完整代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
/**
*Linked list of integers. The key is data. The key is sorted in non-descending order.
*/
typedef struct LinkNode
{
int coefficient;
int exponent;
struct LinkNode *next;
}*LinkList, *NodePtr;
/**
*Initialize the list with a header.
*@return The pointer to the header.
*/
LinkList initLinkList()
{
LinkList tempHeader = (LinkList)malloc(sizeof(struct LinkNode));
tempHeader->coefficient = 0;
tempHeader->exponent = 0;
tempHeader->next = NULL;
return tempHeader;
}//of initLinkList
/**
*Print the list
*@param paraHeader The header of the list.
*/
void printList(LinkList paraHeader)
{
NodePtr p = paraHeader->next;
while (p != NULL)
{
printf("%d * 10^%d + ",p->coefficient, p->exponent);
p = p->next;
}//of while
printf("\r\n");
}//of printList
/**
*Print one node for testing.
*@param paraPtr The pointer to the node.
*@param paraChar The name of the node.
*/
void printNode(NodePtr paraPtr, char paraChar)
{
if(paraPtr == NULL)
{
printf("NULL\r\n");
}
else
{
printf("The element of %c is (%d * 10^%d)\r\n",paraChar,paraPtr->coefficient,paraPtr->exponent);
}//of while
}//of printNode
/**
*Add an element to the tail.
*@param paraCoefficient The coefficient of the new element.
*@param paraExponent The exponent of the new element.
*/
void appendElement(LinkList paraHeader, int paraCoefficient,int paraExponent)
{
NodePtr p, q;
//step 1. Construct a new node.
q= (NodePtr)malloc(sizeof(struct LinkNode));
q->coefficient = paraCoefficient;
q->exponent = paraExponent;
q->next = NULL;
//step 2. Search to the tail.
p = paraHeader;
while (p->next != NULL)
{
p = p->next;
}//of while
//step 3. Now add/link.
p->next = q;
}//of appendElement
/**
*Polynomial addition.
*@param paraList1 The first list.
*@param paraList2 The second list.
*/
void add(NodePtr paraList1,NodePtr paraList2)
{
NodePtr p,q,r,s;
//step 1. Seach to the position.
p = paraList1->next;
printNode(p,'p');
q = paraList2->next;
printNode(q,'q');
r=paraList1;
printNode(r,'r');
free(paraList2);
while((p != NULL) && (q != NULL))
{
if (p->exponent < q->exponent)
{
printf("case 1\r\n");
r->next=p;//看过陈涛同学的代码后,找到老师的bug,没有把链表连接起来
r = p;
printNode(r,'r');
p = p->next;
printNode(p,'p');
}
else if(p->exponent > q->exponent)
{
printf("case 2\r\n");
r->next = q;
r = q;
printNode(r,'r');
q = q->next;
printNode(q,'q');
}
else
{
printf("case 3\r\n");
p->coefficient = p->coefficient + q->coefficient;
printf("The coefficient is %d.\r\n",p->coefficient);
if (p->coefficient == 0)
{
printf("case 3.1\r\n");
s = p;
p = p->next;
printNode(p,'p');
free(s);
}
else
{
printf("case 3.2\r\n");
r = p;
printNode(r,'r');
p = p->next;
printNode(p,'p');
}//of if
s = q;
q = q->next;
free(s);
}//of if
printf("p = %ld, q = %ld \r\n",p,q);
}//of while
printf("End of while.\r\n");
if(p == NULL)
{
r->next = q;
}
else
{
r->next = p;
}//of if
printf("Addition ends.\r\n");
}//of add
/**
* Unit test.
*/
void additionTest(){
// Step 1. Initialize the first polynomial.
LinkList tempList1 = initLinkList();
appendElement(tempList1, 7, 0);
appendElement(tempList1, 3, 1);
appendElement(tempList1, 9, 8);
appendElement(tempList1, 5, 17);
printList(tempList1);
// Step 2. Initialize the second polynomial.
LinkList tempList2 = initLinkList();
appendElement(tempList2, 8, 1);
appendElement(tempList2, 22, 7);
appendElement(tempList2, -9, 8);
printList(tempList2);
// Step 3. Add them to the first.
add(tempList1, tempList2);
printList(tempList1);
}// Of additionTest
/**
* The entrance.
*/
void main(){
additionTest();
printf("Finish.\r\n");
}// Of main
创建链表
typedef struct LinkNode
{
int coefficient;
int exponent;
struct LinkNode *next;
}*LinkList, *NodePtr;
链表初始化
LinkList initLinkList()
{
LinkList tempHeader = (LinkList)malloc(sizeof(struct LinkNode));
tempHeader->coefficient = 0;
tempHeader->exponent = 0;
tempHeader->next = NULL;
return tempHeader;
}//of initLinkList
增加
void appendElement(LinkList paraHeader, int paraCoefficient,int paraExponent)
{
NodePtr p, q;
//step 1. Construct a new node.
q= (NodePtr)malloc(sizeof(struct LinkNode));
q->coefficient = paraCoefficient;
q->exponent = paraExponent;
q->next = NULL;
//step 2. Search to the tail.
p = paraHeader;
while (p->next != NULL)
{
p = p->next;
}//of while
//step 3. Now add/link.
p->next = q;
}//of appendElement
多项式相加
1.
void add(NodePtr paraList1,NodePtr paraList2)
{
NodePtr p,q,r,s;
p = paraList1->next;
printNode(p,'p');
q = paraList2->next;
printNode(q,'q');
r=paraList1;
printNode(r,'r');
free(paraList2);
}
2
while((p != NULL) && (q != NULL))
{
if (p->exponent < q->exponent)
{
printf("case 1\r\n");
r->next=p;//看过陈涛同学的代码后,找到老师的bug,没有把链表连接起来
r = p;
printNode(r,'r');
p = p->next;
printNode(p,'p');
}
else if(p->exponent > q->exponent)
{
printf("case 2\r\n");
r->next = q;
r = q;
printNode(r,'r');
q = q->next;
printNode(q,'q');
}
else
{
printf("case 3\r\n");
p->coefficient = p->coefficient + q->coefficient;
printf("The coefficient is %d.\r\n",p->coefficient);
if (p->coefficient == 0)
{
printf("case 3.1\r\n");
s = p;
p = p->next;
printNode(p,'p');
free(s);
}
else
{
printf("case 3.2\r\n");
r = p;
printNode(r,'r');
p = p->next;
printNode(p,'p');
}//of if
s = q;
q = q->next;
free(s);
}//of if
printf("p = %ld, q = %ld \r\n",p,q);
}//of while
printf("End of while.\r\n");
if(p == NULL)
{
r->next = q;
}
else
{
r->next = p;
}//of if
printf("Addition ends.\r\n");
}//of add
结果
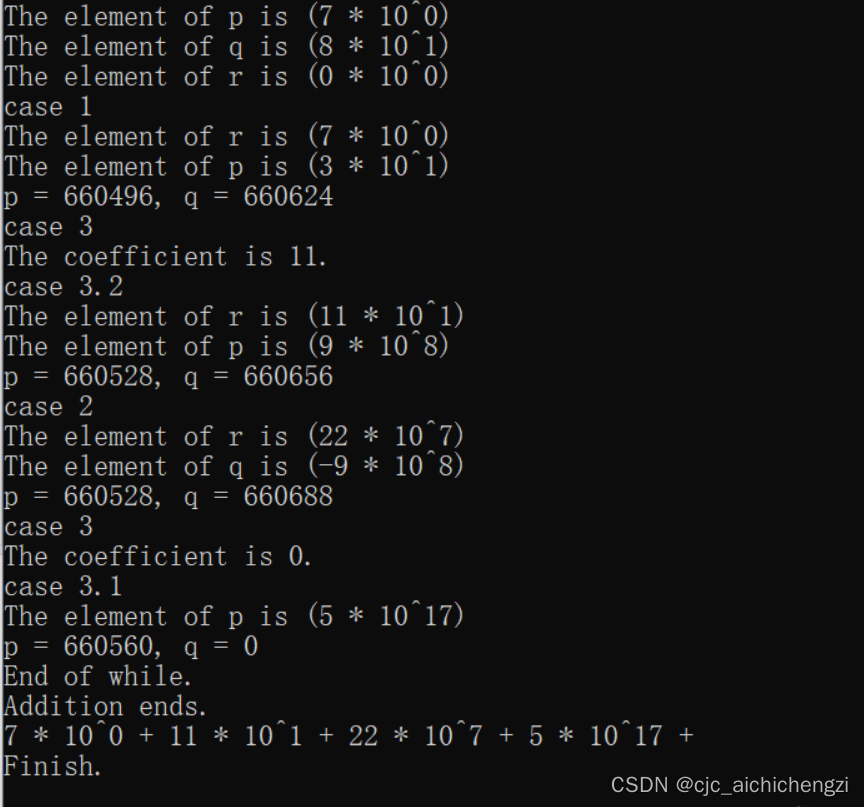





















 767
767











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








