磁盘缓存是将网络资源先保存到系统分配出的内存空间中,当内存中的资源容量达到某个限度时,在将内存中的资源保存的磁盘中。这样做可以有效减少磁盘的读写操作。
OkHttp3的网络缓存主要实现由DiskLruCache这个类来实现。缓存保存在应用指定的内部缓存文件夹中,在调用磁盘缓存时,DisLruCache读取缓存文件快照到内存。涉及到缓存的读写任务都由类DiskLruCache.Edit.java完成。
1. 缓存文件格式
1.1 缓存日志文件
OkHttp3的缓存数据保存在名为journal的文件中。 标准的journal文件格式
libcore.io.DiskLruCache
1
100
2
CLEAN 3400330d1dfc7f3f7f4b8d4d803dfcf6 832 21054
DIRTY 335c4c6028171cfddfbaae1a9c313c52
CLEAN 335c4c6028171cfddfbaae1a9c313c52 3934 2342
REMOVE 335c4c6028171cfddfbaae1a9c313c52
DIRTY 1ab96a171faeeee38496d8b330771a7a
CLEAN 1ab96a171faeeee38496d8b330771a7a 1600 234
READ 335c4c6028171cfddfbaae1a9c313c52
READ 3400330d1dfc7f3f7f4b8d4d803dfcf6
...前五行是文件头部,分别是区分文件格式的MAGIC数(固定为libcore.io.DiskLruCache)、缓存版本、应用版本、Key对应Value值个数和一个空白行。 之后的每行都对应一个Cache实体的状态记录。由状态、键值和可选择具体状态值组成。
- DIRTY 正在创建或更新缓存数据的监视信息。每个成功的DIRTY操作之后都会紧跟一个CLEAN或REMOVE操作。如果没有对应的CLEAN或REMOVE操作说明应该删除掉临时文件。
- CLEAN 可以读取缓存的记录。之后是缓存文件的长度。
- READ 缓存访问记录
- REMOVE 缓存删除记录
journal文件偶尔会丢掉多余的行数来压缩,压缩时使用journal.tmp的临时文件,打开缓存时如果临时文件存在,则删除临时文件。
1.2 缓存文件
DiskLruCache用了两种文件来保存缓存:缓存元数据文件和缓存体文件。
- 缓存元数据文件保存响应的请求和响应的首部信息,如果是HTTPS请求还保存对应的加密和握手协议。
- 缓存体文件保存具体的文件
1.2.1 缓存元数据文件
标准的HTTP META_DATA
http://google.com/foo
GET
2
Accept-Language: fr-CA
Accept-Charset: UTF-8
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
3
Content-Type: image/png
Content-Length: 100
Cache-Control: max-age=600标准的HTTPS META_DATA
https://google.com/foo
GET
2
Accept-Language: fr-CA
Accept-Charset: UTF-8
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
3
Content-Type: image/png
Content-Length: 100
Cache-Control: max-age=600
AES_256_WITH_MD5
2
base64-encoded peerCertificate[0]
base64-encoded peerCertificate[1]
-1
TLSv1.2- 1-2行是URL与请求方法。
- 第3行是HTTP请求Vary头部字段数量,表示请求头部数
- 紧跟之后的是Vary响应字段,表示请求的头部信息。
- 在请求Vary头部字段之后是响应状态。包含HTTP版本,状态码和Message
- 在响应行之后是响应头部数量值。之后是响应头部信息详情。
- 对于HTTPS请求还包含SSL的session信息。由一个空行、密码组、证书链长度、证书链、本地证书长度(
-1表示无本地证书)、最后一行为可选信息(如果有表示TLS的版本号)。
1.2.3 缓存体文件
缓存内容存储的是响应的具体信息。如Json、图片等具体的文件内容。
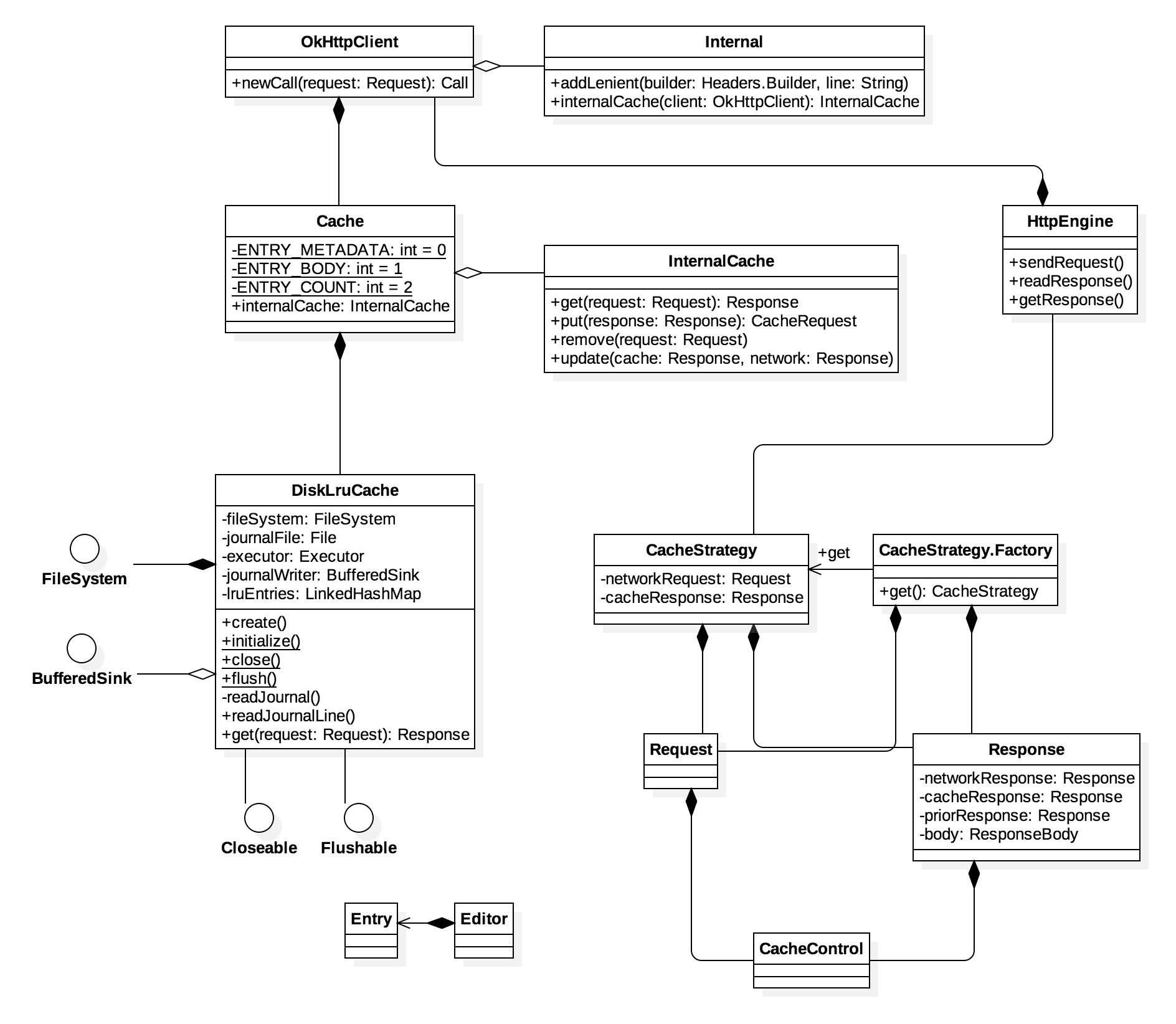
1.3 缓存类的结构
2. 初始化
任何对缓存的操作都会调用缓存的初始化。读取缓存的日志文件,用LinkHashMap.java来存储日志的操作记录,方便删除与查找。
@DiskLruCache.java
public synchronized void initialize() throws IOException {
...
// If a bkp file exists, use it instead.
...
// Prefer to pick up where we left off.
if (fileSystem.exists(journalFile)) {
try {
// [1]
readJournal();
// [2]
processJournal();
initialized = true;
return;
} catch (IOException journalIsCorrupt) {
...
// [3]
delete();
closed = false;
}
}
// [4]
rebuildJournal();
initialized = true;
}2.1 读取本地缓存
@DiskLruCache.java
// [1]
private void readJournal() throws IOException {
BufferedSource source = Okio.buffer(fileSystem.source(journalFile));
try {
// check journal header
...
int lineCount = 0;
while (true) {
try {
// [1.1]
readJournalLine(source.readUtf8LineStrict());
lineCount++;
} catch (EOFException endOfJournal) {
break;
}
}
// 记录有效的缓存操作记录数
redundantOpCount = lineCount - lruEntries.size();
// If we ended on a truncated line, rebuild the journal before appending to it.
...
} finally {
Util.closeQuietly(source);
}
}迭代读取缓存日志文件每行操作,
@DiskLruCache.java
// [1.1]
private void readJournalLine(String line) throws IOException {
// 检查是否是有效的操作行
...
int keyBegin = firstSpace + 1;
int secondSpace = line.indexOf(' ', keyBegin);
final String key;
if (secondSpace == -1) {
// 如果是REMOVE操作,移除内存中对应的失效缓存
...
} else {
key = line.substring(keyBegin, secondSpace);
}
// 读取内存中的Entry,如果没有则创建新的Entry并添加到LinkHashMap中
Entry entry = lruEntries.get(key);
...
if (secondSpace != -1 && firstSpace == CLEAN.length() && line.startsWith(CLEAN)) {
// CLEAN操作
String[] parts = line.substring(secondSpace + 1).split(" ");
entry.readable = true;
entry.currentEditor = null;
entry.setLengths(parts);
} else if (secondSpace == -1 && firstSpace == DIRTY.length() && line.startsWith(DIRTY)) {
// 脏数据,赋值Editor待后续清理
entry.currentEditor = new Editor(entry);
} else if (secondSpace == -1 && firstSpace == READ.length() && line.startsWith(READ)) {
// READ操作
} else {
// 非法操作行数据
throw new IOException("unexpected journal line: " + line);
}
}2.2 处理读取到的缓存
处理读取到Entry链表,清理垃圾缓存和操作
@DiskLruCache.java
// [2] 计算初始大小,回收垃圾缓存。
private void processJournal() throws IOException {
fileSystem.delete(journalFileTmp);
for (Iterator<Entry> i = lruEntries.values().iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) {
Entry entry = i.next();
// entry.currentEditor 如果不是空说明是DIRTY的数据,上面分析过
if (entry.currentEditor == null) {
for (int t = 0; t < valueCount; t++) {
size += entry.lengths[t];
}
} else {
entry.currentEditor = null;
// valueCount = 2
for (int t = 0; t < valueCount; t++) {
fileSystem.delete(entry.cleanFiles[t]);
fileSystem.delete(entry.dirtyFiles[t]);
}
i.remove();
}
}
}2.3 异常处理
读取或处理缓存时发生异常,说明缓存文件已破坏,清空缓存目录下的所有文件
@DiskLruCache.java
// [3] 出现异常时,关闭缓存并删除缓存目录下所有文件
public void delete() throws IOException {
close();
fileSystem.deleteContents(directory);
}2.4 异常后的恢复
出现异常清空缓存目录后,需要重新创建Clean的缓存文件。
@DiskLruCache.java
// [4] 创建新的日志文件,会替换当前存在的日志文件
private synchronized void rebuildJournal() throws IOException {
// 先关闭日志写操作
...
// 创建一个临时文件
BufferedSink writer = Okio.buffer(fileSystem.sink(journalFileTmp));
try {
// 写入日志必要的头信息
...
// 迭代内存中日志记录
for (Entry entry : lruEntries.values()) {
if (entry.currentEditor != null) {
// 写入DIRTY记录
} else {
// 写入CLEAN记录
}
}
} finally {
writer.close();
}
// 备份现有日志文件,保存新日志文件,然后删除备份文件
hasJournalErrors = false;
}3. 缓存读取
@Cache.java
Response get(Request request) {
// 缓存的KEY值实际就是Request的Url的MD5值
String key = urlToKey(request);
DiskLruCache.Snapshot snapshot; // 缓存快照,包装了Source和Sink
...
// [1]
snapshot = cache.get(key);
...
try {
// [2]
entry = new Entry(snapshot.getSource(ENTRY_METADATA));
} catch (IOException e) {
Util.closeQuietly(snapshot);
return null;
}
// [3]
Response response = entry.response(snapshot);
...
return response;
}3.1 缓存文件快照
Snapshot内是缓存文件的Source、每个文件的具体大小。
@DiskLruCache.Snapshot.java
private final String key; // Request key值
private final long sequenceNumber; // 多线程
private final Source[] sources; // 缓存元数据和缓存体文件输入流
private final long[] lengths; // metadata和body缓存文件长度@DiskLruCache.java
// [1]
public synchronized Snapshot get(String key) throws IOException {
...
Entry entry = lruEntries.get(key);
...
// [1.1]
Snapshot snapshot = entry.snapshot();
...
}@DiskLruCache.Entry.java
// [1.1]
Snapshot snapshot() {
...
// valueCount = 2
Source[] sources = new Source[valueCount];
long[] lengths = this.lengths.clone(); // Defensive copy since these can be zeroed out.
try {
for (int i = 0; i < valueCount; i++) {
sources[i] = fileSystem.source(cleanFiles[i]);
}
return new Snapshot(key, sequenceNumber, sources, lengths);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
...
return null;
}
}3.2 构建缓存响应
缓存响应包括请求的详细信息,协议,响应码和响应体CacheResponseBody.java
@Cache.Entry.java
// [3]
public Response response(DiskLruCache.Snapshot snapshot) {
String contentType = responseHeaders.get("Content-Type");
String contentLength = responseHeaders.get("Content-Length");
Request cacheRequest = new Request.Builder()
.url(url)
.method(requestMethod, null)
.headers(varyHeaders)
.build();
return new Response.Builder()
.request(cacheRequest)
.protocol(protocol)
.code(code)
.message(message)
.headers(responseHeaders)
// [3.1]
.body(new CacheResponseBody(snapshot, contentType, contentLength))
.handshake(handshake)
.build();
}@Cache.CacheResponseBody.java
// [3.1]
public CacheResponseBody(final DiskLruCache.Snapshot snapshot,
String contentType, String contentLength) {
...
// 创建缓存体文件Source
// [3.1.1]
Source source = snapshot.getSource(ENTRY_BODY);
bodySource = Okio.buffer(new ForwardingSource(source) {
@Override public void close() throws IOException {
snapshot.close();
super.close();
}
});
}4. 缓存写入
@Cache.java
private CacheRequest put(Response response) throws IOException {
String requestMethod = response.request().method();
if (HttpMethod.invalidatesCache(response.request().method())) {
// OkHttp3只支持GET请求缓存
return null;
}
if (!requestMethod.equals("GET")) {
// Don't cache non-GET responses. We're technically allowed to cache
// HEAD requests and some POST requests, but the complexity of doing
// so is high and the benefit is low.
return null;
}
if (OkHeaders.hasVaryAll(response)) {
return null;
}
Entry entry = new Entry(response);
DiskLruCache.Editor editor = null;
try {
// [1] 将请求的URL的MD5值作为缓存Key值
editor = cache.edit(urlToKey(response.request()));
if (editor == null) {
return null;
}
// [2] 写入请求META_DATA信息
entry.writeTo(editor);
// [3] 初始化缓存请求,用于写入缓存体
return new CacheRequestImpl(editor);
} catch (IOException e) {
// 出现异常,结束Editor任务
return null;
}
}4.1 初始Editor对象
Editor主要作用就是创建写入。
@DiskLruCache.java
// [1]
public Editor edit(String key) throws IOException {
return edit(key, ANY_SEQUENCE_NUMBER);
}
//
private synchronized Editor edit(String key, long expectedSequenceNumber) throws IOException {
// 检查是否初始化,是否关闭,Key值验证
...
Entry entry = lruEntries.get(key);
// Snapshot是否过期,是否已有Editor在运行
...
// 日志文件是否超过最大值
...
// DIRTY记录,防止缓存文件泄露问题,先Flush记录日志
// Flush the journal before creating files to prevent file leaks.
journalWriter.writeUtf8(DIRTY).writeByte(' ').writeUtf8(key).writeByte('\n');
journalWriter.flush();
if (hasJournalErrors) {
return null; // Don't edit; the journal can't be written.
}
...
// 初始化新的Editor
Editor editor = new Editor(entry);
entry.currentEditor = editor;
return editor;
}4.2 写入元数据
@Cache.Entry.java
// [2]
public void writeTo(DiskLruCache.Editor editor) throws IOException {
BufferedSink sink = Okio.buffer(editor.newSink(ENTRY_METADATA));
// 写入缓存元数据,参考缓存元数据节
}4.3 CacheRequest
创建CacheRequestImpl目的是处理缓存输出流的处理。创建一个临时缓存文件来写入缓存。写入成功后,由Editor完成最后的缓存体的处理。
@CacheRequestImpl.java
// [3]
public CacheRequestImpl(final DiskLruCache.Editor editor) throws IOException {
this.editor = editor;
// [3.1] 初始化缓存体
this.cacheOut = editor.newSink(ENTRY_BODY);
this.body = new ForwardingSink(cacheOut) {
@Override public void close() throws IOException {
synchronized (Cache.this) {
if (done) {
return;
}
done = true;
writeSuccessCount++;
}
super.close();
// [3.2] 完成缓存体文件写入
editor.commit();
}
};
}4.3.1 未缓冲的输出流
@DiskLruCache.Editor.java
// [3.1]
public Sink newSink(int index) throws IOException {
synchronized (DiskLruCache.this) {
// 保证编辑的是对应缓存文件
...
if (!entry.readable) {
// 缓存文件是否正在编辑
written[index] = true;
}
// 初始化临时缓存文件
File dirtyFile = entry.dirtyFiles[index];
Sink sink;
try {
// 初始化缓存文件的Sink
sink = fileSystem.sink(dirtyFile);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
return NULL_SINK;
}
// 初始化错误流处理的Sink
return new FaultHidingSink(sink) {
@Override protected void onException(IOException e) {
synchronized (DiskLruCache.this) {
hasErrors = true;
}
}
};
}
}4.3.1 提交写入操作
如果输出流写入缓存文件出现错误,需要删除缓存文件
@DiskLruCache.Edtor.java
// [3.2]
public void commit() throws IOException {
synchronized (DiskLruCache.this) {
if (hasErrors) {
// [3.2.1] 缓存出错,记录REMOVE日志
completeEdit(this, false);
// [3.2.2] 记录REMOVE日志,移除Entry
removeEntry(entry);
} else {
// [3.2.1] 完成缓存体写入
completeEdit(this, true);
}
committed = true;
}
}4.3.1 完成提交
@DiskLruCache.java
// [3.2.1]
private synchronized void completeEdit(Editor editor, boolean success) throws IOException {
// success : true表示成功写入缓存文件
Entry entry = editor.entry;
...
// If this edit is creating the entry for the first time, every index must have a value.
...
// 保存临时缓存文件(成功时且临时文件存在)或删除临时缓存文件(失败时)
// 成功写入缓存文件时,需要更新Map中对应的Entry信息
for (int i = 0; i < valueCount; i++) {
File dirty = entry.dirtyFiles[i];
if (success) {
if (fileSystem.exists(dirty)) {
// 存储临时文件到缓存体文件
File clean = entry.cleanFiles[i];
fileSystem.rename(dirty, clean);
long oldLength = entry.lengths[i];
long newLength = fileSystem.size(clean);
entry.lengths[i] = newLength;
size = size - oldLength + newLength;
}
} else {
// 删除临时缓存文件
fileSystem.delete(dirty);
}
}
...
// 日志记录数
redundantOpCount++;
entry.currentEditor = null;
if (entry.readable | success) {
// 记录CLEAN日志
entry.readable = true;
...
if (success) {
entry.sequenceNumber = nextSequenceNumber++;
}
} else {
// 记录REMOVE日志
}
journalWriter.flush();
// 整理日志大小
if (size > maxSize || journalRebuildRequired()) {
executor.execute(cleanupRunnable);
}
}@DiskLruCache.java
// [3.2.2]
private boolean removeEntry(Entry entry) throws IOException {
if (entry.currentEditor != null) {
entry.currentEditor.hasErrors = true; // Prevent the edit from completing normally.
}
// 删除失效的缓存文件
...
// 记录日志操作数
redundantOpCount++;
// 记录REMOVE操作
journalWriter.writeUtf8(REMOVE).writeByte(' ').writeUtf8(entry.key).writeByte('\n');
lruEntries.remove(entry.key);
// 超过一定操作次数后,对文件进行清理操作
if (journalRebuildRequired()) {
executor.execute(cleanupRunnable);
}
return true;
}5. 缓存更新
更新的操作是在读取缓存操作,使用缓存策略与服务器返回的状态或头部信息来决定是否更新缓存。
@Cache.java
private void update(Response cached, Response network) {
Entry entry = new Entry(network);
// [1] 读取缓存文件快照,cached 是读取缓存得到的Response,由读取缓存小节中知道cached.body()实际上就是CacheResponseBody
DiskLruCache.Snapshot snapshot = ((CacheResponseBody) cached.body()).snapshot;
DiskLruCache.Editor editor = null;
try {
// [2] snapshot.edit调用就是DiskLruCache的edit(String key, long expectedSequenceNumber)方法。
editor = snapshot.edit(); // Returns null if snapshot is not current.
if (editor != null) {
// [3] 更新缓存元数据,参考缓存小节
entry.writeTo(editor);
// [4] 更新缓存体,记录操作日志,参考缓存写入小节
editor.commit();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// 更新出现异常,清理本地缓存文件
abortQuietly(editor);
}
}6. 缓存清理
OkHttp3缓存清理支持手动和自动两种。
- 手动清理缓存文件,直接调用
Cache.remove(Request request)方法,可以清理指定请求的缓存文件,也支持批量缓存清理Cache.evictAll()将缓存文件全部清空 - 自动清理缓存则在运行时自动判断。如果服务器响应的不需要缓存,判断本地是否进行过缓存决定是否清理已有的缓存文件。
@Cache.java
private void remove(Request request) throws IOException {
// [1] 调用DiskLruCache删除缓存
cache.remove(urlToKey(request));
}@DiskLruCache.java
public synchronized boolean remove(String key) throws IOException {
// 一些判断
...
// [1] 清理缓存文件,记录缓存操作,参考写入。
boolean removed = removeEntry(entry);
if (removed && size <= maxSize) mostRecentTrimFailed = false;
return removed;
}7. 关闭缓存
清空全部缓存或调用Cache.close关闭缓存。关闭缓存时会清除所有正在读写操作的缓存任务。
@DiskLruCache.java
public synchronized void close() throws IOException {
if (!initialized || closed) {
closed = true;
return;
}
// Copying for safe iteration.
for (Entry entry : lruEntries.values().toArray(new Entry[lruEntries.size()])) {
if (entry.currentEditor != null) {
entry.currentEditor.abort();
}
}
trimToSize();
journalWriter.close();
journalWriter = null;
closed = true;
}




















 719
719

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








