你想要什么,就去追求什么
今天系统的学习下UI绘制流程,系统是怎么把界面展示到屏幕上的,中间经历了什么.
从Activity的setContentView()方法入手,Activity中的setContentView有三个重载的方法:
public void setContentView(View view) { getWindow().setContentView(view); initWindowDecorActionBar(); }
public void setContentView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) { getWindow().setContentView(view, params); initWindowDecorActionBar(); }
public void setContentView(@LayoutRes int layoutResID) { getWindow().setContentView(layoutResID); initWindowDecorActionBar(); }
前二个是通过加载view以及设置了view的layoutparams然后加载到我们的界面上,在Activity中大部分都是通过第三个方法即通过加载一个xml文件,他的第一行代码:
getWindow().setContentView(layoutResID);
你会发现其实在Activity中并不是把这个layoutResID,直接转成view显示在界面上,而是交给了getWindow()即Window,
public Window getWindow() { return mWindow; }
他的声明:
private Window mWindow;
哦,那我们就知道了他是一个Window对象,但是你点击到Window源码中你会发现,他是一个抽象的类,抽象的类肯定不会new了,必然会有子类了,但是你细心的会发现在Window的注释中会找到答案,哪一个是他的子类,
/** * Abstract base class for a top-level window look and behavior policy. An * instance of this class should be used as the top-level view added to the * window manager. It provides standard UI policies such as a background, title * area, default key processing, etc. * * <p>The only existing implementation of this abstract class is * android.view.PhoneWindow, which you should instantiate when needing a * Window. */
意思是顶层的window会加入到WindowManager中进行管理,他提供了标准的设置背景,标题区域,一些key事件,如果做过TV开发的,对这个key事件理解更多容易,后面有讲PhoneWindow是他的唯一子类,所以Phonewindow最终也是要添加到WindowManager中,在Window类中你会发现:
public abstract void setContentView(@LayoutRes int layoutResID);
setContentView被定义成了一个抽象的方法,那么他的实现就是在PhoneWindow类上了:
@Override public void setContentView(int layoutResID) { // Note: FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS may be set in the process of installing the window // decor, when theme attributes and the like are crystalized. Do not check the feature // before this happens. if (mContentParent == null) { installDecor(); } else if (!hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) { mContentParent.removeAllViews(); } if (hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) { final Scene newScene = Scene.getSceneForLayout(mContentParent, layoutResID, getContext()); transitionTo(newScene); } else { mLayoutInflater.inflate(layoutResID, mContentParent); } mContentParent.requestApplyInsets(); final Callback cb = getCallback(); if (cb != null && !isDestroyed()) { cb.onContentChanged(); } mContentParentExplicitlySet = true; }
阅读这个方法代码,先看上面的一段代码:
if (mContentParent == null) { installDecor(); } else if (!hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) { mContentParent.removeAllViews(); }
这个mContentParent判断是否等于null,等于就进installDecor();方法 这个mContentParent变量到底是啥?点击进去就知道了,
// This is the view in which the window contents are placed. It is either // mDecor itself, or a child of mDecor where the contents go. ViewGroup mContentParent;
他是一个ViewGroup,看他的注释就说他是显示内容的地方,要不是mDecor本身,或者是mDecor的子类,那么这个mDecor是啥东西?
// This is the top-level view of the window, containing the window decor. private DecorView mDecor;
意思这是Window最顶层的view,点击进去DecorView看下他是啥?
public class DecorView extends FrameLayout implements RootViewSurfaceTaker, WindowCallbacks { private static final String TAG = "DecorView"; private static final boolean DEBUG_MEASURE = false; private static final boolean SWEEP_OPEN_MENU = false; // The height of a window which has focus in DIP. private final static int DECOR_SHADOW_FOCUSED_HEIGHT_IN_DIP = 20; // The height of a window which has not in DIP. private final static int DECOR_SHADOW_UNFOCUSED_HEIGHT_IN_DIP = 5; public static final ColorViewAttributes STATUS_BAR_COLOR_VIEW_ATTRIBUTES = new ColorViewAttributes(SYSTEM_UI_FLAG_FULLSCREEN, FLAG_TRANSLUCENT_STATUS, Gravity.TOP, Gravity.LEFT, Gravity.RIGHT, Window.STATUS_BAR_BACKGROUND_TRANSITION_NAME, com.android.internal.R.id.statusBarBackground, FLAG_FULLSCREEN);
你会发现DecorView继承了FrameLayout,相当于也是一个view,现在我们还是回到PhoneWindow的setContentView方法,代码再贴一次:
if (mContentParent == null) { installDecor(); } else if (!hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) { mContentParent.removeAllViews(); }
看下if条件语句也就是installDecor()方法:
private void installDecor() { mForceDecorInstall = false; if (mDecor == null) { mDecor = generateDecor(-1); mDecor.setDescendantFocusability(ViewGroup.FOCUS_AFTER_DESCENDANTS); mDecor.setIsRootNamespace(true); if (!mInvalidatePanelMenuPosted && mInvalidatePanelMenuFeatures != 0) { mDecor.postOnAnimation(mInvalidatePanelMenuRunnable); } } else { mDecor.setWindow(this); } if (mContentParent == null) { mContentParent = generateLayout(mDecor); // Set up decor part of UI to ignore fitsSystemWindows if appropriate. mDecor.makeOptionalFitsSystemWindows(); final DecorContentParent decorContentParent = (DecorContentParent) mDecor.findViewById( R.id.decor_content_parent); if (decorContentParent != null) { mDecorContentParent = decorContentParent; mDecorContentParent.setWindowCallback(getCallback()); if (mDecorContentParent.getTitle() == null) { mDecorContentParent.setWindowTitle(mTitle); } final int localFeatures = getLocalFeatures(); for (int i = 0; i < FEATURE_MAX; i++) { if ((localFeatures & (1 << i)) != 0) { mDecorContentParent.initFeature(i); } } mDecorContentParent.setUiOptions(mUiOptions); if ((mResourcesSetFlags & FLAG_RESOURCE_SET_ICON) != 0 || (mIconRes != 0 && !mDecorContentParent.hasIcon())) { mDecorContentParent.setIcon(mIconRes); } else if ((mResourcesSetFlags & FLAG_RESOURCE_SET_ICON) == 0 && mIconRes == 0 && !mDecorContentParent.hasIcon()) { mDecorContentParent.setIcon( getContext().getPackageManager().getDefaultActivityIcon()); mResourcesSetFlags |= FLAG_RESOURCE_SET_ICON_FALLBACK; } if ((mResourcesSetFlags & FLAG_RESOURCE_SET_LOGO) != 0 || (mLogoRes != 0 && !mDecorContentParent.hasLogo())) { mDecorContentParent.setLogo(mLogoRes); } // Invalidate if the panel menu hasn't been created before this. // Panel menu invalidation is deferred avoiding application onCreateOptionsMenu // being called in the middle of onCreate or similar. // A pending invalidation will typically be resolved before the posted message // would run normally in order to satisfy instance state restoration. PanelFeatureState st = getPanelState(FEATURE_OPTIONS_PANEL, false); if (!isDestroyed() && (st == null || st.menu == null) && !mIsStartingWindow) { invalidatePanelMenu(FEATURE_ACTION_BAR); } } else { mTitleView = findViewById(R.id.title); if (mTitleView != null) { if ((getLocalFeatures() & (1 << FEATURE_NO_TITLE)) != 0) { final View titleContainer = findViewById(R.id.title_container); if (titleContainer != null) { titleContainer.setVisibility(View.GONE); } else { mTitleView.setVisibility(View.GONE); } mContentParent.setForeground(null); } else { mTitleView.setText(mTitle); } } } if (mDecor.getBackground() == null && mBackgroundFallbackResource != 0) { mDecor.setBackgroundFallback(mBackgroundFallbackResource); } // Only inflate or create a new TransitionManager if the caller hasn't // already set a custom one. if (hasFeature(FEATURE_ACTIVITY_TRANSITIONS)) { if (mTransitionManager == null) { final int transitionRes = getWindowStyle().getResourceId( R.styleable.Window_windowContentTransitionManager, 0); if (transitionRes != 0) { final TransitionInflater inflater = TransitionInflater.from(getContext()); mTransitionManager = inflater.inflateTransitionManager(transitionRes, mContentParent); } else { mTransitionManager = new TransitionManager(); } } mEnterTransition = getTransition(mEnterTransition, null, R.styleable.Window_windowEnterTransition); mReturnTransition = getTransition(mReturnTransition, USE_DEFAULT_TRANSITION, R.styleable.Window_windowReturnTransition); mExitTransition = getTransition(mExitTransition, null, R.styleable.Window_windowExitTransition); mReenterTransition = getTransition(mReenterTransition, USE_DEFAULT_TRANSITION, R.styleable.Window_windowReenterTransition); mSharedElementEnterTransition = getTransition(mSharedElementEnterTransition, null, R.styleable.Window_windowSharedElementEnterTransition); mSharedElementReturnTransition = getTransition(mSharedElementReturnTransition, USE_DEFAULT_TRANSITION, R.styleable.Window_windowSharedElementReturnTransition); mSharedElementExitTransition = getTransition(mSharedElementExitTransition, null, R.styleable.Window_windowSharedElementExitTransition); mSharedElementReenterTransition = getTransition(mSharedElementReenterTransition, USE_DEFAULT_TRANSITION, R.styleable.Window_windowSharedElementReenterTransition); if (mAllowEnterTransitionOverlap == null) { mAllowEnterTransitionOverlap = getWindowStyle().getBoolean( R.styleable.Window_windowAllowEnterTransitionOverlap, true); } if (mAllowReturnTransitionOverlap == null) { mAllowReturnTransitionOverlap = getWindowStyle().getBoolean( R.styleable.Window_windowAllowReturnTransitionOverlap, true); } if (mBackgroundFadeDurationMillis < 0) { mBackgroundFadeDurationMillis = getWindowStyle().getInteger( R.styleable.Window_windowTransitionBackgroundFadeDuration, DEFAULT_BACKGROUND_FADE_DURATION_MS); } if (mSharedElementsUseOverlay == null) { mSharedElementsUseOverlay = getWindowStyle().getBoolean( R.styleable.Window_windowSharedElementsUseOverlay, true); } } } }
发现代码还是有点多,也不可能每行都懂,那我不是大神了,肯定是看重点的地方:
if (mContentParent == null) { mContentParent = generateLayout(mDecor);
这个是第一次判断这个mContentParent==null就执行下面的,下面的就是给mContentParent赋值了,进入到这个generateLayout()方法中:
protected ViewGroup generateLayout(DecorView decor) { // Apply data from current theme. TypedArray a = getWindowStyle(); if (false) { System.out.println("From style:"); String s = "Attrs:"; for (int i = 0; i < R.styleable.Window.length; i++) { s = s + " " + Integer.toHexString(R.styleable.Window[i]) + "=" + a.getString(i); } System.out.println(s); } mIsFloating = a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Window_windowIsFloating, false); int flagsToUpdate = (FLAG_LAYOUT_IN_SCREEN|FLAG_LAYOUT_INSET_DECOR) & (~getForcedWindowFlags()); if (mIsFloating) { setLayout(WRAP_CONTENT, WRAP_CONTENT); setFlags(0, flagsToUpdate); } else { setFlags(FLAG_LAYOUT_IN_SCREEN|FLAG_LAYOUT_INSET_DECOR, flagsToUpdate); } if (a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Window_windowNoTitle, false)) { requestFeature(FEATURE_NO_TITLE); } else if (a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Window_windowActionBar, false)) { // Don't allow an action bar if there is no title. requestFeature(FEATURE_ACTION_BAR); } //省略中.......... // Inflate the window decor. int layoutResource; int features = getLocalFeatures(); // System.out.println("Features: 0x" + Integer.toHexString(features)); if ((features & (1 << FEATURE_SWIPE_TO_DISMISS)) != 0) { layoutResource = R.layout.screen_swipe_dismiss; setCloseOnSwipeEnabled(true); } else if ((features & ((1 << FEATURE_LEFT_ICON) | (1 << FEATURE_RIGHT_ICON))) != 0) { if (mIsFloating) { TypedValue res = new TypedValue(); getContext().getTheme().resolveAttribute( R.attr.dialogTitleIconsDecorLayout, res, true); layoutResource = res.resourceId; } else { layoutResource = R.layout.screen_title_icons; } // XXX Remove this once action bar supports these features. removeFeature(FEATURE_ACTION_BAR); // System.out.println("Title Icons!"); } else if ((features & ((1 << FEATURE_PROGRESS) | (1 << FEATURE_INDETERMINATE_PROGRESS))) != 0 && (features & (1 << FEATURE_ACTION_BAR)) == 0) { // Special case for a window with only a progress bar (and title). // XXX Need to have a no-title version of embedded windows. layoutResource = R.layout.screen_progress; // System.out.println("Progress!"); } else if ((features & (1 << FEATURE_CUSTOM_TITLE)) != 0) { // Special case for a window with a custom title. // If the window is floating, we need a dialog layout if (mIsFloating) { TypedValue res = new TypedValue(); getContext().getTheme().resolveAttribute( R.attr.dialogCustomTitleDecorLayout, res, true); layoutResource = res.resourceId; } else { layoutResource = R.layout.screen_custom_title; } // XXX Remove this once action bar supports these features. removeFeature(FEATURE_ACTION_BAR); } else if ((features & (1 << FEATURE_NO_TITLE)) == 0) { // If no other features and not embedded, only need a title. // If the window is floating, we need a dialog layout if (mIsFloating) { TypedValue res = new TypedValue(); getContext().getTheme().resolveAttribute( R.attr.dialogTitleDecorLayout, res, true); layoutResource = res.resourceId; } else if ((features & (1 << FEATURE_ACTION_BAR)) != 0) { layoutResource = a.getResourceId( R.styleable.Window_windowActionBarFullscreenDecorLayout, R.layout.screen_action_bar); } else { layoutResource = R.layout.screen_title; } // System.out.println("Title!"); } else if ((features & (1 << FEATURE_ACTION_MODE_OVERLAY)) != 0) { layoutResource = R.layout.screen_simple_overlay_action_mode; } else { // Embedded, so no decoration is needed. layoutResource = R.layout.screen_simple; // System.out.println("Simple!"); } mDecor.startChanging(); mDecor.onResourcesLoaded(mLayoutInflater, layoutResource); ViewGroup contentParent = (ViewGroup)findViewById(ID_ANDROID_CONTENT); if (contentParent == null) { throw new RuntimeException("Window couldn't find content container view"); } if ((features & (1 << FEATURE_INDETERMINATE_PROGRESS)) != 0) { ProgressBar progress = getCircularProgressBar(false); if (progress != null) { progress.setIndeterminate(true); } } if ((features & (1 << FEATURE_SWIPE_TO_DISMISS)) != 0) { registerSwipeCallbacks(contentParent); } // Remaining setup -- of background and title -- that only applies // to top-level windows. if (getContainer() == null) { final Drawable background; if (mBackgroundResource != 0) { background = getContext().getDrawable(mBackgroundResource); } else { background = mBackgroundDrawable; } mDecor.setWindowBackground(background); final Drawable frame; if (mFrameResource != 0) { frame = getContext().getDrawable(mFrameResource); } else { frame = null; } mDecor.setWindowFrame(frame); mDecor.setElevation(mElevation); mDecor.setClipToOutline(mClipToOutline); if (mTitle != null) { setTitle(mTitle); } if (mTitleColor == 0) { mTitleColor = mTextColor; } setTitleColor(mTitleColor); } mDecor.finishChanging(); return contentParent; }
这方法代码很多,大部分都被我省略了,留了几个重要的部分,这样看起来就容易多了,
if (a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Window_windowNoTitle, false)) { requestFeature(FEATURE_NO_TITLE); } else if (a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Window_windowActionBar, false)) { // Don't allow an action bar if there is no title. requestFeature(FEATURE_ACTION_BAR); }
这个我们肯定是看的懂得,就是设置Activity不要标题栏了,然后你就会发现根据不同的features给layoutResource进行赋值操作了,所以你就知道了为什么设置不要标题要在setContentView()方法之前了吧,就是因为要根据这个features设置不同的布局
最简单的就是这个了screen_simple了,看下这个布局:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!-- /* //device/apps/common/assets/res/layout/screen_simple.xml ** ** Copyright 2006, The Android Open Source Project ** ** Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); ** you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. ** You may obtain a copy of the License at ** ** http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 ** ** Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software ** distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, ** WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. ** See the License for the specific language governing permissions and ** limitations under the License. */ This is an optimized layout for a screen, with the minimum set of features enabled. --> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:fitsSystemWindows="true" android:orientation="vertical"> <ViewStub android:id="@+id/action_mode_bar_stub" android:inflatedId="@+id/action_mode_bar" android:layout="@layout/action_mode_bar" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:theme="?attr/actionBarTheme" /> <FrameLayout android:id="@android:id/content" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:foregroundInsidePadding="false" android:foregroundGravity="fill_horizontal|top" android:foreground="?android:attr/windowContentOverlay" /> </LinearLayout>
ViewStub是一个懒加载,默认是不显示的,而FrameLayout 看系统给他的id什么content就知道,其实我们在activity设置的setContent布局就是这个FrameLaout,后期就验证了. 我们可以画图更直接点:
类关系图:
上面的图在6.0之前是对的,如果在6.0以后DecorView不再是PhoneWindow的内部类了,它单独提出来了.
UI绘制其实是从DecorView开始的,现在就是怎么把我们设置进来的layoutId加入到FrameLayout中,在setContentView()方法中:
if (hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) { final Scene newScene = Scene.getSceneForLayout(mContentParent, layoutResID, getContext()); transitionTo(newScene); } else { mLayoutInflater.inflate(layoutResID, mContentParent); }
看else代码块中,就是把layoutResID,加入到mContentParent中,在generateLayout(DecorView decor)方法中有这段代码:
ViewGroup contentParent = (ViewGroup)findViewById(ID_ANDROID_CONTENT);
其中:
public static final int ID_ANDROID_CONTENT = com.android.internal.R.id.content;
这个id对应的就是布局文件中的FrameLayout,而generateLayout()方法返回值就赋值了给了mContentParent这个变量,这个变量就是我们自己的布局,现在再看下:
mLayoutInflater.inflate(layoutResID, mContentParent);
就是把布局文件加入到mContentParent中的:
public View inflate(XmlPullParser parser, @Nullable ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot) { synchronized (mConstructorArgs) { Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "inflate"); final Context inflaterContext = mContext; final AttributeSet attrs = Xml.asAttributeSet(parser);//把xml文件中的属性变成AttributeSet 对象Context lastContext = (Context) mConstructorArgs[0]; mConstructorArgs[0] = inflaterContext; View result = root; try { // Look for the root node. int type; while ((type = parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.START_TAG && type != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) {//开始xml文件解析 // Empty } if (type != XmlPullParser.START_TAG) {// throw new InflateException(parser.getPositionDescription() + ": No start tag found!"); } final String name = parser.getName();//拿到xml中的根节点 if (DEBUG) { System.out.println("**************************"); System.out.println("Creating root view: " + name); System.out.println("**************************"); } if (TAG_MERGE.equals(name)) {//判断这个根节点是否是merge标签 if (root == null || !attachToRoot) { throw new InflateException("<merge /> can be used only with a valid " + "ViewGroup root and attachToRoot=true"); } rInflate(parser, root, inflaterContext, attrs, false); } else {//不是merge标签的时候 // Temp is the root view that was found in the xml final View temp = createViewFromTag(root, name, inflaterContext, attrs); ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = null; if (root != null) { if (DEBUG) { System.out.println("Creating params from root: " + root); } // Create layout params that match root, if supplied params = root.generateLayoutParams(attrs); if (!attachToRoot) { // Set the layout params for temp if we are not // attaching. (If we are, we use addView, below) temp.setLayoutParams(params); } } if (DEBUG) { System.out.println("-----> start inflating children"); } // Inflate all children under temp against its context. rInflateChildren(parser, temp, attrs, true); if (DEBUG) { System.out.println("-----> done inflating children"); } // We are supposed to attach all the views we found (int temp) // to root. Do that now. if (root != null && attachToRoot) { root.addView(temp, params); } // Decide whether to return the root that was passed in or the // top view found in xml. if (root == null || !attachToRoot) { result = temp; } } } catch (XmlPullParserException e) { final InflateException ie = new InflateException(e.getMessage(), e); ie.setStackTrace(EMPTY_STACK_TRACE); throw ie; } catch (Exception e) { final InflateException ie = new InflateException(parser.getPositionDescription() + ": " + e.getMessage(), e); ie.setStackTrace(EMPTY_STACK_TRACE); throw ie; } finally { // Don't retain static reference on context. mConstructorArgs[0] = lastContext; mConstructorArgs[1] = null; Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW); } return result; }}
mContentParent是我们设置的setContentView()的布局最终变成的view,而DecorView是包含了标题+mContentParent
看下这段if代码:
if (TAG_MERGE.equals(name)) { if (root == null || !attachToRoot) { throw new InflateException("<merge /> can be used only with a valid " + "ViewGroup root and attachToRoot=true"); } rInflate(parser, root, inflaterContext, attrs, false); }
其中TAG_MERGE变量 点击进去找下:
private static final String TAG_MERGE = "merge";
你会发现root就是mContentParent ,而attachToRoot变量的指在这个方法中:
public View inflate(@LayoutRes int resource, @Nullable ViewGroup root) { return inflate(resource, root, root != null); }
从上面的代码中可以看的出来attachToRoot = true,也就是说如果root==null或者attachToRoot = false就会执行这个:
if (root == null || !attachToRoot) { throw new InflateException("<merge /> can be used only with a valid " + "ViewGroup root and attachToRoot=true"); }
我现在写个例子说明下:
<merge xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <Button android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="button1" /> <Button android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="button2" android:layout_marginTop="50dp" /> </merge>
运行起来效果:
你会发现这个layout就是以merge标签为根节点的,通过这个就是说merge作为根节点要添加到root中,也就是父view中,如果root==null就会抛出这个错误:
throw new InflateException("<merge /> can be used only with a valid " + "ViewGroup root and attachToRoot=true");
现在知道要写merge标签的话 要是根节点了.其实这个root就是mContentParent这个变量也就是一个ViewGroup了
再继续分析再如果不是merge标签的话会走到这段代码:
rInflateChildren(parser, temp, attrs, true);
这个从方法名就可以看的出来:
final void rInflateChildren(XmlPullParser parser, View parent, AttributeSet attrs, boolean finishInflate) throws XmlPullParserException, IOException { rInflate(parser, parent, parent.getContext(), attrs, finishInflate); }
void rInflate(XmlPullParser parser, View parent, Context context, AttributeSet attrs, boolean finishInflate) throws XmlPullParserException, IOException { final int depth = parser.getDepth(); int type; boolean pendingRequestFocus = false; while (((type = parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.END_TAG || parser.getDepth() > depth) && type != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) { if (type != XmlPullParser.START_TAG) { continue; } final String name = parser.getName(); if (TAG_REQUEST_FOCUS.equals(name)) { pendingRequestFocus = true; consumeChildElements(parser); } else if (TAG_TAG.equals(name)) { parseViewTag(parser, parent, attrs); } else if (TAG_INCLUDE.equals(name)) { if (parser.getDepth() == 0) { throw new InflateException("<include /> cannot be the root element"); } parseInclude(parser, context, parent, attrs); } else if (TAG_MERGE.equals(name)) { throw new InflateException("<merge /> must be the root element"); } else { final View view = createViewFromTag(parent, name, context, attrs); final ViewGroup viewGroup = (ViewGroup) parent; final ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = viewGroup.generateLayoutParams(attrs); rInflateChildren(parser, view, attrs, true); viewGroup.addView(view, params); } } if (pendingRequestFocus) { parent.restoreDefaultFocus(); } if (finishInflate) { parent.onFinishInflate(); } }
这其中有一个while循环:
while (((type = parser.next()) != XmlPullParser.END_TAG || parser.getDepth() > depth) && type != XmlPullParser.END_DOCUMENT) { if (type != XmlPullParser.START_TAG) { continue; } final String name = parser.getName(); if (TAG_REQUEST_FOCUS.equals(name)) { pendingRequestFocus = true; consumeChildElements(parser); } else if (TAG_TAG.equals(name)) { parseViewTag(parser, parent, attrs); } else if (TAG_INCLUDE.equals(name)) { if (parser.getDepth() == 0) { throw new InflateException("<include /> cannot be the root element"); } parseInclude(parser, context, parent, attrs); } else if (TAG_MERGE.equals(name)) { throw new InflateException("<merge /> must be the root element"); } else { final View view = createViewFromTag(parent, name, context, attrs); final ViewGroup viewGroup = (ViewGroup) parent; final ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = viewGroup.generateLayoutParams(attrs); rInflateChildren(parser, view, attrs, true); viewGroup.addView(view, params); } }
就是不断的遍历xml文件生成view的过程
else if (TAG_INCLUDE.equals(name)) { if (parser.getDepth() == 0) { throw new InflateException("<include /> cannot be the root element"); } parseInclude(parser, context, parent, attrs); } else if (TAG_MERGE.equals(name)) { throw new InflateException("<merge /> must be the root element"); }
看这段代码:
上面的第一个else if()判断就是说include标签不能作为我们xml布局的根节点,下面的else if是merge必须作为根节点
再看下else片段:
else { final View view = createViewFromTag(parent, name, context, attrs); final ViewGroup viewGroup = (ViewGroup) parent; final ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = viewGroup.generateLayoutParams(attrs); rInflateChildren(parser, view, attrs, true); viewGroup.addView(view, params); }
你会发现调用了一个rInflateChildren(),哦,它是一个递归,我们又可以总结下:
现在通过studio工具看下布局层次:
我加载的布局是这个:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context="com.view.MainActivity"> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Hello World!" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent" app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent" app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" /> </RelativeLayout>
来查看view root:
红色区域框才是我们显示的内容,现在自己玩下,我写了这个代码:
public class MainActivity extends Activity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); View view = findViewById(android.R.id.content); view.setBackgroundColor(Color.BLUE); Log.e("MainActivity","view="+view); } }
运行起来:
发现除了标题栏,其他都是蓝色了,也说明了这个content id就是我们设置的布局文件区域,是不是验证了之前留下的一个困惑.
比如我们做弹框从底部,比如项目中用到的选择图片,会弹出一个框,选择是从相册还是拍照,如果是PopWindow做的,是不是要在哪里弹出来,就可以用这个了.
public static void main(String[] args) { Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "ActivityThreadMain"); SamplingProfilerIntegration.start(); // CloseGuard defaults to true and can be quite spammy. We // disable it here, but selectively enable it later (via // StrictMode) on debug builds, but using DropBox, not logs. CloseGuard.setEnabled(false); Environment.initForCurrentUser(); // Set the reporter for event logging in libcore EventLogger.setReporter(new EventLoggingReporter()); // Make sure TrustedCertificateStore looks in the right place for CA certificates final File configDir = Environment.getUserConfigDirectory(UserHandle.myUserId()); TrustedCertificateStore.setDefaultUserDirectory(configDir); Process.setArgV0("<pre-initialized>"); Looper.prepareMainLooper(); ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread(); thread.attach(false); if (sMainThreadHandler == null) { sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler(); } if (false) { Looper.myLooper().setMessageLogging(new LogPrinter(Log.DEBUG, "ActivityThread")); } // End of event ActivityThreadMain. Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER); Looper.loop(); throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited"); }
try { mInstrumentation = new Instrumentation(); ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext( this, getSystemContext().mPackageInfo); mInitialApplication = context.mPackageInfo.makeApplication(true, null); mInitialApplication.onCreate(); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException( "Unable to instantiate Application():" + e.toString(), e); }
mInitialApplication.onCreate();
Application mInitialApplication;
private void handleLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent, String reason) { // If we are getting ready to gc after going to the background, well // we are back active so skip it. unscheduleGcIdler(); mSomeActivitiesChanged = true; if (r.profilerInfo != null) { mProfiler.setProfiler(r.profilerInfo); mProfiler.startProfiling(); } // Make sure we are running with the most recent config. handleConfigurationChanged(null, null); if (localLOGV) Slog.v( TAG, "Handling launch of " + r); // Initialize before creating the activity WindowManagerGlobal.initialize(); Activity a = performLaunchActivity(r, customIntent); if (a != null) { r.createdConfig = new Configuration(mConfiguration); reportSizeConfigurations(r); Bundle oldState = r.state; handleResumeActivity(r.token, false, r.isForward, !r.activity.mFinished && !r.startsNotResumed, r.lastProcessedSeq, reason); if (!r.activity.mFinished && r.startsNotResumed) { // The activity manager actually wants this one to start out paused, because it // needs to be visible but isn't in the foreground. We accomplish this by going // through the normal startup (because activities expect to go through onResume() // the first time they run, before their window is displayed), and then pausing it. // However, in this case we do -not- need to do the full pause cycle (of freezing // and such) because the activity manager assumes it can just retain the current // state it has. performPauseActivityIfNeeded(r, reason); // We need to keep around the original state, in case we need to be created again. // But we only do this for pre-Honeycomb apps, which always save their state when // pausing, so we can not have them save their state when restarting from a paused // state. For HC and later, we want to (and can) let the state be saved as the // normal part of stopping the activity. if (r.isPreHoneycomb()) { r.state = oldState; } } } else { // If there was an error, for any reason, tell the activity manager to stop us. try { ActivityManager.getService() .finishActivity(r.token, Activity.RESULT_CANCELED, null, Activity.DONT_FINISH_TASK_WITH_ACTIVITY); } catch (RemoteException ex) { throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer(); } } }
Activity a = performLaunchActivity(r, customIntent);
activity.attach(appContext, this, getInstrumentation(), r.token, r.ident, app, r.intent, r.activityInfo, title, r.parent, r.embeddedID, r.lastNonConfigurationInstances, config, r.referrer, r.voiceInteractor, window, r.configCallback);
final void attach(Context context, ActivityThread aThread, Instrumentation instr, IBinder token, int ident, Application application, Intent intent, ActivityInfo info, CharSequence title, Activity parent, String id, NonConfigurationInstances lastNonConfigurationInstances, Configuration config, String referrer, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor, Window window, ActivityConfigCallback activityConfigCallback) { attachBaseContext(context); mFragments.attachHost(null /*parent*/); mWindow = new PhoneWindow(this, window, activityConfigCallback); mWindow.setWindowControllerCallback(this); mWindow.setCallback(this); mWindow.setOnWindowDismissedCallback(this); mWindow.getLayoutInflater().setPrivateFactory(this); if (info.softInputMode != WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_STATE_UNSPECIFIED) { mWindow.setSoftInputMode(info.softInputMode); } if (info.uiOptions != 0) { mWindow.setUiOptions(info.uiOptions); } mUiThread = Thread.currentThread(); mMainThread = aThread; mInstrumentation = instr; mToken = token; mIdent = ident; mApplication = application; mIntent = intent; mReferrer = referrer; mComponent = intent.getComponent(); mActivityInfo = info; mTitle = title; mParent = parent; mEmbeddedID = id; mLastNonConfigurationInstances = lastNonConfigurationInstances; if (voiceInteractor != null) { if (lastNonConfigurationInstances != null) { mVoiceInteractor = lastNonConfigurationInstances.voiceInteractor; } else { mVoiceInteractor = new VoiceInteractor(voiceInteractor, this, this, Looper.myLooper()); } } mWindow.setWindowManager( (WindowManager)context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE), mToken, mComponent.flattenToString(), (info.flags & ActivityInfo.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED) != 0); if (mParent != null) { mWindow.setContainer(mParent.getWindow()); } mWindowManager = mWindow.getWindowManager(); mCurrentConfig = config; mWindow.setColorMode(info.colorMode); }
mWindow = new PhoneWindow(this, window, activityConfigCallback);
if (r.isPersistable()) { mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state, r.persistentState); } else { mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state); }
public void callActivityOnCreate(Activity activity, Bundle icicle, PersistableBundle persistentState) { prePerformCreate(activity); activity.performCreate(icicle, persistentState); postPerformCreate(activity); }
final void performCreate(Bundle icicle) { restoreHasCurrentPermissionRequest(icicle); onCreate(icicle); mActivityTransitionState.readState(icicle); performCreateCommon(); }
handleResumeActivity(r.token, false, r.isForward, !r.activity.mFinished && !r.startsNotResumed, r.lastProcessedSeq, reason);
final void handleResumeActivity(IBinder token, boolean clearHide, boolean isForward, boolean reallyResume, int seq, String reason) { ActivityClientRecord r = mActivities.get(token); if (!checkAndUpdateLifecycleSeq(seq, r, "resumeActivity")) { return; } // If we are getting ready to gc after going to the background, well // we are back active so skip it. unscheduleGcIdler(); mSomeActivitiesChanged = true; // TODO Push resumeArgs into the activity for consideration r = performResumeActivity(token, clearHide, reason); if (r != null) { final Activity a = r.activity; if (localLOGV) Slog.v( TAG, "Resume " + r + " started activity: " + a.mStartedActivity + ", hideForNow: " + r.hideForNow + ", finished: " + a.mFinished); final int forwardBit = isForward ? WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_IS_FORWARD_NAVIGATION : 0; // If the window hasn't yet been added to the window manager, // and this guy didn't finish itself or start another activity, // then go ahead and add the window. boolean willBeVisible = !a.mStartedActivity; if (!willBeVisible) { try { willBeVisible = ActivityManager.getService().willActivityBeVisible( a.getActivityToken()); } catch (RemoteException e) { throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer(); } } if (r.window == null && !a.mFinished && willBeVisible) { r.window = r.activity.getWindow(); View decor = r.window.getDecorView(); decor.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE); ViewManager wm = a.getWindowManager(); WindowManager.LayoutParams l = r.window.getAttributes(); a.mDecor = decor; l.type = WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_BASE_APPLICATION; l.softInputMode |= forwardBit; if (r.mPreserveWindow) { a.mWindowAdded = true; r.mPreserveWindow = false; // Normally the ViewRoot sets up callbacks with the Activity // in addView->ViewRootImpl#setView. If we are instead reusing // the decor view we have to notify the view root that the // callbacks may have changed. ViewRootImpl impl = decor.getViewRootImpl(); if (impl != null) { impl.notifyChildRebuilt(); } } if (a.mVisibleFromClient) { if (!a.mWindowAdded) { a.mWindowAdded = true; wm.addView(decor, l); } else { // The activity will get a callback for this {@link LayoutParams} change // earlier. However, at that time the decor will not be set (this is set // in this method), so no action will be taken. This call ensures the // callback occurs with the decor set. a.onWindowAttributesChanged(l); } } // If the window has already been added, but during resume // we started another activity, then don't yet make the // window visible. } else if (!willBeVisible) { if (localLOGV) Slog.v( TAG, "Launch " + r + " mStartedActivity set"); r.hideForNow = true; } // Get rid of anything left hanging around. cleanUpPendingRemoveWindows(r, false /* force */); // The window is now visible if it has been added, we are not // simply finishing, and we are not starting another activity. if (!r.activity.mFinished && willBeVisible && r.activity.mDecor != null && !r.hideForNow) { if (r.newConfig != null) { performConfigurationChangedForActivity(r, r.newConfig); if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Resuming activity " + r.activityInfo.name + " with newConfig " + r.activity.mCurrentConfig); r.newConfig = null; } if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Resuming " + r + " with isForward=" + isForward); WindowManager.LayoutParams l = r.window.getAttributes(); if ((l.softInputMode & WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_IS_FORWARD_NAVIGATION) != forwardBit) { l.softInputMode = (l.softInputMode & (~WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_IS_FORWARD_NAVIGATION)) | forwardBit; if (r.activity.mVisibleFromClient) { ViewManager wm = a.getWindowManager(); View decor = r.window.getDecorView(); wm.updateViewLayout(decor, l); } } r.activity.mVisibleFromServer = true; mNumVisibleActivities++; if (r.activity.mVisibleFromClient) { r.activity.makeVisible(); } } if (!r.onlyLocalRequest) { r.nextIdle = mNewActivities; mNewActivities = r; if (localLOGV) Slog.v( TAG, "Scheduling idle handler for " + r); Looper.myQueue().addIdleHandler(new Idler()); } r.onlyLocalRequest = false; // Tell the activity manager we have resumed. if (reallyResume) { try { ActivityManager.getService().activityResumed(token); } catch (RemoteException ex) { throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer(); } } } else { // If an exception was thrown when trying to resume, then // just end this activity. try { ActivityManager.getService() .finishActivity(token, Activity.RESULT_CANCELED, null, Activity.DONT_FINISH_TASK_WITH_ACTIVITY); } catch (RemoteException ex) { throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer(); } } }
if (r.window == null && !a.mFinished && willBeVisible) { r.window = r.activity.getWindow(); View decor = r.window.getDecorView(); decor.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE); ViewManager wm = a.getWindowManager(); WindowManager.LayoutParams l = r.window.getAttributes(); a.mDecor = decor; l.type = WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_BASE_APPLICATION; l.softInputMode |= forwardBit; if (r.mPreserveWindow) { a.mWindowAdded = true; r.mPreserveWindow = false; // Normally the ViewRoot sets up callbacks with the Activity // in addView->ViewRootImpl#setView. If we are instead reusing // the decor view we have to notify the view root that the // callbacks may have changed. ViewRootImpl impl = decor.getViewRootImpl(); if (impl != null) { impl.notifyChildRebuilt(); } }
if (!a.mWindowAdded) { a.mWindowAdded = true; wm.addView(decor, l); }
public interface WindowManager extends ViewManager {

@Override public void addView(@NonNull View view, @NonNull ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) { applyDefaultToken(params); mGlobal.addView(view, params, mContext.getDisplay(), mParentWindow); }
private final WindowManagerGlobal mGlobal = WindowManagerGlobal.getInstance();
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params, Display display, Window parentWindow) { if (view == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("view must not be null"); } if (display == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("display must not be null"); } if (!(params instanceof WindowManager.LayoutParams)) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Params must be WindowManager.LayoutParams"); } final WindowManager.LayoutParams wparams = (WindowManager.LayoutParams) params; if (parentWindow != null) { parentWindow.adjustLayoutParamsForSubWindow(wparams); } else { // If there's no parent, then hardware acceleration for this view is // set from the application's hardware acceleration setting. final Context context = view.getContext(); if (context != null && (context.getApplicationInfo().flags & ApplicationInfo.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED) != 0) { wparams.flags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED; } } ViewRootImpl root; View panelParentView = null; synchronized (mLock) { // Start watching for system property changes. if (mSystemPropertyUpdater == null) { mSystemPropertyUpdater = new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { synchronized (mLock) { for (int i = mRoots.size() - 1; i >= 0; --i) { mRoots.get(i).loadSystemProperties(); } } } }; SystemProperties.addChangeCallback(mSystemPropertyUpdater); } int index = findViewLocked(view, false); if (index >= 0) { if (mDyingViews.contains(view)) { // Don't wait for MSG_DIE to make it's way through root's queue. mRoots.get(index).doDie(); } else { throw new IllegalStateException("View " + view + " has already been added to the window manager."); } // The previous removeView() had not completed executing. Now it has. } // If this is a panel window, then find the window it is being // attached to for future reference. if (wparams.type >= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FIRST_SUB_WINDOW && wparams.type <= WindowManager.LayoutParams.LAST_SUB_WINDOW) { final int count = mViews.size(); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { if (mRoots.get(i).mWindow.asBinder() == wparams.token) { panelParentView = mViews.get(i); } } } root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display); view.setLayoutParams(wparams); mViews.add(view); mRoots.add(root); mParams.add(wparams); // do this last because it fires off messages to start doing things try { root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView); } catch (RuntimeException e) { // BadTokenException or InvalidDisplayException, clean up. if (index >= 0) { removeViewLocked(index, true); } throw e; } } }
root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display); view.setLayoutParams(wparams); mViews.add(view); mRoots.add(root); mParams.add(wparams); // do this last because it fires off messages to start doing things try { root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView); } catch (RuntimeException e) { // BadTokenException or InvalidDisplayException, clean up. if (index >= 0) { removeViewLocked(index, true); } throw e; }
view.assignParent(this);view
/* * Caller is responsible for calling requestLayout if necessary. * (This allows addViewInLayout to not request a new layout.) */ void assignParent(ViewParent parent) { if (mParent == null) { mParent = parent; } else if (parent == null) { mParent = null; } else { throw new RuntimeException("view " + this + " being added, but" + " it already has a parent"); } }
@CallSuper public void requestLayout() { if (mMeasureCache != null) mMeasureCache.clear(); if (mAttachInfo != null && mAttachInfo.mViewRequestingLayout == null) { // Only trigger request-during-layout logic if this is the view requesting it, // not the views in its parent hierarchy ViewRootImpl viewRoot = getViewRootImpl(); if (viewRoot != null && viewRoot.isInLayout()) { if (!viewRoot.requestLayoutDuringLayout(this)) { return; } } mAttachInfo.mViewRequestingLayout = this; } mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT; mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_INVALIDATED; if (mParent != null && !mParent.isLayoutRequested()) { mParent.requestLayout(); } if (mAttachInfo != null && mAttachInfo.mViewRequestingLayout == this) { mAttachInfo.mViewRequestingLayout = null; } }
if (mParent != null && !mParent.isLayoutRequested()) { mParent.requestLayout(); }
@Override public void requestLayout() { if (!mHandlingLayoutInLayoutRequest) { checkThread(); mLayoutRequested = true; scheduleTraversals(); } }
void scheduleTraversals() { if (!mTraversalScheduled) { mTraversalScheduled = true; mTraversalBarrier = mHandler.getLooper().getQueue().postSyncBarrier(); mChoreographer.postCallback( Choreographer.CALLBACK_TRAVERSAL, mTraversalRunnable, null); if (!mUnbufferedInputDispatch) { scheduleConsumeBatchedInput(); } notifyRendererOfFramePending(); pokeDrawLockIfNeeded(); } }
mChoreographer.postCallback( Choreographer.CALLBACK_TRAVERSAL, mTraversalRunnable, null);
final class TraversalRunnable implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { doTraversal(); } }
void doTraversal() { if (mTraversalScheduled) { mTraversalScheduled = false; mHandler.getLooper().getQueue().removeSyncBarrier(mTraversalBarrier); if (mProfile) { Debug.startMethodTracing("ViewAncestor"); } performTraversals(); if (mProfile) { Debug.stopMethodTracing(); mProfile = false; } } }
private void performMeasure(int childWidthMeasureSpec, int childHeightMeasureSpec) { if (mView == null) { return; } Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "measure"); try { mView.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec); } finally { Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW); } }
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { boolean optical = isLayoutModeOptical(this); if (optical != isLayoutModeOptical(mParent)) { Insets insets = getOpticalInsets(); int oWidth = insets.left + insets.right; int oHeight = insets.top + insets.bottom; widthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.adjust(widthMeasureSpec, optical ? -oWidth : oWidth); heightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.adjust(heightMeasureSpec, optical ? -oHeight : oHeight); } // Suppress sign extension for the low bytes long key = (long) widthMeasureSpec << 32 | (long) heightMeasureSpec & 0xffffffffL; if (mMeasureCache == null) mMeasureCache = new LongSparseLongArray(2); final boolean forceLayout = (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT) == PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT; // Optimize layout by avoiding an extra EXACTLY pass when the view is // already measured as the correct size. In API 23 and below, this // extra pass is required to make LinearLayout re-distribute weight. final boolean specChanged = widthMeasureSpec != mOldWidthMeasureSpec || heightMeasureSpec != mOldHeightMeasureSpec; final boolean isSpecExactly = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY && MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec) == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY; final boolean matchesSpecSize = getMeasuredWidth() == MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec) && getMeasuredHeight() == MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec); final boolean needsLayout = specChanged && (sAlwaysRemeasureExactly || !isSpecExactly || !matchesSpecSize); if (forceLayout || needsLayout) { // first clears the measured dimension flag mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET; resolveRtlPropertiesIfNeeded(); int cacheIndex = forceLayout ? -1 : mMeasureCache.indexOfKey(key); if (cacheIndex < 0 || sIgnoreMeasureCache) { // measure ourselves, this should set the measured dimension flag back onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT; } else { long value = mMeasureCache.valueAt(cacheIndex); // Casting a long to int drops the high 32 bits, no mask needed setMeasuredDimensionRaw((int) (value >> 32), (int) value); mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT; } // flag not set, setMeasuredDimension() was not invoked, we raise // an exception to warn the developer if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET) != PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET) { throw new IllegalStateException("View with id " + getId() + ": " + getClass().getName() + "#onMeasure() did not set the" + " measured dimension by calling" + " setMeasuredDimension()"); } mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED; } mOldWidthMeasureSpec = widthMeasureSpec; mOldHeightMeasureSpec = heightMeasureSpec; mMeasureCache.put(key, ((long) mMeasuredWidth) << 32 | (long) mMeasuredHeight & 0xffffffffL); // suppress sign extension }
if (cacheIndex < 0 || sIgnoreMeasureCache) { // measure ourselves, this should set the measured dimension flag back onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT; } else { long value = mMeasureCache.valueAt(cacheIndex); // Casting a long to int drops the high 32 bits, no mask needed setMeasuredDimensionRaw((int) (value >> 32), (int) value); mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT; }
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec), getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec)); }
protected final void setMeasuredDimension(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) { boolean optical = isLayoutModeOptical(this); if (optical != isLayoutModeOptical(mParent)) { Insets insets = getOpticalInsets(); int opticalWidth = insets.left + insets.right; int opticalHeight = insets.top + insets.bottom; measuredWidth += optical ? opticalWidth : -opticalWidth; measuredHeight += optical ? opticalHeight : -opticalHeight; } setMeasuredDimensionRaw(measuredWidth, measuredHeight); }

private int dipToPx(int dip) { final DisplayMetrics displayMetrics = mContext.getResources().getDisplayMetrics(); return (int) (displayMetrics.density * dip + 0.5f); }
int childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mWidth, lp.width); int childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mHeight, lp.height); if (DEBUG_LAYOUT) Log.v(mTag, "Ooops, something changed! mWidth=" + mWidth + " measuredWidth=" + host.getMeasuredWidth() + " mHeight=" + mHeight + " measuredHeight=" + host.getMeasuredHeight() + " coveredInsetsChanged=" + contentInsetsChanged); // Ask host how big it wants to be performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
WindowManager.LayoutParams lp = mWindowAttributes;
final WindowManager.LayoutParams mWindowAttributes = new WindowManager.LayoutParams();
public LayoutParams() { super(LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT); type = TYPE_APPLICATION; format = PixelFormat.OPAQUE; }
private static int getRootMeasureSpec(int windowSize, int rootDimension) { int measureSpec; switch (rootDimension) { case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT: // Window can't resize. Force root view to be windowSize. measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY); break; case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT: // Window can resize. Set max size for root view. measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.AT_MOST); break; default: // Window wants to be an exact size. Force root view to be that size. measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(rootDimension, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY); break; } return measureSpec; }
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context="com.view.MainActivity"> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Hello World!" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent" app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent" app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" /> </RelativeLayout>
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
*/ public static final int UNSPECIFIED = 0 << MODE_SHIFT; /** * Measure specification mode: The parent has determined an exact size * for the child. The child is going to be given those bounds regardless * of how big it wants to be. */ public static final int EXACTLY = 1 << MODE_SHIFT; /** * Measure specification mode: The child can be as large as it wants up * to the specified size. */ public static final int AT_MOST = 2 << MODE_SHIFT;
@Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { int count = getChildCount(); final boolean measureMatchParentChildren = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY || MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY; mMatchParentChildren.clear(); int maxHeight = 0; int maxWidth = 0; int childState = 0; for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { final View child = getChildAt(i); if (mMeasureAllChildren || child.getVisibility() != GONE) { measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec, 0); final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams(); maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin); maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin); childState = combineMeasuredStates(childState, child.getMeasuredState()); if (measureMatchParentChildren) { if (lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT || lp.height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) { mMatchParentChildren.add(child); } } } }
measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec, 0);
protected void measureChildWithMargins(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int widthUsed, int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed) { final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams(); final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec, mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin + widthUsed, lp.width); final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec, mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin + heightUsed, lp.height); child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec); }
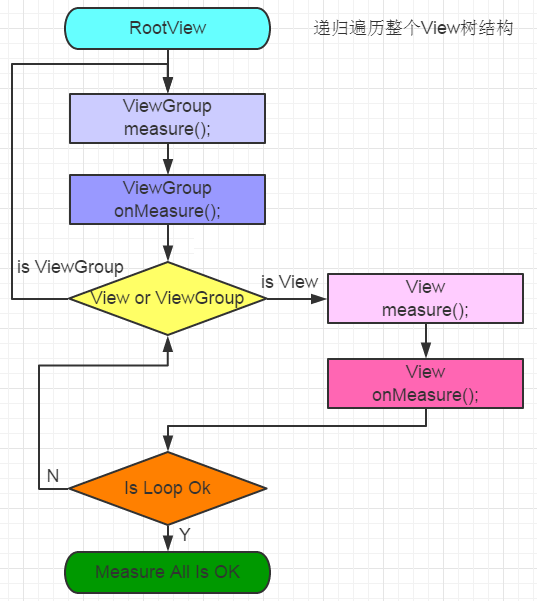
发现调到了ViewGroup去了,最后一行代码是调用了child.measure()是调用了View中的measure()方法去了,这个child可能是view,也可能是ViewGroup
<com.custom.view.MyRelativeLayout android:id="@+id/rootview" android:layout_width="300dp" android:layout_height="300dp" android:background="#66ee99" > <com.custom.view.MyFrameLayout android:layout_width="300dp" android:layout_height="300dp" > <TextView android:layout_width="100px" android:layout_height="100px" android:text="11111111" /> <TextView android:layout_width="100px" android:layout_height="100px" android:text="22222222222" /> </com.custom.view.MyFrameLayout> <com.custom.view.TouchView android:layout_width="240dp" android:layout_height="240dp" android:background="#66eeee" ></com.custom.view.TouchView> </com.custom.view.MyRelativeLayout>
@Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); }
@Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { if (mDirtyHierarchy) { mDirtyHierarchy = false; sortChildren(); } int myWidth = -1; int myHeight = -1; int width = 0; int height = 0;





























 794
794

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








