x264代码剖析(九):x264_encoder_encode()函数之x264_slice's'_write()函数
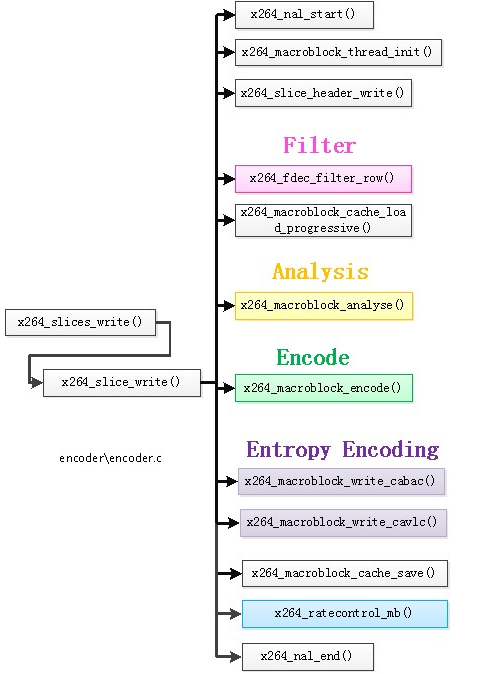
x264_encoder_encode()函数的核心函数就是x264_slices_write()函数。在x264_slices_write()函数中,最主要的工作就是调用了x264_slice_write()函数(注意“x264_slices_write()”和“x264_slice_write()”名字差了一个“s”),x264_slice_write()函数才是真正完成编码的核心函数,如下图所示。
1、x264_slices_write()函数
在x264_slices_write()函数中,最主要的工作就是调用了x264_slice_write()函数,需要注意,x264_slices_write()调用了x264_slice_write()。其中x264_slices_write()的单位为帧,而x264_slice_write()的单位为Slice。最常见的情况下一个帧里面只有一个Slice,但是也有可能一个帧里面有多个Slice。对应的代码如下:
/******************************************************************/
/******************************************************************/
/*
======Analysed by RuiDong Fang
======Csdn Blog:http://blog.csdn.net/frd2009041510
======Date:2016.03.10
*/
/******************************************************************/
/******************************************************************/
/************====== x264_slices_write()函数 ======************/
/*
功能:编码数据(最关键的步骤),其中调用了x264_slice_write()完成了编码的工作
(注意“x264_slices_write()”和“x264_slice_write()”名字差了一个“s”)。
*/
static void *x264_slices_write( x264_t *h )
{
int i_slice_num = 0;
int last_thread_mb = h->sh.i_last_mb;
/* init stats */
memset( &h->stat.frame, 0, sizeof(h->stat.frame) );
h->mb.b_reencode_mb = 0;
//循环每一个slice(一幅图像可以由多个Slice构成)
while( h->sh.i_first_mb + SLICE_MBAFF*h->mb.i_mb_stride <= last_thread_mb )
{
h->sh.i_last_mb = last_thread_mb;
if( !i_slice_num || !x264_frame_new_slice( h, h->fdec ) )
{
if( h->param.i_slice_max_mbs )
{
if( SLICE_MBAFF )
{
// convert first to mbaff form, add slice-max-mbs, then convert back to normal form
int last_mbaff = 2*(h->sh.i_first_mb % h->mb.i_mb_width)
+ h->mb.i_mb_width*(h->sh.i_first_mb / h->mb.i_mb_width)
+ h->param.i_slice_max_mbs - 1;
int last_x = (last_mbaff % (2*h->mb.i_mb_width))/2;
int last_y = (last_mbaff / (2*h->mb.i_mb_width))*2 + 1;
h->sh.i_last_mb = last_x + h->mb.i_mb_stride*last_y;
}
else
{
h->sh.i_last_mb = h->sh.i_first_mb + h->param.i_slice_max_mbs - 1;
if( h->sh.i_last_mb < last_thread_mb && last_thread_mb - h->sh.i_last_mb < h->param.i_slice_min_mbs )
h->sh.i_last_mb = last_thread_mb - h->param.i_slice_min_mbs;
}
i_slice_num++;
}
else if( h->param.i_slice_count && !h->param.b_sliced_threads )
{
int height = h->mb.i_mb_height >> PARAM_INTERLACED;
int width = h->mb.i_mb_width << PARAM_INTERLACED;
i_slice_num++;
h->sh.i_last_mb = (height * i_slice_num + h->param.i_slice_count/2) / h->param.i_slice_count * width - 1;
}
}
h->sh.i_last_mb = X264_MIN( h->sh.i_last_mb, last_thread_mb );
//真正的编码——编码1个Slice
//x264_stack_align()应该是平台优化过程中内存对齐的工作
//实际上就是调用x264_slice_write()
if( x264_stack_align( x264_slice_write, h ) ) //调用x264_slice_write(),进入核心编码函数块
goto fail;
h->sh.i_first_mb = h->sh.i_last_mb + 1;//注意这里对i_first_mb进行了赋值
// if i_first_mb is not the last mb in a row then go to the next mb in MBAFF order
if( SLICE_MBAFF && h->sh.i_first_mb % h->mb.i_mb_width )
h->sh.i_first_mb -= h->mb.i_mb_stride;
}
return (void *)0;
fail:
/* Tell other threads we're done, so they wouldn't wait for it */
if( h->param.b_sliced_threads )
x264_threadslice_cond_broadcast( h, 2 );
return (void *)-1;
}
2、x264_slice_write()函数
x264_slice_write()是完成编码工作的函数。该函数中包含了去块效应滤波,运动估计,宏块编码,熵编码等模块。x264_slice_write()调用了如下函数:
x264_nal_start():开始写一个NALU。
x264_macroblock_thread_init():初始化宏块重建数据缓存fdec_buf[]和编码数据缓存fenc_buf[]。
x264_slice_header_write():输出 Slice Header。
x264_fdec_filter_row():滤波模块。该模块包含了环路滤波,半像素插值,SSIM/PSNR的计算。
x264_macroblock_cache_load():将要编码的宏块的周围的宏块的信息读进来。
x264_macroblock_analyse():分析模块。该模块包含了帧内预测模式分析以及帧间运动估计等。
x264_macroblock_encode():宏块编码模块。该模块通过对残差的DCT变换、量化等方式对宏块进行编码。
x264_macroblock_write_cabac():CABAC熵编码模块。
x264_macroblock_write_cavlc():CAVLC熵编码模块。
x264_macroblock_cache_save():保存当前宏块的信息。
x264_ratecontrol_mb():码率控制。
x264_nal_end():结束写一个NALU。
x264_slice_write()用于编码一个Slice。该函数的定义位于encoder\encoder.c,对应的代码分析如下:
/******************************************************************/
/******************************************************************/
/*
======Analysed by RuiDong Fang
======Csdn Blog:http://blog.csdn.net/frd2009041510
======Date:2016.03.10
*/
/******************************************************************/
/******************************************************************/
/************====== x264_slice_write()函数 ======************/
/*
功能:编码一个Slice
*/
static intptr_t x264_slice_write( x264_t *h )
{
int i_skip;
int mb_xy, i_mb_x, i_mb_y;//宏块的序号,以及序号对应的x,y坐标
/* NALUs other than the first use a 3-byte startcode.
* Add one extra byte for the rbsp, and one more for the final CABAC putbyte.
* Then add an extra 5 bytes just in case, to account for random NAL escapes and
* other inaccuracies. */
int overhead_guess = (NALU_OVERHEAD - (h->param.b_annexb && h->out.i_nal)) + 1 + h->param.b_cabac + 5;
int slice_max_size = h->param.i_slice_max_size > 0 ? (h->param.i_slice_max_size-overhead_guess)*8 : 0;
int back_up_bitstream_cavlc = !h->param.b_cabac && h->sps->i_profile_idc < PROFILE_HIGH;
int back_up_bitstream = slice_max_size || back_up_bitstream_cavlc;
int starting_bits = bs_pos(&h->out.bs);
int b_deblock = h->sh.i_disable_deblocking_filter_idc != 1;
int b_hpel = h->fdec->b_kept_as_ref;
int orig_last_mb = h->sh.i_last_mb;
int thread_last_mb = h->i_threadslice_end * h->mb.i_mb_width - 1;
uint8_t *last_emu_check;
#define BS_BAK_SLICE_MAX_SIZE 0
#define BS_BAK_CAVLC_OVERFLOW 1
#define BS_BAK_SLICE_MIN_MBS 2
#define BS_BAK_ROW_VBV 3
x264_bs_bak_t bs_bak[4];
b_deblock &= b_hpel || h->param.b_full_recon || h->param.psz_dump_yuv;
bs_realign( &h->out.bs );
/* Slice */
x264_nal_start( h, h->i_nal_type, h->i_nal_ref_idc ); //开始输出一个NAL,后面对应着x264_nal_end()
h->out.nal[h->out.i_nal].i_first_mb = h->sh.i_first_mb;
/* Slice header */
//存储宏块像素的缓存fdec_buf和fenc_buf的初始化
//宏块编码缓存p_fenc[0],p_fenc[1],p_fenc[2]
//宏块重建缓存p_fdec[0],p_fdec[1],p_fdec[2]
//[0]存Y,[1]存U,[2]存V
x264_macroblock_thread_init( h ); //初始化宏块重建数据缓存fdec_buf[]和编码数据缓存fenc_buf[]
/* Set the QP equal to the first QP in the slice for more accurate CABAC initialization. */
h->mb.i_mb_xy = h->sh.i_first_mb;
h->sh.i_qp = x264_ratecontrol_mb_qp( h );
h->sh.i_qp = SPEC_QP( h->sh.i_qp );
h->sh.i_qp_delta = h->sh.i_qp - h->pps->i_pic_init_qp;
x264_slice_header_write( &h->out.bs, &h->sh, h->i_nal_ref_idc ); //输出 Slice Header
if( h->param.b_cabac )//如果使用CABAC,需要初始化
{
/* alignment needed */
bs_align_1( &h->out.bs );
/* init cabac */
x264_cabac_context_init( h, &h->cabac, h->sh.i_type, x264_clip3( h->sh.i_qp-QP_BD_OFFSET, 0, 51 ), h->sh.i_cabac_init_idc );
x264_cabac_encode_init ( &h->cabac, h->out.bs.p, h->out.bs.p_end );
last_emu_check = h->cabac.p;
}
else
last_emu_check = h->out.bs.p;
h->mb.i_last_qp = h->sh.i_qp;
h->mb.i_last_dqp = 0;
h->mb.field_decoding_flag = 0;
i_mb_y = h->sh.i_first_mb / h->mb.i_mb_width;//宏块位置-纵坐标(初始值)
i_mb_x = h->sh.i_first_mb % h->mb.i_mb_width;//宏块位置-横坐标(初始值)
i_skip = 0;
//一个大循环
//对一个slice中每个宏块进行编码
while( 1 )
{
mb_xy = i_mb_x + i_mb_y * h->mb.i_mb_width;//宏块序号。由i_mb_x和i_mb_y计算而来。
int mb_spos = bs_pos(&h->out.bs) + x264_cabac_pos(&h->cabac);
if( i_mb_x == 0 )//一行的开始
{
if( x264_bitstream_check_buffer( h ) )
return -1;
if( !(i_mb_y & SLICE_MBAFF) && h->param.rc.i_vbv_buffer_size )
x264_bitstream_backup( h, &bs_bak[BS_BAK_ROW_VBV], i_skip, 1 );
if( !h->mb.b_reencode_mb )
x264_fdec_filter_row( h, i_mb_y, 0 ); //滤波模块。该模块包含了环路滤波,半像素插值,SSIM/PSNR的计算(一次处理一行宏块)
}
if( back_up_bitstream )
{
if( back_up_bitstream_cavlc )
x264_bitstream_backup( h, &bs_bak[BS_BAK_CAVLC_OVERFLOW], i_skip, 0 );
if( slice_max_size && !(i_mb_y & SLICE_MBAFF) )
{
x264_bitstream_backup( h, &bs_bak[BS_BAK_SLICE_MAX_SIZE], i_skip, 0 );
if( (thread_last_mb+1-mb_xy) == h->param.i_slice_min_mbs )
x264_bitstream_backup( h, &bs_bak[BS_BAK_SLICE_MIN_MBS], i_skip, 0 );
}
}
if( PARAM_INTERLACED )
{
if( h->mb.b_adaptive_mbaff )
{
if( !(i_mb_y&1) )
{
/* FIXME: VSAD is fast but fairly poor at choosing the best interlace type. */
h->mb.b_interlaced = x264_field_vsad( h, i_mb_x, i_mb_y );
memcpy( &h->zigzagf, MB_INTERLACED ? &h->zigzagf_interlaced : &h->zigzagf_progressive, sizeof(h->zigzagf) );
if( !MB_INTERLACED && (i_mb_y+2) == h->mb.i_mb_height )
x264_expand_border_mbpair( h, i_mb_x, i_mb_y );
}
}
h->mb.field[mb_xy] = MB_INTERLACED;
}
/* load cache */
//将要编码的宏块的周围的宏块的值读进来
//主要是上面、左边块的值
if( SLICE_MBAFF )
x264_macroblock_cache_load_interlaced( h, i_mb_x, i_mb_y ); //将要编码的宏块的周围的宏块的信息读进来
else
x264_macroblock_cache_load_progressive( h, i_mb_x, i_mb_y ); //将要编码的宏块的周围的宏块的信息读进来
x264_macroblock_analyse( h ); //分析模块。该模块包含了帧内预测模式分析以及帧间运动估计等
/* encode this macroblock -> be careful it can change the mb type to P_SKIP if needed */
reencode:
x264_macroblock_encode( h ); //宏块编码模块。该模块通过对残差的DCT变换、量化等方式对宏块进行编码
//输出CABAC
if( h->param.b_cabac )
{
if( mb_xy > h->sh.i_first_mb && !(SLICE_MBAFF && (i_mb_y&1)) )
x264_cabac_encode_terminal( &h->cabac );
if( IS_SKIP( h->mb.i_type ) )
x264_cabac_mb_skip( h, 1 );
else
{
if( h->sh.i_type != SLICE_TYPE_I )
x264_cabac_mb_skip( h, 0 );
x264_macroblock_write_cabac( h, &h->cabac ); //CABAC熵编码模块
}
}
else
{
//输出CAVLC
if( IS_SKIP( h->mb.i_type ) )
i_skip++;
else
{
if( h->sh.i_type != SLICE_TYPE_I )
{
bs_write_ue( &h->out.bs, i_skip ); /* skip run */
i_skip = 0;
}
x264_macroblock_write_cavlc( h ); //CAVLC熵编码模块
/* If there was a CAVLC level code overflow, try again at a higher QP. */
if( h->mb.b_overflow )
{
h->mb.i_chroma_qp = h->chroma_qp_table[++h->mb.i_qp];
h->mb.i_skip_intra = 0;
h->mb.b_skip_mc = 0;
h->mb.b_overflow = 0;
x264_bitstream_restore( h, &bs_bak[BS_BAK_CAVLC_OVERFLOW], &i_skip, 0 );
goto reencode;
}
}
}
int total_bits = bs_pos(&h->out.bs) + x264_cabac_pos(&h->cabac);
int mb_size = total_bits - mb_spos;
if( slice_max_size && (!SLICE_MBAFF || (i_mb_y&1)) )
{
/* Count the skip run, just in case. */
if( !h->param.b_cabac )
total_bits += bs_size_ue_big( i_skip );
/* Check for escape bytes. */
uint8_t *end = h->param.b_cabac ? h->cabac.p : h->out.bs.p;
for( ; last_emu_check < end - 2; last_emu_check++ )
if( last_emu_check[0] == 0 && last_emu_check[1] == 0 && last_emu_check[2] <= 3 )
{
slice_max_size -= 8;
last_emu_check++;
}
/* We'll just re-encode this last macroblock if we go over the max slice size. */
if( total_bits - starting_bits > slice_max_size && !h->mb.b_reencode_mb )
{
if( !x264_frame_new_slice( h, h->fdec ) )
{
/* Handle the most obnoxious slice-min-mbs edge case: we need to end the slice
* because it's gone over the maximum size, but doing so would violate slice-min-mbs.
* If possible, roll back to the last checkpoint and try again.
* We could try raising QP, but that would break in the case where a slice spans multiple
* rows, which the re-encoding infrastructure can't currently handle. */
if( mb_xy <= thread_last_mb && (thread_last_mb+1-mb_xy) < h->param.i_slice_min_mbs )
{
if( thread_last_mb-h->param.i_slice_min_mbs < h->sh.i_first_mb+h->param.i_slice_min_mbs )
{
x264_log( h, X264_LOG_WARNING, "slice-max-size violated (frame %d, cause: slice-min-mbs)\n", h->i_frame );
slice_max_size = 0;
goto cont;
}
x264_bitstream_restore( h, &bs_bak[BS_BAK_SLICE_MIN_MBS], &i_skip, 0 );
h->mb.b_reencode_mb = 1;
h->sh.i_last_mb = thread_last_mb-h->param.i_slice_min_mbs;
break;
}
if( mb_xy-SLICE_MBAFF*h->mb.i_mb_stride != h->sh.i_first_mb )
{
x264_bitstream_restore( h, &bs_bak[BS_BAK_SLICE_MAX_SIZE], &i_skip, 0 );
h->mb.b_reencode_mb = 1;
if( SLICE_MBAFF )
{
// set to bottom of previous mbpair
if( i_mb_x )
h->sh.i_last_mb = mb_xy-1+h->mb.i_mb_stride*(!(i_mb_y&1));
else
h->sh.i_last_mb = (i_mb_y-2+!(i_mb_y&1))*h->mb.i_mb_stride + h->mb.i_mb_width - 1;
}
else
h->sh.i_last_mb = mb_xy-1;
break;
}
else
h->sh.i_last_mb = mb_xy;
}
else
slice_max_size = 0;
}
}
cont:
h->mb.b_reencode_mb = 0;
/* save cache */
//保存当前宏块的的值,用于以后的宏块的编码
//包括Intra4x4宏块帧内预测模式,DCT非零系数,运动矢量,参考帧序号等等
x264_macroblock_cache_save( h ); //保存当前宏块的信息
if( x264_ratecontrol_mb( h, mb_size ) < 0 ) //码率控制
{
x264_bitstream_restore( h, &bs_bak[BS_BAK_ROW_VBV], &i_skip, 1 );
h->mb.b_reencode_mb = 1;
i_mb_x = 0;
i_mb_y = i_mb_y - SLICE_MBAFF;
h->mb.i_mb_prev_xy = i_mb_y * h->mb.i_mb_stride - 1;
h->sh.i_last_mb = orig_last_mb;
continue;
}
/* accumulate mb stats */
//对stat结构体中的统计信息进行赋值
h->stat.frame.i_mb_count[h->mb.i_type]++;
int b_intra = IS_INTRA( h->mb.i_type );
int b_skip = IS_SKIP( h->mb.i_type );
if( h->param.i_log_level >= X264_LOG_INFO || h->param.rc.b_stat_write )
{
if( !b_intra && !b_skip && !IS_DIRECT( h->mb.i_type ) )
{
if( h->mb.i_partition != D_8x8 )
h->stat.frame.i_mb_partition[h->mb.i_partition] += 4;
else
for( int i = 0; i < 4; i++ )
h->stat.frame.i_mb_partition[h->mb.i_sub_partition[i]] ++;
if( h->param.i_frame_reference > 1 )
for( int i_list = 0; i_list <= (h->sh.i_type == SLICE_TYPE_B); i_list++ )
for( int i = 0; i < 4; i++ )
{
int i_ref = h->mb.cache.ref[i_list][ x264_scan8[4*i] ];
if( i_ref >= 0 )
h->stat.frame.i_mb_count_ref[i_list][i_ref] ++;
}
}
}
if( h->param.i_log_level >= X264_LOG_INFO )
{
if( h->mb.i_cbp_luma | h->mb.i_cbp_chroma )
{
if( CHROMA444 )
{
for( int i = 0; i < 4; i++ )
if( h->mb.i_cbp_luma & (1 << i) )
for( int p = 0; p < 3; p++ )
{
int s8 = i*4+p*16;
int nnz8x8 = M16( &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[s8]+0] )
| M16( &h->mb.cache.non_zero_count[x264_scan8[s8]+8] );
h->stat.frame.i_mb_cbp[!b_intra + p*2] += !!nnz8x8;
}
}
else
{
int cbpsum = (h->mb.i_cbp_luma&1) + ((h->mb.i_cbp_luma>>1)&1)
+ ((h->mb.i_cbp_luma>>2)&1) + (h->mb.i_cbp_luma>>3);
h->stat.frame.i_mb_cbp[!b_intra + 0] += cbpsum;
h->stat.frame.i_mb_cbp[!b_intra + 2] += !!h->mb.i_cbp_chroma;
h->stat.frame.i_mb_cbp[!b_intra + 4] += h->mb.i_cbp_chroma >> 1;
}
}
if( h->mb.i_cbp_luma && !b_intra )
{
h->stat.frame.i_mb_count_8x8dct[0] ++;
h->stat.frame.i_mb_count_8x8dct[1] += h->mb.b_transform_8x8;
}
if( b_intra && h->mb.i_type != I_PCM )
{
if( h->mb.i_type == I_16x16 )
h->stat.frame.i_mb_pred_mode[0][h->mb.i_intra16x16_pred_mode]++;
else if( h->mb.i_type == I_8x8 )
for( int i = 0; i < 16; i += 4 )
h->stat.frame.i_mb_pred_mode[1][h->mb.cache.intra4x4_pred_mode[x264_scan8[i]]]++;
else //if( h->mb.i_type == I_4x4 )
for( int i = 0; i < 16; i++ )
h->stat.frame.i_mb_pred_mode[2][h->mb.cache.intra4x4_pred_mode[x264_scan8[i]]]++;
h->stat.frame.i_mb_pred_mode[3][x264_mb_chroma_pred_mode_fix[h->mb.i_chroma_pred_mode]]++;
}
h->stat.frame.i_mb_field[b_intra?0:b_skip?2:1] += MB_INTERLACED;
}//对stat结构体中的统计信息进行赋值结束
/* calculate deblock strength values (actual deblocking is done per-row along with hpel) */
//计算去块效应滤波器强度Bs
//这里没有滤波
if( b_deblock )
x264_macroblock_deblock_strength( h );
if( mb_xy == h->sh.i_last_mb )//如果处理完最后一个宏块,就跳出大循环
break;
if( SLICE_MBAFF )
{
i_mb_x += i_mb_y & 1;
i_mb_y ^= i_mb_x < h->mb.i_mb_width;
}
else
i_mb_x++; //宏块序号x加1
if( i_mb_x == h->mb.i_mb_width )//处理完一行宏块
{
//该处理下一行了
i_mb_y++;//宏块序号y加1
i_mb_x = 0;//宏块序号x设置为0
}
}
if( h->sh.i_last_mb < h->sh.i_first_mb )
return 0;
h->out.nal[h->out.i_nal].i_last_mb = h->sh.i_last_mb;
if( h->param.b_cabac )//熵编码的收尾工作
{
x264_cabac_encode_flush( h, &h->cabac );
h->out.bs.p = h->cabac.p;
}
else
{
if( i_skip > 0 )
bs_write_ue( &h->out.bs, i_skip ); /* last skip run */
/* rbsp_slice_trailing_bits */
bs_rbsp_trailing( &h->out.bs );
bs_flush( &h->out.bs );
}
//结束输出一个NAL
//前面对应着x264_nal_start()
if( x264_nal_end( h ) ) //结束写一个NALU
return -1;
if( h->sh.i_last_mb == (h->i_threadslice_end * h->mb.i_mb_width - 1) )
{
h->stat.frame.i_misc_bits = bs_pos( &h->out.bs )
+ (h->out.i_nal*NALU_OVERHEAD * 8)
- h->stat.frame.i_tex_bits
- h->stat.frame.i_mv_bits;
x264_fdec_filter_row( h, h->i_threadslice_end, 0 );
if( h->param.b_sliced_threads )
{
/* Tell the main thread we're done. */
x264_threadslice_cond_broadcast( h, 1 );
/* Do hpel now */
for( int mb_y = h->i_threadslice_start; mb_y <= h->i_threadslice_end; mb_y++ )
x264_fdec_filter_row( h, mb_y, 1 );
x264_threadslice_cond_broadcast( h, 2 );
/* Do the first row of hpel, now that the previous slice is done */
if( h->i_thread_idx > 0 )
{
x264_threadslice_cond_wait( h->thread[h->i_thread_idx-1], 2 );
x264_fdec_filter_row( h, h->i_threadslice_start + (1 << SLICE_MBAFF), 2 );
}
}
/* Free mb info after the last thread's done using it */
if( h->fdec->mb_info_free && (!h->param.b_sliced_threads || h->i_thread_idx == (h->param.i_threads-1)) )
{
h->fdec->mb_info_free( h->fdec->mb_info );
h->fdec->mb_info = NULL;
h->fdec->mb_info_free = NULL;
}
}
return 0;
}
根据源代码简单梳理了x264_slice_write()的流程,如下所示:
(1)、调用x264_nal_start()开始输出一个NALU。
(2)、x264_macroblock_thread_init():初始化宏块重建像素缓存fdec_buf[]和编码像素缓存fenc_buf[]。
(3)、调用x264_slice_header_write()输出 Slice Header。
(4)、进入一个循环,该循环每执行一遍编码一个宏块:
a)、 每处理一行宏块,调用一次x264_fdec_filter_row()执行滤波模块。
b)、 调用x264_macroblock_cache_load_progressive()将要编码的宏块的周围的宏块的信息读进来。
c) 、调用x264_macroblock_analyse()执行分析模块。
d) 、调用x264_macroblock_encode()执行宏块编码模块。
e) 、调用x264_macroblock_write_cabac()/x264_macroblock_write_cavlc()执行熵编码模块。
f) 、调用x264_macroblock_cache_save()保存当前宏块的信息。
g) 、调用x264_ratecontrol_mb()执行码率控制。
h) 、准备处理下一个宏块。
(5)、调用x264_nal_end()结束输出一个NALU。
到这儿,其实还没进入真正的H.264视频编码算法,后续将正式进入,依次分析帧内预测、帧间预测、变换与量化、去方块滤波、熵编码、码率控制等等。























 321
321

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








