一.32位和64位的概念
所谓32位和64位,指的是CPU的字长,其实主要是 GPRS(General Purpose Regisers,通用寄存器)的数据宽度。电脑内部都是实行2进制运算,处理器(CPU)一次处理数据的能力也是2的倍数。8位处理器、16位处理器、32位处理器和64位处理器,其计数都是2的倍数。一次处理的数据越大,该电脑处理信息的能力越来越大。所谓32位处理器就是一次只能处理32位,也就是4个字节的数据,而64位处理器一次就能处理64位,即8个字节的数据。CPU从32位提升到64位,主要的变化如下:
1)是处理能力的提升。比如原来要两个周期做的事,可以在一个周期搞定。
2)64bit的CPU有更大的寻址能力。原本32位CPU32根地址线只可以寻址2^32(4GB)的内存(所以,如果我们装32位系统,搞8G的内存实际上是没有用的)。而64位CPU理论上的寻址能力是2^64,这个相当相当的大,目前的硬件还达不到这个水平,当然我们更用不到这么大的内存。
3)数据的精度提升。一些数据类型可以用更大的字长表示,可以表示更大范围或者更精确的数。CPU分为32位和64位。在这基础上就有了32位操作系统和64位操作系统。进而还有32位程序和64位程序。
说点儿跟我们有关系的,在编程的时候,怎么选择Win32还是x64:
我们打开VS(12或者13),默认的工程设置是32位的。要修改的话可以通过编译选项进行修改:

对于32位和64的区别,贴吧有位大神给出了一个比较详细的解释: ·传送门·
二.32位64位下各种数据类型大小的对比
1.基本数据类型大小的对比
关于数据类型的大小,总是记不住,这里也算有个记录,顺便看一下32位和64位之间的差别:我写了一小段测试代码:
// C++Test.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
//main
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
cout << "sizeof(char):" << sizeof(char) << endl;
cout << "sizeof(short):" << sizeof(short) << endl;
cout << "sizeof(int):" << sizeof(int) << endl;
cout << "sizeof(long):" << sizeof(long) << endl;
cout << "sizeof(long long):" << sizeof(long long) << endl;
cout << "sizeof(unsigned int):" << sizeof(unsigned int) << endl;
cout << "sizeof(float):" << sizeof(float) << endl;
cout << "sizeof(double):" << sizeof(double) << endl;
void* pointer;
cout << "sizeof(pointer):" << sizeof(pointer) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}看一下结果:
WIN32下:
sizeof(char):1
sizeof(short):2
sizeof(int):4
sizeof(long):4
sizeof(long long):8
sizeof(unsigned int):4
sizeof(float):4
sizeof(double):8
sizeof(pointer):4
请按任意键继续. . .
x64下:
sizeof(char):1
sizeof(short):2
sizeof(int):4
sizeof(long):4
sizeof(long long):8
sizeof(unsigned int):4
sizeof(float):4
sizeof(double):8
sizeof(pointer):8
32位和64位系统在Windows下基本数据类型的大小都是一样的。只有指针的大小不一样!32位指针大小为4byte,而64位的指针大小为8byte。
注:Linux下,long型是64位的,这一点是和Windows不同的地方。
PS:64位系统下是可以运行32位程序的。但是反过来的话是运行不了的。我在一台32位的机器上运行上面的64位的程序,就会弹出如下提示:
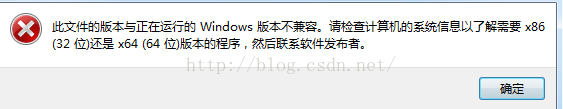
2.为什么Windowsx64下long也为4byte?
我们知道,正常标准的话,long应该也是64位即8byte。但是在Windows下,我们的结果却是4byte。为什么会这样呢?这里引用MSDN的一段关于x64下的解释:Platform SDK: 64-bit Windows Programming
Abstract Data Models
Every application and every operating system has an abstract data model. Many applications do not explicitly expose this data model, but the model guides the way in which the application's code is written. In the 32-bit programming model (known as the ILP32
model), integer, long, and pointer data types are 32 bits in length. Most developers have used this model without realizing it. For the history of the Win32? API, this has been a valid (although not necessarily safe) assumption to make.
In 64-bit Microsoft? Windows?, this assumption of parity in data type sizes is invalid. Making all data types 64 bits in length would waste space, because most applications do not need the increased size. However, applications do need pointers to 64-bit data,
and they need the ability to have 64-bit data types in selected cases. These considerations led to the selection of an abstract data model called LLP64 (or P64). In the LLP64 data model, only pointers expand to 64 bits; all other basic data types (integer
and long) remain 32 bits in length.
Initially, most applications that run on 64-bit Windows will have been ported from 32-bit Windows. It is a goal that the same source, carefully written, should run on both 32- and 64-bit Windows. Defining the data model does not make this task easier. However,
ensuring that the data model affects only pointer data types is the first step. The second step is to define a set of new data types that allow developers to automatically size their pointer-related data. This allows data associated with pointers to change
size as the pointer size changes from 32 bits to 64 bits. Basic data types remain 32 bits in length, so there is no change in the size of data on the disk, data shared over a network, or data shared through memory-mapped files. This relieves developers of
much of the effort involved in porting 32-bit code to 64-bit Windows.
These new data types have been added to the Windows API header files. Therefore, you can start using the new types now. For more information, see The New Data Types.
简单解释一下:
我们编程时很少关注数据类型真正的大小,毕竟即使不关注这个也可以编程,而且我们习惯了Win32,到64位下,只有指针因为寻址需要是必须变成64位的,64位的指针寻址范围是0~2^64-1,而其他的数据类型基本已经够用,如果把所有数据类型变成64位,明显是浪费空间。再者,为了让32位和64位程序兼容运行,能少修改还是少修改,所以Windows仅将指针大小进行了修改。这样,程序可以兼容运行。
3.指针的大小
我们看看指针到底有多大?指向不同类型对象的指针大小是不是会有不同?看一个小例子:// C++Test.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
int num;
string name;
};
//一个函数指针
typedef void(*pFunc)(void);
void PrintHello(void)
{
cout << "hello world" << endl;
}
//main
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
int* pInt;
void* pVoid;
Test* pTest = new Test();
pFunc pfunc = PrintHello;
cout << "sizeof(pInt):" << sizeof(pInt) << endl;
cout << "sizeof(pVoid):" << sizeof(pVoid) << endl;
cout << "sizeof(pTest):" << sizeof(pTest) << endl;
cout << "sizeof(pFunc):" << sizeof(pfunc) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}Win32下:
sizeof(pInt):4
sizeof(pVoid):4
sizeof(pTest):4
sizeof(pFunc):4
请按任意键继续. . .
x64下:
sizeof(pInt):8
sizeof(pVoid):8
sizeof(pTest):8
sizeof(pFunc):8
请按任意键继续. . .
可见,不管指针指向张三李四还是王二麻子,都是一样大的。能够影响指针大小的,还是位数。32位下指针大小为4,64位下指针的大小为8.
4.string的大小
关于string的大小,我们写一小段代码测试一下:// C++Test.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
//main
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
string empty("");
string name("hehe");
string longstr("dfaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa");
cout << sizeof(empty) << endl;
cout << sizeof(name) << endl;
cout << sizeof(longstr) << endl;
cout << sizeof(string) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}结果:
Win32下:
28
28
28
28
请按任意键继续. . .
x64下:
32
32
32
32
请按任意键继续. . .
32位和64位下string差4byte,其实就是一个指针的差别。string内部并不保存字符串本身,而是保存了一个指向字符串开头的指针。






















 3536
3536











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








