原文地址
http://www.cnblogs.com/taoweiji/archive/2012/12/14/2818787.html
GridBagLayout是java里面最重要的布局管理器之一,可以做出很复杂的布局,可以说GridBagLayout是必须要学好的的,
GridBagLayout 类是一个灵活的布局管理器,它不要求组件的大小相同便可以将组件垂直、水平或沿它们的基线对齐。
每个 GridBagLayout 对象维持一个动态的矩形单元网格,每个组件占用一个或多个这样的单元,该单元被称为显示区域。
下面就通过一个记事本案例去说明GridBagLayout的使用方法。
分析:
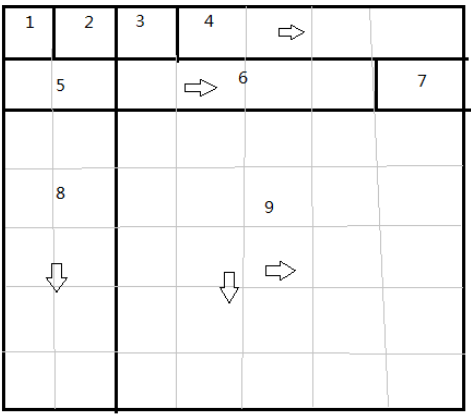
带有箭头的说明可以拉伸的。
4占用4个格子,6占用4个格子。如果设置6可以拉伸了,那么4也会跟着拉伸。
但是如果设置4拉伸,那么7所在的列也可以拉伸,所以4不能设置拉伸。我们应该设置4是跟随6进行拉伸。
灰色的线是为了看清布局的大概,组件占用的格子数。
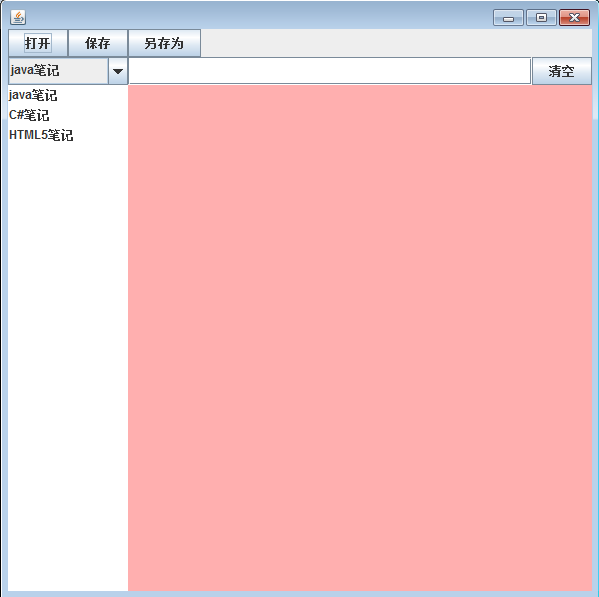
运行时的显示效果
package TestGridBagDemo;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class GridBagDemo extends JFrame {
public static void main(String args[]) {
GridBagDemo demo = new GridBagDemo();
}
public GridBagDemo() {
init();
this.setSize(600,600);
this.setVisible(true);
}
public void init() {
j1 = new JButton("打开");
j2 = new JButton("保存");
j3 = new JButton("另存为");
j4 = new JPanel();
String[] str = { "java笔记", "C#笔记", "HTML5笔记" };
j5 = new JComboBox(str);
j6 = new JTextField();
j7 = new JButton("清空");
j8 = new JList(str);
j9 = new JTextArea();
j9.setBackground(Color.PINK);
GridBagLayout layout = new GridBagLayout();
this.setLayout(layout);
this.add(j1);//把组件添加进jframe
this.add(j2);
this.add(j3);
this.add(j4);
this.add(j5);
this.add(j6);
this.add(j7);
this.add(j8);
this.add(j9);
GridBagConstraints s= new GridBagConstraints();//定义一个GridBagConstraints,
//是用来控制添加进的组件的显示位置
s.fill = GridBagConstraints.BOTH;
//该方法是为了设置如果组件所在的区域比组件本身要大时的显示情况
//NONE:不调整组件大小。
//HORIZONTAL:加宽组件,使它在水平方向上填满其显示区域,但是不改变高度。
//VERTICAL:加高组件,使它在垂直方向上填满其显示区域,但是不改变宽度。
//BOTH:使组件完全填满其显示区域。
s.gridwidth=1;//该方法是设置组件水平所占用的格子数,如果为0,就说明该组件是该行的最后一个
s.weightx = 0;//该方法设置组件水平的拉伸幅度,如果为0就说明不拉伸,不为0就随着窗口增大进行拉伸,0到1之间
s.weighty=0;//该方法设置组件垂直的拉伸幅度,如果为0就说明不拉伸,不为0就随着窗口增大进行拉伸,0到1之间
layout.setConstraints(j1, s);//设置组件
s.gridwidth=1;
s.weightx = 0;
s.weighty=0;
layout.setConstraints(j2, s);
s.gridwidth=1;
s.weightx = 0;
s.weighty=0;
layout.setConstraints(j3, s);
s.gridwidth=0;//该方法是设置组件水平所占用的格子数,如果为0,就说明该组件是该行的最后一个
s.weightx = 0;//不能为1,j4是占了4个格,并且可以横向拉伸,
//但是如果为1,后面行的列的格也会跟着拉伸,导致j7所在的列也可以拉伸
//所以应该是跟着j6进行拉伸
s.weighty=0;
layout.setConstraints(j4, s);
s.gridwidth=2;
s.weightx = 0;
s.weighty=0;
layout.setConstraints(j5, s);
;s.gridwidth=4;
s.weightx = 1;
s.weighty=0;
layout.setConstraints(j6, s);
;s.gridwidth=0;
s.weightx = 0;
s.weighty=0;
layout.setConstraints(j7, s);
;s.gridwidth=2;
s.weightx = 0;
s.weighty=1;
layout.setConstraints(j8, s);
;s.gridwidth=5;
s.weightx = 0;
s.weighty=1;
layout.setConstraints(j9, s);
}
JButton j1;
JButton j2;
JButton j3;
JPanel j4;
JComboBox j5;
JTextField j6;
JButton j7;
JList j8;
JTextArea j9;
}
























 6230
6230

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








