1.优先级
1-MIN_PRIORITY
10-MAX_PRIORITY
5-NORM_PRIORITY
(默认为5,比如主线程)
2.示例:
class ThRun implements Runnable {
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + i);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public class ThreadDemo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(new ThRun(), "A");
Thread t2 = new Thread(new ThRun(), "B");
Thread t3 = new Thread(new ThRun(), "C");
t1.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);
t2.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);
t3.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}结果:
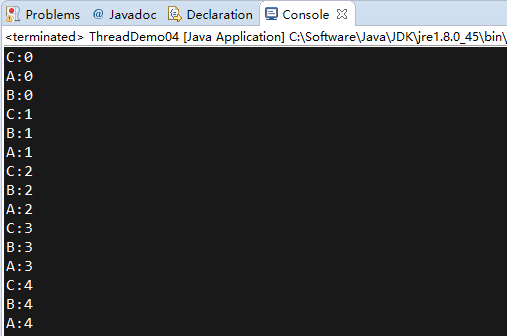
优先级越高,争取CPU资源的机会越大























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








