+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
- >>> def f(x, y, z):
- return x + y + z
- >>> args = (1,2,3)
- >>> print f(args)
- Traceback (most recent call last):
- File "<pyshell#6>", line 1, in <module>
- print f(args)
- TypeError: f() takes exactly 3 arguments (1 given)
*args,才是将元祖中的每个元素作为参数
- >>> f(*args)
- 6
- >>> def f(a,b,c,d):
- ... print a,b,c,d
- ...
- >>> args = (1,2,3,4)
- >>> f(**args)
- Traceback (most recent call last):
- File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
- TypeError: f() argument after ** must be a mapping, not tuple
【错误分析】错误原因**匹配并收集在字典中所有包含位置的参数,但传递进去的却是个元祖。
所以修改传递参数如下:
- >>> args = {'a':1,'b':2,'c':3}
- >>> args['d'] = 4
- >>> f(**args)
- 1 2 3 4
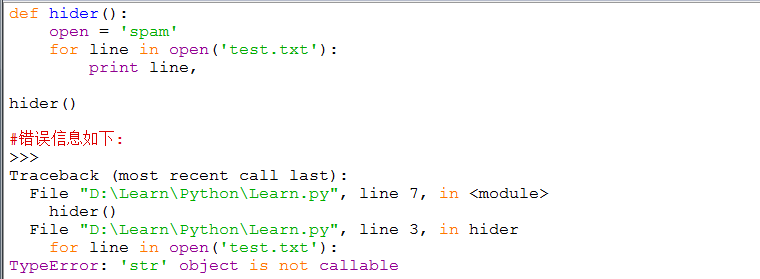
【错误分析】在函数hider()内使用了内置变量open,但根据Python作用域规则LEGB的优先级:
先是查找本地变量==》模块内的其他函数==》全局变量==》内置变量,查到了即停止查找。
所以open在这里只是个字符串,不能作为打开文件来使用,所以报错,更改变量名即可。
可以导入__builtin__模块看到所有内置变量:异常错误、和内置方法
>>> import __builtin__
>>> dir(__builtin__)
['ArithmeticError', 'AssertionError', 'AttributeError',..
.........................................zip,filter,map]
++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
- In [105]: T1 = (1)
- In [106]: T2 = (2,3)
- In [107]: T1 + T2
- ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
- TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
- <ipython-input-107-b105c7b32d90> in <module>()
- ----> 1 T1 + T2;
- TypeError: unsupported operand type(s) for +: 'int' and 'tuple'
- In [108]: type(T1)
- Out[108]: int
- In [109]: T1 = (1,)
- In [110]: T2 = (2,3)
- In [111]: T1 + T2
- Out[111]: (1, 2, 3)
- >>> hash(1,(2,[3,4]))
- Traceback (most recent call last):
- File "<pyshell#95>", line 1, in <module>
- hash((1,2,(2,[3,4])))
- TypeError: unhashable type: 'list'
【错误分析】字典中的键必须是不可变对象,如(整数,浮点数,字符串,元祖).
可用hash()判断某个对象是否可哈希
- >>> hash('string')
- -1542666171
但列表中元素是可变对象,所以是不可哈希的,所以会报上面的错误.
如果要用列表作为字典中的键,最简单的办法是:
- >>> D = {}
- >>> D[tuple([3,4])] = 5
- >>> D
- {(3, 4): 5}
- >>> L = [2,1,4,3]
- >>> L.reverse().sort()
- Traceback (most recent call last):
- File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
- AttributeError: 'NoneType' object has no attribute 'sort'
- >>> L
- [3, 4, 1, 2]
【错误分析】列表属于可变对象,其append(),sort(),reverse()会在原处修改对象,不会有返回值,
或者说返回值为空,所以要实现反转并排序,不能并行操作,要分开来写
- >>> L = [2,1,4,3]
- >>> L.reverse()
- >>> L.sort()
- >>> L
- [1, 2, 3, 4]
或者用下面的方法实现:
- In [103]: sorted(reversed([2,1,4,3]))
- Out[103]: [1, 2, 3, 4]
- >>> class = 78
- SyntaxError: invalid syntax
同样,保留字不能作为模块名来导入,比如说,有个and.py,但不能将其作为模块导入
- >>> import and
- SyntaxError: invalid syntax
- >>> f = open('D:\new\text.data','r')
- Traceback (most recent call last):
- File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
- IOError: [Errno 22] invalid mode ('r') or filename: 'D:\new\text.data'
- >>> f = open(r'D:\new\text.data','r')
- >>> f.read()
- 'Very\ngood\naaaaa'
【错误分析】\n默认为换行,\t默认为TAB键.
所以在D:\目录下找不到ew目录下的ext.data文件,将其改为raw方式输入即可。
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++- try:
- print 1 / 0
- except ZeroDivisionError:
- print 'integer division or modulo by zero'
- finally:
- print 'Done'
- else:
- print 'Continue Handle other part'
- 报错如下:
- D:\>python Learn.py
- File "Learn.py", line 11
- else:
- ^
- SyntaxError: invalid syntax
【错误分析】错误原因,else, finally执行位置;正确的程序应该如下:
- try:
- print 1 / 0
- except ZeroDivisionError:
- print 'integer division or modulo by zero'
- else:
- print 'Continue Handle other part'
- finally:
- print 'Done'
- >>> [x,y for x in range(2) for y in range(3)]
- File "<stdin>", line 1
- [x,y for x in range(2) for y in range(3)]
- ^
- SyntaxError: invalid syntax
- >>> [(x,y) for x in range(2) for y in range(3)]
- [(0, 0), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 0), (1, 1), (1, 2)]
- class JustCounter:
- __secretCount = 0
- def count(self):
- self.__secretCount += 1
- print 'secretCount is:', self.__secretCount
- count1 = JustCounter()
- count1.count()
- count1.count()
- count1.__secretCount
- >>>
- secretCount is: 1
- secretCount is: 2
- Traceback (most recent call last):
- File "D:\Learn\Python\Learn.py", line 13, in <module>
- count1.__secretCount
- AttributeError: JustCounter instance has no attribute '__secretCount'
【错误分析】双下划线的类属性__secretCount不可访问,所以会报无此属性的错误.
解决办法如下:
- # 1. 可以通过其内部成员方法访问
- # 2. 也可以通过访问
- ClassName._ClassName__Attr
- #或
- ClassInstance._ClassName__Attr
- #来访问,比如:
- print count1._JustCounter__secretCount
- print JustCounter._JustCounter__secretCount
- >>> print x
- Traceback (most recent call last):
- File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
- NameError: name 'x' is not defined
- >>> x = 1
- >>> print x
- 1
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
- >>> t = (1,2)
- >>> t.append(3)
- Traceback (most recent call last):
- File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
- AttributeError: 'tuple' object has no attribute 'append'
- >>> t.remove(2)
- Traceback (most recent call last):
- File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
- AttributeError: 'tuple' object has no attribute 'remove'
- >>> t.pop()
- Traceback (most recent call last):
- File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
- AttributeError: 'tuple' object has no attribute 'pop'
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
- >>> t = ()
- >>> t[0]
- Traceback (most recent call last):
- File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
- IndexError: tuple index out of range
- >>> l = []
- >>> l[0]
- Traceback (most recent call last):
- File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
- IndexError: list index out of range
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
- >>> if X>Y:
- ... X,Y = 3,4
- ... print X,Y
- File "<stdin>", line 3
- print X,Y
- ^
- IndentationError: unexpected indent
- >>> t = (1,2,3,4)
- File "<stdin>", line 1
- t = (1,2,3,4)
- ^
- IndentationError: unexpected indent
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
- >>> f = file('1.txt')
- >>> f.readline()
- 'AAAAA\n'
- >>> f.readline()
- 'BBBBB\n'
- >>> f.next()
- 'CCCCC\n'
- >>> f.next() #
- Traceback (most recent call last):
- File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
- StopIteration
有可迭代的对象的next方法,会前进到下一个结果,而在一系列结果的末尾时,会引发StopIteration的异常.
next()方法属于Python的魔法方法,这种方法的效果就是:逐行读取文本文件的最佳方式就是根本不要去读取。
取而代之的用for循环去遍历文件,自动调用next()去调用每一行,且不会报错
- for line in open('test.txt','r'):
- print line
- >>> string = 'SPAM'
- >>> a,b,c = string
- Traceback (most recent call last):
- File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
- ValueError: too many values to unpack
- >>> a,b,c,d = string
- >>> a,d
- ('S', 'M')
- #除非用切片的方式
- >>> a,b,c = string[0],string[1],string[2:]
- >>> a,b,c
- ('S', 'P', 'AM')
- 或者
- >>> a,b,c = list(string[:2]) + [string[2:]]
- >>> a,b,c
- ('S', 'P', 'AM')
- 或者
- >>> (a,b),c = string[:2],string[2:]
- >>> a,b,c
- ('S', 'P', 'AM')
- 或者
- >>> ((a,b),c) = ('SP','AM')
- >>> a,b,c
- ('S', 'P', 'AM')
- 简单点就是:
- >>> a,b = string[:2]
- >>> c = string[2:]
- >>> a,b,c
- ('S', 'P', 'AM')
- >>> mydic={'a':1,'b':2}
- >>> mydic['a']
- 1
- >>> mydic['c']
- Traceback (most recent call last):
- File "<stdin>", line 1, in ?
- KeyError: 'c'
- >>> 'a' in mydic.keys()
- True
- >>> 'c' in mydic.keys() #用in做成员归属测试
- False
- >>> D.get('c','"c" is not exist!') #用get或获取键,如不存在,会打印后面给出的错误信息
- '"c" is not exist!'
- File "study.py", line 3
- return None
- ^
- dentationError: unexpected indent
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
- >>>def A():
- return A()
- >>>A() #无限循环,等消耗掉所有内存资源后,报最大递归深度的错误
- File "<pyshell#2>", line 2, in A return A()RuntimeError: maximum recursion depth exceeded
- class Bird:
- def __init__(self):
- self.hungry = True
- def eat(self):
- if self.hungry:
- print "Ahaha..."
- self.hungry = False
- else:
- print "No, Thanks!"
- 该类定义鸟的基本功能吃,吃饱了就不再吃
- 输出结果:
- >>> b = Bird()
- >>> b.eat()
- Ahaha...
- >>> b.eat()
- No, Thanks!
- 下面一个子类SingBird,
- class SingBird(Bird):
- def __init__(self):
- self.sound = 'squawk'
- def sing(self):
- print self.sound
- 输出结果:
- >>> s = SingBird()
- >>> s.sing()
- squawk
- SingBird是Bird的子类,但如果调用Bird类的eat()方法时,
- >>> s.eat()
- Traceback (most recent call last):
- File "<pyshell#5>", line 1, in <module>
- s.eat()
- File "D:\Learn\Python\Person.py", line 42, in eat
- if self.hungry:
- AttributeError: SingBird instance has no attribute 'hungry'
- class SingBird(Bird):
- def __init__(self):
- self.sound = 'squawk'
- self.hungry = Ture #加这么一句
- def sing(self):
- print self.sound
- class Bird:
- def __init__(self):
- self.hungry = True
- def eat(self):
- if self.hungry:
- print "Ahaha..."
- self.hungry = False
- else:
- print "No, Thanks!"
- class SingBird(Bird):
- def __init__(self):
- super(SingBird,self).__init__()
- self.sound = 'squawk'
- def sing(self):
- print self.sound
- >>> sb = SingBird()
- Traceback (most recent call last):
- File "<pyshell#5>", line 1, in <module>
- sb = SingBird()
- File "D:\Learn\Python\Person.py", line 51, in __init__
- super(SingBird,self).__init__()
- TypeError: must be type, not classobj
- __metaclass__=type
- class Bird:
- def __init__(self):
- self.hungry = True
- def eat(self):
- if self.hungry:
- print "Ahaha..."
- self.hungry = False
- else:
- print "No, Thanks!"
- class SingBird(Bird):
- def __init__(self):
- super(SingBird,self).__init__()
- self.sound = 'squawk'
- def sing(self):
- print self.sound
- >>> S = SingBird()
- >>> S.
- SyntaxError: invalid syntax
- >>> S.
- SyntaxError: invalid syntax
- >>> S.eat()
- Ahaha...
- >>> T
- (1, 2, 3, 4)
- >>> T[0] = 22
- Traceback (most recent call last):
- File "<pyshell#129>", line 1, in <module>
- T[0] = 22
- TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment
- >>> T = (1,2,3,4)
- >>> (22,) + T[1:]
- (22, 2, 3, 4)
- >>> X = 1;
- >>> Y = 2;
- >>> X + = Y
- File "<stdin>", line 1
- X + = Y
- ^
- SyntaxError: invalid syntax
【错误分析】增强行赋值不能分开来写,必须连着写比如说 +=, *=






















 5434
5434











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








