V V V
* v V V V V
* v V V V V
* v V V V V
*
* fdec_buf详细存储示例(YUV420P)
* y、u、v为预测要用到的数据
* Y、U、V为像素数据
* 每行32像素
*
* p_fdec[0] = fdec_buf + 2*32;
* p_fenc[1] = fenc_buf + 19*32;
* p_fenc[2] = fenc_buf + 19*32+16;
*
*
* 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 y
* y y y y y y y y y y y y y y y y 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 y
* Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 y
* Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 y
* Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 y
* Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 y
* ...
* Y一共16行
* ...
* Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 y
* Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 y
* Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 u
* u u u u u u u u 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 v v v v v v v v v 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 u
* U U U U U U U U 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 v V V V V V V V V 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 u
* U U U U U U U U 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 v V V V V V V V V 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 u
* U U U U U U U U 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 v V V V V V V V V 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 u
* U U U U U U U U 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 v V V V V V V V V 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 u
* ...
* UV一共8行
* ...
*
* =============================================================================
*
* fenc_buf详细存储示例(YUV420P)
* Y、U、V为像素数据
* 每行16像素
*
* p_fdec[0] = fdec_buf + 0;
* p_fenc[1] = fenc_buf + 16*32;
* p_fenc[2] = fenc_buf + 16*32+8;
*
* Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
* Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
* Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
* Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
* ...
* Y一共16行
* ...
* Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
* Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
* Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
* U U U U U U U U V V V V V V V V
* U U U U U U U U V V V V V V V V
* U U U U U U U U V V V V V V V V
* U U U U U U U U V V V V V V V V
* ...
* UV一共8行
* ...
*/
//fenc(编码帧)结构比较简单,Y、U、V像素“挨着”存放
h->mb.pic.p_fenc[0] = h->mb.pic.fenc_buf;
//fdec(重建帧)结构比较复杂,需要当前宏块左边以及上边宏块的信息
//第1行为空,第2行用于存储上边宏块下边缘的像素
h->mb.pic.p_fdec[0] = h->mb.pic.fdec_buf + 2*FDEC_STRIDE;
//U
h->mb.pic.p_fenc[1] = h->mb.pic.fenc_buf + 16*FENC_STRIDE;
h->mb.pic.p_fdec[1] = h->mb.pic.fdec_buf + 19*FDEC_STRIDE;
//V
if( CHROMA444 )
{
h->mb.pic.p_fenc[2] = h->mb.pic.fenc_buf + 32*FENC_STRIDE;
h->mb.pic.p_fdec[2] = h->mb.pic.fdec_buf + 36*FDEC_STRIDE;
}
else
{
//注意+8和+16
h->mb.pic.p_fenc[2] = h->mb.pic.fenc_buf + 16*FENC_STRIDE + 8;
h->mb.pic.p_fdec[2] = h->mb.pic.fdec_buf + 19*FDEC_STRIDE + 16;
}
}从源代码可以看出,x264_macroblock_thread_init()设定了宏块编码数据指针p_fenc[0],p_fenc[1],p_fenc[2]在fenc_buf[]中的位置,以及宏块重建数据指针p_fdec[0],p_fdec[1],p_fdec[2] 在fdec_buf[]中的位置。由于前文中已经介绍过fenc_buf[]和fdec_buf[]的结构,在这里不再重复。
x264_slice_header_write()
x264_slice_header_write()用于输出Slice Header。该函数的定义位于encoder\encoder.c,如下所示。//输出 slice header
static void x264_slice_header_write( bs_t *s, x264_slice_header_t *sh, int i_nal_ref_idc )
{
if( sh->b_mbaff )
{
int first_x = sh->i_first_mb % sh->sps->i_mb_width;
int first_y = sh->i_first_mb / sh->sps->i_mb_width;
assert( (first_y&1) == 0 );
bs_write_ue( s, (2*first_x + sh->sps->i_mb_width*(first_y&~1) + (first_y&1)) >> 1 );
}
else
bs_write_ue( s, sh->i_first_mb );//first_mb_in_slice: Slice中的第一个宏块的地址
//slice_type: Slice类型(I,B,P,SI,SP)
bs_write_ue( s, sh->i_type + 5 ); /* same type things */
//pic_parameter_set_id: PPS的索引号
bs_write_ue( s, sh->i_pps_id );
//frame_num: 指明了各图像的解码顺序
bs_write( s, sh->sps->i_log2_max_frame_num, sh->i_frame_num & ((1<<sh->sps->i_log2_max_frame_num)-1) );
if( !sh->sps->b_frame_mbs_only )
{
bs_write1( s, sh->b_field_pic );
if( sh->b_field_pic )
bs_write1( s, sh->b_bottom_field );
}
if( sh->i_idr_pic_id >= 0 ) /* NAL IDR */
bs_write_ue( s, sh->i_idr_pic_id );//idr_pic_id: IDR图像的标识
if( sh->sps->i_poc_type == 0 )
{
bs_write( s, sh->sps->i_log2_max_poc_lsb, sh->i_poc & ((1<<sh->sps->i_log2_max_poc_lsb)-1) );
if( sh->pps->b_pic_order && !sh->b_field_pic )
bs_write_se( s, sh->i_delta_poc_bottom );
}
if( sh->pps->b_redundant_pic_cnt )
bs_write_ue( s, sh->i_redundant_pic_cnt );
if( sh->i_type == SLICE_TYPE_B )
bs_write1( s, sh->b_direct_spatial_mv_pred );
if( sh->i_type == SLICE_TYPE_P || sh->i_type == SLICE_TYPE_B )
{
bs_write1( s, sh->b_num_ref_idx_override );
if( sh->b_num_ref_idx_override )
{
bs_write_ue( s, sh->i_num_ref_idx_l0_active - 1 );
if( sh->i_type == SLICE_TYPE_B )
bs_write_ue( s, sh->i_num_ref_idx_l1_active - 1 );
}
}
/* ref pic list reordering */
if( sh->i_type != SLICE_TYPE_I )
{
bs_write1( s, sh->b_ref_pic_list_reordering[0] );
if( sh->b_ref_pic_list_reordering[0] )
{
for( int i = 0; i < sh->i_num_ref_idx_l0_active; i++ )
{
bs_write_ue( s, sh->ref_pic_list_order[0][i].idc );
bs_write_ue( s, sh->ref_pic_list_order[0][i].arg );
}
bs_write_ue( s, 3 );
}
}
if( sh->i_type == SLICE_TYPE_B )
{
bs_write1( s, sh->b_ref_pic_list_reordering[1] );
if( sh->b_ref_pic_list_reordering[1] )
{
for( int i = 0; i < sh->i_num_ref_idx_l1_active; i++ )
{
bs_write_ue( s, sh->ref_pic_list_order[1][i].idc );
bs_write_ue( s, sh->ref_pic_list_order[1][i].arg );
}
bs_write_ue( s, 3 );
}
}
sh->b_weighted_pred = 0;
if( sh->pps->b_weighted_pred && sh->i_type == SLICE_TYPE_P )
{
sh->b_weighted_pred = sh->weight[0][0].weightfn || sh->weight[0][1].weightfn || sh->weight[0][2].weightfn;
/* pred_weight_table() */
bs_write_ue( s, sh->weight[0][0].i_denom );
bs_write_ue( s, sh->weight[0][1].i_denom );
for( int i = 0; i < sh->i_num_ref_idx_l0_active; i++ )
{
int luma_weight_l0_flag = !!sh->weight[i][0].weightfn;
int chroma_weight_l0_flag = !!sh->weight[i][1].weightfn || !!sh->weight[i][2].weightfn;
bs_write1( s, luma_weight_l0_flag );
if( luma_weight_l0_flag )
{
bs_write_se( s, sh->weight[i][0].i_scale );
bs_write_se( s, sh->weight[i][0].i_offset );
}
bs_write1( s, chroma_weight_l0_flag );
if( chroma_weight_l0_flag )
{
for( int j = 1; j < 3; j++ )
{
bs_write_se( s, sh->weight[i][j].i_scale );
bs_write_se( s, sh->weight[i][j].i_offset );
}
}
}
}
else if( sh->pps->b_weighted_bipred == 1 && sh->i_type == SLICE_TYPE_B )
{
/* TODO */
}
if( i_nal_ref_idc != 0 )
{
if( sh->i_idr_pic_id >= 0 )
{
bs_write1( s, 0 ); /* no output of prior pics flag */
bs_write1( s, 0 ); /* long term reference flag */
}
else
{
bs_write1( s, sh->i_mmco_command_count > 0 ); /* adaptive_ref_pic_marking_mode_flag */
if( sh->i_mmco_command_count > 0 )
{
for( int i = 0; i < sh->i_mmco_command_count; i++ )
{
bs_write_ue( s, 1 ); /* mark short term ref as unused */
bs_write_ue( s, sh->mmco[i].i_difference_of_pic_nums - 1 );
}
bs_write_ue( s, 0 ); /* end command list */
}
}
}
if( sh->pps->b_cabac && sh->i_type != SLICE_TYPE_I )
bs_write_ue( s, sh->i_cabac_init_idc );
//slice_qp_delta: 指出在用于当前片的所有宏块的量化参数的初始值
//SliceQP = 26 + pic_init_qp_minus26 + slice_qp_delta
bs_write_se( s, sh->i_qp_delta ); /* slice qp delta */
if( sh->pps->b_deblocking_filter_control )
{
bs_write_ue( s, sh->i_disable_deblocking_filter_idc );
if( sh->i_disable_deblocking_filter_idc != 1 )
{
bs_write_se( s, sh->i_alpha_c0_offset >> 1 );
bs_write_se( s, sh->i_beta_offset >> 1 );
}
}
}有关x264_slice_header_write()的源代码不再做详细的分析。其中Slice Header的结构参考《H.264标准》即可。
x264_fdec_filter_row()
x264_fdec_filter_row()属于滤波模块,完成几种滤波工作:(1)半像素内插下面简单记录一下半像素内插和环路滤波的概念(后续文章再对源代码进行分析)。
(2)环路滤波
(3)PSNR/SSIM计算
(1)半像素插值知识简述
简单记录一下半像素插值的知识。《H.264标准》中规定,运动估计为1/4像素精度。因此在H.264编码和解码的过程中,需要将画面中的像素进行插值——简单地说就是把原先的1个像素点拓展成4x4一共16个点。下图显示了H.264编码和解码过程中像素插值情况。可以看出原先的G点的右下方通过插值的方式产生了a、b、c、d等一共16个点。
(1)半像素内插。这一步通过6抽头滤波器获得5个半像素点。图中半像素内插点为b、m、h、s、j五个点。半像素内插方法是对整像素点进行6 抽头滤波得出,滤波器的权重为(1/32, -5/32, 5/8, 5/8, -5/32, 1/32)。例如b的计算公式为:
(2)线性内插。这一步通过简单的线性内插获得剩余的1/4像素点。
b=round( (E - 5F + 20G + 20H - 5I + J ) / 32)
剩下几个半像素点的计算关系如下:
m:由B、D、H、N、S、U计算
h:由A、C、G、M、R、T计算
s:由K、L、M、N、P、Q计算
j:由cc、dd、h、m、ee、ff计算。需要注意j点的运算量比较大,因为cc、dd、ee、ff都需要通过半像素内插方法进行计算。
在获得半像素点之后,就可以通过简单的线性内插获得1/4像素内插点了。1/4像素内插的方式如下图所示。例如图中a点的计算公式如下:
A=round( (G+b)/2 )
在这里有一点需要注意:位于4个角的e、g、p、r四个点并不是通过j点计算计算的,而是通过b、h、s、m四个半像素点计算的。
(2)环路滤波相关知识简述
简单记录一下环路滤波(去块效应滤波)的知识。X264的重建帧(通过解码得到)一般情况下会出现方块效应。产生这种效应的原因主要有两个:(1)DCT变换后的量化造成误差(主要原因)。正是由于这种块效应的存在,才需要添加环路滤波器调整相邻的“块”边缘上的像素值以减轻这种视觉上的不连续感。下面一张图显示了环路滤波的效果。图中左边的图没有使用环路滤波,而右边的图使用了环路滤波。
(2)运动补偿

环路滤波分类
环路滤波器根据滤波的强度可以分为两种:(1)普通滤波器。针对边界的Bs(边界强度)为1、2、3的滤波器。此时环路滤波涉及到方块边界周围的6个点(边界两边各3个点):p2,p1,p0,q0,q1,q2。需要处理4个点(边界两边各2个点,只以p点为例):
(2)强滤波器。针对边界的Bs(边界强度)为4的滤波器。此时环路滤波涉及到方块边界周围的8个点(边界两边各4个点):p3,p2,p1,p0,q0,q1,q2,q3。需要处理6个点(边界两边各3个点,只以p点为例):
其中上文中提到的边界强度Bs的判定方式如下。
条件(针对两边的图像块) | Bs |
有一个块为帧内预测 + 边界为宏块边界 | 4 |
有一个块为帧内预测 | 3 |
有一个块对残差编码 | 2 |
运动矢量差不小于1像素 | 1 |
运动补偿参考帧不同 | 1 |
其它 | 0 |
环路滤波的门限
并不是所有的块的边界处都需要环路滤波。例如画面中物体的边界正好和块的边界重合的话,就不能进行滤波,否则会使画面中物体的边界变模糊。因此需要区别开物体边界和块效应边界。一般情况下,物体边界两边的像素值差别很大,而块效应边界两边像素值差别比较小。《H.264标准》以这个特点定义了2个变量alpha和beta来判决边界是否需要进行环路滤波。只有满足下面三个条件的时候才能进行环路滤波:x264_macroblock_cache_load()
x264_slice_write()根据是否包含隔行扫描,会分别调用x264_macroblock_cache_load_progressive()或者x264_macroblock_cache_load_interlaced()加载当前宏块的周边宏块的信息。这两个函数都会调用同一个函数x264_macroblock_cache_load()。上述两个函数的定义位于common\macroblock.c,如下所示。//加载Cache-逐行扫描
//即将要编码的宏块的周围的宏块的值读进来
void x264_macroblock_cache_load_progressive( x264_t *h, int mb_x, int mb_y )
{
x264_macroblock_cache_load( h, mb_x, mb_y, 0 );
}
//加载Cache-隔行扫描
void x264_macroblock_cache_load_interlaced( x264_t *h, int mb_x, int mb_y )
{
x264_macroblock_cache_load( h, mb_x, mb_y, 1 );
}x264_macroblock_cache_load()的定义位于common\macroblock.c,如下所示。
//加载Cache
//即将要编码的宏块的周围的宏块的值读进来
static void ALWAYS_INLINE x264_macroblock_cache_load( x264_t *h, int mb_x, int mb_y, int b_mbaff )
{
x264_macroblock_cache_load_neighbours( h, mb_x, mb_y, b_mbaff );
//左边宏块
int *left = h->mb.i_mb_left_xy;
//上边宏块
int top = h->mb.i_mb_top_xy;
int top_y = h->mb.i_mb_top_y;
int s8x8 = h->mb.i_b8_stride;
int s4x4 = h->mb.i_b4_stride;
int top_8x8 = (2*top_y+1) * s8x8 + 2*mb_x;
int top_4x4 = (4*top_y+3) * s4x4 + 4*mb_x;
int lists = (1 << h->sh.i_type) & 3;
/* GCC pessimizes direct loads from heap-allocated arrays due to aliasing. */
/* By only dereferencing them once, we avoid this issue. */
int8_t (*i4x4)[8] = h->mb.intra4x4_pred_mode;
//DCT非0系数个数
uint8_t (*nnz)[48] = h->mb.non_zero_count;
//CBP值
int16_t *cbp = h->mb.cbp;
const x264_left_table_t *left_index_table = h->mb.left_index_table;
h->mb.cache.deblock_strength = h->deblock_strength[mb_y&1][h->param.b_sliced_threads?h->mb.i_mb_xy:mb_x];
/*
*
* 关于多次出现的scan8
*
* scan8是和cache配合使用的
* cache是一个表格。表格中存储了一整个宏块的信息,每一个元素代表了一个“4x4亮度块”(H.264中最小的亮度处理单位)。
* scan8[]则存储了宏块信息在cache中的索引值
*
* scan8[]中的“8”,意思应该是按照8x8为单元来扫描?
* 因此可以理解为“按照8x8为单元来扫描4x4的块”?
*
* scan8中按照顺序分别存储了Y,U,V信息在cache中的索引值。具体的存储还是在相应的cache中。
*
* cache中首先存储Y,然后存储U和V。cache中的存储方式如下所示。
* 其中数字代表了scan8[]中元素的索引值
*
* +---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+
* | | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
* +---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+
* | 0 | 48| | | | y| y| y| y|
* | 1 | | | | y| 0| 1| 4| 5|
* | 2 | | | | y| 2| 3| 6| 7|
* | 3 | | | | y| 8| 9| 12| 13|
* | 4 | | | | y| 10| 11| 14| 15|
* | 5 | 49| | | | u| u| u| u|
* | 6 | | | | u| 16| 17| 20| 21|
* | 7 | | | | u| 18| 19| 22| 23|
* | 8 | | | | u| 24| 25| 28| 29|
* | 9 | | | | u| 26| 27| 30| 31|
* |10 | 50| | | | v| v| v| v|
* |11 | | | | v| 32| 33| 36| 37|
* |12 | | | | v| 34| 35| 38| 39|
* |13 | | | | v| 40| 41| 44| 45|
* |14 | | | | v| 42| 43| 46| 47|
* |---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+
* | |
*
* 扫描方式:
* o-o o-o
* / / /
* o-o o-o
* ,---'
* o-o o-o
* / / /
* o-o o-o
*
*/
/* load cache */
if( h->mb.i_neighbour & MB_TOP )
{
h->mb.cache.i_cbp_top = cbp[top];
/* load intra4x4 */
/*
* 填充intra4x4_pred_mode[]
* 在这里相当于在intra4x4_pred_mode[]填充了“y”,如下所示(没有U、V)
* |
* --+--------------
* | 0 0 0 0 y y y y
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
*/
CP32( &h->mb.cache.intra4x4_pred_mode[x264_scan8[0] - 8], &i4x4[top][0] );
/* load non_zero_count */
/*
* 填充non_zero_count[]
* 在这里相当于在non_zero_count[]填充了“y”,如下所示(只列出了Y。U、V是类似的)
* |
* --+--------------
* | 0 0 0 0 y y y y
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
*/
CP32( &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[ 0] - 8], &nnz[top][12] ); //Y
CP32( &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[16] - 8], &nnz[top][16-4 + (16>>CHROMA_V_SHIFT)] ); //U
CP32( &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[32] - 8], &nnz[top][32-4 + (16>>CHROMA_V_SHIFT)] ); //V
/* Finish the prefetching */
for( int l = 0; l < lists; l++ )
{
x264_prefetch( &h->mb.mv[l][top_4x4-1] );
/* Top right being not in the same cacheline as top left will happen
* once every 4 MBs, so one extra prefetch is worthwhile */
x264_prefetch( &h->mb.mv[l][top_4x4+4] );
x264_prefetch( &h->mb.ref[l][top_8x8-1] );
x264_prefetch( &h->mb.mvd[l][top] );
}
}
else
{
//没有相关信息的时候,填充下列数据
h->mb.cache.i_cbp_top = -1;
/* load intra4x4 */
M32( &h->mb.cache.intra4x4_pred_mode[x264_scan8[0] - 8] ) = 0xFFFFFFFFU;
/* load non_zero_count */
M32( &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[ 0] - 8] ) = 0x80808080U;
M32( &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[16] - 8] ) = 0x80808080U;
M32( &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[32] - 8] ) = 0x80808080U;
}
if( h->mb.i_neighbour & MB_LEFT )
{
int ltop = left[LTOP];
int lbot = b_mbaff ? left[LBOT] : ltop;
if( b_mbaff )
{
const int16_t top_luma = (cbp[ltop] >> (left_index_table->mv[0]&(~1))) & 2;
const int16_t bot_luma = (cbp[lbot] >> (left_index_table->mv[2]&(~1))) & 2;
h->mb.cache.i_cbp_left = (cbp[ltop] & 0xfff0) | (bot_luma<<2) | top_luma;
}
else
h->mb.cache.i_cbp_left = cbp[ltop];
/* load intra4x4 */
/*
* 填充intra4x4_pred_mode[]
* 在这里相当于在intra4x4_pred_mode[]填充了“y”,如下所示(没有U、V)
* |
* --+--------------
* | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
* | 0 0 0 y Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 y Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 y Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 y Y Y Y Y
*/
h->mb.cache.intra4x4_pred_mode[x264_scan8[ 0] - 1] = i4x4[ltop][left_index_table->intra[0]];
h->mb.cache.intra4x4_pred_mode[x264_scan8[ 2] - 1] = i4x4[ltop][left_index_table->intra[1]];
h->mb.cache.intra4x4_pred_mode[x264_scan8[ 8] - 1] = i4x4[lbot][left_index_table->intra[2]];
h->mb.cache.intra4x4_pred_mode[x264_scan8[10] - 1] = i4x4[lbot][left_index_table->intra[3]];
/* load non_zero_count */
/*
* 填充non_zero_count[]
* 在这里相当于在non_zero_count[]填充了“y”,如下所示(只列出了Y,U、V是类似的)
* |
* --+--------------
* | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
* | 0 0 0 y Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 y Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 y Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 y Y Y Y Y
*/
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[ 0] - 1] = nnz[ltop][left_index_table->nnz[0]];
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[ 2] - 1] = nnz[ltop][left_index_table->nnz[1]];
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[ 8] - 1] = nnz[lbot][left_index_table->nnz[2]];
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[10] - 1] = nnz[lbot][left_index_table->nnz[3]];
if( CHROMA_FORMAT >= CHROMA_422 )
{
int offset = (4>>CHROMA_H_SHIFT) - 4;
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[16+ 0] - 1] = nnz[ltop][left_index_table->nnz[0]+16+offset];
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[16+ 2] - 1] = nnz[ltop][left_index_table->nnz[1]+16+offset];
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[16+ 8] - 1] = nnz[lbot][left_index_table->nnz[2]+16+offset];
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[16+10] - 1] = nnz[lbot][left_index_table->nnz[3]+16+offset];
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[32+ 0] - 1] = nnz[ltop][left_index_table->nnz[0]+32+offset];
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[32+ 2] - 1] = nnz[ltop][left_index_table->nnz[1]+32+offset];
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[32+ 8] - 1] = nnz[lbot][left_index_table->nnz[2]+32+offset];
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[32+10] - 1] = nnz[lbot][left_index_table->nnz[3]+32+offset];
}
else
{
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[16+ 0] - 1] = nnz[ltop][left_index_table->nnz_chroma[0]];
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[16+ 2] - 1] = nnz[lbot][left_index_table->nnz_chroma[1]];
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[32+ 0] - 1] = nnz[ltop][left_index_table->nnz_chroma[2]];
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[32+ 2] - 1] = nnz[lbot][left_index_table->nnz_chroma[3]];
}
}
else
{
//没有相关信息的时候,填充下列数据
h->mb.cache.i_cbp_left = -1;
h->mb.cache.intra4x4_pred_mode[x264_scan8[ 0] - 1] =
h->mb.cache.intra4x4_pred_mode[x264_scan8[ 2] - 1] =
h->mb.cache.intra4x4_pred_mode[x264_scan8[ 8] - 1] =
h->mb.cache.intra4x4_pred_mode[x264_scan8[10] - 1] = -1;
/* load non_zero_count */
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[ 0] - 1] =
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[ 2] - 1] =
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[ 8] - 1] =
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[10] - 1] =
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[16+ 0] - 1] =
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[16+ 2] - 1] =
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[32+ 0] - 1] =
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[32+ 2] - 1] = 0x80;
if( CHROMA_FORMAT >= CHROMA_422 )
{
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[16+ 8] - 1] =
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[16+10] - 1] =
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[32+ 8] - 1] =
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[32+10] - 1] = 0x80;
}
}
if( h->pps->b_transform_8x8_mode )
{
h->mb.cache.i_neighbour_transform_size =
( (h->mb.i_neighbour & MB_LEFT) && h->mb.mb_transform_size[left[0]] )
+ ( (h->mb.i_neighbour & MB_TOP) && h->mb.mb_transform_size[top] );
}
if( b_mbaff )
{
h->mb.pic.i_fref[0] = h->i_ref[0] << MB_INTERLACED;
h->mb.pic.i_fref[1] = h->i_ref[1] << MB_INTERLACED;
}
if( !b_mbaff )
{
//没有“宏块级帧场自适应”情况的时候
//亮度
//拷贝上一个宏块最右边一列(共16个)像素(p_fdec[0]+15)
//作为这一个宏块最左边再靠左的一列像素(p_fdec[0]-1)
//一次拷贝8个(起始点上面4个下面4个),拷贝2次
x264_copy_column8( h->mb.pic.p_fdec[0]-1+ 4*FDEC_STRIDE, h->mb.pic.p_fdec[0]+15+ 4*FDEC_STRIDE );
x264_copy_column8( h->mb.pic.p_fdec[0]-1+12*FDEC_STRIDE, h->mb.pic.p_fdec[0]+15+12*FDEC_STRIDE );
//加载图像相关的指针
//第4个参数:指明了第几个分量(Y、U、V)
//第5个参数:指明了是否为色度
x264_macroblock_load_pic_pointers( h, mb_x, mb_y, 0, 0, 0 );
if( CHROMA444 )
{
x264_copy_column8( h->mb.pic.p_fdec[1]-1+ 4*FDEC_STRIDE, h->mb.pic.p_fdec[1]+15+ 4*FDEC_STRIDE );
x264_copy_column8( h->mb.pic.p_fdec[1]-1+12*FDEC_STRIDE, h->mb.pic.p_fdec[1]+15+12*FDEC_STRIDE );
x264_copy_column8( h->mb.pic.p_fdec[2]-1+ 4*FDEC_STRIDE, h->mb.pic.p_fdec[2]+15+ 4*FDEC_STRIDE );
x264_copy_column8( h->mb.pic.p_fdec[2]-1+12*FDEC_STRIDE, h->mb.pic.p_fdec[2]+15+12*FDEC_STRIDE );
x264_macroblock_load_pic_pointers( h, mb_x, mb_y, 1, 0, 0 );
x264_macroblock_load_pic_pointers( h, mb_x, mb_y, 2, 0, 0 );
}
else
{
//U和V
//YUV420P的情况下
//拷贝上一个宏块最右边一列(共8个)像素
//作为这一个宏块最左边再靠左的一列像素
//一次拷贝8个
x264_copy_column8( h->mb.pic.p_fdec[1]-1+ 4*FDEC_STRIDE, h->mb.pic.p_fdec[1]+ 7+ 4*FDEC_STRIDE );
x264_copy_column8( h->mb.pic.p_fdec[2]-1+ 4*FDEC_STRIDE, h->mb.pic.p_fdec[2]+ 7+ 4*FDEC_STRIDE );
if( CHROMA_FORMAT == CHROMA_422 )
{
x264_copy_column8( h->mb.pic.p_fdec[1]-1+12*FDEC_STRIDE, h->mb.pic.p_fdec[1]+ 7+12*FDEC_STRIDE );
x264_copy_column8( h->mb.pic.p_fdec[2]-1+12*FDEC_STRIDE, h->mb.pic.p_fdec[2]+ 7+12*FDEC_STRIDE );
}
x264_macroblock_load_pic_pointers( h, mb_x, mb_y, 1, 1, 0 );
}
}
else
{
x264_macroblock_load_pic_pointers( h, mb_x, mb_y, 0, 0, 1 );
if( CHROMA444 )
{
x264_macroblock_load_pic_pointers( h, mb_x, mb_y, 1, 0, 1 );
x264_macroblock_load_pic_pointers( h, mb_x, mb_y, 2, 0, 1 );
}
else
x264_macroblock_load_pic_pointers( h, mb_x, mb_y, 1, 1, 1 );
}
if( h->fdec->integral )
{
int offset = 16 * (mb_x + mb_y * h->fdec->i_stride[0]);
for( int list = 0; list < 2; list++ )
for( int i = 0; i < h->mb.pic.i_fref[list]; i++ )
h->mb.pic.p_integral[list][i] = &h->fref[list][i]->integral[offset];
}
x264_prefetch_fenc( h, h->fenc, mb_x, mb_y );
/* load ref/mv/mvd */
for( int l = 0; l < lists; l++ )
{
int16_t (*mv)[2] = h->mb.mv[l];
int8_t *ref = h->mb.ref[l];
int i8 = x264_scan8[0] - 1 - 1*8;
if( h->mb.i_neighbour & MB_TOPLEFT )
{
//填充宏块左上方信息
int ir = b_mbaff ? 2*(s8x8*h->mb.i_mb_topleft_y + mb_x-1)+1+s8x8 : top_8x8 - 1;
int iv = b_mbaff ? 4*(s4x4*h->mb.i_mb_topleft_y + mb_x-1)+3+3*s4x4 : top_4x4 - 1;
if( b_mbaff && h->mb.topleft_partition )
{
/* Take motion vector from the middle of macroblock instead of
* the bottom right as usual. */
iv -= 2*s4x4;
ir -= s8x8;
}
/*
* 填充参考帧序号ref[]
* 在这里相当于在ref[]填充了“y”,
* |
* --+--------------
* | 0 0 0 y 0 0 0 0
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
*/
//参考帧序号
h->mb.cache.ref[l][i8] = ref[ir];
/*
* 填充运动矢量mv[]
* 在这里相当于在mv[]填充了“y”,
* |
* --+--------------
* | 0 0 0 y 0 0 0 0
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
*/
//运动矢量
CP32( h->mb.cache.mv[l][i8], mv[iv] );
}
else
{
h->mb.cache.ref[l][i8] = -2;
M32( h->mb.cache.mv[l][i8] ) = 0;
}
i8 = x264_scan8[0] - 8;
if( h->mb.i_neighbour & MB_TOP )
{
//填充宏块上方信息
/*
* 填充参考帧序号ref[]
* 在这里相当于在ref[]分别填充了“1”和“2”,
* |
* --+--------------
* | 0 0 0 0 1 1 2 2
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
*/
h->mb.cache.ref[l][i8+0] =
h->mb.cache.ref[l][i8+1] = ref[top_8x8 + 0];
h->mb.cache.ref[l][i8+2] =
h->mb.cache.ref[l][i8+3] = ref[top_8x8 + 1];
/*
* 填充运动矢量mv[]
* 在这里相当于在mv[]填充了y,
* |
* --+--------------
* | 0 0 0 0 y y y y
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 0 Y Y Y Y
*/
CP128( h->mb.cache.mv[l][i8], mv[top_4x4] );
}
else
{
M128( h->mb.cache.mv[l][i8] ) = M128_ZERO;
M32( &h->mb.cache.ref[l][i8] ) = (uint8_t)(-2) * 0x01010101U;
}
i8 = x264_scan8[0] + 4 - 1*8;
if( h->mb.i_neighbour & MB_TOPRIGHT )
{
//填充宏块右上方信息
int ir = b_mbaff ? 2*(s8x8*h->mb.i_mb_topright_y + (mb_x+1))+s8x8 : top_8x8 + 2;
int iv = b_mbaff ? 4*(s4x4*h->mb.i_mb_topright_y + (mb_x+1))+3*s4x4 : top_4x4 + 4;
h->mb.cache.ref[l][i8] = ref[ir];
CP32( h->mb.cache.mv[l][i8], mv[iv] );
}
else
h->mb.cache.ref[l][i8] = -2;
i8 = x264_scan8[0] - 1;
if( h->mb.i_neighbour & MB_LEFT )
{
//填充宏块左边信息
if( b_mbaff )
{
h->mb.cache.ref[l][i8+0*8] = ref[h->mb.left_b8[LTOP] + 1 + s8x8*left_index_table->ref[0]];
h->mb.cache.ref[l][i8+1*8] = ref[h->mb.left_b8[LTOP] + 1 + s8x8*left_index_table->ref[1]];
h->mb.cache.ref[l][i8+2*8] = ref[h->mb.left_b8[LBOT] + 1 + s8x8*left_index_table->ref[2]];
h->mb.cache.ref[l][i8+3*8] = ref[h->mb.left_b8[LBOT] + 1 + s8x8*left_index_table->ref[3]];
CP32( h->mb.cache.mv[l][i8+0*8], mv[h->mb.left_b4[LTOP] + 3 + s4x4*left_index_table->mv[0]] );
CP32( h->mb.cache.mv[l][i8+1*8], mv[h->mb.left_b4[LTOP] + 3 + s4x4*left_index_table->mv[1]] );
CP32( h->mb.cache.mv[l][i8+2*8], mv[h->mb.left_b4[LBOT] + 3 + s4x4*left_index_table->mv[2]] );
CP32( h->mb.cache.mv[l][i8+3*8], mv[h->mb.left_b4[LBOT] + 3 + s4x4*left_index_table->mv[3]] );
}
else
{
//不考虑“宏块级帧场自适应”的时候
const int ir = h->mb.i_b8_xy - 1;
const int iv = h->mb.i_b4_xy - 1;
/*
* 填充参考帧序号ref[]
* 在这里相当于在ref[]分别填充了“1”和“2”,
* |
* --+--------------
* | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
* | 0 0 0 1 Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 1 Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 2 Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 2 Y Y Y Y
*/
h->mb.cache.ref[l][i8+0*8] =
h->mb.cache.ref[l][i8+1*8] = ref[ir + 0*s8x8];
h->mb.cache.ref[l][i8+2*8] =
h->mb.cache.ref[l][i8+3*8] = ref[ir + 1*s8x8];
/*
* 填充运动矢量mv[]
* 在这里相当于在mv[]填充了y,
* |
* --+--------------
* | 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
* | 0 0 0 y Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 y Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 y Y Y Y Y
* | 0 0 0 y Y Y Y Y
*/
CP32( h->mb.cache.mv[l][i8+0*8], mv[iv + 0*s4x4] );
CP32( h->mb.cache.mv[l][i8+1*8], mv[iv + 1*s4x4] );
CP32( h->mb.cache.mv[l][i8+2*8], mv[iv + 2*s4x4] );
CP32( h->mb.cache.mv[l][i8+3*8], mv[iv + 3*s4x4] );
}
}
else
{
for( int i = 0; i < 4; i++ )
{
h->mb.cache.ref[l][i8+i*8] = -2;
M32( h->mb.cache.mv[l][i8+i*8] ) = 0;
}
}
/* Extra logic for top right mv in mbaff.
* . . . d . . a .
* . . . e . . . .
* . . . f b . c .
* . . . . . . . .
*
* If the top right of the 4x4 partitions labeled a, b and c in the
* above diagram do not exist, but the entries d, e and f exist (in
* the macroblock to the left) then use those instead.
*/
if( b_mbaff && (h->mb.i_neighbour & MB_LEFT) )
{
if( MB_INTERLACED && !h->mb.field[h->mb.i_mb_xy-1] )
{
h->mb.cache.topright_ref[l][0] = ref[h->mb.left_b8[0] + 1 + s8x8*0];
h->mb.cache.topright_ref[l][1] = ref[h->mb.left_b8[0] + 1 + s8x8*1];
h->mb.cache.topright_ref[l][2] = ref[h->mb.left_b8[1] + 1 + s8x8*0];
CP32( h->mb.cache.topright_mv[l][0], mv[h->mb.left_b4[0] + 3 + s4x4*(left_index_table->mv[0]+1)] );
CP32( h->mb.cache.topright_mv[l][1], mv[h->mb.left_b4[0] + 3 + s4x4*(left_index_table->mv[1]+1)] );
CP32( h->mb.cache.topright_mv[l][2], mv[h->mb.left_b4[1] + 3 + s4x4*(left_index_table->mv[2]+1)] );
}
else if( !MB_INTERLACED && h->mb.field[h->mb.i_mb_xy-1] )
{
// Looking at the bottom field so always take the bottom macroblock of the pair.
h->mb.cache.topright_ref[l][0] = ref[h->mb.left_b8[0] + 1 + s8x8*2 + s8x8*left_index_table->ref[0]];
h->mb.cache.topright_ref[l][1] = ref[h->mb.left_b8[0] + 1 + s8x8*2 + s8x8*left_index_table->ref[0]];
h->mb.cache.topright_ref[l][2] = ref[h->mb.left_b8[0] + 1 + s8x8*2 + s8x8*left_index_table->ref[2]];
CP32( h->mb.cache.topright_mv[l][0], mv[h->mb.left_b4[0] + 3 + s4x4*4 + s4x4*left_index_table->mv[0]] );
CP32( h->mb.cache.topright_mv[l][1], mv[h->mb.left_b4[0] + 3 + s4x4*4 + s4x4*left_index_table->mv[1]] );
CP32( h->mb.cache.topright_mv[l][2], mv[h->mb.left_b4[0] + 3 + s4x4*4 + s4x4*left_index_table->mv[2]] );
}
}
//使用了CABAC的时候才会运行
if( h->param.b_cabac )
{
uint8_t (*mvd)[8][2] = h->mb.mvd[l];
if( h->mb.i_neighbour & MB_TOP )
CP64( h->mb.cache.mvd[l][x264_scan8[0] - 8], mvd[top][0] );
else
M64( h->mb.cache.mvd[l][x264_scan8[0] - 8] ) = 0;
if( h->mb.i_neighbour & MB_LEFT && (!b_mbaff || h->mb.cache.ref[l][x264_scan8[0]-1] >= 0) )
{
CP16( h->mb.cache.mvd[l][x264_scan8[0 ] - 1], mvd[left[LTOP]][left_index_table->intra[0]] );
CP16( h->mb.cache.mvd[l][x264_scan8[2 ] - 1], mvd[left[LTOP]][left_index_table->intra[1]] );
}
else
{
M16( h->mb.cache.mvd[l][x264_scan8[0]-1+0*8] ) = 0;
M16( h->mb.cache.mvd[l][x264_scan8[0]-1+1*8] ) = 0;
}
if( h->mb.i_neighbour & MB_LEFT && (!b_mbaff || h->mb.cache.ref[l][x264_scan8[0]-1+2*8] >=0) )
{
CP16( h->mb.cache.mvd[l][x264_scan8[8 ] - 1], mvd[left[LBOT]][left_index_table->intra[2]] );
CP16( h->mb.cache.mvd[l][x264_scan8[10] - 1], mvd[left[LBOT]][left_index_table->intra[3]] );
}
else
{
M16( h->mb.cache.mvd[l][x264_scan8[0]-1+2*8] ) = 0;
M16( h->mb.cache.mvd[l][x264_scan8[0]-1+3*8] ) = 0;
}
}
/* If motion vectors are cached from frame macroblocks but this
* macroblock is a field macroblock then the motion vector must be
* halved. Similarly, motion vectors from field macroblocks are doubled. */
if( b_mbaff )
{
#define MAP_MVS\
if( FIELD_DIFFERENT(h->mb.i_mb_topleft_xy) )\
MAP_F2F(mv, ref, x264_scan8[0] - 1 - 1*8)\
if( FIELD_DIFFERENT(top) )\
{\
MAP_F2F(mv, ref, x264_scan8[0] + 0 - 1*8)\
MAP_F2F(mv, ref, x264_scan8[0] + 1 - 1*8)\
MAP_F2F(mv, ref, x264_scan8[0] + 2 - 1*8)\
MAP_F2F(mv, ref, x264_scan8[0] + 3 - 1*8)\
}\
if( FIELD_DIFFERENT(h->mb.i_mb_topright_xy) )\
MAP_F2F(mv, ref, x264_scan8[0] + 4 - 1*8)\
if( FIELD_DIFFERENT(left[0]) )\
{\
MAP_F2F(mv, ref, x264_scan8[0] - 1 + 0*8)\
MAP_F2F(mv, ref, x264_scan8[0] - 1 + 1*8)\
MAP_F2F(mv, ref, x264_scan8[0] - 1 + 2*8)\
MAP_F2F(mv, ref, x264_scan8[0] - 1 + 3*8)\
MAP_F2F(topright_mv, topright_ref, 0)\
MAP_F2F(topright_mv, topright_ref, 1)\
MAP_F2F(topright_mv, topright_ref, 2)\
}
if( MB_INTERLACED )
{
#define FIELD_DIFFERENT(macroblock) (macroblock >= 0 && !h->mb.field[macroblock])
#define MAP_F2F(varmv, varref, index)\
if( h->mb.cache.varref[l][index] >= 0 )\
{\
h->mb.cache.varref[l][index] <<= 1;\
h->mb.cache.varmv[l][index][1] /= 2;\
h->mb.cache.mvd[l][index][1] >>= 1;\
}
MAP_MVS
#undef MAP_F2F
#undef FIELD_DIFFERENT
}
else
{
#define FIELD_DIFFERENT(macroblock) (macroblock >= 0 && h->mb.field[macroblock])
#define MAP_F2F(varmv, varref, index)\
if( h->mb.cache.varref[l][index] >= 0 )\
{\
h->mb.cache.varref[l][index] >>= 1;\
h->mb.cache.varmv[l][index][1] <<= 1;\
h->mb.cache.mvd[l][index][1] <<= 1;\
}
MAP_MVS
#undef MAP_F2F
#undef FIELD_DIFFERENT
}
}
}
if( b_mbaff && mb_x == 0 && !(mb_y&1) )
{
if( h->mb.i_mb_top_xy >= h->sh.i_first_mb )
h->mb.field_decoding_flag = h->mb.field[h->mb.i_mb_top_xy];
else
h->mb.field_decoding_flag = 0;
}
/* Check whether skip here would cause decoder to predict interlace mode incorrectly.
* FIXME: It might be better to change the interlace type rather than forcing a skip to be non-skip. */
h->mb.b_allow_skip = 1;
if( b_mbaff )
{
if( MB_INTERLACED != h->mb.field_decoding_flag &&
(mb_y&1) && IS_SKIP(h->mb.type[h->mb.i_mb_xy - h->mb.i_mb_stride]) )
h->mb.b_allow_skip = 0;
}
//使用了CABAC的时候才会运行
if( h->param.b_cabac )
{
if( b_mbaff )
{
int left_xy, top_xy;
/* Neighbours here are calculated based on field_decoding_flag */
int mb_xy = mb_x + (mb_y&~1)*h->mb.i_mb_stride;
left_xy = mb_xy - 1;
if( (mb_y&1) && mb_x > 0 && h->mb.field_decoding_flag == h->mb.field[left_xy] )
left_xy += h->mb.i_mb_stride;
if( h->mb.field_decoding_flag )
{
top_xy = mb_xy - h->mb.i_mb_stride;
if( !(mb_y&1) && top_xy >= 0 && h->mb.slice_table[top_xy] == h->sh.i_first_mb && h->mb.field[top_xy] )
top_xy -= h->mb.i_mb_stride;
}
else
top_xy = mb_x + (mb_y-1)*h->mb.i_mb_stride;
h->mb.cache.i_neighbour_skip = (mb_x > 0 && h->mb.slice_table[left_xy] == h->sh.i_first_mb && !IS_SKIP( h->mb.type[left_xy] ))
+ (top_xy >= 0 && h->mb.slice_table[top_xy] == h->sh.i_first_mb && !IS_SKIP( h->mb.type[top_xy] ));
}
else
{
h->mb.cache.i_neighbour_skip = ((h->mb.i_neighbour & MB_LEFT) && !IS_SKIP( h->mb.i_mb_type_left[0] ))
+ ((h->mb.i_neighbour & MB_TOP) && !IS_SKIP( h->mb.i_mb_type_top ));
}
}
/* load skip */
//处理“skip”类型宏块
if( h->sh.i_type == SLICE_TYPE_B )
{
h->mb.bipred_weight = h->mb.bipred_weight_buf[MB_INTERLACED][MB_INTERLACED&(mb_y&1)];
h->mb.dist_scale_factor = h->mb.dist_scale_factor_buf[MB_INTERLACED][MB_INTERLACED&(mb_y&1)];
if( h->param.b_cabac )
{
uint8_t skipbp;
x264_macroblock_cache_skip( h, 0, 0, 4, 4, 0 );
if( b_mbaff )
{
skipbp = (h->mb.i_neighbour & MB_LEFT) ? h->mb.skipbp[left[LTOP]] : 0;
h->mb.cache.skip[x264_scan8[0] - 1] = (skipbp >> (1+(left_index_table->mv[0]&~1))) & 1;
skipbp = (h->mb.i_neighbour & MB_LEFT) ? h->mb.skipbp[left[LBOT]] : 0;
h->mb.cache.skip[x264_scan8[8] - 1] = (skipbp >> (1+(left_index_table->mv[2]&~1))) & 1;
}
else
{
skipbp = (h->mb.i_neighbour & MB_LEFT) ? h->mb.skipbp[left[0]] : 0;
h->mb.cache.skip[x264_scan8[0] - 1] = skipbp & 0x2;
h->mb.cache.skip[x264_scan8[8] - 1] = skipbp & 0x8;
}
skipbp = (h->mb.i_neighbour & MB_TOP) ? h->mb.skipbp[top] : 0;
h->mb.cache.skip[x264_scan8[0] - 8] = skipbp & 0x4;
h->mb.cache.skip[x264_scan8[4] - 8] = skipbp & 0x8;
}
}
if( h->sh.i_type == SLICE_TYPE_P )
x264_mb_predict_mv_pskip( h, h->mb.cache.pskip_mv );
/*
* i_neightbour8把一个宏块分成4个8x8的子块,编号如下,用于记录它们邻块的可用性
* +--------+--------+
* | | |
* | 0 | 1 |
* | | |
* +--------+--------+
* | | |
* | 2 | 3 |
* | | |
* +--------+--------+
*
* i_neightbour4把一个宏块分成16个4x4的子块,编号如下,用于记录它们邻块的可用性
* (实际上也是类似scan8[]读取cache的顺序)
* +----+----+----+----+
* | 0 | 1 | 4 | 5 |
* +----+----+----+----+
* | 2 | 3 | 6 | 7 |
* +----+----+----+----+
* | 8 | 9 | 12 | 13 |
* +----+----+----+----+
* | 10 | 11 | 14 | 15 |
* +----+----+----+----+
*
*/
h->mb.i_neighbour4[0] =
h->mb.i_neighbour8[0] = (h->mb.i_neighbour_intra & (MB_TOP|MB_LEFT|MB_TOPLEFT))
| ((h->mb.i_neighbour_intra & MB_TOP) ? MB_TOPRIGHT : 0);
h->mb.i_neighbour4[4] =
h->mb.i_neighbour4[1] = MB_LEFT | ((h->mb.i_neighbour_intra & MB_TOP) ? (MB_TOP|MB_TOPLEFT|MB_TOPRIGHT) : 0);
h->mb.i_neighbour4[2] =
h->mb.i_neighbour4[8] =
h->mb.i_neighbour4[10] =
h->mb.i_neighbour8[2] = MB_TOP|MB_TOPRIGHT | ((h->mb.i_neighbour_intra & MB_LEFT) ? (MB_LEFT|MB_TOPLEFT) : 0);
h->mb.i_neighbour4[5] =
h->mb.i_neighbour8[1] = MB_LEFT | (h->mb.i_neighbour_intra & MB_TOPRIGHT)
| ((h->mb.i_neighbour_intra & MB_TOP) ? MB_TOP|MB_TOPLEFT : 0);
}x264_macroblock_cache_load()源代码比较长,比较关键的地方都做了注释,在这里就不详细记录了。总体说来该函数的流程如下所示:
(1)加载Intra4x4帧内预测模式intra4x4_pred_mode[]和DCT非零系数non_zero_count[]缓存Cache的宏块周边信息。加载顺序为:上->左->左上。(2)加载宏块重建像素p_fdec[]的周边像素,以及宏块编码像素p_fenc[]。对于p_fdec[]来说,在本函数中直接加载当前宏块左边的像素;调用函数x264_macroblock_load_pic_pointers()加载当前宏块上面的像素。对于p_fenc[]来说,调用x264_macroblock_load_pic_pointers()从图像上拷贝数据。
(3)加载参考帧序号ref[]和运动矢量mv[]缓存Cache的宏块周边信息。加载顺序为:左上->上->左。
(4)加载其它信息。
下面简单浏览一下x264_macroblock_load_pic_pointers()的源代码。
x264_macroblock_load_pic_pointers()
x264_macroblock_load_pic_pointers()用于给宏块重建像素p_fdec[]和宏块编码像素p_fenc[]加载数据,并且加载图像的半像素数据。它的定义位于common\macroblock.c,如下所示。//加载图像相关的指针
static void ALWAYS_INLINE x264_macroblock_load_pic_pointers( x264_t *h, int mb_x, int mb_y, int i, int b_chroma, int b_mbaff )
{
int mb_interlaced = b_mbaff && MB_INTERLACED;
int height = b_chroma ? 16 >> CHROMA_V_SHIFT : 16;
int i_stride = h->fdec->i_stride[i];
int i_stride2 = i_stride << mb_interlaced;
int i_pix_offset = mb_interlaced
? 16 * mb_x + height * (mb_y&~1) * i_stride + (mb_y&1) * i_stride
: 16 * mb_x + height * mb_y * i_stride;
//从一整个重建帧中读取一部分像素,赋值到重建帧宏块中
//i_pix_offset为宏块相对于整个帧起始位置的偏移量
pixel *plane_fdec = &h->fdec->plane[i][i_pix_offset];
int fdec_idx = b_mbaff ? (mb_interlaced ? (3 + (mb_y&1)) : (mb_y&1) ? 2 : 4) : !(mb_y&1);
//前一行宏块的底部边界像素
pixel *intra_fdec = &h->intra_border_backup[fdec_idx][i][mb_x*16];
int ref_pix_offset[2] = { i_pix_offset, i_pix_offset };
/* ref_pix_offset[0] references the current field and [1] the opposite field. */
if( mb_interlaced )
ref_pix_offset[1] += (1-2*(mb_y&1)) * i_stride;
h->mb.pic.i_stride[i] = i_stride2;
h->mb.pic.p_fenc_plane[i] = &h->fenc->plane[i][i_pix_offset];
if( b_chroma )
{
//色度
//编码帧p_fenc
h->mc.load_deinterleave_chroma_fenc( h->mb.pic.p_fenc[1], h->mb.pic.p_fenc_plane[1], i_stride2, height );
//重建帧p_fdec
memcpy( h->mb.pic.p_fdec[1]-FDEC_STRIDE, intra_fdec, 8*sizeof(pixel) );
memcpy( h->mb.pic.p_fdec[2]-FDEC_STRIDE, intra_fdec+8, 8*sizeof(pixel) );
h->mb.pic.p_fdec[1][-FDEC_STRIDE-1] = intra_fdec[-1-8];
h->mb.pic.p_fdec[2][-FDEC_STRIDE-1] = intra_fdec[-1];
}
else
{
//编码帧p_fenc
h->mc.copy[PIXEL_16x16]( h->mb.pic.p_fenc[i], FENC_STRIDE, h->mb.pic.p_fenc_plane[i], i_stride2, 16 );
//重建帧p_fdec
//上一行宏块的底部边界像素
memcpy( h->mb.pic.p_fdec[i]-FDEC_STRIDE, intra_fdec, 24*sizeof(pixel) );
//左上角的1个像素
h->mb.pic.p_fdec[i][-FDEC_STRIDE-1] = intra_fdec[-1];
}
if( b_mbaff || h->mb.b_reencode_mb )
{
for( int j = 0; j < height; j++ )
if( b_chroma )
{
//把一整个重建帧中宏块对应像素的地址,赋值到宏块的重建帧指针上
h->mb.pic.p_fdec[1][-1+j*FDEC_STRIDE] = plane_fdec[-2+j*i_stride2];
h->mb.pic.p_fdec[2][-1+j*FDEC_STRIDE] = plane_fdec[-1+j*i_stride2];
}
else
h->mb.pic.p_fdec[i][-1+j*FDEC_STRIDE] = plane_fdec[-1+j*i_stride2];
}
pixel *plane_src, **filtered_src;
//P Slice 的情况
//fref[0]后面的[0]代表list0
for( int j = 0; j < h->mb.pic.i_fref[0]; j++ )
{
// Interpolate between pixels in same field.
if( mb_interlaced )
{
plane_src = h->fref[0][j>>1]->plane_fld[i];
filtered_src = h->fref[0][j>>1]->filtered_fld[i];
}
else
{
plane_src = h->fref[0][j]->plane[i];
/*
* filtered_src指向半像素插值之后的得到的内插点数据
* filtered_src[1]存储了H半像素内插点
* filtered_src[2]存储了V半像素内插点
* filtered_src[3]存储了C半像素(对角线)内插点
*
* 示意(“X”代表像素点):
* X H X
*
* V C
*
* X X
*
*/
filtered_src = h->fref[0][j]->filtered[i];
}
//注意
//i为输入参数,代表处理的分量(0代表Y,1代表U,2代表V)
//j为参考帧序号
//处理亮度的时候相当于将plane_src赋值给了p_fref[0][j][0]
h->mb.pic.p_fref[0][j][i*4] = plane_src + ref_pix_offset[j&1];
if( !b_chroma )
{
//半像素插值之后的filtered_src赋值给mb.pic.p_fref
//注意
//i为输入参数,代表处理的分量(0代表Y,1代表U,2代表V)
//j为参考帧序号
//处理亮度的时候相当于将filtered_src[1]赋值给了p_fref[][][1];
//filtered_src[2]赋值给了p_fref[][][2];filtered_src[3]赋值给了p_fref[][][3]
//
for( int k = 1; k < 4; k++ )
h->mb.pic.p_fref[0][j][i*4+k] = filtered_src[k] + ref_pix_offset[j&1];
if( !i )
{
if( h->sh.weight[j][0].weightfn )
h->mb.pic.p_fref_w[j] = &h->fenc->weighted[j >> mb_interlaced][ref_pix_offset[j&1]];
else
h->mb.pic.p_fref_w[j] = h->mb.pic.p_fref[0][j][0];
}
}
}
//B Slice 的情况
//fref[1]后面的[1]代表list1
//与P Slice处理方式类似
if( h->sh.i_type == SLICE_TYPE_B )
for( int j = 0; j < h->mb.pic.i_fref[1]; j++ )
{
if( mb_interlaced )
{
plane_src = h->fref[1][j>>1]->plane_fld[i];
filtered_src = h->fref[1][j>>1]->filtered_fld[i];
}
else
{
plane_src = h->fref[1][j]->plane[i];
filtered_src = h->fref[1][j]->filtered[i];
}
h->mb.pic.p_fref[1][j][i*4] = plane_src + ref_pix_offset[j&1];
if( !b_chroma )
for( int k = 1; k < 4; k++ )
h->mb.pic.p_fref[1][j][i*4+k] = filtered_src[k] + ref_pix_offset[j&1];
}
}从源代码可以看出,x264_macroblock_load_pic_pointers()最主要做了两个步骤:
(1)加载编码宏块mb.pic.p_fenc[]的像素数据,以及重建宏块mb.pic.p_fenc[]上边的像素数据。
(2)加载参考帧的半像素数据(除了整像素外,还包含了:H,V,C三组半像素数据点)。
x264_macroblock_analyse()
x264_macroblock_analyse()用于分析宏块的编码模式。对于帧内宏块来说,主要分析使用Intra16x16合适还是使用Intra4x4合适;对于帧间宏块来说,主要分析它的划分模式,并且进行运动估计。下面简单整理一下相关的知识(具体的源代码在后续文章中再进行分析)。(1)帧内预测
简述
简单记录一下帧内预测的方法。帧内预测根据宏块左边和上边的边界像素值推算宏块内部的像素值,帧内预测的效果如下图所示。其中左边的图为图像原始画面,右边的图为经过帧内预测后没有叠加残差的画面。

模式 | 描述 |
Vertical | 由上边像素推出相应像素值 |
Horizontal | 由左边像素推出相应像素值 |
DC | 由上边和左边像素平均值推出相应像素值 |
Plane | 由上边和左边像素推出相应像素值 |
4x4帧内预测模式一共有9种,如下图所示。

SAD、SATD相关知识简述
简单记录几个编码模式判断中两个像素计算的方法:SAD和SATD。它们的定义如下:
SAD(Sum of Absolute Difference)也可以称为SAE(Sum of Absolute Error),即绝对误差和。它的计算方法就是求出两个像素块对应像素点的差值,将这些差值分别求绝对值之后再进行累加。
SATD(Sum of Absolute Transformed Difference)即Hadamard变换后再绝对值求和。它和SAD的区别在于多了一个“变换”。
H.264中使用SAD和SATD进行宏块预测模式的判断。早期的编码器使用SAD进行计算,近期的编码器多使用SATD进行计算。为什么使用SATD而不使用SAD呢?关键原因在于编码之后码流的大小是和图像块DCT变换后频域信息紧密相关的,而和变换前的时域信息关联性小一些。SAD只能反应时域信息;SATD却可以反映频域信息,而且计算复杂度也低于DCT变换,因此是比较合适的模式选择的依据。
使用SAD进行模式选择的示例如下所示。下面这张图代表了一个普通的Intra16x16的宏块的像素。它的下方包含了使用Vertical,Horizontal,DC和Plane四种帧内预测模式预测的像素。通过计算可以得到这几种预测像素和原始像素之间的SAD(SAE)分别为3985,5097,4991,2539。由于Plane模式的SAD取值最小,由此可以断定Plane模式对于这个宏块来说是最好的帧内预测模式。

(2)帧间预测知识简述
简述
运动估计的理论基础就是活动图像邻近帧中的景物存在着一定的相关性。因此在压缩编码中不需要传递每一帧的所有信息,而只需要传递帧与帧之间差值就可以了(可以想象,如果画面背景是静止的,那么只需要传递很少的数据)。在视频编码的运动估计步骤中,会查找与当前宏块或者子宏块“长得像”的宏块作为“匹配块”,然后编码传输匹配块的位置(运动矢量,参考帧)和当前宏块与匹配块之间的微小差别(残差数据)。例如下图中,当前宏块中一个“车轮”在参考帧中找到了形状同样为一个“轮子”的匹配块。


《H.264标准》中对运动估计的精度要求又有了提升,变成了1/4像素精度。因此H.264编码器对系统性能要求又有了更高的要求。一些实验证明,1/4像素精度基本上达到了运动估计性能提升的极限。更高精度的运动估计并不能更明显的提升性能,却会导致计算复杂度的显著提升。因此现存主流的编解码标准在运动估计方面都采用了1/4精度。曾经有人压缩对比过1/2、1/4、1/8精度的运动估计下编码的视频质量,如下图所示。

宏块划分(帧间预测)
《H.264标准》中规定,每个16x16的宏块可以划分为16x16,16x8,8x16,8x8四种类型。而如果宏块划分为8x8类型的时候,每个8x8宏块又可以划分为8x8,8x4,4x8,4x4四种小块。它们之间的关系下图所示。

单向预测与双向预测
在运动估计的过程中,不仅仅只可以选择一个图像作为参考帧(P帧),而且还可以选择两张图片作为参考帧(B帧)。使用一张图像作为参考帧称为单向预测,而使用一张图像作为参考帧称为双向预测。使用单向预测的时候,直接将参考帧上的匹配块的数据“搬移下来”作后续的处理(“赋值”),而使用双向预测的时候,需要首先将两个参考帧上的匹配块的数据求平均值(“求平均”),然后再做后续处理。毫无疑问双向预测可以得到更好的压缩效果,但是也会使码流变得复杂一些。双向预测的示意图如下所示。

x264_macroblock_encode()
x264_macroblock_encode()用于编码宏块。它主要完成了两个工作:编码(DCT变换和量化)和重建(DCT反变换和反量化)。在这里简单总结一下这方面的知识(后续文章中再对源代码进行详细分析)。(1) DCT相关知识简述
简单记录一下DCT相关的知识。DCT变换的核心理念就是把图像的低频信息(对应大面积平坦区域)变换到系数矩阵的左上角,而把高频信息变换到系数矩阵的右下角,这样就可以在压缩的时候(量化)去除掉人眼不敏感的高频信息(位于矩阵右下角的系数)从而达到压缩数据的目的。二维8x8DCT变换常见的示意图如下所示。





(2) 量化相关知识简述
简单记录一下量化的概念。量化是H.264视频压缩编码中对视频质量影响最大的地方,也是会导致“信息丢失”的地方。量化的原理可以表示为下面公式:
在H.264 中,量化步长Qstep 共有52个值,如下表所示。其中QP 是量化参数,是量化步长的序号。当QP 取最小值0 时代表最精细的量化,当QP 取最大值51 时代表最粗糙的量化。QP 每增加6,Qstep 增加一倍。

sign()为符号函数。
Wij为DCT变换后的系数。
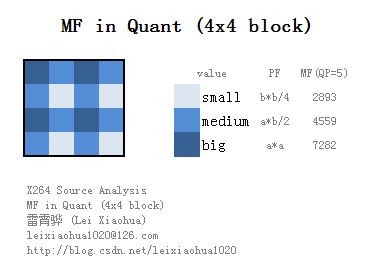
MF的值如下表所示。表中只列出对应QP 值为0 到5 的MF 值。QP大于6之后,将QP实行对6取余数操作,再找到MF的值。
qbits计算公式为“qbits = 15 + floor(QP/6)”。即它的值随QP 值每增加6 而增加1。
f 是偏移量(用于改善恢复图像的视觉效果)。对帧内预测图像块取2^qbits/3,对帧间预测图像块取2^qbits/6。

x264_macroblock_write_cabac()
x264_macroblock_write_cabac()属于“熵编码”模块,这一部分内容在后续文章中再进行详细分析。x264_macroblock_write_cavlc()
x264_macroblock_write_cavlc()属于“熵编码”模块,这一部分内容在后续文章中再进行详细分析。x264_macroblock_cache_save()
x264_macroblock_cache_save()用于保存当前宏块的信息以供后面宏块编码作为参考。它的作用与x264_macroblock_cache_load()是相对应的。该函数定义位于common\macroblock.c,如下所示。//保存当前宏块的的值,用于以后的宏块的编码
//包括Intra4x4宏块帧内预测模式,DCT非零系数,运动矢量,参考帧序号等等
void x264_macroblock_cache_save( x264_t *h )
{
const int i_mb_xy = h->mb.i_mb_xy;
const int i_mb_type = x264_mb_type_fix[h->mb.i_type];
const int s8x8 = h->mb.i_b8_stride;
const int s4x4 = h->mb.i_b4_stride;
const int i_mb_4x4 = h->mb.i_b4_xy;
const int i_mb_8x8 = h->mb.i_b8_xy;
/* GCC pessimizes direct stores to heap-allocated arrays due to aliasing. */
/* By only dereferencing them once, we avoid this issue. */
//Intra4x4帧内预测模式
int8_t *i4x4 = h->mb.intra4x4_pred_mode[i_mb_xy];
//DCT非零系数
uint8_t *nnz = h->mb.non_zero_count[i_mb_xy];
if( SLICE_MBAFF )
{
x264_macroblock_backup_intra( h, h->mb.i_mb_x, h->mb.i_mb_y, 1 );
x264_macroblock_store_pic( h, h->mb.i_mb_x, h->mb.i_mb_y, 0, 0, 1 );
if( CHROMA444 )
{
x264_macroblock_store_pic( h, h->mb.i_mb_x, h->mb.i_mb_y, 1, 0, 1 );
x264_macroblock_store_pic( h, h->mb.i_mb_x, h->mb.i_mb_y, 2, 0, 1 );
}
else
x264_macroblock_store_pic( h, h->mb.i_mb_x, h->mb.i_mb_y, 1, 1, 1 );
}
else
{
x264_macroblock_backup_intra( h, h->mb.i_mb_x, h->mb.i_mb_y, 0 );
//将当前宏块重建的像素数据保存到整张图片的像素数据中
x264_macroblock_store_pic( h, h->mb.i_mb_x, h->mb.i_mb_y, 0, 0, 0 );
if( CHROMA444 )
{
x264_macroblock_store_pic( h, h->mb.i_mb_x, h->mb.i_mb_y, 1, 0, 0 );
x264_macroblock_store_pic( h, h->mb.i_mb_x, h->mb.i_mb_y, 2, 0, 0 );
}
else
x264_macroblock_store_pic( h, h->mb.i_mb_x, h->mb.i_mb_y, 1, 1, 0 );
}
x264_prefetch_fenc( h, h->fdec, h->mb.i_mb_x, h->mb.i_mb_y );
h->mb.type[i_mb_xy] = i_mb_type;
h->mb.slice_table[i_mb_xy] = h->sh.i_first_mb;
h->mb.partition[i_mb_xy] = IS_INTRA( i_mb_type ) ? D_16x16 : h->mb.i_partition;
h->mb.i_mb_prev_xy = i_mb_xy;
/* save intra4x4 */
//保存Intra4x4预测模式
if( i_mb_type == I_4x4 )
{
CP32( &i4x4[0], &h->mb.cache.intra4x4_pred_mode[x264_scan8[10]] );
M32( &i4x4[4] ) = pack8to32( h->mb.cache.intra4x4_pred_mode[x264_scan8[5] ],
h->mb.cache.intra4x4_pred_mode[x264_scan8[7] ],
h->mb.cache.intra4x4_pred_mode[x264_scan8[13] ], 0);
}
else if( !h->param.b_constrained_intra || IS_INTRA(i_mb_type) )
M64( i4x4 ) = I_PRED_4x4_DC * 0x0101010101010101ULL;
else
M64( i4x4 ) = (uint8_t)(-1) * 0x0101010101010101ULL;
if( i_mb_type == I_PCM )
{
h->mb.qp[i_mb_xy] = 0;
h->mb.i_last_dqp = 0;
h->mb.i_cbp_chroma = CHROMA444 ? 0 : 2;
h->mb.i_cbp_luma = 0xf;
h->mb.cbp[i_mb_xy] = (h->mb.i_cbp_chroma << 4) | h->mb.i_cbp_luma | 0x700;
h->mb.b_transform_8x8 = 0;
for( int i = 0; i < 48; i++ )
h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[i]] = h->param.b_cabac ? 1 : 16;
}
else
{
if( h->mb.i_type != I_16x16 && h->mb.i_cbp_luma == 0 && h->mb.i_cbp_chroma == 0 )
h->mb.i_qp = h->mb.i_last_qp;
//保存QP
h->mb.qp[i_mb_xy] = h->mb.i_qp;
h->mb.i_last_dqp = h->mb.i_qp - h->mb.i_last_qp;
h->mb.i_last_qp = h->mb.i_qp;
}
/* save non zero count */
//保存DCT非零系数
CP32( &nnz[ 0+0*4], &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[ 0]] );
CP32( &nnz[ 0+1*4], &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[ 2]] );
CP32( &nnz[ 0+2*4], &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[ 8]] );
CP32( &nnz[ 0+3*4], &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[10]] );
CP32( &nnz[16+0*4], &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[16+0]] );
CP32( &nnz[16+1*4], &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[16+2]] );
CP32( &nnz[32+0*4], &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[32+0]] );
CP32( &nnz[32+1*4], &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[32+2]] );
if( CHROMA_FORMAT >= CHROMA_422 )
{
CP32( &nnz[16+2*4], &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[16+ 8]] );
CP32( &nnz[16+3*4], &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[16+10]] );
CP32( &nnz[32+2*4], &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[32+ 8]] );
CP32( &nnz[32+3*4], &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[32+10]] );
}
if( h->mb.i_cbp_luma == 0 && h->mb.i_type != I_8x8 )
h->mb.b_transform_8x8 = 0;
h->mb.mb_transform_size[i_mb_xy] = h->mb.b_transform_8x8;
//不是Intra宏块的时候,保存运动矢量,参考帧序号
if( h->sh.i_type != SLICE_TYPE_I )
{
int16_t (*mv0)[2] = &h->mb.mv[0][i_mb_4x4];
int16_t (*mv1)[2] = &h->mb.mv[1][i_mb_4x4];
int8_t *ref0 = &h->mb.ref[0][i_mb_8x8];
int8_t *ref1 = &h->mb.ref[1][i_mb_8x8];
if( !IS_INTRA( i_mb_type ) )
{
ref0[0+0*s8x8] = h->mb.cache.ref[0][x264_scan8[0]];
ref0[1+0*s8x8] = h->mb.cache.ref[0][x264_scan8[4]];
ref0[0+1*s8x8] = h->mb.cache.ref[0][x264_scan8[8]];
ref0[1+1*s8x8] = h->mb.cache.ref[0][x264_scan8[12]];
CP128( &mv0[0*s4x4], h->mb.cache.mv[0][x264_scan8[0]+8*0] );
CP128( &mv0[1*s4x4], h->mb.cache.mv[0][x264_scan8[0]+8*1] );
CP128( &mv0[2*s4x4], h->mb.cache.mv[0][x264_scan8[0]+8*2] );
CP128( &mv0[3*s4x4], h->mb.cache.mv[0][x264_scan8[0]+8*3] );
if( h->sh.i_type == SLICE_TYPE_B )
{
ref1[0+0*s8x8] = h->mb.cache.ref[1][x264_scan8[0]];
ref1[1+0*s8x8] = h->mb.cache.ref[1][x264_scan8[4]];
ref1[0+1*s8x8] = h->mb.cache.ref[1][x264_scan8[8]];
ref1[1+1*s8x8] = h->mb.cache.ref[1][x264_scan8[12]];
CP128( &mv1[0*s4x4], h->mb.cache.mv[1][x264_scan8[0]+8*0] );
CP128( &mv1[1*s4x4], h->mb.cache.mv[1][x264_scan8[0]+8*1] );
CP128( &mv1[2*s4x4], h->mb.cache.mv[1][x264_scan8[0]+8*2] );
CP128( &mv1[3*s4x4], h->mb.cache.mv[1][x264_scan8[0]+8*3] );
}
}
else
{
M16( &ref0[0*s8x8] ) = (uint8_t)(-1) * 0x0101;
M16( &ref0[1*s8x8] ) = (uint8_t)(-1) * 0x0101;
M128( &mv0[0*s4x4] ) = M128_ZERO;
M128( &mv0[1*s4x4] ) = M128_ZERO;
M128( &mv0[2*s4x4] ) = M128_ZERO;
M128( &mv0[3*s4x4] ) = M128_ZERO;
if( h->sh.i_type == SLICE_TYPE_B )
{
M16( &ref1[0*s8x8] ) = (uint8_t)(-1) * 0x0101;
M16( &ref1[1*s8x8] ) = (uint8_t)(-1) * 0x0101;
M128( &mv1[0*s4x4] ) = M128_ZERO;
M128( &mv1[1*s4x4] ) = M128_ZERO;
M128( &mv1[2*s4x4] ) = M128_ZERO;
M128( &mv1[3*s4x4] ) = M128_ZERO;
}
}
}
if( h->param.b_cabac )
{
uint8_t (*mvd0)[2] = h->mb.mvd[0][i_mb_xy];
uint8_t (*mvd1)[2] = h->mb.mvd[1][i_mb_xy];
if( IS_INTRA(i_mb_type) && i_mb_type != I_PCM )
h->mb.chroma_pred_mode[i_mb_xy] = x264_mb_chroma_pred_mode_fix[h->mb.i_chroma_pred_mode];
else
h->mb.chroma_pred_mode[i_mb_xy] = I_PRED_CHROMA_DC;
if( (0x3FF30 >> i_mb_type) & 1 ) /* !INTRA && !SKIP && !DIRECT */
{
CP64( mvd0[0], h->mb.cache.mvd[0][x264_scan8[10]] );
CP16( mvd0[4], h->mb.cache.mvd[0][x264_scan8[5 ]] );
CP16( mvd0[5], h->mb.cache.mvd[0][x264_scan8[7 ]] );
CP16( mvd0[6], h->mb.cache.mvd[0][x264_scan8[13]] );
if( h->sh.i_type == SLICE_TYPE_B )
{
CP64( mvd1[0], h->mb.cache.mvd[1][x264_scan8[10]] );
CP16( mvd1[4], h->mb.cache.mvd[1][x264_scan8[5 ]] );
CP16( mvd1[5], h->mb.cache.mvd[1][x264_scan8[7 ]] );
CP16( mvd1[6], h->mb.cache.mvd[1][x264_scan8[13]] );
}
}
else
{
M128( mvd0[0] ) = M128_ZERO;
if( h->sh.i_type == SLICE_TYPE_B )
M128( mvd1[0] ) = M128_ZERO;
}
if( h->sh.i_type == SLICE_TYPE_B )
{
if( i_mb_type == B_SKIP || i_mb_type == B_DIRECT )
h->mb.skipbp[i_mb_xy] = 0xf;
else if( i_mb_type == B_8x8 )
{
int skipbp = ( h->mb.i_sub_partition[0] == D_DIRECT_8x8 ) << 0;
skipbp |= ( h->mb.i_sub_partition[1] == D_DIRECT_8x8 ) << 1;
skipbp |= ( h->mb.i_sub_partition[2] == D_DIRECT_8x8 ) << 2;
skipbp |= ( h->mb.i_sub_partition[3] == D_DIRECT_8x8 ) << 3;
h->mb.skipbp[i_mb_xy] = skipbp;
}
else
h->mb.skipbp[i_mb_xy] = 0;
}
}
}从源代码可以看出,x264_macroblock_cache_save()保存了当前宏块的各种信息,例如Intra4x4宏块帧内预测模式,DCT非零系数,运动矢量,参考帧序号等等。
至此有关x264_slice_write()的结构分析就基本完成了。从下一篇文章开始,将会对x264_slice_write()中的几个关键模块进行分析:
分析(Analysis)模块
宏块编码(Encode)模块
熵编码(Entropy Encoding)模块
滤波(Filter)模块
雷霄骅
leixiaohua1020@126.com
http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020
























 339
339

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








