MongoDB属于 NoSql 中的基于分布式文件存储的文档型数据库,是非关系数据库当中功能最丰富,最像关系数据库的。它支持的数据结构非常松散,是类似 json 的 bson 格式,因此可以存储比较复杂的数据类型。Mongo 最大的特点是它支持的查询语言非常强大,其语法有点类似于面向对象的查询语言,几乎可以实现类似关系数据库单表查询的绝大部分功能,但是写起来并不简单。若能集算器 SPL 语言结合,处理起来就相对容易多了。
现在我们针对 MongoDB 在计算方面的问题进行讨论分析,通过集算器 SPL 语言加以改进,方便用户使用 MongoDB。现从如下情况加以说明:
1. 单表内嵌数组结构的统计............................................... 1
2. 单表内嵌文档求和......................................................... 3
3. 分段分组结构................................................................ 5
4. 同构表合并................................................................... 6
5. 关联嵌套结构情况 1...................................................... 8
6. 关联嵌套结构情况 2..................................................... 10
7. 关联嵌套结构情况 3..................................................... 11
8. 多字段分组统计........................................................... 14
9. 两表关联查询............................................................... 16
10. 多表关联查询............................................................. 17
11. 指定数组查找............................................................. 19
12. 关联表中的数组查找................................................... 20
1. 单表内嵌数组结构的统计
对嵌套数组结构中的数据统计处理。查询考试科目的平均分及每个学生的总成绩情况。
测试数据:

期待统计结果:

脚本:
db.student.aggregate( [
{\
$unwind
:
"\$scroe"
},
{\
$group
: {
"_id"
: {
"lesson"
:
"\$scroe.lesson"
} ,
"qty"
:{
"\$avg"
:
"\$scroe.mark"
}
}
}
] )
db.student.aggregate( [
{\
$unwind
:
"\$scroe"
},
{\
$group
: {
"_id"
: {
"name"
:
"\$name"
} ,
"qty"
:{
"\$sum"
:
"\$scroe.mark"
}
}
}
] )
由于各科分数 scroe 是按课目、成绩记录的数组结构,统计前需要将它拆解,将每科成绩与学生对应,然后再实现分组计算。这需要熟悉 unwind 与 group 组合的应用。
SPL 脚本:

按课目统计的总分数

每个学生的总成绩

脚本说明:
A1:连接 mongo 数据库。
A2:获取 student 表中的数据。
A3:将 scroe 数据合并成序表,再按课程分组,计算平均分。
A4:统计每个学生的成绩后返回列名为 NAME、TOTAL 的序表。new 函数表示生成新序表。
A5:关闭数据库连接。
这个比较常用嵌套结构统计的例子许多人遭遇过、需要先拆解,主要是熟悉 mongodb 对嵌套数据结构的处理
2. 单表内嵌文档求和
对内嵌文档中的数据求和处理, 下面要统计每条记录的 income,output 的数量和。
测试数据:

期待统计结果

Mongodb脚本:
var
fields = [
"income"
,
"output"
];
db.computer.aggregate([
{
\
$project
:{
"values"
:{
\
$filter
:{
input:{
"\$objectToArray"
:
"\$\$ROOT"
},
cond:{
\
$in
:[
"\$\$this.k"
,
fields
]
}
}
}
}
},
{
\
$unwind
:
"\$values"
},
{
\
$project
:{
key:
"\$values.k"
,
values:{
"\$sum"
:{
"\$let"
:{
"vars"
:{
"item"
:{
"\$objectToArray"
:
"\$values.v"
}
},
"in"
:
"\$\$item.v"
}
}
}
}
},
{\
$sort
: {
"_id"
:-
1
}},
{
"\$group"
: {
"_id"
:
"\$_id"
,
'income'
:{
"\$first"
:
"\$values"
},
"output"
:{
"\$last"
:
"\$values"
}
}},
]);
filter将income,output 部分信息存放到数组中,用 unwind 拆解成记录,再累计各项值求和,按 _id 分组合并数据。
SPL 脚本:

统计结果

脚本说明:
A1:连接数据库
A2:获取 computer 表中的数据
A3:将 income、output 字段中的数据分别转换成序列求和,再与 ID 组合生成新序表
A4:关闭数据库连接。
获取子记录的字段值,然后求和,相对于 mongo 脚本简化了不少。这个内嵌文档与内嵌数组在组织结构上有点类似,不小心容易混淆,注意与上例中的 scroe 数组结构比较,写出的脚本有所不同。
3. 分段分组结构
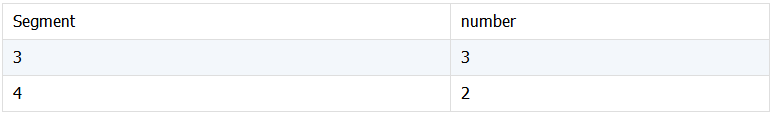
统计各段内的记录数量。下面按销售量分段,统计各段内的数据量,数据如下:

分段方法:0-3000;3000-5000;5000-7500;7500-10000;10000 以上。
期望结果:
Mongo 脚本
var
a_count=
;
var
b_count=
;
var
c_count=
;
var
d_count=
;
var
e_count=
;
db.sales.find({
}).
forEach
(
function
(myDoc)
{
if
(myDoc.SALES <
3000
) {
a_count +=
1
;
}
else
if
(myDoc.SALES <
5000
) {
b_count +=
1
;
}
else
if
(myDoc.SALES <
7500
) {
c_count +=
1
;
}
else
if
(myDoc.SALES <
10000
) {
d_count +=
1
;
}
else
{
e_count +=
1
;
}
}
);
print
(
"a_count="
+a_count)
print
(
"b_count="
+b_count)
print
(
"c_count="
+c_count)
print
(
"d_count="
+d_count)
print
(
"e_count="
+e_count)
这个需求按条件分段分组,mongodb 没有提供对应的 api,实现起来有点繁琐,上面的程序是其中实现的一个例子参考,当然也可以写成其它实现形式。下面看看集算器脚本的实现。
SPL 脚本:
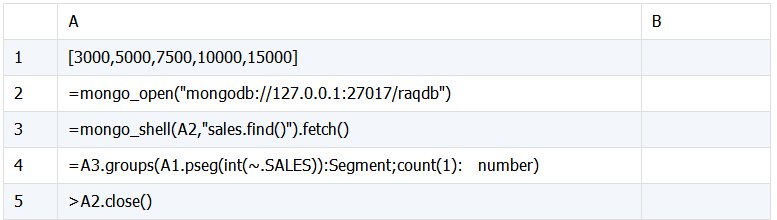
脚本说明:
A1:定义 SALES 分组区间。
A2:连接 mongodb 数据库。
A3:获取 sales 表中的数据。
A4:根据 SALES 区间分组统计员工数。其中函数 pseg()表示返回成员在序列中的区段序号,int() 表示转换成整数。
A5:关闭数据库连接。
pseg 的使用让 SPL 脚本精简了不少。
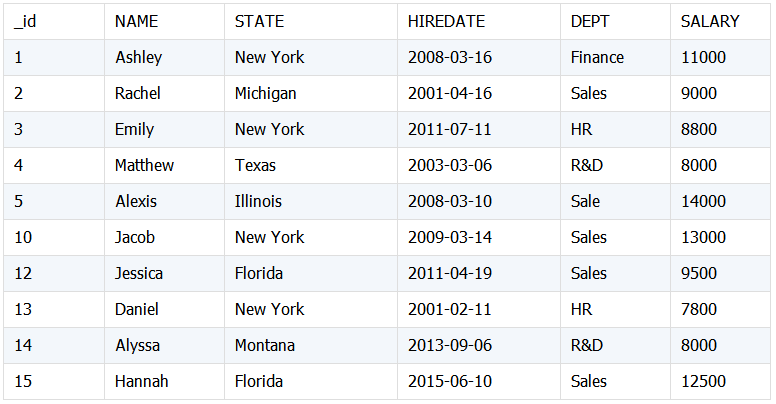
4. 同构表合并
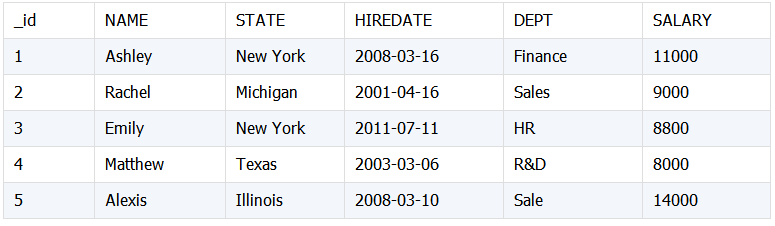
具有相同结构的多表数据合并。下面将两个员工表数据合并。
Emp1:
Emp2:
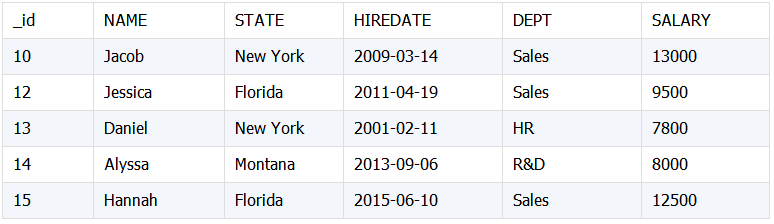
合并数据结果:
Mongo 脚本:
db.emp1.aggregate([
{
"\$limit"
:
1
},
{
"\$facet"
: {
"collection1"
: [
{
"\$limit"
:
1
},
{
"\$lookup"
: {
"from"
:
"emp1"
,
"pipeline"
: [{
"\$match"
: {} }],
"as"
:
"collection1"
}}
],
"collection2"
: [
{
"\$limit"
:
1
},
{
"\$lookup"
: {
"from"
:
"emp2"
,
"pipeline"
: [{
"\$match"
: {} }],
"as"
:
"collection2"
}}
]
}},
{
"\$project"
: {
"data"
: {
"\$concatArrays"
: [
{
"\$arrayElemAt"
: [
"\$collection1.collection1"
,
] },
{
"\$arrayElemAt"
: [
"\$collection2.collection2"
,
] },
]
}
}},
{
"\$unwind"
:
"\$data"
},
{
"\$replaceRoot"
: {
"newRoot"
:
"\$data"
} }
])
通过 facet 将两表数据先存入各自的数组中,然后 concatArrays 将数组合并,unwind 拆解子记录后,并将它呈现在最外层。SPL 脚本实现则没有那么多“花样”。
SPL 脚本:
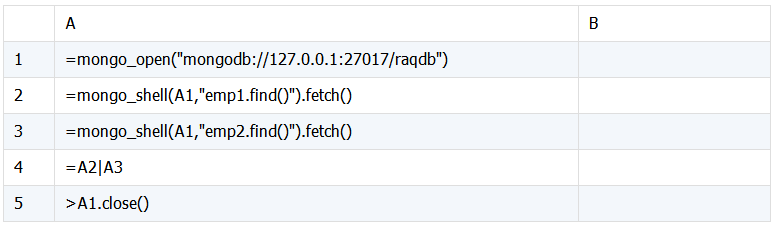
脚本说明:
A1:连接 mongodb 数据库。
A2:获取 emp1 表中的数据。
A3:获取 emp2 表中的数据。
A4:合并两表数据。
A5:关闭数据库连接。
熟悉 sql 语句的 mongo 初学者面对数据合并的 mongo 脚本,估计首次遇到时有点“懵”,SPL 脚本就显得自然易懂了。
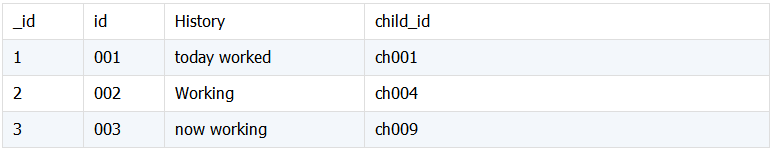
5. 关联嵌套结构情况 1
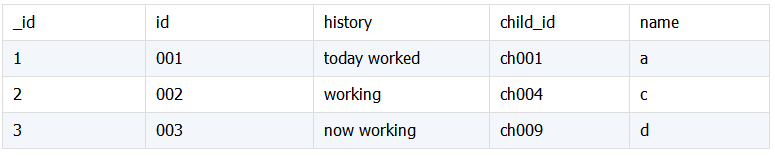
两个关联表,表 A 与表 B 中的内嵌文档信息关联, 且返回的信息在内嵌文档中。表 childsgroup 字段 childs 是嵌套数组结构,需要合并的信息 name 在其下。
history:
childsgroup:
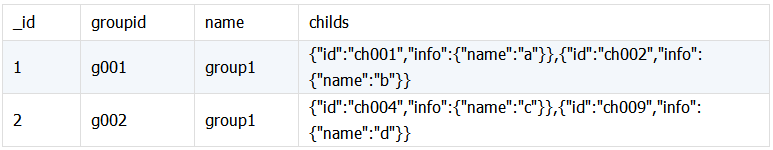
表History中的child_id与表childsgroup中的childs.id关联,希望得到下面结果:
{
“_id” : ObjectId(“5bab2ae8ab2f1bdb4f434bc3”),
“id” : “001”,
“history” : “today worked”,
“child_id” : “ch001”,
“childInfo” :
{
“name” : “a”
}
………………
}
Mongo 脚本
db.history.aggregate([
{\
$lookup
: {
from:
"childsgroup"
,
let
: {child_id:
"\$child_id"
},
pipeline: [
{\
$match
: { \
$expr
: { \
$in
: [
"\$\$child_id"
,
"\$childs.id"
] } } },
{\
$unwind
:
"\$childs"
},
{\
$match
: { \
$expr
: { \
$eq
: [
"\$childs.id"
,
"\$\$child_id"
] } } },
{\
$replaceRoot
: { newRoot:
"\$childs.info"
} }
],
as:
"childInfo"
}},
{
"\$unwind"
:
"\$childInfo"
}
])
这个脚本用了几个函数lookup、pipeline、match、unwind、replaceRoot处理,一般 mongodb 用户不容易写出这样复杂脚本;那我们再看看 spl 脚本的实现:
SPL 脚本:
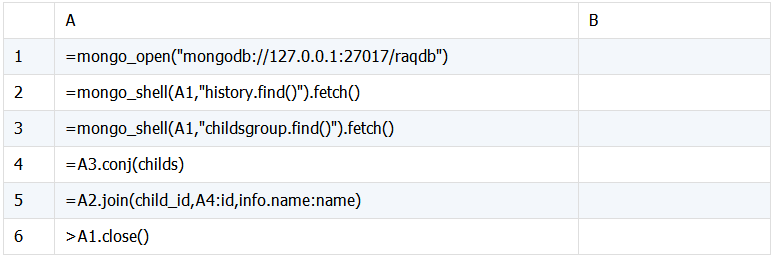
关联查询结果:
脚本说明:
A1:连接 mongodb 数据库。
A2:获取 history 表中的数据。
A3:获取 childsgroup 表中的数据。
A4:将 childsgroup 中的 childs 数据提取出来合并成序表。
A5:表 history 中的 child_id 与表 childs 中的 id 关联查询,追加 name 字段, 返回序表。
A6:关闭数据库连接。
相对 mongodb 脚本写法,SPL 脚本的难度降低了不少,省去了熟悉有关 mongo 函数的用法,如何去组合处理数据等,节约了不少时间。
6. 关联嵌套结构情况 2
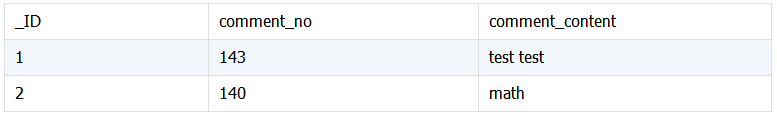
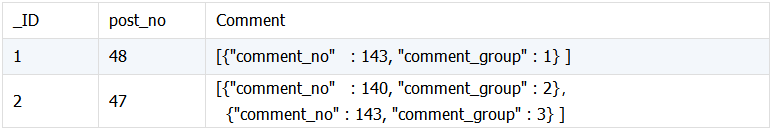
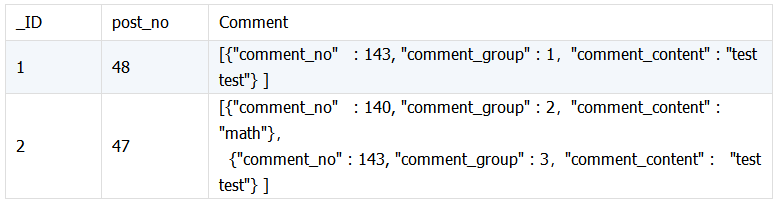
两个关联表,表 A 与表 B 中的内嵌文档信息关联, 将信息合并到内嵌文档中。表 txtPost 字段 comment 是嵌套数组结构,需要把 comment_content 合并到其下。
txtComment:
txtPost
期望结果:
Mongo 脚本
db.getCollection(
"txtPost"
).aggregate([
{
"\$unwind"
:
"\$comment"
},
{
"\$lookup"
: {
"from"
:
"txtComment"
,
"localField"
:
"comment.comment_no"
,
"foreignField"
:
"comment_no"
,
"as"
:
"comment.comment_content"
}},
{
"\$unwind"
:
"\$comment.comment_content"
},
{
"\$addFields"
: {
"comment.comment_content"
:
"\$comment.comment_content.comment_content"
}},
{
"\$group"
: {
"_id"
:
"\$_id"
,
'post_no'
:{
"\$first"
:
"\$post_no"
},
"comment"
: {
"\$push"
:
"\$comment"
}
}},
]).pretty()
表txtPost 按 comment 拆解成记录,然后与表 txtComment 关联查询,将其结果放到数组中,再将数组拆解成记录,将comment_content 值移到 comment 下,最后分组合并。
SPL 脚本:
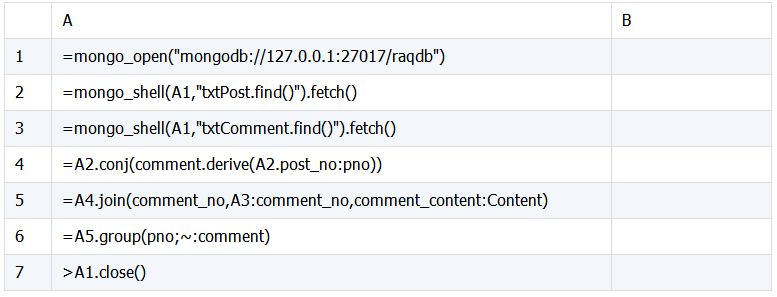
脚本说明:
A1:连接 mongodb 数据库。
A2:获取 txtPost 表中的数据。
A3:获取 txtComment 表中的数据。
A4:将序表 A2 下的 comment 与 post_no 组合成序表,其中 post_no 改名为 pno。
A5:序表 A4 通过 comment_no 与序表 A3 关联,追加字段 comment_content,将其改名为 Content。
A6:按 pno 分组返回序表,~ 表示当前记录。
A7:关闭数据库连接。
7. 关联嵌套结构情况 3
两个关联表,表 A 与表 B 中的内嵌文档信息关联, 且返回的信息在记录上。表 collection2 字段 product 是嵌套数组结构,返回的信息是 isCompleted 等字段。
测试数据:
collection1:
{
_id: '5bc2e44a106342152cd83e97',
description:
{
status: 'Good',
machine: 'X'
},
order: 'A',
lot: '1'
};
collection2:
{
_id: '5bc2e44a106342152cd83e80',
isCompleted: false,
serialNo: '1',
batchNo: '2',
product: [ // note the subdocuments here
{order: 'A', lot: '1'},
{order: 'A', lot: '2'}
]
}
期待结果
{
_id: 5bc2e44a106342152cd83e97,
description:
{
status: 'Good',
machine: 'X',
},
order: 'A',
lot: '1' ,
isCompleted: false,
serialNo: '1',
batchNo: '2'
}
Mongo 脚本
db.collection1.aggregate([{
\
$lookup
: {
from:
"collection2"
,
let: {order:
"\$order"
, lot:
"\$lot"
},
pipeline: [{
\
$match
: {
\
$expr
:{ \
$in
: [ { order:
"\$\$order"
, lot:
"\$\$lot"
},
"\$product"
] }
}
}],
as
:
"isCompleted"
}
}, {
\
$addFields
: {
"isCompleted"
: {\
$arrayElemAt
: [
"\$isCompleted"
,
] }
}
}, {
\
$addFields
: {
// add the required fields to the top level structure
"isCompleted"
:
"\$isCompleted.isCompleted"
,
"serialNo"
:
"\$isCompleted.serialNo"
,
"batchNo"
:
"\$isCompleted.batchNo"
}
}])
lookup 两表关联查询,首个 addFields获取isCompleted数组的第一个记录,后一个addFields 转换成所需要的几个字段信息
SPL 脚本:
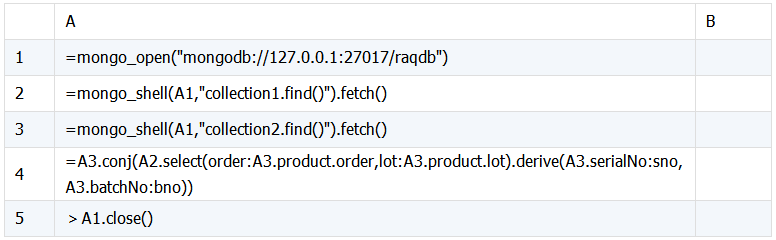
脚本说明:
A1:连接 mongodb 数据库。
A2:获取 collection1 表中的数据。
A3:获取 collection2 表中的数据。
A4:根据条件 order, lot 从序表 A2 中查询记录,然后追加序表 A3 中的字段serialNo, batchNo,返回合并后的序表。
A5:关闭数据库连接。
实现从数据记录中的内嵌结构中筛选,将符合条件的数据合并成新序表。
8. 多字段分组统计
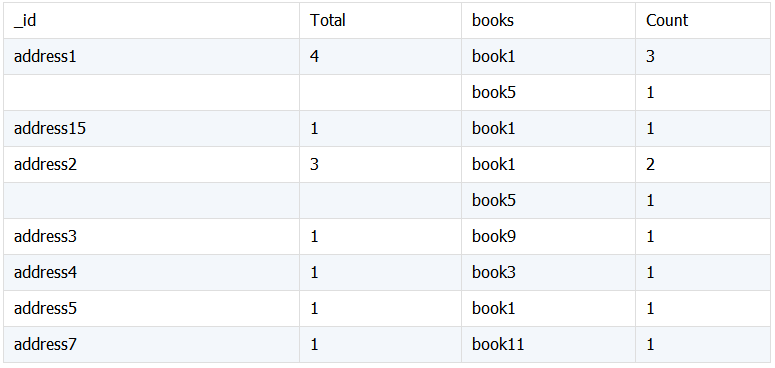
统计分类项下的总数及各子项数。下面统计按 addr 分类 book 数及其下不同的 book 数。
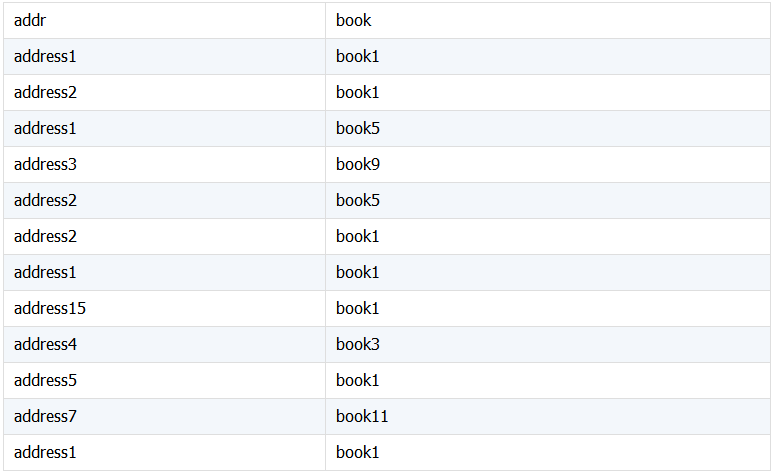
期望结果:
Mongo 脚本
db.books.aggregate([
{
"\$group"
: {
"_id"
: {
"addr"
:
"\$addr"
,
"book"
:
"\$book"
},
"bookCount"
: {
"\$sum"
:
1
}
}},
{
"\$group"
: {
"_id"
:
"\$_id.addr"
,
"books"
: {
"\$push"
: {
"book"
:
"\$_id.book"
,
"count"
:
"\$bookCount"
},
},
"count"
: {
"\$sum"
:
"\$bookCount"
}
}},
{
"\$sort"
: {
"count"
: -
1
} },
{
"\$project"
: {
"books"
: {
"\$slice"
: [
"\$books"
,
2
] },
"count"
:
1
}}
]).pretty()
先按 addr,book 分组统计 book 数,再按 addr 分组统计 book 数,调整显示顺序
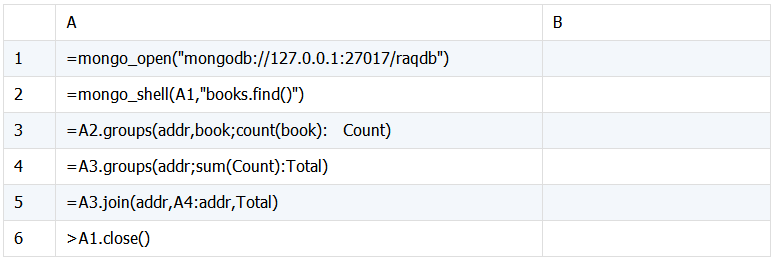
SPL脚本:
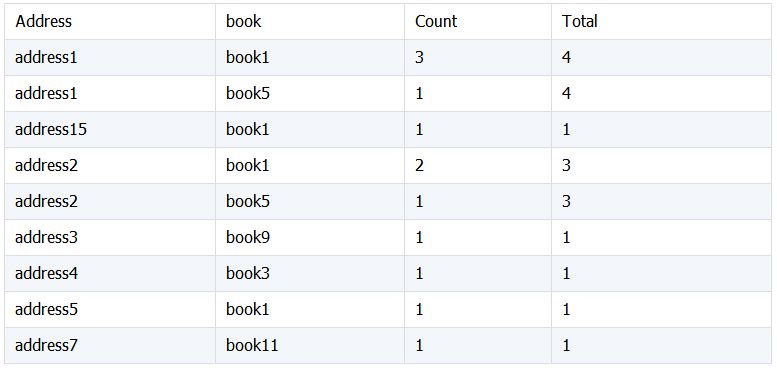
计算结果:
脚本说明:
A1:连接 mongodb 数据库。
A2:获取books表中的数据。
A3:按 addr,book 分组统计 book 数,
A4:再按 addr 分组统计 book 数。
A5:将 A4 中的 Total 按 addr 关联后合并到序表中。
A6:关闭数据库连接。
9. 两表关联查询
从关联表中选择所需要的字段组合成新表。
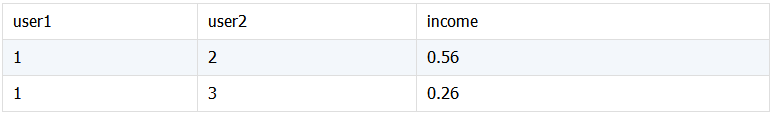
Collection1:
collection2:

期望结果:

Mongo 脚本
db.c1.aggregate([
{
"\$lookup"
: {
"from"
:
"c2"
,
"localField"
:
"user1"
,
"foreignField"
:
"user1"
,
"as"
:
"collection2_doc"
}},
{
"\$unwind"
:
"\$collection2_doc"
},
{
"\$redact"
: {
"\$cond"
: [
{
"\$eq"
: [
"\$user2"
,
"\$collection2_doc.user2"
] },
"\$\$KEEP"
,
"\$\$PRUNE"
]
}},
{
"\$project"
: {
"user1"
:
1
,
"user2"
:
1
,
"income"
:
"\$income"
,
"output"
:
"\$collection2_doc. output"
}}
]).pretty()
lookup 两表进行关联查询,redact 对记录根据条件进行遍历处理,project 选择要显示的字段。
SPL脚本:

脚本说明:
A1:连接 mongodb 数据库。
A2:获取c1表中的数据。
A3:获取c2表中的数据。
A4:两表按字段 user1,user2 关联,追加序表 A3 中的 output 字段,返回序表。
A5:关闭数据库连接。
通过 join 把两个关联表不同的字段合并成新表。
10. 多表关联查询
多于两个表的关联查询,结合成一张大表。
Doc1:

Doc2:

Doc3:

合并后的结果:
{
"_id" : ObjectId("5901a4c63541b7d5d3293766"),
"firstName" : "shubham",
"lastName" : "verma",
"address" : {
"address" : "Gurgaon"
},
"social" : {
"fbURLs" : " http://www.facebook.com ",
"twitterURLs" : " http://www.twitter.com "
}
}
Mongo 脚本
db.doc1.aggregate([
{\
$match
: { _id: ObjectId(
"5901a4c63541b7d5d3293766"
) } },
{
\
$lookup
:
{
from:
"doc2"
,
local
Field:
"_id"
,
foreignField:
"userId"
,
as:
"address"
}
},
{
\
$unwind
:
"\$address"
},
{
\
$project
: {
"address._id"
:
,
"address.userId"
:
,
"address.mob"
:
}
},
{
\
$lookup
:
{
from:
"doc3"
,
local
Field:
"_id"
,
foreignField:
"userId"
,
as:
"social"
}
},
{
\
$unwind
:
"\$social"
},
{
\
$project
: {
"social._id"
:
,
"social.userId"
:
}
}
]).pretty();
由于 Mongodb 数据结构原因,写法也多样化,展示也各不相同。
SPL 脚本:

此脚本与上面例子类似,只是多了一个关联表,每次 join 就新增加字段,最后叠加构成一张大表。.
SPL 脚本的简洁性、统一性就非常明显。
11. 指定数组查找
从指定的数组中查找符合条件的记录。所给的数组为:["Chemical", "Biology", "Math"]。
测试数据:

期望结果:

Mongodb 脚本
var field = [
"Chemical"
,
"Biology"
,
"Math"
]
db.student.aggregate([
{
"\$project"
: {
"name"
:
1
,
"lessons"
: {
"\$filter"
: {
"input"
:
"\$lesson"
,
"cond"
: {
"\$in"
: [
"\$\$this"
,
field
]
}
}
},
}},
{
"\$project"
: {
"name"
:
1
,
"lessons"
:
1
,
"sizeOflesson"
: {
"\$size"
:
"\$lessons"
} }},
{ \$match: {
"sizeOflesson"
:{ \$gt:
}}}
])
查询选修课包含["Chemical", "Biology", "Math"]的同学。
SPL 脚本:

脚本说明:
A1:定义查询条件科目数组。
A2:连接 mongodb 数据库。
A3:获取 student 表中的数据。
A4:查询存在数组中的科目记录。
A5:生成字段为 name, lesson 的新序表,其中符合条件的值存放在字段 lesson 中
A6:关闭数据库连接。
集算器对给定数组中查询记录的实现更简明易懂。
12. 关联表中的数组查找
从关联表记录数据组中查找符合条件的记录, 用给定的字段组合成新表。
测试数据:
users:

workouts:

期望结果:

Mongo 脚本
db.users.aggregate([
{
"\$lookup"
: {
"from"
:
"workouts"
,
"localField"
:
"workouts"
,
"foreignField"
:
"_id"
,
"as"
:
"workoutDocumentsArray"
}},
{\
$project
: { _id:
,workouts:
} } ,
{
"\$unwind"
:
"\$workoutDocumentsArray"
},;
{
"\$replaceRoot"
: {
"newRoot"
: { \
$mergeObjects
: [
"\$\$ROOT"
,
"\$workoutDocumentsArray"
] } }
},
{
$project
: { workoutDocumentsArray:
} }
]).pretty()
把关联表 users,workouts 查询结果放到数组中,再将数组拆解,提升子记录的位置,去掉不需要的字段。
SPL 脚本:

脚本说明:
A1:连接 mongodb 数据库。
A2:获取 users 表中的数据。
A3:获取 workouts 表中的数据。
A4:查询序表 A3 的 _id 值存在于序表 A2 中 workouts 数组的记录, 并追加 name 字段, 返回合并的序表。
A5:关闭数据库连接。
由于需要获取序列的交集不为空为条件,故将 _id 转换成序列。
Mongo 存储的数据结构相对关联数据库更复杂、更灵活,其提供的查询语言也非常强、能适应不同的情况,需要了解函数也不少,函数之间的结合更是变化无穷,因此要掌握并熟悉应用它并非易事。集算器的离散性、易用性恰好能弥补 Mongo 这方面的不足,它降低了 mongo 学习成本及使用 mongo 操作的复杂度、难度,让 mongo 的功能得到更充分的展现,同时也希望 mongo 越来越受到广大爱好者的青睐。
来自 “ ITPUB博客 ” ,链接:http://blog.itpub.net/31543054/viewspace-2284790/,如需转载,请注明出处,否则将追究法律责任。
转载于:http://blog.itpub.net/31543054/viewspace-2284790/





















 6285
6285

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








