项目图
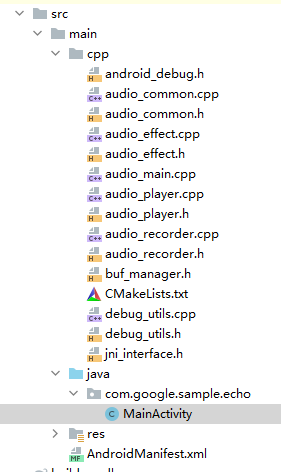
运行界面
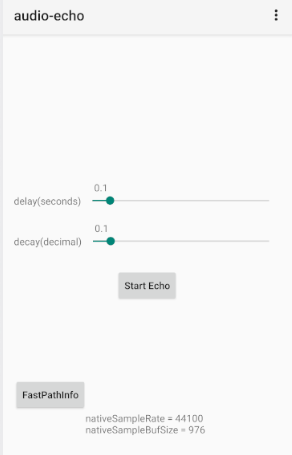
界面分析
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);//设置布局文件
controlButton = (Button)findViewById((R.id.capture_control_button));
statusView = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.statusView);{
private void queryNativeAudioParameters() {
supportRecording = true;
AudioManager myAudioMgr = (AudioManager) getSystemService(Context.AUDIO_SERVICE);//获取audioManager的服务
if(myAudioMgr == null) {
supportRecording = false;
return;
}
nativeSampleRate = myAudioMgr.getProperty(AudioManager.PROPERTY_OUTPUT_SAMPLE_RATE);//audio的采样率
nativeSampleBufSize =myAudioMgr.getProperty(AudioManager.PROPERTY_OUTPUT_FRAMES_PER_BUFFER);//每个sample的大小
{
-
音频源:我们可以使用麦克风作为采集音频的数据源。
-
采样率:一秒钟对声音数据的采样次数,采样率越高,音质越好。
-
音频通道:单声道,双声道等,
-
音频格式:一般选用PCM格式,即原始的音频样本。
-
缓冲区大小:音频数据写入缓冲区的总数,可以通过AudioRecord.getMinBufferSize获取最小的缓冲区。(将音频采集到缓冲区中然后再从缓冲区中读取)
}
// hardcoded channel to mono: both sides -- C++ and Java sides
int recBufSize = AudioRecord.getMinBufferSize(
Integer.parseInt(nativeSampleRate),
AudioFormat.CHANNEL_IN_MONO,
AudioFormat.ENCODING_PCM_16BIT);
if (recBufSize == AudioRecord.ERROR ||
recBufSize == AudioRecord.ERROR_BAD_VALUE) {
supportRecording = false;
}
}}
queryNativeAudioParameters();
delaySeekBar = (SeekBar)findViewById(R.id.delaySeekBar);
curDelayTV = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.curDelay);
echoDelayProgress = delaySeekBar.getProgress() * 1000 / delaySeekBar.getMax();设置seekbar的监听器
delaySeekBar.setOnSeekBarChangeListener(new SeekBar.OnSeekBarChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onProgressChanged(SeekBar seekBar, int progress, boolean fromUser) {
float curVal = (float)progress / delaySeekBar.getMax();
curDelayTV.setText(String.format("%s", curVal));
{
//设置坐标
private void setSeekBarPromptPosition(SeekBar seekBar, TextView label) {
float thumbX = (float)seekBar.getProgress()/ seekBar.getMax() *
seekBar.getWidth() + seekBar.getX();
label.setX(thumbX - label.getWidth()/2.0f);
}}
setSeekBarPromptPosition(delaySeekBar, curDelayTV);
if (!fromUser) return;
echoDelayProgress = progress * 1000 / delaySeekBar.getMax();
{
static native boolean configureEcho(int delayInMs, float decay);}
configureEcho(echoDelayProgress, echoDecayProgress);
}
@Override
public void onStartTrackingTouch(SeekBar seekBar) {}
@Override
public void onStopTrackingTouch(SeekBar seekBar) {}
});//当前view 在attachedToWindow之后执行操作
delaySeekBar.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
setSeekBarPromptPosition(delaySeekBar, curDelayTV);
}
});private void startEcho() {
if(!supportRecording){
return;
}
if (!isPlaying) {
if(!createSLBufferQueueAudioPlayer()) {
statusView.setText(getString(R.string.player_error_msg));
return;
}
if(!createAudioRecorder()) {
deleteSLBufferQueueAudioPlayer();
statusView.setText(getString(R.string.recorder_error_msg));
return;
}
startPlay(); // startPlay() triggers startRecording()
statusView.setText(getString(R.string.echoing_status_msg));
} else {
stopPlay(); // stopPlay() triggers stopRecording()
updateNativeAudioUI();
deleteAudioRecorder();
deleteSLBufferQueueAudioPlayer();
}
isPlaying = !isPlaying;
controlButton.setText(getString(isPlaying ?
R.string.cmd_stop_echo: R.string.cmd_start_echo));
}jni function 声明
/*
* jni function declarations
*/
static native void createSLEngine(int rate, int framesPerBuf,
long delayInMs, float decay);
static native void deleteSLEngine();
static native boolean configureEcho(int delayInMs, float decay);
static native boolean createSLBufferQueueAudioPlayer();
static native void deleteSLBufferQueueAudioPlayer();
static native boolean createAudioRecorder();
static native void deleteAudioRecorder();
static native void startPlay();
static native void stopPlay();OpenSL ES
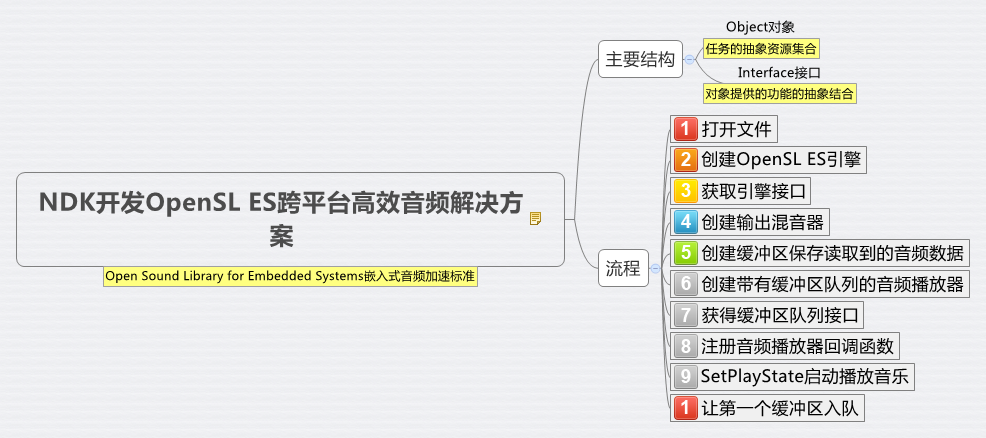
以上图片引用自:https://www.jianshu.com/p/82da5f87314f
OpensSL ES是无授权费,跨平台的,针对嵌入式精心优化的硬件音频加速API。
对象和接口的概念:
对象:提供一组资源及其状态的抽象

接口:提供特定功能的方法的抽象
对象与接口的关系:
对象暴露的接口,有以下三个方面决定:
1)对象的类型
2)应用程序在对象创建期间的,接口请求。
3)在对象声明周期,接口的添加和移除。
一个对象的类型,表明了它有implicat interfaces,implicat interface的含义是:无论应用程序是否request,它都存在对象暴露的接口函数中。
在对象创建的时候,如果有应用请求才暴露的接口,被称为explicit interfaces。
对象定义的可以动态添加和移除的接口,被称为dynamic interfaces.SLDynamicInterfaceManagementItf
EchoAudioEngine
struct EchoAudioEngine {
SLmilliHertz fastPathSampleRate_;
uint32_t fastPathFramesPerBuf_;
uint16_t sampleChannels_;
uint16_t bitsPerSample_;
SLObjectItf slEngineObj_;
SLEngineItf slEngineItf_;
AudioRecorder *recorder_;
AudioPlayer *player_;
AudioQueue *freeBufQueue_; // Owner of the queue
AudioQueue *recBufQueue_; // Owner of the queue
sample_buf *bufs_;
uint32_t bufCount_;
uint32_t frameCount_;
int64_t echoDelay_;
float echoDecay_;
AudioDelay *delayEffect_;
};
static EchoAudioEngine engine;SLObjectItf:任何对象都暴露这个接口。每个方法创建一个对象,都返回这个接口SLObjectItf. 销毁对象通过destory().应用程序获取其他的接口,通过type ID 使用GetInterface来返回。通过SLObjectItf接口的Realize和resume来控制状态。
SLEngineItf:应用程序开启一个回话的方式,是通过创建一个engine对象的。Engine对象的创建是通过一个SLCreateEngine()来获取的,返回一个SLObjectItf.
当Engine对象创建后,可以获取它的SLEngineItf。
SLBufferQueueItf:被用于流式的音频数据,填充到一个player object或者record object的buffer队列里面。


1)对于recorder对象,当recorder的状态处于SL_RECORDSTATE_RECORDING时。这个对象被SLRecordItf接口控制添加buffer,来隐含开始填充的进程。如果队列中没有足够的buffer,这个auido的数据的填充将会停止和在buffer队列中的要被录制的audio数据会丢失。这个录制仍旧是SL_RECORDSTATE_RECORDING状态。一旦入队了额外的buffer,
填充音频数据将与当前音频数据一起恢复,而不是从饥饿开始了。如果recorder没有处于录制状态,额外的buffer并没有填充队列中任何buffer.
2)在播放对象中的buffer被就地使用,并不会被设备拷贝。应用程序的开发者应该注意到,修改在已经入队的buffer的内容是无效的和会引起音频数据损坏的。
3)一旦入队列的buffer完成了播放或者填充,有callback进行通知,它是安全删除buffer。它也是安全的用新数据填充buffer,和在在播放对象入队buffer和再次入队buffer在录制对象。
4)状态转换为SL_PLAYSTATE_STOPPED,通过release所有的buffer来清空队列,和设置cursor为0.每一个buffer被释放,都会回调被带有SL_BUFFERQUEUENVENT_STOP的flag.
5)一旦转换为了SL_RECORDSTATE_STOPPED状态,应用程序应该继续放buffer到队列中,来取回系统中剩余的buffer。获取剩余的buffer完成的标志是回调方法带有了SL_BUFFERQUEUEEVNENT_CONTEN_END的事件flag。空的buffer可以被用于下一个录制的回话。录制的cursor被设置为0.
6)一旦转化为SL_PLAYSTATE_PAUSEDor SL_RECORDSTATE_PAUSED,cursor仍旧保留在当前的位置。


createSLEngine
engine.fastPathSampleRate_ = static_cast<SLmilliHertz>(sampleRate) * 1000;
engine.fastPathFramesPerBuf_ = static_cast<uint32_t>(framesPerBuf);
engine.sampleChannels_ = AUDIO_SAMPLE_CHANNELS;
engine.bitsPerSample_ = SL_PCMSAMPLEFORMAT_FIXED_16;
/*
SL_API SLresultSLAPIENTRY slCreateEngine(
SLObjectItf *pEngine,
SLuint32 numOptions
const SLEngineOption *pEngineOptions,
SLuint32 numInterfaces,
const SLInterfaceID *pInterfaceIds,
const SLboolean * pInterfaceRequired
)
*/
result = slCreateEngine(&engine.slEngineObj_, 0, NULL, 0, NULL, NULL);
SLASSERT(result);
//Realizing the object in synchronous mode. */
result =
(*engine.slEngineObj_)->Realize(engine.slEngineObj_, SL_BOOLEAN_FALSE);
SLASSERT(result);//获取slEngineItf_
result = (*engine.slEngineObj_)
->GetInterface(engine.slEngineObj_, SL_IID_ENGINE,
&engine.slEngineItf_);// compute the RECOMMENDED fast audio buffer size:
// the lower latency required
// *) the smaller the buffer should be (adjust it here) AND
// *) the less buffering should be before starting player AFTER
// receiving the recorder buffer
// Adjust the bufSize here to fit your bill [before it busts]
uint32_t bufSize = engine.fastPathFramesPerBuf_ * engine.sampleChannels_ *
engine.bitsPerSample_;
bufSize = (bufSize + 7) >> 3; // bits --> byte
engine.bufCount_ = BUF_COUNT;
engine.bufs_ = allocateSampleBufs(engine.bufCount_, bufSize);
assert(engine.bufs_);//创建缓冲队列,freeBufQueue是指空闲的buffer队列,主要是提供空的采样数组。recBufQueue是接收缓冲队列,主要是用来存储已采集到的音频数据,同样也是播放数据的来源。引擎初始化完毕之后会初始化freeBufQueue,初始化了16个空的大小为480字节的数组。至此音频引擎的初始化结束。
engine.freeBufQueue_ = new AudioQueue(engine.bufCount_);
engine.recBufQueue_ = new AudioQueue(engine.bufCount_);
assert(engine.freeBufQueue_ && engine.recBufQueue_);
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < engine.bufCount_; i++) {
engine.freeBufQueue_->push(&engine.bufs_[i]);
}//创建AudioDelay
engine.echoDelay_ = delayInMs;
engine.echoDecay_ = decay;
engine.delayEffect_ = new AudioDelay(
engine.fastPathSampleRate_, .sampleChannels_, engine.bitsPerSample_,
engine.echoDelay_, engine.echoDecay_);
assert(engine.delayEffect_);AudioPlayer
构造方法
SLresult result;
assert(sampleFormat);
sampleInfo_ = *sampleFormat;
/*
SLresult (*CreateOutputMix) (
SLEngineItf self,
SLObjectItf* pMix,
SLuint32 numInterfaces,
const SLInterfaceID * pInterfaceIds,
const SLboolean * pInterfaceRequired
);
创建混音器的对象
*/
result = (*slEngine)
->CreateOutputMix(slEngine, &outputMixObjectItf_, 0, NULL, NULL);
SLASSERT(result);
// realize the output mix
result =
(*outputMixObjectItf_)->Realize(outputMixObjectItf_, SL_BOOLEAN_FALSE);
SLASSERT(result);// configure audio source,配置audio source
SLDataLocator_AndroidSimpleBufferQueue loc_bufq = {
SL_DATALOCATOR_ANDROIDSIMPLEBUFFERQUEUE, DEVICE_SHADOW_BUFFER_QUEUE_LEN};
SLAndroidDataFormat_PCM_EX format_pcm;
ConvertToSLSampleFormat(&format_pcm, &sampleInfo_);
SLDataSource audioSrc = {&loc_bufq, &format_pcm};// configure audio sink,配置音频的输出
SLDataLocator_OutputMix loc_outmix = {SL_DATALOCATOR_OUTPUTMIX,
outputMixObjectItf_};
SLDataSink audioSnk = {&loc_outmix, NULL};/*
* create fast path audio player: SL_IID_BUFFERQUEUE and SL_IID_VOLUME
* and other non-signal processing interfaces are ok.,创建audioplayer
*/
SLInterfaceID ids[2] = {SL_IID_BUFFERQUEUE, SL_IID_VOLUME};
SLboolean req[2] = {SL_BOOLEAN_TRUE, SL_BOOLEAN_TRUE};
/*
SLresult (*CreateAudioPlayer) (
SLEngineItf self,
SLObjectItf* pPlayer,
const SLDataSource *pAudioSrc,
const SLDataSink *pAudioSnk,
SLuint32 numInterfaces,
const SLInterfaceID * pInterfaceIds,
const SLboolean * pInterfaceRequired
);
创建音频播放器
*/
result = (*slEngine)->CreateAudioPlayer(
slEngine, &playerObjectItf_, &audioSrc, &audioSnk,
sizeof(ids) / sizeof(ids[0]), ids, req);
SLASSERT(result);// realize the player,实现播放器
result = (*playerObjectItf_)->Realize(playerObjectItf_, SL_BOOLEAN_FALSE);
SLASSERT(result);// get the play interface,获取播放接口
result = (*playerObjectItf_)
->GetInterface(playerObjectItf_, SL_IID_PLAY, &playItf_);
SLASSERT(result);// get the buffer queue interface,获取bufferq queue的接口
result = (*playerObjectItf_)
->GetInterface(playerObjectItf_, SL_IID_BUFFERQUEUE,
&playBufferQueueItf_);
SLASSERT(result);// register callback on the buffer queue,在bufferq queue上注册接口
result = (*playBufferQueueItf_)
->RegisterCallback(playBufferQueueItf_, bqPlayerCallback, this);
SLASSERT(result);//设置播放状态
result = (*playItf_)->SetPlayState(playItf_, SL_PLAYSTATE_STOPPED);
SLASSERT(result);// create an empty queue to track deviceQueue
devShadowQueue_ = new AudioQueue(DEVICE_SHADOW_BUFFER_QUEUE_LEN);
assert(devShadowQueue_);
silentBuf_.cap_ = (format_pcm.containerSize >> 3) * format_pcm.numChannels *
sampleInfo_.framesPerBuf_;
silentBuf_.buf_ = new uint8_t[silentBuf_.cap_];
memset(silentBuf_.buf_, 0, silentBuf_.cap_);
silentBuf_.size_ = silentBuf_.cap_;AudioPlayer::Start
//首先获取播放状态
SLuint32 state;
SLresult result = (*playItf_)->GetPlayState(playItf_, &state);
if (result != SL_RESULT_SUCCESS) {
return SL_BOOLEAN_FALSE;
}
if (state == SL_PLAYSTATE_PLAYING) {
return SL_BOOLEAN_TRUE;
}
//先设置播放状态是STOPPED状态
result = (*playItf_)->SetPlayState(playItf_, SL_PLAYSTATE_STOPPED);
SLASSERT(result);
//然后如队列相应的buffer。
result =
(*playBufferQueueItf_)
->Enqueue(playBufferQueueItf_, silentBuf_.buf_, silentBuf_.size_);
SLASSERT(result);
devShadowQueue_->push(&silentBuf_);
//设置播放的状态为playing
result = (*playItf_)->SetPlayState(playItf_, SL_PLAYSTATE_PLAYING);
SLASSERT(result);
return SL_BOOLEAN_TRUE;ProcessSLCallback
注册callback:
void bqPlayerCallback(SLAndroidSimpleBufferQueueItf bq, void *ctx) {
(static_cast<AudioPlayer *>(ctx))->ProcessSLCallback(bq);
}void AudioPlayer::ProcessSLCallback(SLAndroidSimpleBufferQueueItf bq) {
#ifdef ENABLE_LOG
logFile_->logTime();
#endif
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(stopMutex_);
// retrieve the finished device buf and put onto the free queue
// so recorder could re-use it,获取已经完成的device buf,并把它放到空闲队列的缓冲区。recorder可以重复使用它
sample_buf *buf;devShadowQueue_->pop();
if (buf != &silentBuf_) {
buf->size_ = 0;
freeQueue_->push(buf);
if (!playQueue_->front(&buf)) {
#ifdef ENABLE_LOG
logFile_->log("%s", "====Warning: running out of the Audio buffers");
#endif
return;
}devShadowQueue_->push(buf);
(*bq)->Enqueue(bq, buf->buf_, buf->size_);//在从播放队列中,获取一个buffer并入队列。
playQueue_->pop();//如果播放队列的大小小于kickstart buffer的数量。入队列silent数据。
playQueue是播放队列,如果为空的话表示没有缓冲数据,这里回调到用的地方做错误处理,若是成功取出,那么先将其存入中转队列,并且将其传入调用播放的方法中开启播放,最后在播放队列中删除该已经播放的数组,在播放完成之后会进入Player播放队列注册的回调中。
if (playQueue_->size() < PLAY_KICKSTART_BUFFER_COUNT) {
(*bq)->Enqueue(bq, buf->buf_, buf->size_);
devShadowQueue_->push(&silentBuf_);
return;
}//填充要播放的数据。
for (int32_t idx = 0; idx < PLAY_KICKSTART_BUFFER_COUNT; idx++) {
playQueue_->front(&buf);
playQueue_->pop();
devShadowQueue_->push(buf);//devshadow的queue的作用是中转队列。
(*bq)->Enqueue(bq, buf->buf_, buf->size_);
}AudioPlayer::stop
SLuint32 state;
SLresult result = (*playItf_)->GetPlayState(playItf_, &state);
SLASSERT(result);
if (state == SL_PLAYSTATE_STOPPED) return;
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(stopMutex_);
result = (*playItf_)->SetPlayState(playItf_, SL_PLAYSTATE_STOPPED);
SLASSERT(result);
(*playBufferQueueItf_)->Clear(playBufferQueueItf_);
#ifdef ENABLE_LOG
if (logFile_) {
delete logFile_;
logFile_ = nullptr;
}
#endifAudioPlayer:~AudioPlayer
AudioPlayer::~AudioPlayer() {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(stopMutex_);
// destroy buffer queue audio player object, and invalidate all associated
// interfaces
if (playerObjectItf_ != NULL) {
(*playerObjectItf_)->Destroy(playerObjectItf_);
}
// Consume all non-completed audio buffers,消耗掉所有未完成的buffer
sample_buf *buf = NULL;
while (devShadowQueue_->front(&buf)) {
buf->size_ = 0;
devShadowQueue_->pop();
if(buf != &silentBuf_) {
freeQueue_->push(buf);
}
}
delete devShadowQueue_;
//把正在播放的队列,放audiobuffer到freeQueue
while (playQueue_->front(&buf)) {
buf->size_ = 0;
playQueue_->pop();
freeQueue_->push(buf);
}
//销毁混音器的对象接口
// destroy output mix object, and invalidate all associated interfaces
if (outputMixObjectItf_) {
(*outputMixObjectItf_)->Destroy(outputMixObjectItf_);
}
delete[] silentBuf_.buf_;
}AudioRecorder
AudioRecorder::AudioRecorder
//转为SL的格式
SLresult result;
sampleInfo_ = *sampleFormat;
SLAndroidDataFormat_PCM_EX format_pcm;
ConvertToSLSampleFormat(&format_pcm, &sampleInfo_);// configure audio source,配置audiosource,SL_DATALOCATOR_IODEVICE Data will be generated or consumed by the
specified IO device. Note: for audio output use
the output mix.
SL_DEFAULTDEVICEID_AUDIOINPUTIdentifier denoting the set of input devicesfrom
whichthe implementation receives audio from by
default.
SLDataLocator_IODevice loc_dev = {SL_DATALOCATOR_IODEVICE, SL_IODEVICE_AUDIOINPUT, SL_DEFAULTDEVICEID_AUDIOINPUT, NULL}; SLDataSource audioSrc = {&loc_dev, NULL};
// configure audio sink,配置audi sink
SLDataLocator_AndroidSimpleBufferQueue loc_bq = {
SL_DATALOCATOR_ANDROIDSIMPLEBUFFERQUEUE, DEVICE_SHADOW_BUFFER_QUEUE_LEN};SLDataSink audioSnk = {&loc_bq, &format_pcm};
//创建audiorecorder的object
// create audio recorder
// (requires the RECORD_AUDIO permission)
const SLInterfaceID id[2] = {SL_IID_ANDROIDSIMPLEBUFFERQUEUE,
SL_IID_ANDROIDCONFIGURATION};
const SLboolean req[2] = {SL_BOOLEAN_TRUE, SL_BOOLEAN_TRUE};
result = (*slEngine)->CreateAudioRecorder(
slEngine, &recObjectItf_, &audioSrc, &audioSnk,
sizeof(id) / sizeof(id[0]), id, req);
SLASSERT(result);
// Configure the voice recognition preset which has no
// signal processing for lower latency.
/*
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Android AudioRecorder configuration */
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/** Audio recording preset */
/** Audio recording preset key */
#define SL_ANDROID_KEY_RECORDING_PRESET ((const SLchar*) "androidRecordingPreset")
/** Audio recording preset values */
/** preset "none" cannot be set, it is used to indicate the current settings
* do not match any of the presets. */
#define SL_ANDROID_RECORDING_PRESET_NONE ((SLuint32) 0x00000000)
/** generic recording configuration on the platform */
#define SL_ANDROID_RECORDING_PRESET_GENERIC ((SLuint32) 0x00000001)
/** uses the microphone audio source with the same orientation as the camera
* if available, the main device microphone otherwise */
#define SL_ANDROID_RECORDING_PRESET_CAMCORDER ((SLuint32) 0x00000002)
/** uses the main microphone tuned for voice recognition */
#define SL_ANDROID_RECORDING_PRESET_VOICE_RECOGNITION ((SLuint32) 0x00000003)
/** uses the main microphone tuned for audio communications */
#define SL_ANDROID_RECORDING_PRESET_VOICE_COMMUNICATION ((SLuint32) 0x00000004)
/** uses the main microphone unprocessed */
#define SL_ANDROID_RECORDING_PRESET_UNPROCESSED ((SLuint32) 0x00000005)
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Android AudioPlayer configuration */
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/** Audio playback stream type */
/** Audio playback stream type key */
#define SL_ANDROID_KEY_STREAM_TYPE ((const SLchar*) "androidPlaybackStreamType")
/** Audio playback stream type values */
/* same as android.media.AudioManager.STREAM_VOICE_CALL */
#define SL_ANDROID_STREAM_VOICE ((SLint32) 0x00000000)
/* same as android.media.AudioManager.STREAM_SYSTEM */
#define SL_ANDROID_STREAM_SYSTEM ((SLint32) 0x00000001)
/* same as android.media.AudioManager.STREAM_RING */
#define SL_ANDROID_STREAM_RING ((SLint32) 0x00000002)
/* same as android.media.AudioManager.STREAM_MUSIC */
#define SL_ANDROID_STREAM_MEDIA ((SLint32) 0x00000003)
/* same as android.media.AudioManager.STREAM_ALARM */
#define SL_ANDROID_STREAM_ALARM ((SLint32) 0x00000004)
/* same as android.media.AudioManager.STREAM_NOTIFICATION */
#define SL_ANDROID_STREAM_NOTIFICATION ((SLint32) 0x00000005)
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Android AudioPlayer and AudioRecorder configuration */
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/** Audio Performance mode.
* Performance mode tells the framework how to configure the audio path
* for a player or recorder according to application performance and
* functional requirements.
* It affects the output or input latency based on acceptable tradeoffs on
* battery drain and use of pre or post processing effects.
* Performance mode should be set before realizing the object and should be
* read after realizing the object to check if the requested mode could be
* granted or not.
*/
/** Audio Performance mode key */
#define SL_ANDROID_KEY_PERFORMANCE_MODE ((const SLchar*) "androidPerformanceMode")
/** Audio performance values */
/* No specific performance requirement. Allows HW and SW pre/post processing. */
#define SL_ANDROID_PERFORMANCE_NONE ((SLuint32) 0x00000000)
/* Priority given to latency. No HW or software pre/post processing.
* This is the default if no performance mode is specified. */
#define SL_ANDROID_PERFORMANCE_LATENCY ((SLuint32) 0x00000001)
/* Priority given to latency while still allowing HW pre and post processing. */
#define SL_ANDROID_PERFORMANCE_LATENCY_EFFECTS ((SLuint32) 0x00000002)
/* Priority given to power saving if latency is not a concern.
* Allows HW and SW pre/post processing. */
#define SL_ANDROID_PERFORMANCE_POWER_SAVING ((SLuint32) 0x00000003)
在采集选项中包含
xxx_RECORDING_PRESET_GENERIC(通用配置,不知道是啥意思)
xxx_RECORDING_PRESET_CAMCORDER(录像中优先使用摄像头同方向的Mic,如果没有同方向的就使用主Mic)
xxx_RECORDING_PRESET_VOICE_RECOGNITION(针对语音识别业务进行了优化,可能使用降噪Mic)
xxx_RECORDING_PRESET_VOICE_COMMUNICATION(针对电话或网络电话优化,可能会硬件AEC、NS、AGC)
xxx_RECORDING_PRESET_UNPROCESSED(使用主Mic采集,不经过任何优化处理)
在渲染选项中包含
xxx_STREAM_VOICE(VoIP或者电话,音量需要通过通话音量调节)
xxx_STREAM_SYSTEM(系统音量,我的华为P10没有这个音量选项)
xxx_STREAM_RING(铃声音量)
xxx_STREAM_MEDIA(媒体音量)
xxx_STREAM_ALARM(闹钟音量)
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「everlastxc」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_29621351/article/details/94562600
*/
SLAndroidConfigurationItf inputConfig;
result = (*recObjectItf_)
->GetInterface(recObjectItf_, SL_IID_ANDROIDCONFIGURATION,
&inputConfig);
if (SL_RESULT_SUCCESS == result) {
SLuint32 presetValue = SL_ANDROID_RECORDING_PRESET_VOICE_RECOGNITION;
(*inputConfig)
->SetConfiguration(inputConfig, SL_ANDROID_KEY_RECORDING_PRESET,
&presetValue, sizeof(SLuint32));
}
result = (*recObjectItf_)->Realize(recObjectItf_, SL_BOOLEAN_FALSE);
SLASSERT(result);//获取recordobjectItf
result =
(*recObjectItf_)->GetInterface(recObjectItf_, SL_IID_RECORD, &recItf_);
SLASSERT(result);//获取对象中的bufferqueue
result = (*recObjectItf_)
->GetInterface(recObjectItf_, SL_IID_ANDROIDSIMPLEBUFFERQUEUE,
&recBufQueueItf_);
SLASSERT(result);//注册bufferqueue中的callback回调接口
result = (*recBufQueueItf_)
->RegisterCallback(recBufQueueItf_, bqRecorderCallback, this);
SLASSERT(result);
//创建中转的缓冲区
devShadowQueue_ = new AudioQueue(DEVICE_SHADOW_BUFFER_QUEUE_LEN);
assert(devShadowQueue_);AudioRecorder::Start
// in case already recording, stop recording and clear buffer queue,先暂停录制和情况buffer queue队列
result = (*recItf_)->SetRecordState(recItf_, SL_RECORDSTATE_STOPPED);
SLASSERT(result);
result = (*recBufQueueItf_)->Clear(recBufQueueItf_);
SLASSERT(result);for (int i = 0; i < RECORD_DEVICE_KICKSTART_BUF_COUNT; i++) {
sample_buf *buf = NULL;
if (!freeQueue_->front(&buf)) {
LOGE("=====OutOfFreeBuffers @ startingRecording @ (%d)", i);
break;
}
freeQueue_->pop();
assert(buf->buf_ && buf->cap_ && !buf->size_);
result = (*recBufQueueItf_)->Enqueue(recBufQueueItf_, buf->buf_, buf->cap_);//把空闲的buffer,输入进去
SLASSERT(result);
devShadowQueue_->push(buf);//并把这个buffer放到这个中转队列
}//设置录制状态为RECORDING
result = (*recItf_)->SetRecordState(recItf_, SL_RECORDSTATE_RECORDING);
SLASSERT(result);AudioRecorder::ProcessSLCallback
assert(bq == recBufQueueItf_);
sample_buf *dataBuf = NULL;
devShadowQueue_->front(&dataBuf);
devShadowQueue_->pop();
dataBuf->size_ = dataBuf->cap_; // device only calls us when it is really
// full
callback_(ctx_, ENGINE_SERVICE_MSG_RECORDED_AUDIO_AVAILABLE, dataBuf);//callback,audio数据已经存在
recQueue_->push(dataBuf);
//重新设置空闲的buffer到如队列
sample_buf *freeBuf;
while (freeQueue_->front(&freeBuf) && devShadowQueue_->push(freeBuf)) {
freeQueue_->pop();
SLresult result = (*bq)->Enqueue(bq, freeBuf->buf_, freeBuf->cap_);
SLASSERT(result);
}Audio Delay
当信号输入进来时,使信号的输出波形比输入滞后设定的时间值比如100ms
把信号持续输入看成一个和时间相关的数据流,设定一个缓冲Buffer,大小根据delay的最大值设定,比如delay最大值为2000ms、那么对于96Khz采样频率的处理来说B u f f e r = 96 ∗ 2000 Buffer = 96 * 2000Buffer=96∗2000; Buffer的大小可能还需要加上DSP一次运算的样本点数比如128,这样最终的数据缓冲值B u f f e r = 192128 Buffer = 192128Buffer=192128;
设定一个结构体,内部含有缓冲区信号样本点输入计数器指针∗ i n P *inP∗inP和样本信号计数器输出指针∗ o u t P *outP∗outP、以及延迟设置值D l y DlyDly;
∗ o u t P *outP∗outP的值根据∗ i n P *inP∗inP和D l y DlyDly之差来确定,要注意∗ i n P *inP∗inP比D l y DlyDly小的情况,这种情况下 ∗ o u t P *outP∗outP的值应该取上一个Buffer的数据,即∗ o u t P *outP∗outP位于∗ i n P *inP∗inP上一个Buffer中而不是同属一个Buffer里面
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「Flynn2019」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/bentengdema/article/details/102495512
AudioDelay::AudioDelay
feedbackFactor_ = static_cast<int32_t>(decayWeight_ * kFloatToIntMapFactor);
liveAudioFactor_ = kFloatToIntMapFactor - feedbackFactor_;
allocateBuffer();allocteBuffer
//转为s
float floatDelayTime = (float)delayTime_ / kMsPerSec;
//转为1s的总帧数
float fNumFrames = floatDelayTime * (float)sampleRate_ / kMsPerSec;
//总帧数
size_t sampleCount = static_cast<uint32_t>(fNumFrames + 0.5f) * channelCount_;//字节数
uint32_t bytePerSample = format_ / 8;
assert(bytePerSample <= 4 && bytePerSample);//每帧的字节数
uint32_t bytePerFrame = channelCount_ * bytePerSample;// get bufCapacity in bytes
bufCapacity_ = sampleCount * bytePerSample;
bufCapacity_ =
((bufCapacity_ + bytePerFrame - 1) / bytePerFrame) * bytePerFrame;//按每帧的字节数对齐
buffer_ = new uint8_t[bufCapacity_];
assert(buffer_);
memset(buffer_, 0, bufCapacity_);
curPos_ = 0;
// bufSize_ is in Frames ( not samples, not bytes )
bufSize_ = bufCapacity_ / bytePerFrame;AudioDelay::process
process() filter live audio with "echo" effect:
* delay time is run-time adjustable
* decay time could also be adjustable, but not used
* in this sample, hardcoded to .5
*
* @param liveAudio is recorded audio stream
* @param channelCount for liveAudio, must be 2 for stereo
* @param numFrames is length of liveAudio in Frames ( not in byte )// process every sample,处理每一帧
int32_t sampleCount = channelCount_ * numFrames;
int16_t* samples = &static_cast<int16_t*>(buffer_)[curPos_ * channelCount_];for (size_t idx = 0; idx < sampleCount; idx++) {
#if 1
int32_t curSample =
(samples[idx] * feedbackFactor_ + liveAudio[idx] * liveAudioFactor_) /
kFloatToIntMapFactor;//当前帧和上一阵的根据相应的因素的叠加 if (curSample > SHRT_MAX)
curSample = SHRT_MAX;
else if (curSample < SHRT_MIN)
curSample = SHRT_MIN;
liveAudio[idx] = samples[idx];
samples[idx] = static_cast<int16_t>(curSample);
#else
// Pure delay
int16_t tmp = liveAudio[idx];
liveAudio[idx] = samples[idx];
samples[idx] = tmp;
#endif
}
curPos_ += numFrames;
lock_.unlock();Audio Common
void ConvertToSLSampleFormat(SLAndroidDataFormat_PCM_EX* pFormat,
SampleFormat* pSampleInfo_) {// Only support 2 channels,设置声道数
// For channelMask, refer to wilhelm/src/android/channels.c for details
if (pSampleInfo_->channels_ <= 1) {
pFormat->numChannels = 1;
pFormat->channelMask = SL_SPEAKER_FRONT_LEFT;
} else {
pFormat->numChannels = 2;
pFormat->channelMask = SL_SPEAKER_FRONT_LEFT | SL_SPEAKER_FRONT_RIGHT;
}case SL_ANDROID_PCM_REPRESENTATION_FLOAT:
pFormat->bitsPerSample = SL_PCMSAMPLEFORMAT_FIXED_32;//设置每一帧的bit数
pFormat->containerSize = SL_PCMSAMPLEFORMAT_FIXED_32;//设置container的大小
pFormat->formatType = SL_ANDROID_DATAFORMAT_PCM_EX;//设置数据类型
break;audio_main
分别创建audioplayer和audio record,同时注册了
engine.player_->SetBufQueue(engine.recBufQueue_, engine.freeBufQueue_);
engine.player_->RegisterCallback(EngineService, (void *)&engine);
engine.recorder_->SetBufQueues(engine.freeBufQueue_, engine.recBufQueue_);
engine.recorder_->RegisterCallback(EngineService, (void *)&engine);
bool EngineService(void *ctx, uint32_t msg, void *data) {
assert(ctx == &engine);
switch (msg) {
case ENGINE_SERVICE_MSG_RETRIEVE_DUMP_BUFS: {
*(static_cast<uint32_t *>(data)) = dbgEngineGetBufCount();
break;
}
case ENGINE_SERVICE_MSG_RECORDED_AUDIO_AVAILABLE: {//当有录制的audio数据时
// adding audio delay effect
sample_buf *buf = static_cast<sample_buf *>(data);
assert(engine.fastPathFramesPerBuf_ ==
buf->size_ / engine.sampleChannels_ / (engine.bitsPerSample_ / 8));
engine.delayEffect_->process(reinterpret_cast<int16_t *>(buf->buf_),
engine.fastPathFramesPerBuf_);//达到延迟的效果
break;
}
default:
assert(false);
return false;
}
return true;
}






















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








