为什么需要exec函数?
- fork子进程是为了执行新程序(fork创建了子进程后,子进程和父进程同时被OS调度执行,因此子进程可以单独的执行一个程序,这个程序宏观上将会和父进程程序同时进行)
- 可以直接在子进程的if中写入新程序打代码。但这样不够灵活,因为我们只能把子进程程序的源代码贴过来执行(必须知道源代码,而且源代码太长了也不好控制)。例如我们希望子进程来执行ls -la命令就不行了(没有源代码,只有编译好打可执行程序)。
- 使用exec族函数运行新的可执行程序。exec族函数可以直接把一个编译好的可执行程序直接加载运行。
- 有了exec族函数后,典型打父子进程程序是这样的:子进程需要运行的程序被单独编写、单独编译链接成一个可执行程序(hello)。主进程为父进程,fork创建了子进程后在子进程中exec来执行hello,达到父子进程分别做不同程序同时(宏观上)运行的效果。
exec族函数
#include <unistd.h>
extern char **environ;
int execl(const char *path, const char *arg, ...
/* (char *) NULL */)
int execlp(const char *file, const char *arg, ...
/* (char *) NULL */);
int execle(const char *path, const char *arg, ...
/*, (char *) NULL, char * const envp[] */);
int execv(const char *path, char *const argv[]);
int execvp(const char *file, char *const argv[]);
int execvpe(const char *file, char *const argv[],char *const envp[]);
(1)execl和execv
int execl(const char *path, const char *arg, ...
/* (char *) NULL */)
int execv(const char *path, char *const argv[]);这两个函数是最基本的exec,都可以用来执行一个程序,区别是传参的格式不同。execl是把参数列表(本质上是多个字符串,必须以NULL结尾)依次排列而成(l其实就是list的缩写),execv是把参数列表事先放入一个字符串数组中,再把这个字符串数组传给execv函数。
(2)execlp和execvp
int execlp(const char *file, const char *arg, ...
/* (char *) NULL */);
int execvp(const char *file, char *const argv[]);这个两个函数在上面两个函数打基础上加了p,较上面2个来说,区别是:上面两个函数执行程序时必须指定可执行程序打全路径(如果exec没有找到path这个文件,则直接报错),而加了p的传递打可以是file,也可以是path。加了p的这两个函数会首先会去环境变量PATH所指定的目录下去找,如果找到则执行,如果没有找到则会去当前目录下找file,如果找到则执行,如果没有找到则报错。
(3)execle和execvpe
int execle(const char *path, const char *arg, ...
/*, (char *) NULL, char * const envp[] */);
int execvpe(const char *file, char *const argv[],char *const envp[]);这两个函数较基本exec来说是加了e,函数的参数列表中也多了一个字符串数组envp形参,e是environment环境变量的意思,和基本版本的exec的区别就是:执行可执行程序时会多传一个环境变量打字符串数组给待执行打程序。
实例
(1)使用execl运行ls -la
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
int main(void)
{
pid_t pid;
if((pid = fork()) < 0)
{
perror("fork");
exit(1);
}
else if(pid == 0)
{
/* child */
execl("/bin/ls", "ls", "-l", "-a",NULL);
}
else
{
printf("parent, child id = %d.\n",pid);
}
return 0;
}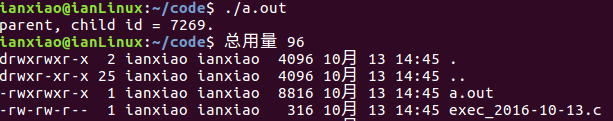
注意execl("/bin/ls", "ls", "-l", "-a",NULL);
传的参数arg是从第二个字符串开始看的(从”-l”开始),但是如果没有”ls”会出现警告。把”ls”改成”pwd”,结果不会变,说明执行的可执行程序还是”/bin/ls”。”ls”相当于argv[0],是我们执行程序的程序名。
(2)使用execv运行ls -la
在(1)打代码基础上做些许改动即可。
else if(pid == 0)
{
/* child */
//execl("/bin/ls", "ls", "-l", "-a",NULL);
char* const argv[] = {"ls", "-l", "-a", NULL};
execv("/bin/ls", argv);
}
(3)使用execl运行自己写的程序hello
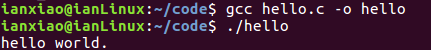
在(1)打代码里做些许改动。
else if(pid == 0)
{
/* child */
execl("./hello", "hello",NULL);
}
(4)execle的使用
main函数的原型其实不只是int main(int argc, char *argv[]),也可以有int main(int argc, char *argv[], char *env[])。
第三个参数是一个字符串数组,内容是环境变量。
如果用户在执行程序时没有传递第三个参数,则程序会自动从父进程继承一份环境变量(默认打,最早来源与OS中打环境变量); 如果我们exec时使用的是execlp或者execvpe去传一个envp数组,则程序中的实际环境变量是我们传递的这一份(取代了默认的从父进程继承来的那一份环境变量)。
hello.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[], char *env[])
{
int i;
printf("argc = %d\n", argc);
i = 0;
while(NULL != argv[i])
{
printf("argv[%d] = %s\n", i, argv[i]);
i++;
}
i = 0;
while(NULL != env[i])
{
printf("env[%d] = %s\n", i, env[i]);
i++;
}
return 0;
}exec_2016-10-13.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
int main(void)
{
pid_t pid;
if((pid = fork()) < 0)
{
perror("fork");
exit(1);
}
else if(pid == 0)
{
/* child */
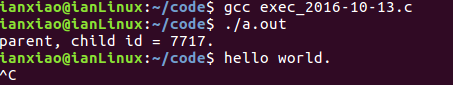
execl("./hello", "hello", "-l", "-a", NULL);
}
else
{
printf("parent, child id = %d.\n",pid);
}
return 0;
}从父进程继承来的环境变量。
使用execle。修改后的exec_2016-10-13.c。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
int main(void)
{
pid_t pid;
if((pid = fork()) < 0)
{
perror("fork");
exit(1);
}
else if(pid == 0)
{
/* child */
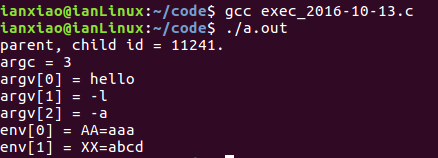
char* const envp[] = {"AA=aaa", "XX=abcd", NULL};
execle("./hello", "hello", "-l", "-a", NULL, envp);
}
else
{
printf("parent, child id = %d.\n",pid);
}
return 0;
}取代后。

























 409
409

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








