一、算法或原理的实现思想[1]
1、先来先服务算法(FCFS)First Come First Service
这是一种比较简单的磁盘调度算法。它根据进程请求访问磁盘的先后次序进行调度。此算法的优点是公平、简单,且每个进程的请求都能依次得到处理,不会出现某一进程的请求长期得不到满足的情况。此算法由于未对寻道进行优化,在对磁盘的访问请求比较多的情况下,此算法将降低设备服务的吞吐量,致使平均寻道时间可能较长,但各进程得到服务的响应时间的变化幅度较小。
2、最短寻道时间优先算法(SSTF) Shortest Seek Time First
该算法选择这样的进程,其要求访问的磁道与当前磁头所在的磁道距离最近,以使每次的寻道时间最短,该算法可以得到比较好的吞吐量,但却不能保证平均寻道时间最短。其缺点是对用户的服务请求的响应机会不是均等的,因而导致响应时间的变化幅度很大。在服务请求很多的情况下,对内外边缘磁道的请求将会无限期的被延迟,有些请求的响应时间将不可预期。
3、扫描算法(SCAN)电梯调度
扫描算法不仅考虑到欲访问的磁道与当前磁道的距离,更优先考虑的是磁头的当前移动方向。例如,当磁头正在自里向外移动时,扫描算法所选择的下一个访问对象应是其欲访问的磁道既在当前磁道之外,又是距离最近的。这样自里向外地访问,直到再无更外的磁道需要访问才将磁臂换向,自外向里移动。这时,同样也是每次选择这样的进程来调度,即其要访问的磁道,在当前磁道之内,从而避免了饥饿现象的出现。由于这种算法中磁头移动的规律颇似电梯的运行,故又称为电梯调度算法。此算法基本上克服了最短寻道时间优先算法的服务集中于中间磁道和响应时间变化比较大的缺点,而具有最短寻道时间优先算法的优点即吞吐量较大,平均响应时间较小,但由于是摆动式的扫描方法,两侧磁道被访问的频率仍低于中间磁道。
4、循环扫描算法(CSCAN)
循环扫描算法是对扫描算法的改进。如果对磁道的访问请求是均匀分布的,当磁头到达磁盘的一端,并反向运动时落在磁头之后的访问请求相对较少。这是由于这些磁道刚被处理,而磁盘另一端的请求密度相当高,且这些访问请求等待的时间较长,为了解决这种情况,循环扫描算法规定磁头单向移动。例如,只自里向外移动,当磁头移到最外的被访问磁道时,磁头立即返回到最里的欲访磁道,即将最小磁道号紧接着最大磁道号构成循环,进行扫描。
二、程序(带注释)
(更方便阅读的形式已上传至博客)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define MAXLEN 100
int listLen;
int currentlyTrack;
int input[MAXLEN] = {0};
void fcfs();
void sstf();
void scan();
void cscan();
typedef struct Node
{
bool flag;
int data;
}NODE;
int main()
{
int choice = 0;
printf("------------- Welcome to the Banker Algorithm Simulator!-------------\n");
printf("Please input the number of the access sequence:\n");
scanf("%d", &listLen);
if (listLen > MAXLEN) // The most access sequence is 100
{
printf("ERROR! No more than 100!");
exit(0);
}
else
{
printf("Please input the access sequence:\n"); // input the access sequence
for (int i=0; i < listLen; i++)
scanf("%d", &input[i]);
}
printf("Please input current track:\n"); // input current track
scanf("%d", ¤tlyTrack);
printf("Please choose a scheduling algorithm:\n");// choose algorithm
printf("0. FCFS 1. SSTF 2. SCAN 3. CSCAN\n");
scanf("%d", &choice);
system("cls");
printf("------------- Welcome to the Banker Algorithm Simulator!-------------\n");
printf("The access sequence is :\n"); // output the sequence
for (int i=0; i < listLen; i++)
printf("%d ", input[i]);
printf("\n");
printf("Current track is : %d\n", currentlyTrack);// output current track
switch(choice)
{
case 0: fcfs(); break;
case 1: sstf(); break;
case 2: scan(); break;
case 3: cscan();break;
default: printf("ERROR! Not a legal algorithm number!");exit(0);
}
return 0;
}
void fcfs() // First come first serve
{
printf("Next track\t\tMoving distance\n");
printf("%d\t\t\t%d\n", input[0], abs(input[0]-currentlyTrack));
for (int i=1; i < listLen; i++)
printf("%d\t\t\t%d\n", input[i], abs(input[i]-input[i-1]));
}
void sstf() // Shortest seek time priority
{
int index = currentlyTrack;
int newListLen = listLen + 1;
NODE in[newListLen];
int out[newListLen];
int count = 0;
for (int i=0; i < listLen; i++) // package a struct
{
in[i].data = input[i];
in[i].flag = true; // flag to describe if it is assign
}
in[listLen].data=currentlyTrack,in[listLen].flag=false; // add the current track to the sequence
for (int i=0; i < newListLen-1; i++) // sort the sequence
for (int j=0; j < newListLen-1-i; j++)
if (in[j].data > in[j+1].data)
{
NODE tmp = in[j];
in[j] = in[j+1];
in[j+1] = tmp;
}
for (int i=0; i < newListLen; i++) // find out the current track's index
if (!in[i].flag)
{
index = i;
break;
}
while (true)
{
out[count++] = in[index].data;
int i=index,j=index;
while (!in[i].flag)
i--;
while (!in[j].flag)
j++;
if (i<0 && j>=newListLen) // all track was assigned
break;
else if (i < 0) // i is invalid
index = j;
else if (j > newListLen) // j is invalid
index = i;
else
index = in[i].data>in[j].data?i:j; // find out the bigger one's index
in[index].flag = false; // sign out this track was assigned
}
printf("Next track\t\tMoving distance\n");
for (int i=1; i < newListLen; i++)
printf("%d\t\t\t%d\n", out[i], abs(out[i]-out[i-1]));
}
void scan() //Scan
{
int choice = 0;
int index = currentlyTrack;
int newListLen = listLen + 1;
NODE in[newListLen];
int out[newListLen];
int count = 0;
printf("Please input the current access direction:\n0. increase\t\t1. decrease\n");
scanf("%d", &choice);
if (choice!=0 && choice!=1)
{
printf("ERROR! %d is not a valid direction! Input again!", choice);
scan();
}
for (int i=0; i < listLen; i++)
{
in[i].data = input[i];
in[i].flag = true;
}
in[listLen].data=currentlyTrack,in[listLen].flag=false;
for (int i=0; i < newListLen-1; i++)
for (int j=0; j < newListLen-1-i; j++)
if (in[j].data > in[j+1].data)
{
NODE tmp = in[j];
in[j] = in[j+1];
in[j+1] = tmp;
}
for (int i=0; i < newListLen; i++)
if (!in[i].flag)
{
index = i;
break;
}
out[count++] = currentlyTrack;
if (!choice)
{
for (int i=index+1; i < newListLen; i++) // if increase direction, assign back of the current track
out[count++] = in[i].data;
for (int i=index-1; i >= 0; i--) // then assign pre of it
out[count++] = in[i].data;
}
else
{
for (int i=index-1; i >= 0; i--)
out[count++] = in[i].data;
for (int i=index+1; i < newListLen; i++)
out[count++] = in[i].data;
}
printf("Next track\t\tMoving distance\n");
for (int i=1; i < count; i++)
printf("%d\t\t\t%d\n", out[i], abs(out[i]-out[i-1]));
}
void cscan() //Cycle scan
{
int choice = 0;
int index = currentlyTrack;
int newListLen = listLen + 1;
NODE in[newListLen];
int out[newListLen];
int count = 0;
printf("Please input the current access direction:\n0. increase\t\t1. decrease\n");
scanf("%d", &choice);
if (choice!=0 && choice!=1)
{
printf("ERROR! %d is not a valid direction! Input again!", choice);
scan();
}
for (int i=0; i < listLen; i++)
{
in[i].data = input[i];
in[i].flag = true;
}
in[listLen].data=currentlyTrack,in[listLen].flag=false;
for (int i=0; i < newListLen-1; i++)
for (int j=0; j < newListLen-1-i; j++)
if (in[j].data > in[j+1].data)
{
NODE tmp = in[j];
in[j] = in[j+1];
in[j+1] = tmp;
}
for (int i=0; i < newListLen; i++)
if (!in[i].flag)
{
index = i;
break;
}
out[count++] = currentlyTrack;
if (!choice)
{
for (int i=index+1; i < newListLen; i++)
out[count++] = in[i].data;
for (int i=0; i < index; i++)
out[count++] = in[i].data;
}
else
{
for (int i=0; i < index; i++)
out[count++] = in[i].data;
for (int i=index+1; i < newListLen; i++)
out[count++] = in[i].data;
}
printf("Next track\t\tMoving distance\n");
for (int i=1; i < count; i++)
printf("%d\t\t\t%d\n", out[i], abs(out[i]-out[i-1]));
}
三、程序的输入和输出
测试数据1:
7
55 58 39 18 90 160 150
100
0
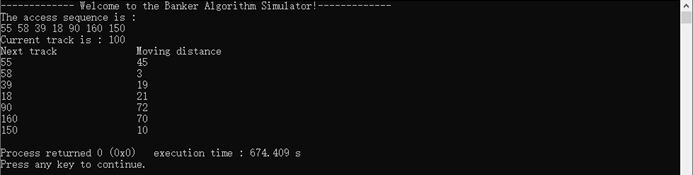
测试数据2:
7
55 58 39 18 90 160 150
100
1
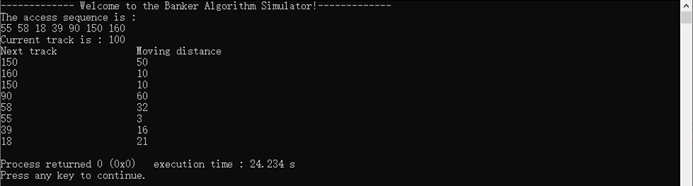
测试数据3:
7
55 58 39 18 90 160 150
100
2
0
测试数据4:
7
55 58 39 18 90 160 150
100
2
1
测试数据5:
7
55 58 39 18 90 160 150
100
3
0
测试数据6:
7
55 58 39 18 90 160 150
100
3
1

四、参考文献
[1] 磁盘调度算法的设计思想
[2] SSTF算法实现
五、感想、体会或收获
进行sstf算法实现时遇到了Codeblocks无debug的问题。
初始思路为将已调度的磁道序号置为-1,但因为不能debug,并且未能解决,在阅读一个Java实现的代码后,发现他为磁盘号创建一个类,内部设flag作为是否调度的标志,于是想到用结构体为序列封装,增加flag表示是否完成调度,得以解决问题。
另外发现,以先排序再调度的方法实现算法,SSTF、SCAN和CSCAN算法实现函数的耦合度极高,但时间紧迫,因此未对耦合部分抽离为函数。且排序算法为了简单选用了冒泡排序,后期优化为快速排序。





















 896
896











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








